Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Applications of Integration Summary
Uploaded by
Faisal Rao0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views3 pagesCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views3 pagesApplications of Integration Summary
Uploaded by
Faisal RaoCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
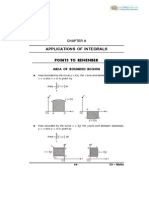
Applications of Integration Summary 1.
Area under curve:
y = f (x)
Area of shaded region= f ( x)dx
a
y = f ( x)
Area of shaded region=| f ( x)dx |
a
y b x = g ( y)
a
O
Area of shaded region= g ( y )dy
a
b x = g ( y)
a x
O
Area of shaded region=| g ( y )dy |
a
2. Volume:
y = f ( x)
Volume of shaded region revolved 2 about the x axis = [ f ( x)] dx
2 a
y = f (x)
y=k
Volume of shaded region revolved 2 about the y = k line = [ f ( x) k ] dx
2 a
Volume of shaded region revolved 2 about the x axis = [ f ( x)] dx k 2 (b a)
2 a b
( )
y b x = g ( y)
a O
Volume of shaded region revolved 2 about the y axis = [g ( y )] dy
2 a
y b x = g ( y)
a
O x=k
b
x
2
Volume of shaded region revolved 2 about the x = k line = [g ( y ) k ] dy
a
Volume of shaded region revolved 2 about the y axis = [g ( y )] dy k 2 (b a)
2 a b
( )
You might also like
- Calculus Reference (SparkCharts)Document2 pagesCalculus Reference (SparkCharts)www_webb100% (1)
- Calculus Cheat Sheet Integrals ReducedDocument3 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet Integrals ReducedShahnaz GazalNo ratings yet
- Calc Study PDFDocument7 pagesCalc Study PDFRussell FromUpNo ratings yet
- Function Summary: Domain, Range, Tests, Transformations & SeriesDocument82 pagesFunction Summary: Domain, Range, Tests, Transformations & SeriesthatsparklexNo ratings yet
- Applications of IntegrationDocument75 pagesApplications of IntegrationweglisotterNo ratings yet
- Group 11: Areas and VolumesDocument32 pagesGroup 11: Areas and VolumesLuxemberg NgNo ratings yet
- Calculus Cheat Sheet Integrals ReducedDocument3 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet Integrals ReducedFadzilah YayaNo ratings yet
- Inverse Function: Determine Whether A Function Is One-To-One, and Find The Inverse of A One-To-One FunctionDocument16 pagesInverse Function: Determine Whether A Function Is One-To-One, and Find The Inverse of A One-To-One FunctionLee Ming ShengNo ratings yet
- CALCULUS OF INTEGRALSDocument7 pagesCALCULUS OF INTEGRALSurfriend_jjn05No ratings yet
- Pure M Ath - Geom Etric Applications of Definite Integrals: Area of Plane FiguresDocument4 pagesPure M Ath - Geom Etric Applications of Definite Integrals: Area of Plane FiguresFrancis WongNo ratings yet
- Areas (Part 1)Document7 pagesAreas (Part 1)Sachin KumarNo ratings yet
- H2 Mathematics Cheat Sheet by Sean LimDocument27 pagesH2 Mathematics Cheat Sheet by Sean LimGale HawthorneNo ratings yet
- Sakshieducation Area FormulasDocument2 pagesSakshieducation Area FormulasPrahlad RebalaNo ratings yet
- Area and Differterterterterential EquationsDocument8 pagesArea and Differterterterterential EquationsPrithviraj NetkeNo ratings yet
- Calculus Ich 13Document29 pagesCalculus Ich 13nqnghia22No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - Integration Part 4 DNDDocument30 pagesCHAPTER 2 - Integration Part 4 DNDmuhdkamal11No ratings yet
- Area of BodedDocument5 pagesArea of BodedthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Volume Calculations Using Definite IntegralsDocument21 pagesVolume Calculations Using Definite IntegralsAfiqah ZainuddinNo ratings yet
- 12 Maths Key Notes CH 08 Application of IntegralsDocument1 page12 Maths Key Notes CH 08 Application of IntegralsSachin YadavNo ratings yet
- Integrals MATH 101Document5 pagesIntegrals MATH 101Cris JacksonNo ratings yet
- 02-Applications of The IntegralsDocument32 pages02-Applications of The IntegralsGeeta MNo ratings yet
- n-1 n-1 -j2πnk/N n=0: Explain the Properties of 2D discrete Fourier Transform 1. SeparabilityDocument7 pagesn-1 n-1 -j2πnk/N n=0: Explain the Properties of 2D discrete Fourier Transform 1. SeparabilityArun EceNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 - Area Between CurvesDocument26 pagesLecture 11 - Area Between CurvesbananaNo ratings yet
- 10 - Areas of Bounded Regions PDFDocument8 pages10 - Areas of Bounded Regions PDFthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Integration PDFDocument8 pagesIntegration PDFAre Peace El MananaNo ratings yet
- 12 Mathematics Impq Applications of Integrals 01Document5 pages12 Mathematics Impq Applications of Integrals 01ManjotSinghNo ratings yet
- Assignment3 1Document1 pageAssignment3 1Viplav Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Application of Integration-Lecture - VolumeDocument3 pagesApplication of Integration-Lecture - Volumesevenkenny0123No ratings yet
- Slides Ch8 Bài 2. Tính Diện Tích Của Mặt Tròn XoayDocument46 pagesSlides Ch8 Bài 2. Tính Diện Tích Của Mặt Tròn XoayAn NguyễnNo ratings yet
- GUC MATH203 Chapter 2 Integration ApplicationsDocument17 pagesGUC MATH203 Chapter 2 Integration ApplicationsAmr Ashraf KhalilNo ratings yet
- Note15 The Definite Integral and Area Under A Curve PDFDocument30 pagesNote15 The Definite Integral and Area Under A Curve PDF李华夏No ratings yet
- 20.3 The Curl of A Vector Field: N Area (D) 0 CDocument2 pages20.3 The Curl of A Vector Field: N Area (D) 0 CthgnguyenNo ratings yet
- Areas of Bounded Regions: B Fxdxor Ydx A D Fydyor Xdy CDocument1 pageAreas of Bounded Regions: B Fxdxor Ydx A D Fydyor Xdy CRaja KushwahNo ratings yet
- Area Calculations for Curves and FunctionsDocument11 pagesArea Calculations for Curves and FunctionsAmimul IhsanNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of antiderivatives and integralsDocument5 pagesFundamentals of antiderivatives and integralsJc QuintosNo ratings yet
- Calculating areas and volumes using calculusDocument4 pagesCalculating areas and volumes using calculustejas chikhlikarNo ratings yet
- DEFINITE INTEGRAL CALCULATIONDocument64 pagesDEFINITE INTEGRAL CALCULATIONAqila EsyNo ratings yet
- Calculus - Final Review SetDocument10 pagesCalculus - Final Review SetAaron David ReidNo ratings yet
- 20BCT0177 VL2020210106194 Ast02 PDFDocument8 pages20BCT0177 VL2020210106194 Ast02 PDFSahil KalingNo ratings yet
- Identifying functions, inverses, domains and rangesDocument1 pageIdentifying functions, inverses, domains and rangesreacharunkNo ratings yet
- AP BC ReviewDocument7 pagesAP BC ReviewchowmeinnoodleNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 55 - Elementary Analysis III SummaryDocument5 pagesMathematics 55 - Elementary Analysis III SummaryMarian Galvez-LuisNo ratings yet
- Calculate Volume Using Double IntegralsDocument22 pagesCalculate Volume Using Double IntegralsYiauw ShenqNo ratings yet
- Solid of RevolutionDocument7 pagesSolid of RevolutionEden エデン Eusebio SombongNo ratings yet
- Area Between CurvesDocument6 pagesArea Between CurvesPattrawut RukkachartNo ratings yet
- MAT 3612 Calculus 2 Tutorial 4 ProblemsDocument4 pagesMAT 3612 Calculus 2 Tutorial 4 ProblemsJay KayyNo ratings yet
- 7-1-2-3 Area-VolumesDocument1 page7-1-2-3 Area-Volumesjax328No ratings yet
- Application of Integrals: 8.1 OverviewDocument9 pagesApplication of Integrals: 8.1 OverviewKoyal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Schaumcalculus p2Document131 pagesSchaumcalculus p2plokplokplokNo ratings yet
- Quiz On Integral CalculusDocument2 pagesQuiz On Integral CalculusShivansh JangidNo ratings yet
- Math 55 First Long Exam Reviewer: X y X y ZDocument5 pagesMath 55 First Long Exam Reviewer: X y X y Zrawry_xoxNo ratings yet
- Application of Definite IntegralDocument15 pagesApplication of Definite IntegralKirkD'costaNo ratings yet
- Double integrals and applicationsDocument4 pagesDouble integrals and applicationsJimuel Adrian Punzalan100% (1)
- Lecture 21 - MTH101 IIT KanpurDocument3 pagesLecture 21 - MTH101 IIT KanpurAsish MahapatraNo ratings yet
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- HP ScanDocument1 pageHP ScanFaisal RaoNo ratings yet
- Integrating Factor For 1st Order Differential EquationDocument1 pageIntegrating Factor For 1st Order Differential EquationFaisal RaoNo ratings yet
- GresikDocument41 pagesGresikFaisal RaoNo ratings yet
- Integration Techniques SummaryDocument6 pagesIntegration Techniques SummaryJess Ryan OlayonNo ratings yet
- Functions SummaryDocument3 pagesFunctions SummaryFaisal RaoNo ratings yet
- Facts and FiguresDocument1 pageFacts and FiguresFaisal RaoNo ratings yet
- Investopedia - Financial Ratio TutorialDocument55 pagesInvestopedia - Financial Ratio TutorialKoh See Hui RoxanneNo ratings yet
- Finding The Inverse of A Composite FunctionDocument1 pageFinding The Inverse of A Composite FunctionFaisal RaoNo ratings yet
- B. Jack CopelandDocument26 pagesB. Jack CopelandFaisal RaoNo ratings yet
- Graphing Techniques SummaryDocument8 pagesGraphing Techniques SummaryFaisal RaoNo ratings yet
- Cost AccountingDocument46 pagesCost AccountingTejaswini ChoudhariNo ratings yet
- Financial Formulas - Ratios (Sheet)Document3 pagesFinancial Formulas - Ratios (Sheet)carmo-netoNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Integrals With Modulus FunctionsDocument2 pagesEvaluating Integrals With Modulus FunctionsFaisal RaoNo ratings yet
- Complex Numbers SummaryDocument3 pagesComplex Numbers SummarySun ZeqiNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations SummaryDocument3 pagesDifferential Equations SummaryFaisal RaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Breakeven AnalysisDocument10 pagesChapter 13 Breakeven Analysisoo2011No ratings yet
- Arithmetic and Geometric Progressions APGP SummaryDocument4 pagesArithmetic and Geometric Progressions APGP SummaryFaisal RaoNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Techniques SummaryDocument3 pagesDifferentiation Techniques SummaryFaisal RaoNo ratings yet
- Binomial Series SummaryDocument3 pagesBinomial Series SummaryFaisal RaoNo ratings yet
- Break-Even Point PDFDocument2 pagesBreak-Even Point PDFFaisal Rao67% (3)
- Central Limit Theorem Estimation SummaryDocument4 pagesCentral Limit Theorem Estimation SummaryFaisal RaoNo ratings yet
- Article Theme Accounting For InventoryDocument7 pagesArticle Theme Accounting For InventoryULLASH5050No ratings yet
- AQA A-Level Mathematics - MPC3 Module SyllabusDocument3 pagesAQA A-Level Mathematics - MPC3 Module SyllabusFaisal RaoNo ratings yet
- 02 Break Even AnalysisDocument10 pages02 Break Even AnalysisJitender ThakurNo ratings yet
- Binomial/Poisson Distributions Summary Binomial Poisson: Independent Trials, Whereby Each TrialDocument4 pagesBinomial/Poisson Distributions Summary Binomial Poisson: Independent Trials, Whereby Each TrialFaisal RaoNo ratings yet
- Basic AccountingDocument13 pagesBasic AccountingSghaireenNo ratings yet
- Basic Accounting Part 2Document71 pagesBasic Accounting Part 2Faisal RaoNo ratings yet
- Applications of Differentiation SummaryDocument4 pagesApplications of Differentiation SummaryFaisal RaoNo ratings yet
- Alan Turing YearDocument35 pagesAlan Turing YearFaisal RaoNo ratings yet