Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organization of Muscle Fibers and Neuromuscular Junction
Uploaded by
pazucena0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views1 pageAnatomy
Original Title
Organization of Muscle Fiber
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAnatomy
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views1 pageOrganization of Muscle Fibers and Neuromuscular Junction
Uploaded by
pazucenaAnatomy
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Organization of Muscle Fiber
Smallest unit is endomysium
Several bundles become fascicle
o Connected be CT perimysium
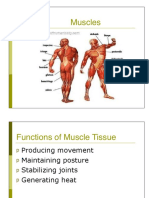
Functions of muscle
o Movement
o Posture
o Generates heat
I vs H vs M bands
I Z an Asshole
Myosin in thin and thick filament
Myosin
o 2 heads and a tail
o F actin strands twirled on each other
o Trpopomyosin holds them together
Actin, tropomyosin and troponin
sarcolema - invaginations toward center of the muscle
space inside the tubule - T tubule - transverse -
junction of the A and I band
Pouches on each side of the cytoplasmic reticulum
terminal cisterns
o Junction of A and I band
Triad
o One cistern, t tubule, sarcolemma
T system
T tubule goes to deep part of muscle
EM of triad
Dystrophin
o Glycoprotein complex
o Provides strength by providing scaffolding
for fibrils
o Clinical manif: muscle weakness
o X-linked
o Destruction of muscles
o Dystrophinopathy
o Beckers???
Dystophin-glycoprotein complex
Protein that anchors triad to basal lamina
Provides stiffness to muscles
Motor unit
Motor neuron and all muscles it innervates
Low innervation vs High innervation
High innervation faster movements
Low innervation slow, sustained movements
Depends on function of muscle
Neuromuscular junction
Bet nerve and muscle
Prejunction nerve; postjunction muscle
Saltatory conduction
o Impulse starts at axon hillock
o Along nodes of Ranvier
Also called endplate
Vesicles pinch off from ER
SNAP25 snare proteins where botulitin toxin acts
VAMP
Proteins identified for endocytosis
You might also like
- The Muscular System: Types, Structure & FunctionDocument50 pagesThe Muscular System: Types, Structure & FunctionArina GainaNo ratings yet
- Muscle Physio PDFDocument41 pagesMuscle Physio PDFCamille MagdirilaNo ratings yet
- Nsca CPTDocument4 pagesNsca CPTRichard Marcus SeigelNo ratings yet
- Muscle Physiology and NeurophysiologyDocument68 pagesMuscle Physiology and NeurophysiologyAlan MagpantayNo ratings yet
- Azantee Yazmie Abdul Wahab Dept. of Obstetrics & Gynaecology Kulliyyah of Medicine IIUM KuantanDocument51 pagesAzantee Yazmie Abdul Wahab Dept. of Obstetrics & Gynaecology Kulliyyah of Medicine IIUM KuantanNur ShafilaNo ratings yet
- The Muscular SystemDocument9 pagesThe Muscular SystemKathleenJoyGalAlmasinNo ratings yet
- Muscle System 2019Document32 pagesMuscle System 2019ZNA EntertainmentNo ratings yet
- Muscle PhysiologyDocument7 pagesMuscle PhysiologyNicole Erin TomaquinNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument15 pagesNotesGizem OsmanogluNo ratings yet
- Understanding Muscle PhysiologyDocument88 pagesUnderstanding Muscle Physiologyandre andreNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissueDocument30 pagesMuscle Tissued20231107667No ratings yet
- The Muscular System: Skeletal, Cardiac, and Smooth Muscle TypesDocument3 pagesThe Muscular System: Skeletal, Cardiac, and Smooth Muscle TypessharonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Muscular SystemDocument69 pagesLecture 4 Muscular SystemLouella ArtatesNo ratings yet
- Muscularsyst EM: Actin and Myosin MyofilamentsDocument16 pagesMuscularsyst EM: Actin and Myosin MyofilamentsCatherine Joy delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Faal Otot Dan GerakDocument46 pagesFaal Otot Dan GerakElsya Nur FadhillaNo ratings yet
- Locomotion & Movement (Muscles)Document41 pagesLocomotion & Movement (Muscles)DEEPANKAR SAHANo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology GMCDocument15 pagesAnatomy and Physiology GMCsamantha tanoNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle Physiology ExplainedDocument26 pagesSkeletal Muscle Physiology ExplainedUSAMA AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Human Muscular System: Types of Movement in Human BeingDocument4 pagesHuman Muscular System: Types of Movement in Human Beingaadeshthite476No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - An Introduction To Muscle TissueDocument7 pagesChapter 10 - An Introduction To Muscle Tissuetomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue Lesson 1Document5 pagesMuscle Tissue Lesson 1Steves LeeboyNo ratings yet
- Muscular System Functions and StructureDocument5 pagesMuscular System Functions and StructureMayet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Muscle A&P: Structure, Types, Sensory Feedback & ContractionDocument23 pagesMuscle A&P: Structure, Types, Sensory Feedback & ContractionjhnnolanNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Skeletal & Smooth MusclesDocument10 pagesPhysiology of Skeletal & Smooth MusclesAli AlhamadNo ratings yet
- Chap11muscular TissueDocument64 pagesChap11muscular TissueCalvo AdrianNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle Classification and StructureDocument43 pagesSkeletal Muscle Classification and StructureHusnain WattoNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue Week 15 HGAPDocument4 pagesMuscle Tissue Week 15 HGAPboultonbaileyNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Muscular SystemDocument7 pagesAnaphy Muscular SystemYo1No ratings yet
- Module 4 Read OnlyDocument18 pagesModule 4 Read Onlybejeweled1308No ratings yet
- 6.muscular TissueDocument40 pages6.muscular Tissuemero wowNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System: Myo and Mys - Muscle Sarco - FleshDocument4 pagesThe Muscular System: Myo and Mys - Muscle Sarco - FleshDCRUZNo ratings yet
- Types of Muscle TissueDocument11 pagesTypes of Muscle TissueAndrea Louise ReyesNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY - Muscular SystemDocument11 pagesANAPHY - Muscular SystemSoleil RiegoNo ratings yet
- Skeletal MuscleDocument72 pagesSkeletal Musclekiedd_0467% (3)
- Muscular Tissue I Reading: Chapter 10Document34 pagesMuscular Tissue I Reading: Chapter 10Marc Andreo MalalaNo ratings yet
- Chapte 3 MuscleDocument128 pagesChapte 3 MuscleErmias HadguNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Structure and FunctionDocument15 pagesChapter 1 - Structure and Functiontjewert23No ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue NotesDocument11 pagesMuscle Tissue NotesAubrey Unique EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Physiology Chapter 10 & 11 OutlineDocument8 pagesPhysiology Chapter 10 & 11 OutlineArtinDaryabariNo ratings yet
- 6 Contraction of Skeletal MuscleDocument109 pages6 Contraction of Skeletal MuscleHaslinNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue-Wl06.11Document54 pagesMuscle Tissue-Wl06.11api-19641337No ratings yet
- Human Physiology 4PHYM001W: Lecture 7 - Muscle Bradley Elliott B.elliott@westminster - Ac.uk @brads - ScienceDocument32 pagesHuman Physiology 4PHYM001W: Lecture 7 - Muscle Bradley Elliott B.elliott@westminster - Ac.uk @brads - ScienceNajma AhmedNo ratings yet
- Sarcolemma - Cell MembraneDocument66 pagesSarcolemma - Cell MembraneAman SyedNo ratings yet
- Locomotion and MovementDocument9 pagesLocomotion and Movementpoojari.dedeepyaNo ratings yet
- MuscleDocument1 pageMuscledjames12345No ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Study Guide: Chapter 10: Muscle Tissue and OrganizationDocument5 pagesHuman Anatomy Study Guide: Chapter 10: Muscle Tissue and OrganizationSuperjunior8No ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Muscle Tissue: VoluntaryDocument13 pagesChapter 10: Muscle Tissue: VoluntaryClyde BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue Types and Contraction MechanismsDocument39 pagesMuscle Tissue Types and Contraction MechanismsJennifer WootenNo ratings yet
- FF Raumenys PDFDocument34 pagesFF Raumenys PDFLaura PaškevičiūtėNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue OutlineDocument4 pagesMuscle Tissue OutlinePeachy PieNo ratings yet
- Skeletal MuscleDocument106 pagesSkeletal MusclePhysiology by Dr RaghuveerNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka (Mini Projek)Document18 pagesDaftar Pustaka (Mini Projek)herfikaNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy,: First Edition Mckinley & O'LoughlinDocument77 pagesHuman Anatomy,: First Edition Mckinley & O'LoughlinHarman BainzNo ratings yet
- M T (DR Sadiq)Document62 pagesM T (DR Sadiq)DR-Muhammad ZahidNo ratings yet
- Joints and Muscle Movement FinalDocument10 pagesJoints and Muscle Movement FinalNevandi ThenuwaraNo ratings yet
- Anaphy-Muscular HandoutDocument7 pagesAnaphy-Muscular HandoutAEGEL DARO TORRALBANo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 Life Processes-Movement in Animals and PlantsDocument15 pagesChapter - 3 Life Processes-Movement in Animals and PlantsArchanna VyassNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Growing Up in Filipino FamiliesDocument2 pagesGrowing Up in Filipino FamiliespazucenaNo ratings yet
- Harrison SLEDocument11 pagesHarrison SLEpazucenaNo ratings yet
- Inflammation PlenaryDocument52 pagesInflammation PlenarypazucenaNo ratings yet
- Ajss Psychology Rev - Answer SheetDocument59 pagesAjss Psychology Rev - Answer SheetpazucenaNo ratings yet
- Kalusugan PangkalahatanDocument4 pagesKalusugan PangkalahatanpazucenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter10 12 MemoDocument2 pagesChapter10 12 MemopazucenaNo ratings yet
- AJSSFinals - PsychologyDocument38 pagesAJSSFinals - PsychologypazucenaNo ratings yet
- AJSS Psychology RevDocument40 pagesAJSS Psychology RevpazucenaNo ratings yet
- AJSS Psychology RevDocument40 pagesAJSS Psychology RevpazucenaNo ratings yet
- Books For Learning Unit 3Document2 pagesBooks For Learning Unit 3pazucenaNo ratings yet
- Cook Time: 1 Hour, 10 Minutes Total Time: 1 Hour, 10 MinutesDocument2 pagesCook Time: 1 Hour, 10 Minutes Total Time: 1 Hour, 10 MinutespazucenaNo ratings yet
- Growing Up in Filipino FamiliesDocument2 pagesGrowing Up in Filipino FamiliespazucenaNo ratings yet
- Story PyramidDocument1 pageStory PyramidpazucenaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Health Primer and Legal IssuesDocument83 pagesReproductive Health Primer and Legal IssueskasamahumanrightsNo ratings yet
- Growing Up in Filipino FamiliesDocument2 pagesGrowing Up in Filipino FamiliespazucenaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document10 pagesLecture 5pazucenaNo ratings yet
- OS 203 06262013 Integumentary SystemDocument5 pagesOS 203 06262013 Integumentary SystempazucenaNo ratings yet
- Comb 1Document12 pagesComb 1pazucenaNo ratings yet
- The philosophical theory of solipsism explainedDocument9 pagesThe philosophical theory of solipsism explainedpazucena100% (1)
- 793Document7 pages793pazucenaNo ratings yet
- SonnetDocument8 pagesSonnetpazucenaNo ratings yet
- Pigeon Hole PrincipleDocument13 pagesPigeon Hole Principleapi-184588206No ratings yet
- Social PsychologyDocument1 pageSocial PsychologypazucenaNo ratings yet
- PhiloDocument1 pagePhilopazucenaNo ratings yet
- Social Psychology PSYC250Document21 pagesSocial Psychology PSYC250pazucenaNo ratings yet
- KierkegaardDocument7 pagesKierkegaardpazucenaNo ratings yet
- Big Bang Theory and The Origin of EarthDocument8 pagesBig Bang Theory and The Origin of EarthpazucenaNo ratings yet
- Arete and the Mean (MesotesDocument8 pagesArete and the Mean (MesotespazucenaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument4 pagesIntegumentary SystempazucenaNo ratings yet