Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Schizophrenia Symptoms, Nursing Diagnoses, Interventions and Outcomes
Uploaded by
اسيرالاحزانOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Schizophrenia Symptoms, Nursing Diagnoses, Interventions and Outcomes
Uploaded by
اسيرالاحزانCopyright:
Available Formats
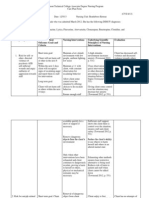
SCHIZOPHRENIA
S & Sx
:
(positive symptoms)
Hallucinations
Delusion
Disorganised speech/thinking/ behaviour
Catatonic behaviours
Delusion of reference
(negative symptoms)
Affective Flattening
Alogia
Avolition
Anhedonia
Attention(poor)
NCP
Nursing Diagnosis 1: Disturbed Thought Processes
Defining Characteristics
Inaccurate interpretation of stimuli (people
thinking his thoughts, trying to take
information from his brain).
Cognitive dysfunction, including memory
deficits, difficulty in problem solving and
abstraction.
Suspiciousness
Hallucinations
Confusion/disorientation
Impulsivity
Related Factors
Uncompensated alterations in brain
activity.
Inappropriate social behavior
Outcomes
Initial
1. Recognize changes in thinking and
Discharge
6. 6. Use coping strategies to deal with
behavior.
hallucinations and delusions.
2. Learn coping strategies to deal
7. 7. Communicate clearly with others.
effectively with hallucinations and
8. 8. Agree to take antipsychotic medication
delusions.
as prescribed.
3. Express delusional material less
9. 9. Maintain reality orientation.
frequently.
4. Take Risperdal as prescribed orally.
5. Participate in unit activities according to
treatment plan.
Interventions
Interventions
Initiate a nurse-patient
Rationale
A therapeutic relationship
Ongoing Assessment
Determine whether or not
relationship by
will provide PT support
PT can engage in a
demonstrating an
as he develops an
relationship.
acceptance of PT as a
awareness of
worthwhile human being
schizophrenia and the
through the use of
implications of the
nonjudgmental statements
disorder.
and behavior. Approach in
a calm, nurturing manner.
Be patient (patients brain
is not processing data
normally) and nurturing.
Assist PT in differentiating
between his own thoughts
Initially, PT will be unable
Determine if PT is
and reality. Validate the
to determine whether or
convinced that his
presence of
not his hallucinations are
perceptual experiences
hallucinations. Identify
reality based. Because
are hallucinations.
them as a part of the
hallucinations tend to be
disorder and explain that
repeated, the patient
they are present because
learns that recurring
of the metabolic changes
perceptual experiences
that are occurring in his
that are not confirmed by
brain. Focus on reality-
others are hallucinations.
oriented aspects of the
The patient can learn to
communication.
focus on reality and
ignore the perceptual
Teach PT about his disorder.
Assure him that the
experience.
Helping PT understand his
Assess whether or not PT
symptoms can be
disorder will give him a
can process the
improved and that he can
sense of control over his
information. Has the
manage the disorder.
disorder and give him
confusion been
the information he needs
alleviated?
to manage the
Administer Risperdal as
prescribed. Teach about
symptoms.
Risperdal is a
Observe for relief of
the action, side effects,
monoaminergic
positive symptoms and
and dosage of medication.
antagonist of D2 and 5-
assess for side effects,
Emphasize the importance
HT2 postsynaptic. It is
especially extrapyramidal
of taking medication after
indicated for the
symptoms (specifically
discharge, even if
management of the
acute dystonic reactions,
symptoms go away
manifestations of
akathisia,
completely. Ask patient
psychotic disorders.
pseudoparkinsonism).
for a commitment to take
Observe for orthostatic
the medication.
hypotension.
When patient is
hallucinating, determine
By refocusing PTs
Determine whether or not
the significance to the
attention from
the hallucination is
patient (what are the
hallucinations to reality,
frightening to the patient
voices telling him?), then
he will begin to develop
or giving patient
try to reassure PT that he
coping skills to control
command, especially to
is not alone and then
the perceptual
harm self or others.
redirect him to the here-
experience. It is
Assess patients response
and-now.
important for the nurse
to the hallucination.
to understand the context
Assess his ability to be
of the hallucination to
redirected to the here-
provide the appropriate
and-now.
When patient is making
delusional statements,
supportive intervention.
Delusions, by definition, are Assess the meaning of the
assess the significance of
fixed false beliefs. They
delusion to the patient.
the delusion to the patient
cannot be changed
Determine if the patient
(it is frightening), support
through logical
can be redirected.
patient if necessary, and
argument. Because the
redirect to the here-and-
patient is convinced of
now. Do not try to
the truth of the delusion,
convince PT that the
the individual should be
delusion is false.
supported if the delusion
Assist patient in
communicating
is upsetting to him.
Patients with schizophrenia
Determine situations that
effectively. Encourage
typically have problems
cause PT the most
patient to attend
because of the disordered
problem in
communication groups.
thought process.
communicating.
Improving
communication skills
will help the patient cope
Assess ability for self-care
activities. Identify areas
with the disorder.
The negative symptoms of
Monitor patients actual
of physical care for which
schizophrenia can
ability to complete self-
the patient needs
interfere with the
care activities. Assist
assistance. Note level of
patients ability to
when necessary.
motivation and interest in
complete daily living
appearance.
activities.
Assess sleep and rest
patterns. If problems with
PT was unable to sleep
sleep continue after
before admission. The
initiation of medication,
prescribed medications
explore techniques that
are sedating and may
may promote sleep.
reverse the insomnia.
Observe patients sleep
cycle.
Structure times for sleep,
rest, and diversional
activities.
Evaluation
Outcomes
Within the safety of the
nurse-patient
Revised Outcomes
Continue to learn about
schizophrenia.
Interventions
Refer to symptom
management group at the
relationship, PT
mental health center.
acknowledges that his
thinking and behavior
have changed from the
beginning of school
until now. He is
perplexed by the
change.
PT continues to have
Use strategies to reduce
Encourage PT to practice
hallucinations and
hallucinations and
strategies that reduce
delusional thinking. He
delusions. Structure daily
hallucinations and
is beginning to develop
activities to avoid
delusions. Discuss the
strategies for dealing
isolation, withdrawal,
development of a daily
with the unusual
and negative symptoms.
routine with PT and his
perceptual experiences.
parents.
He is also having
problems with being
motivated to complete
daily activities.
PT understood that he had a
disorder called
Continue to learn about
schizophrenia.
Refer to case manager and
recommend individual
schizophrenia, but was
supportive therapy at the
not sure what it meant.
mental health clinic.
The medication has
decreased the intensity
Continue to take medication
as prescribed.
of the hallucinations and
Refer to medication group
at the mental health
center.
the frequency of
delusional thoughts. He
agrees to take the
Risperdal as prescribed.
Through attending the unit
Develop communication
Discuss the possibility of a
activities, PT was able
skills to interact with
day treatment program for
to improve his
others.
PT that will help him
communication skills
improve his
and maintain reality
communication skills.
orientation.
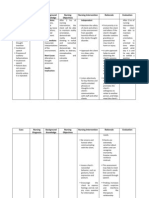
Nursing Diagnosis 2: Risk for Violence
Defining Characteristics
Assaultive toward others, self, and
Related Factors
Frightened, secondary to auditory
environment
hallucination and delusional thinking
Presence of pathophysiologic risk factors:
delusional thinking
Excessive activity and explosive agitated
comments (catatonic excitement)
Poor impulse control
Dysfunctional communication patterns
Outcomes
Initial
1. Avoid hurting self or assaulting other
patients or staff, with assistance from
Discharge
3. Control behavior with assistance from
staff and parents.
staff.
2. Decrease agitation and aggression.
Interventions
Interventions
Acknowledge patients fear,
Rationale
Hallucinations and
Ongoing Assessment
Determine if patient is able
hallucinations, and
delusions change an
to hear you. Assess his
delusions. Be genuine and
individuals perception of
response to your
empathetic. Assure patient
environmental stimuli.
comments and his ability
that you will help him
Patient is truly frightened
to concentrate on what is
control behavior and keep
and is responding out of
being said.
him safe. Begin to
his need to preserve his
establish a trusting
own safety.
relationship.
Offer patient choices of
By giving patient choices,
Listen for his response to
maintaining safety:
he will begin to develop a
choices. Is he able to
staying in the seclusion
sense of control over his
make choices at this
room, medications to help
behavior. Seclusion and
time? Is he starting to
him relax. Avoid
restraint are options only
engage in the nurse-
mechanical restraints and
for persons exhibiting
patient relationship?
a show of force by having
serious, persistent
several persons
aggression. The persons
approaching him at once.
safety must be protected at
all times.
Administer Ativan 2 mg.
The exact mechanisms of
Observe for relief of
Offer oral medication
action are not understood,
agitation and side effects:
first. If IM necessary, give
but the medication is
drowsiness, dizziness,
injections deep into
believed to potentiate the
constipation, diarrhea, dry
muscle mass; monitor
inhibitory neurotransmitter
mouth, nausea.
injection sites.
aminobutyric acid. It
relieves anxiety and
produces a sedative effect.
Ativan is rapidly absorbed,
thus produces desired
effects quickly.
Evaluation
Outcomes
PT was placed in seclusion
Revised Outcomes
Demonstrate control of
Interventions
Teach PT about the effects
with constant observation.
behavior by resisting
of hallucinations and
Ativan decreased his
hallucinations and
delusions. Problem-solve
agitation and was
delusions.
with him ways of
administered three times.
controlling auditory
After 2 days he was less
hallucinations if they
agitated and less
continue.
aggressive. On his third
day in the hospital, he was
able to come out of the
seclusion room for brief
periods of time. At these
times he would stand in
one spot for as long as 20
minutes without moving
except to shake his head
once in a while.
Nursing Diagnosis 3: Imbalanced Nutrition: Less than Body Requirements
Defining Characteristics
Inadequate food intake less than
recommended daily requirement.
Related Factors
Refusal to eat because of delusional
thinking: He has the Power.
Outcomes
Initial
Discharge
1. Food intake will match energy
3. Weight will be between 160 and 174 lb.
expenditures (roughly 2,000-3,000
4. PT will be able to describe the food
calories)
pyramid and identify foods he likes and
2. PT will eat at least 3 meals per day, with
amounts for each section.
snacks in late afternoon and late evening.
Interventions
Interventions
Offer small frequent meals.
Rationale
For someone who has not
Ongoing Assessment
Intake and output and a
been eating well, small
calorie count until fluid
meals are easier to
intake is adequate and
tolerate.
calorie intake is 2,500 to
3,000 cal.
Suggest parents bring meals
Familiar foods are more
Intake and output when
that PT likes when they
likely to be eaten.
family members present.
visit; encourage family to
Observe family interaction.
visit at mealtimes
occasionally.
Allow PT to eat alone
Being comfortable when
Observe PTs interaction
initially; gradually allow
eating is important. A
with others to know when
him to eat with increasing
patient who is
he should be encouraged to
numbers of patients at
uncomfortable with
eat with others.
mealtimes.
others may not eat in
front of other people.
After medications have
PT will not be able to retain
Assess cognitive
improved PTs attention
information while
functioning to determine
span, teach him about
confused and
when teaching can be
nutritious food selection
disoriented.
implemented.
and the food pyramid.
Evaluation
Outcomes
PT is eating all meals and
Revised Outcomes
Interventions
Maintain adequate nutrition. Explore the need to
snacks with other patients.
continue nutritional
He has a healthy appetite
education based on plans
and has been consuming
for PT and his family
at least 3,000 calories a
after discharge.
day. He weighs 158 lb.
PT can identify the foods in
the food pyramid but
states his mother knows
what foods to boy.
You might also like
- Schizophrenia Care Plan RNDocument8 pagesSchizophrenia Care Plan RNlisa75% (4)
- Care Plan For SchizophreniaDocument6 pagesCare Plan For SchizophreniaAllea Likestolaugh Brown100% (2)
- Bipolar Disorders Care Plan Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesBipolar Disorders Care Plan Nursing Care PlanAnne de Vera0% (1)
- SCHIZOPHRENIA Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageSCHIZOPHRENIA Nursing Care Planrinkai130% (1)
- NCP For SchizoDocument5 pagesNCP For SchizoRichelene Mae Canja100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plans SchizDocument27 pagesNursing Care Plans SchizClariza Castro76% (17)
- A NCP SchizoDocument5 pagesA NCP SchizoJoseph Wilson Macasa50% (4)
- NCP PsychosisDocument3 pagesNCP Psychosisinagasi100% (7)
- Schizophrenia NCPDocument2 pagesSchizophrenia NCPNicole cuencos100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan - SchizophreniaDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan - SchizophreniaJasmin Jacob76% (46)
- NCP FinalDocument22 pagesNCP FinalAlmira Ahamad100% (1)
- Paranoid Schizophrenia NCPDocument8 pagesParanoid Schizophrenia NCPCherubim Lei DC Flores67% (3)
- NCPDocument1 pageNCPNneka Andrea Datiles0% (2)
- NCP BSN 3rd Yr Psychiatric WardDocument9 pagesNCP BSN 3rd Yr Psychiatric WardMary Margarett BoadoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanJewelyn Bronda100% (2)
- NCP PsychDocument2 pagesNCP PsychJray Inocencio50% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan 1 Risk For Violence, Self DirectedDocument9 pagesNursing Care Plan 1 Risk For Violence, Self Directeddbryant010193% (14)
- Cues Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: StoDocument3 pagesCues Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: StoSuzette Rae TateNo ratings yet
- Altered Sensory and Disturbed Thought ProcessDocument4 pagesAltered Sensory and Disturbed Thought ProcessRosecinie Torrente100% (2)
- 4 NCP SchizophreniaDocument9 pages4 NCP SchizophreniaHazel Banday100% (4)
- NCP DisturbedThoughtProcessesDocument1 pageNCP DisturbedThoughtProcessesJoan KarlaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument8 pagesNCPTrixia Diaz67% (3)
- ND - Disturbed Thought ProcessDocument2 pagesND - Disturbed Thought ProcessHu DawiNo ratings yet
- NCP SchizophreniaDocument7 pagesNCP SchizophreniaSteffi Raye Madrid50% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan PsychDocument12 pagesNursing Care Plan Psychblarehead88% (24)
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With SchizophreniaDocument14 pagesNursing Care Plan For A Patient With SchizophreniaMary Luz De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- NursingDx ImpairedVerbalComm SchizophreniaDocument8 pagesNursingDx ImpairedVerbalComm Schizophreniajmanipon_1100% (1)
- NCP Assessment Diagnosis Planning Short-Term GoalDocument4 pagesNCP Assessment Diagnosis Planning Short-Term GoalJessieRamosAnicetoNo ratings yet
- Xi. Nursing Care PlansDocument4 pagesXi. Nursing Care PlansNic Ji100% (1)
- NCP Psyche2Document6 pagesNCP Psyche2Nica RTNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint of Undifferentiated SchizophreniaDocument14 pagesPowerpoint of Undifferentiated SchizophreniaGian Carlo Soriente0% (1)
- Bipolar NCPDocument4 pagesBipolar NCPcandy19agustin100% (1)
- Submitted By: Charisa S. Simbajon BSN IvDocument8 pagesSubmitted By: Charisa S. Simbajon BSN IvCharisa Simbajon100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plans For Acute ConfusionDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plans For Acute Confusionynecesity75% (4)
- BPD NCP 1Document4 pagesBPD NCP 1Jordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- NCP SchizophreniaDocument2 pagesNCP Schizophreniajoshua canja100% (5)
- Scizophrenia NCP2Document12 pagesScizophrenia NCP2Kholid Abu Mohammad AlfaizinNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective: "I Drink Alcohol and General: Independent: Independent: Goals Met GenreralDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective: "I Drink Alcohol and General: Independent: Independent: Goals Met GenreralRomzy BasañesNo ratings yet
- Care Plan 27Document10 pagesCare Plan 27Oroma TobiasNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia NCPDocument4 pagesSchizophrenia NCPGladys Barcelona91% (55)
- N C PDocument3 pagesN C PTrixia Diaz100% (1)
- Psych Care PlanDocument3 pagesPsych Care Plancwarrington0967% (3)
- Care Plan For Schizoaffective DisorderDocument2 pagesCare Plan For Schizoaffective DisorderThalia Peart100% (13)
- NCP For Bipolar Risk For Injury Related To Extreme Hyperactivity As Evidenced by Excessive and Constant Motor ActivityDocument3 pagesNCP For Bipolar Risk For Injury Related To Extreme Hyperactivity As Evidenced by Excessive and Constant Motor Activitydana75% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan For Paranoid SchizophreniaDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Paranoid SchizophreniaAyra Batore Laguitao88% (17)
- Defensive coping nursing diagnosisDocument3 pagesDefensive coping nursing diagnosisRoch Oconer100% (1)
- 5 NCPDocument3 pages5 NCPAllord Lacanilao Bungay0% (1)
- 5 Prioritized Problems Bipolar 1Document18 pages5 Prioritized Problems Bipolar 1Joseph D. Wang100% (30)
- NCP For SchizoDocument6 pagesNCP For SchizoGILIANNE MARIE JIMENEANo ratings yet
- NCP SchizDocument12 pagesNCP SchizKristine Reyes - MerleNo ratings yet
- Major Depression NCPDocument2 pagesMajor Depression NCPSeann LorescoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - SchizophreniaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan - SchizophreniaJasmin Jacob80% (5)
- Introduction of SchezophreniaDocument9 pagesIntroduction of SchezophreniasuryantieyNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Study GuideDocument18 pagesPsychiatric Study Guiderebeccacampbell100% (1)
- Disorders of thought form and memory disordersDocument41 pagesDisorders of thought form and memory disordersRohini SelvarajahNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans For Delusional DisorderDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plans For Delusional Disorderkirill61195% (22)
- Understanding Delusions and Their Management in Psychiatric NursingDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Delusions and Their Management in Psychiatric Nursingrmconvidhya sri2015No ratings yet
- Rather Than Desirable, Outcomes.: What Is Impulsivity?Document7 pagesRather Than Desirable, Outcomes.: What Is Impulsivity?Suresh LukoseNo ratings yet
- HESI PsyDocument16 pagesHESI PsyKrista Howe100% (13)
- Management of Psychotic SymptomsDocument25 pagesManagement of Psychotic Symptomsmisstheatricality130No ratings yet
- Central Venous Line Insertion & CareDocument34 pagesCentral Venous Line Insertion & Careاسيرالاحزان100% (2)
- Central Venous Line Insertion & CareDocument34 pagesCentral Venous Line Insertion & Careاسيرالاحزان100% (2)
- Standard PrecautionDocument15 pagesStandard PrecautionاسيرالاحزانNo ratings yet
- السكري (تم حفظه تلقائيا)Document31 pagesالسكري (تم حفظه تلقائيا)اسيرالاحزانNo ratings yet
- Clinical Manual of Addiction PsychopharmacologyDocument403 pagesClinical Manual of Addiction Psychopharmacologyاسيرالاحزان100% (6)
- Schizophrenia Symptoms, Nursing Diagnoses, Interventions and OutcomesDocument9 pagesSchizophrenia Symptoms, Nursing Diagnoses, Interventions and Outcomesاسيرالاحزان100% (1)
- 11-GI DrugsDocument56 pages11-GI DrugsاسيرالاحزانNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan GuidelinesDocument4 pagesHealth Teaching Plan GuidelinesaltianNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument72 pagesDrugs Acting On Peripheral Nervous SystemاسيرالاحزانNo ratings yet
- What Is Diabetes Mellitus (Type II) ?Document4 pagesWhat Is Diabetes Mellitus (Type II) ?اسيرالاحزانNo ratings yet
- Cerebral PalsyDocument20 pagesCerebral PalsyاسيرالاحزانNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument52 pagesUrinary SystemاسيرالاحزانNo ratings yet
- Forensic Psychiatry 2Document33 pagesForensic Psychiatry 2joglekar.vp6207100% (6)
- Difference Between PTSD and Developmental/Complex TraumaDocument10 pagesDifference Between PTSD and Developmental/Complex Traumaaqib aliNo ratings yet
- 04-04 SpenceDocument2 pages04-04 SpenceKaya SNo ratings yet
- 237 Dementia Awareness Answers - OdtDocument3 pages237 Dementia Awareness Answers - OdtThakurainChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Catatonia: FeaturesDocument6 pagesCatatonia: FeaturesfirehuNo ratings yet
- The Enneagram Types and Personality DisordersDocument28 pagesThe Enneagram Types and Personality DisordersKaiwan Shepherd100% (1)
- PERDEV REVIEWER 2nd QuarterDocument1 pagePERDEV REVIEWER 2nd QuarterDell OleahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mental HealthDocument36 pagesIntroduction To Mental HealthXo Yem100% (2)
- Counseling QuestionnaireDocument4 pagesCounseling QuestionnaireEva JocsonNo ratings yet
- Clinical Psychology Case Study AllisonDocument9 pagesClinical Psychology Case Study AllisonIoana VoinaNo ratings yet
- Dolores Mosquera, Anabel Gonzalez, Onno Van Der Hart - Borderline Personality Disorder PDFDocument30 pagesDolores Mosquera, Anabel Gonzalez, Onno Van Der Hart - Borderline Personality Disorder PDFGoguta100% (1)
- Komorbiditas Anak Gangguan Spektrum AutismeDocument6 pagesKomorbiditas Anak Gangguan Spektrum AutismeIrvan Wahyu PutraNo ratings yet
- Case Study of PhobiasDocument8 pagesCase Study of PhobiasNsengimana Eric MaxigyNo ratings yet
- Psyc1002-Ch.14 Lec NotesDocument4 pagesPsyc1002-Ch.14 Lec NotesNadya B.No ratings yet
- Understanding The Mental Status Examination: With The Help of VideosDocument38 pagesUnderstanding The Mental Status Examination: With The Help of Videosdev100% (1)
- Death Anxiety and Its Association With Hypochondriasis PDFDocument8 pagesDeath Anxiety and Its Association With Hypochondriasis PDFRebeca SilvaNo ratings yet
- DipressionDocument8 pagesDipressionImtiaz Hussain100% (1)
- Patient Write-Up Example 2Document6 pagesPatient Write-Up Example 2Meliara101No ratings yet
- Antisocial Personality Disorder ExplainedDocument16 pagesAntisocial Personality Disorder ExplainedSiti Musliha100% (1)
- APA - (2011) DSM-5 Development. Personality and Personality DisordersDocument16 pagesAPA - (2011) DSM-5 Development. Personality and Personality DisordersRodrigo Middleton InfanteNo ratings yet
- Top 7 Natural Homeopathic Medicines For Schizophrenia - HomeopathyDocument118 pagesTop 7 Natural Homeopathic Medicines For Schizophrenia - HomeopathyMadhu RondaNo ratings yet
- Paranoia Is A Disturbed Thought Process Characterized by Excessive Anxiety or FearDocument11 pagesParanoia Is A Disturbed Thought Process Characterized by Excessive Anxiety or FearNaresh MaliNo ratings yet
- Somatisation Definitions, Symptoms and CausesDocument5 pagesSomatisation Definitions, Symptoms and CausesNaifa Claresta SalsabyllaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Community PsychologyDocument84 pagesPrinciples of Community PsychologyAditya Putra KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Mcqs PsychiatryDocument27 pagesMcqs Psychiatrypriya009100% (6)
- University of The Punjab - Life-SciencesDocument14 pagesUniversity of The Punjab - Life-SciencesNadir IqbalNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Mental Health Nursing & Psychiatric Papers QPDocument15 pages2.3 Mental Health Nursing & Psychiatric Papers QPTapobrata SarkarNo ratings yet
- 5 PTSD Symptom Set in A Long-TermDocument13 pages5 PTSD Symptom Set in A Long-TermAnya RomanovNo ratings yet
- Evidence Based Assessment of OCDDocument17 pagesEvidence Based Assessment of OCDDanitza YhovannaNo ratings yet