Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Comparison Papers
Uploaded by
Aparna Bhardwaj0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesA comparison between various techniques
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA comparison between various techniques
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesComparison Papers
Uploaded by
Aparna BhardwajA comparison between various techniques
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
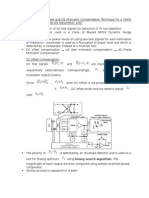
Paper 1: Uses adequate pair of DC test signals for detection of Tx non-idealities
Envelope detector used is a Class- B Biased NMOS Dynamic Range
Compressor
The polarity of the power levels on using two test signals for each estimation
of imbalance parameter is used as a fluctuation of power level test which is
detected by a comparator instead of a multi-bit ADC
DC offset compensation I/Q Gain mismatch compensation I/Q Phase
Mismatch Compensation
DC offset Compensation:
The polarity of
P1P2
is detected by an envelope detector and is used as a
test for finding optimum
C I using binary search algorithm. The
magnitudes of each output are then compared using sample-and-hold based
comparator.
Similar process is repeated for Q path!
No requirement for the detector to be linear as only polarity is used as a
condition. The non-linear property automatically compresses the dynamic
range of the signal essentially taking the place of variable gain circuit.
Paper 2: No training sequence
Adaptive LMS compensation independent of the statistic of the transmitted
data
Separate treatment of the three existing errors:
(i)
Quadrature Error
''
The envelope of
o' ( t )
is squared to obtain
E Q2 ( t )
Mean is obtained after multiplication with signum function i.e we
normalize the complex signal.
(ii)
Residual Carrier
After obtaining
' x'
and
' y '
Ec 2 ( t ) , we multiply by
to obtain residual errors
and
sign(x ( t ) )
and
respectively as
sign( y ( t ))
(iii)
Gain Imbalance Error
''
Improved Technique:
An adaptive setting of the reference squared envelope level using
simple LMS
Solution converges in about 2000 iterations for each error
Non-linearities in the ED will be taken into account
Paper 3: A complete offline technique for compensation
LMS Algorithm is used for compensation
Adaptation of Gain and Phase Imbalance
Adaptation is complete when all 4 phases give the same output
ve
from
the ED.
Error Signals are difference between test signal outputs in pairs:
Paper 4:
Compensates both frequency and non-frequency dependent compensation
parameters
Uses recursive algorithms to estimate the impairments from the
instantaneous power if the transmitted signal
Estimation and compensation are performed in the regular operation mode
Convergence Analysis is covered
Further convergence Analysis yet to be understood !
You might also like
- Agilent E4438C ESG Vector Signal Generator Differential I/Q OutputsDocument20 pagesAgilent E4438C ESG Vector Signal Generator Differential I/Q OutputsAparna BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Adl 5375Document36 pagesAdl 5375Aparna BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Spf5189z Data SheetDocument11 pagesSpf5189z Data SheetAparna BhardwajNo ratings yet
- TutorialDocument37 pagesTutorialAparna BhardwajNo ratings yet
- ADF4350Document32 pagesADF4350kolisavraNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra - Paul DawkinsDocument342 pagesLinear Algebra - Paul Dawkinssumeet141792% (13)
- An 1039Document8 pagesAn 1039Aparna BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Comparison PapersDocument7 pagesComparison PapersAparna BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Spf5189z Data SheetDocument11 pagesSpf5189z Data SheetAparna BhardwajNo ratings yet
- An 1039Document8 pagesAn 1039Aparna BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Spf5189z Data SheetDocument11 pagesSpf5189z Data SheetAparna BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Adl 5375Document36 pagesAdl 5375Aparna BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Adl 5375Document36 pagesAdl 5375Aparna BhardwajNo ratings yet
- CGHV27100Document10 pagesCGHV27100Aparna BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Av02 0050en - DS - Atf 52189 - 2013 11 11Document19 pagesAv02 0050en - DS - Atf 52189 - 2013 11 11Aparna BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Shield Beads: Fair-Rite Products CorpDocument5 pagesShield Beads: Fair-Rite Products CorpAparna BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Adl 5375Document36 pagesAdl 5375Aparna BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Ade 1Document2 pagesAde 1Ian McNairNo ratings yet
- Ptfa220121m-V4 Ds 08Document20 pagesPtfa220121m-V4 Ds 08Aparna BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Sky13286-359Lf: 0.1-6.0 GHZ High Isolation SPDT Absorptive SwitchDocument9 pagesSky13286-359Lf: 0.1-6.0 GHZ High Isolation SPDT Absorptive SwitchAparna BhardwajNo ratings yet
- RLM 23 1WL+Document2 pagesRLM 23 1WL+Aparna BhardwajNo ratings yet
- SYM-25DMHW+ DatasheetDocument2 pagesSYM-25DMHW+ DatasheetAparna BhardwajNo ratings yet
- RLM 23 1WL+ - NpaDocument1 pageRLM 23 1WL+ - NpaAparna BhardwajNo ratings yet
- SPF 5189zDocument10 pagesSPF 5189zAparna BhardwajNo ratings yet
- CGH09120FDocument12 pagesCGH09120FAparna BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Power Splitter/Combiner: SCN-3-16+ SCN-3-16Document1 pagePower Splitter/Combiner: SCN-3-16+ SCN-3-16Aparna BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Frequency Mixer SYM-25DMHW+: Typical Performance DataDocument5 pagesFrequency Mixer SYM-25DMHW+: Typical Performance DataAparna BhardwajNo ratings yet
- CGH25120FDocument11 pagesCGH25120FAparna BhardwajNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)