Professional Documents
Culture Documents
For You To Read Representing Motion Kilometers and Miles: Safety
Uploaded by
Reeja Mathew0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pageactivity physics
Original Title
92
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentactivity physics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pageFor You To Read Representing Motion Kilometers and Miles: Safety
Uploaded by
Reeja Mathewactivity physics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
CS_Ch2_Safety
2/24/05
12:05 AM
Page 92
Safety
FOR YOU TO READ
Kilometers and Miles
Representing Motion
One way to show motion is
with the use of strobe photos.
A strobe photo is a multiple-exposure photo in
which a moving object is photographed at
regular time intervals.The sketches you used in
Steps 1, 2, and 3 in For You To Do are similar
to strobe photos. Here is a strobe photo of a car
traveling at the average speed of 50 mph.
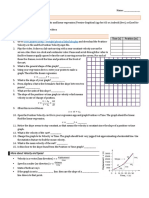
Another way to represent motion is with graphs.
The graph below shows a car traveling at the
average speed of 50 mph.
Distance (miles)
200
Highway signs and speed limits in the USA are
given in miles per hour, or mph.
Almost every other country in
the world uses kilometers to
measure distances. A
kilometer is a little less than
two-thirds of a mile. Kilometers
per hour (km/h) is used to
measure highway driving speed. Shorter
distances, such as for track events and
experiments in a science class,
are measured in meters
per second, m/s.
You will use mph when
working with driving
speeds, but meters per
second for data you collect in
class.The good news is that you
do not need to change measures
between systems. It is important to
be able to understand and compare measures.
To help you relate the speeds with which you are
comfortable to the data you collect in class, the
chart below gives approximate comparisons.
150
100
50
1
Time (hours)
School zone
25 mph
40 km/h
11 m/s
Residential
street
35 mph
55 km/h
16 m/s
Suburban
interstate
55 mph
90 km/h
25 m/s
Rural
interstate
75 mph
120 km/h
34 m/s
92
Active Physics
You might also like
- Measuring Speed with Mile Markers and a WristwatchDocument7 pagesMeasuring Speed with Mile Markers and a WristwatchRio CarthiisNo ratings yet
- 1DKin2 PDFDocument4 pages1DKin2 PDFRane Arielle0% (1)
- Kinematics Motion SpeedDocument10 pagesKinematics Motion SpeedDyna MoNo ratings yet
- Speed and VelocityDocument4 pagesSpeed and VelocityMarwa ChidiakNo ratings yet
- VelocityDocument4 pagesVelocityMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Ch02-Walding 4th Forces and Motion PDFDocument31 pagesCh02-Walding 4th Forces and Motion PDFJosh FlandersNo ratings yet
- Glencoe Inquiry Motion and MomentumDocument28 pagesGlencoe Inquiry Motion and Momentumapi-234699598No ratings yet
- Year 7 Science Forces Activity PackDocument47 pagesYear 7 Science Forces Activity PackAnasua BasuNo ratings yet
- Speed and VelocityDocument25 pagesSpeed and VelocityCriselAlamagNo ratings yet
- Speed and VelocityDocument4 pagesSpeed and VelocityMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- G12 Physics A1.1Document1 pageG12 Physics A1.1Janella QuirozNo ratings yet
- Quiz BeeDocument9 pagesQuiz BeejellyB RafaelNo ratings yet
- Motion Notes Part 3Document2 pagesMotion Notes Part 3api-247084136No ratings yet
- SpeedDocument4 pagesSpeedSusanne OngkowidjajaNo ratings yet
- Chap - 02 Textbook Glencoe MotionDocument30 pagesChap - 02 Textbook Glencoe MotionAnonymous PAZRKwBILGNo ratings yet
- Year10 Motion SummaryDocument3 pagesYear10 Motion SummaryWet waterNo ratings yet
- Speed: Submitted To: Submitted By: Mr. R. Ramesh Priyaal Gupta Physics Teacher IX O'Document18 pagesSpeed: Submitted To: Submitted By: Mr. R. Ramesh Priyaal Gupta Physics Teacher IX O'Megha GuptaNo ratings yet
- POGIL - KinematicsDocument4 pagesPOGIL - KinematicsmagiclcjNo ratings yet
- Speed Velocity and AccelerationDocument31 pagesSpeed Velocity and AccelerationJoric MagusaraNo ratings yet
- Physics 01-03Document3 pagesPhysics 01-03KevleenNo ratings yet
- Calculating SpeedDocument3 pagesCalculating SpeedMaridjan Wiwaha50% (2)
- Prof. Ismat M. ElhassanDocument30 pagesProf. Ismat M. ElhassanDaniel HailuNo ratings yet
- Units of SpeedDocument2 pagesUnits of SpeedmgrfanNo ratings yet
- LINEAR MOTION BASICSDocument9 pagesLINEAR MOTION BASICSAidi AmarNo ratings yet
- Spot Speed Study Report - Thein Than OoDocument16 pagesSpot Speed Study Report - Thein Than OoKiskadi ThomasNo ratings yet
- Speed RevisonDocument10 pagesSpeed RevisonMamdouhNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Speed Detection in Video Image Sequences Using CVS MethodDocument9 pagesVehicle Speed Detection in Video Image Sequences Using CVS MethodrevathyirsNo ratings yet
- SPEED & MOTION: UNDERSTANDING MOTION THROUGH GRAPHSDocument6 pagesSPEED & MOTION: UNDERSTANDING MOTION THROUGH GRAPHSHien DuongNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument5 pagesSciencearmain.mislang07No ratings yet
- 11-Kinematics Practice Test PDFDocument2 pages11-Kinematics Practice Test PDFD'ferti Anggraeni0% (2)
- Science 5 q3 Mod 1Document31 pagesScience 5 q3 Mod 1erikauclos856No ratings yet
- Speed and Velocity Worksheet 2.4.23Document3 pagesSpeed and Velocity Worksheet 2.4.23Richard WhittNo ratings yet
- Calculating Speed XCDocument3 pagesCalculating Speed XCLuisito GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Distance Displacement Key PDFDocument5 pagesLesson 3 Distance Displacement Key PDFDIPTENDU BISWASNo ratings yet
- Third Term Science 5 Modules 1-4Document17 pagesThird Term Science 5 Modules 1-4Kathleen FernandezNo ratings yet
- Speed and AccelerationDocument17 pagesSpeed and AccelerationDan Warren Loyola NuestroNo ratings yet
- SpeedDocument21 pagesSpeeddrexelNo ratings yet
- AP Physics Lab Report 1Document5 pagesAP Physics Lab Report 1abryant2113No ratings yet
- An Introduction to the Physics of SportsFrom EverandAn Introduction to the Physics of SportsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Guidence For Transport Engineering SurveyDocument73 pagesGuidence For Transport Engineering SurveyfaizmalfaNo ratings yet
- Calculating speed, time, distance and accelerationDocument3 pagesCalculating speed, time, distance and accelerationSherine Lois QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Q4 Intro To KinematicsDocument54 pagesScience 9 Q4 Intro To KinematicsSire WillNo ratings yet
- Understanding Speed and VelocityDocument12 pagesUnderstanding Speed and VelocityGopuNo ratings yet
- Pretest Postest Describing MotionDocument14 pagesPretest Postest Describing MotionRaymond ManalastasNo ratings yet
- Kin Unit Test 2014Document4 pagesKin Unit Test 2014Nicholas ChevalierNo ratings yet
- Speed, Time, and DistanceDocument53 pagesSpeed, Time, and Distancegracesilvaespiritu1202No ratings yet
- Explanation of Chano Da GreatDocument2 pagesExplanation of Chano Da GreatChanoNo ratings yet
- Physics of Everyday Phenomena A Conceptual Introduction To Physics 8th Edition Griffith Test BankDocument16 pagesPhysics of Everyday Phenomena A Conceptual Introduction To Physics 8th Edition Griffith Test BankMarkMannjbcaw100% (20)
- What is SpeedDocument2 pagesWhat is SpeedMarvin MelisNo ratings yet
- Speed & VelocityDocument8 pagesSpeed & VelocityDaniel BerryNo ratings yet
- Hitchcock - Motion Notes and Practice ProblemsDocument3 pagesHitchcock - Motion Notes and Practice Problemspkdm6n8g84No ratings yet
- Repaso de Examen 1 Fisica IDocument18 pagesRepaso de Examen 1 Fisica IAna MarquezNo ratings yet
- Physics KinematicsDocument34 pagesPhysics KinematicsSammasterzNo ratings yet
- KISS Notes Moving AboutDocument41 pagesKISS Notes Moving AboutJenniferBackhus100% (8)
- Units Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesUnits Lesson Plananj pianoNo ratings yet
- Ans 1 Dkin 2Document4 pagesAns 1 Dkin 2Dolores LocañasNo ratings yet
- Forces and Motion Chapter ExplainedDocument11 pagesForces and Motion Chapter ExplainedMaridjan WiwahaNo ratings yet
- Exposure Mastery: Aperture, Shutter Speed & ISO: The Difference Between Good and Breathtaking PhotographsFrom EverandExposure Mastery: Aperture, Shutter Speed & ISO: The Difference Between Good and Breathtaking PhotographsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Recreational Mechanics: A Source Book for Walkers and Track CoachesFrom EverandRecreational Mechanics: A Source Book for Walkers and Track CoachesNo ratings yet
- Calculate frequencies and energies of visible light wavelengthsDocument1 pageCalculate frequencies and energies of visible light wavelengthsReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of The ElementsDocument2 pagesPeriodic Table of The ElementsReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Solubility Rules: Checking UpDocument1 pageSolubility Rules: Checking UpReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Copper 1083 2336 Mercury 357 Oxygen: Preparing For The Chapter ChallengeDocument1 pageCopper 1083 2336 Mercury 357 Oxygen: Preparing For The Chapter ChallengeReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- The Law of Definite Proportions: Checking UpDocument1 pageThe Law of Definite Proportions: Checking UpReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- The Law of Definite Proportions: Checking UpDocument1 pageThe Law of Definite Proportions: Checking UpReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table: ExampleDocument1 pageThe Periodic Table: ExampleReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Volume and Mass of WaterDocument1 pageVolume and Mass of WaterReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Inverse Square Relation Light Intensity DistanceDocument1 pageInverse Square Relation Light Intensity DistanceReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- For You To Do: Patterns and PredictionsDocument1 pageFor You To Do: Patterns and PredictionsReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Freezing Point of Water, When Water Changes From A Liquid To A SolidDocument1 pageFreezing Point of Water, When Water Changes From A Liquid To A SolidReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Speed of The Car Relative To The Board: Activity 5 A Moving Frame of ReferenceDocument1 pageSpeed of The Car Relative To The Board: Activity 5 A Moving Frame of ReferenceReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Distance To Distance Current in Side of Area of Board (M) Squared Galvanometers (A) Square (CM) Square (CM)Document1 pageDistance To Distance Current in Side of Area of Board (M) Squared Galvanometers (A) Square (CM) Square (CM)Reeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Boiling Liquid Gas Added Condensation Gas Liquid Removed Evaporation Freezing Melting Deposition Gas Sublimation Solid VaporizationDocument1 pageBoiling Liquid Gas Added Condensation Gas Liquid Removed Evaporation Freezing Melting Deposition Gas Sublimation Solid VaporizationReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Symbols For Some Elements: Movie Special EffectsDocument1 pageSymbols For Some Elements: Movie Special EffectsReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- CriteriaDocument1 pageCriteriaReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Let Us Entertain You: Amplitude Time For Pulse To Travel From One End To The Other Average Time SpeedDocument1 pageLet Us Entertain You: Amplitude Time For Pulse To Travel From One End To The Other Average Time SpeedReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Calculating Force to Stop an Object in a Short TimeDocument1 pageCalculating Force to Stop an Object in a Short TimeReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Toys For Understanding: Direction of RotationDocument1 pageToys For Understanding: Direction of RotationReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Let Us Entertain YouDocument1 pageLet Us Entertain YouReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- CS_Ch2_Safety Measuring Response Time & Designing Car Safety DevicesDocument1 pageCS_Ch2_Safety Measuring Response Time & Designing Car Safety DevicesReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- How string length affects pitchDocument1 pageHow string length affects pitchReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- For You To Read Wave Vocabulary: Activity 1 Making WavesDocument2 pagesFor You To Read Wave Vocabulary: Activity 1 Making WavesReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- DC Generator: Toys For UnderstandingDocument1 pageDC Generator: Toys For UnderstandingReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Let Us Entertain You: (CM) (CM) 549 15 56 25 20 50 18 91 14 142Document1 pageLet Us Entertain You: (CM) (CM) 549 15 56 25 20 50 18 91 14 142Reeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Making Waves ExperimentDocument1 pageMaking Waves ExperimentReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Reflecting On The Activity and The ChallengeDocument1 pageReflecting On The Activity and The ChallengeReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Compare seat belt opinions by age groupDocument1 pageCompare seat belt opinions by age groupReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Newton's Second Law Explanation:: SafetyDocument1 pageNewton's Second Law Explanation:: SafetyReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- HarrodsDocument2 pagesHarrodsCristina BobocNo ratings yet
- GE8151 Python Programming Unit 3 Question Bank With Sample CodeDocument25 pagesGE8151 Python Programming Unit 3 Question Bank With Sample CodeN.VivekananthamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Vocab&GrammarDocument166 pagesVocab&GrammarWan AzliaNo ratings yet
- الإطار المفاهيمي للتنمية المستدامةDocument16 pagesالإطار المفاهيمي للتنمية المستدامةboualemdzNo ratings yet
- NDRRMC Update SitRep No. 7 For Typhoon KABAYAN (Muifa)Document6 pagesNDRRMC Update SitRep No. 7 For Typhoon KABAYAN (Muifa)Hiro Cerce Wilhelm ALDEN Abareta TonioNo ratings yet
- Desain LRT PDFDocument754 pagesDesain LRT PDFWahyu SaputraNo ratings yet
- Safety Can Chemical Compatibility ChartDocument1 pageSafety Can Chemical Compatibility ChartMan NamNo ratings yet
- 2021 TAMC Roads Bridges Annual ReportDocument36 pages2021 TAMC Roads Bridges Annual ReportWXMINo ratings yet
- Contract of Lease - Knoxport 2024 (Sept-Feb)Document8 pagesContract of Lease - Knoxport 2024 (Sept-Feb)Lexter Owen ApeladoNo ratings yet
- Gauhati University MPhil and PhD Admission NotificationDocument6 pagesGauhati University MPhil and PhD Admission NotificationAminul SikdarNo ratings yet
- The Spiritual Awakening Guide Kundalini Psychic Abilities and The Conditioned Layers of RealityDocument3 pagesThe Spiritual Awakening Guide Kundalini Psychic Abilities and The Conditioned Layers of RealitySolárioNo ratings yet
- ACCAF5 - Qbank2017 - by First Intuition Downloaded FromDocument384 pagesACCAF5 - Qbank2017 - by First Intuition Downloaded FromAbdul Jabbar Al-Shaer100% (4)
- Como Agua para Chocolate English PDFDocument2 pagesComo Agua para Chocolate English PDFDavidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Sample QuestionsDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Sample Questionschristina thearasNo ratings yet
- NCERT Class 10 Geography Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources SolutionsDocument3 pagesNCERT Class 10 Geography Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources SolutionsHemant SinghNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Distortions Handout TemplateDocument3 pagesCognitive Distortions Handout TemplateLand Bank CatanauanNo ratings yet
- Controlador Bomba Jockey Fta 550fDocument7 pagesControlador Bomba Jockey Fta 550fRubén VélezNo ratings yet
- Hydrologic Cycle IntroductionDocument18 pagesHydrologic Cycle IntroductionzeyadNo ratings yet
- All I Want For Christmas Is YouDocument3 pagesAll I Want For Christmas Is YoujoostNo ratings yet
- Course Outline: Return To Course IndexDocument9 pagesCourse Outline: Return To Course Indexoswaldo58No ratings yet
- ChucrutDocument6 pagesChucrutPAOLANo ratings yet
- ARTA MC 2022 05 - Annex A. CSM QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesARTA MC 2022 05 - Annex A. CSM QuestionnaireKaye Ashley TandasNo ratings yet
- Update to Kill Team Kommando rulesDocument2 pagesUpdate to Kill Team Kommando rulesPierreluc Dureau (Kikord)No ratings yet
- Elc151 - RT March 2022Document12 pagesElc151 - RT March 2022Batrisyia Awliya Ali AzwanNo ratings yet
- Aspectsofproductionspart1 1Document41 pagesAspectsofproductionspart1 1Michelle Melody OlivarNo ratings yet
- CLASS II Cavity PreparationDocument10 pagesCLASS II Cavity PreparationNguyễn Huy LongNo ratings yet
- Dragon Magazine Spells v304Document62 pagesDragon Magazine Spells v304wbrackney2350% (2)
- Experiment No 1 Preparation of CheeseDocument5 pagesExperiment No 1 Preparation of CheeseArmiee InfiniteNo ratings yet
- DEVELOPMENT of Material ResourcesDocument21 pagesDEVELOPMENT of Material ResourcesJennifer ManaogNo ratings yet
- MDHA Write-Up For Prospective StudentsDocument1 pageMDHA Write-Up For Prospective StudentsprashantNo ratings yet