Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DC Generator: Toys For Understanding
Uploaded by
Reeja MathewOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DC Generator: Toys For Understanding
Uploaded by
Reeja MathewCopyright:
Available Formats
CS_Ch4_Toys
2/24/05
1:16 AM
Page 232
Toys for Understanding
DC Generator
6. Your teacher will explain and demonstrate a hand-operated,
direct current (DC) generator. During the demonstration,
make the observations needed to answer these questions:
a) When the DC generator is used to light a bulb, describe
the brightness of the bulb when the generator is cranked
slowly, and rapidly. Write your observations in your log.
b) When the DC generator is connected to a galvanometer,
describe the action of the galvanometer needle when the
generator is cranked slowly, and rapidly.
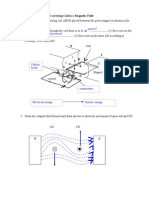
7. The diagram shows important parts of a DC generator. As
in Step 3, build a model of the generator to help you analyze
how it works.
Direction of
rotation
8. Use a graph similar to the one shown below. Complete the
graph using the same pattern of analysis applied to the AC
generator.
Drive shaft
Copper coil
C
Permanent
magnet
Split ring
a) At the instant shown in the DC generator diagram, the
induced current is maximum. The instant corresponds to
the rotating coil II. Plot a point on the graph directly above
1
the 4 -turn mark at a height equal to the top of the vertical
axis to represent maximum current flow at that instant.
1
b) At the instant 4 -turn earlier than the instant shown in
the DC generator figure, corresponding to the zero mark
of rotation, the current would have been zero because all
sides of the coil would have been moving parallel to the
direction of the magnetic field. Therefore, plot a point at
the origin of the graph.
c) Similarly, the induced current again would be zero at
1
the instant 4 -turn later than the instant shown in
the DC generator figure; therefore, plot a point on the
1
horizontal axis at the 2 -turn mark.
The current induced by a DC generator during one
rotation of the generator coil
Current
No current
1
4
232
Active Physics
Coil rotation,
fraction of turn
0
1
2
3
4
You might also like
- Toys For Understanding: Direction of RotationDocument1 pageToys For Understanding: Direction of RotationReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- 8 - DC Machines FundDocument20 pages8 - DC Machines FundSamiNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Physics AcDocument2 pagesProject Report On Physics AcAyyappan SudharshanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 DC MachinesDocument97 pagesChapter 2 DC Machinesb14.00010.20No ratings yet
- DC Generator2021Document28 pagesDC Generator2021Maysara BalakiNo ratings yet
- Ac GeneratorDocument2 pagesAc GeneratorDevansh JoshiNo ratings yet
- Electromechanical Energy ConversionDocument283 pagesElectromechanical Energy ConversionjcmeeNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion IDocument129 pagesEnergy Conversion IKhalil BahrEldinNo ratings yet
- Unit-I DC GeneratorsDocument45 pagesUnit-I DC GeneratorsParameshwar TummetiNo ratings yet
- AP X Physics Working of Motar and GeneratorDocument3 pagesAP X Physics Working of Motar and GeneratorVenkatesh P AtpNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - CHAPTER 5 240311 105505Document19 pagesMicrosoft Word - CHAPTER 5 240311 105505thivaa2703No ratings yet
- 2 Armature ReactionDocument10 pages2 Armature Reactionapi-328781544No ratings yet
- UNIT-2 Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument26 pagesUNIT-2 Basic Electrical Engineeringabhi shekNo ratings yet
- DC Motor QuestionsDocument8 pagesDC Motor Questionsankitj747No ratings yet
- complete chapter1 and tutorialDocument19 pagescomplete chapter1 and tutorialstevennguimsNo ratings yet
- 2,3. DC Generators & MotorsDocument84 pages2,3. DC Generators & MotorsnakkasrinuNo ratings yet
- How AC Motors Work Using Rotating Magnetic FieldsDocument5 pagesHow AC Motors Work Using Rotating Magnetic FieldsMathews IndiaNo ratings yet
- AC Fundamentals..Document32 pagesAC Fundamentals..Adil MehmoodNo ratings yet
- AC GENERATOR TITLEDocument6 pagesAC GENERATOR TITLESuman DasNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 DC Machines IDocument18 pagesTopic 8 DC Machines IThairu MuiruriNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current (Ac) Electrical MachineDocument18 pagesAlternating Current (Ac) Electrical MachineLaw Boon Khang TennarasuNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Notes On DC GeneratorDocument40 pagesMicrosoft Word - Notes On DC GeneratorDr. Deepika YadavNo ratings yet
- EASA Mod 3 BK 4 Ac & DC Mech PDFDocument76 pagesEASA Mod 3 BK 4 Ac & DC Mech PDFNavaraj BaniyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 4 AC Machinery FundamentalsDocument27 pagesChapter # 4 AC Machinery FundamentalsSamiNo ratings yet
- EE-260 : Electrical Machines Lecture#16Document23 pagesEE-260 : Electrical Machines Lecture#16Shafaq TauqirNo ratings yet
- A.C. GeneratorDocument6 pagesA.C. GeneratorChandan Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Rotating Field TheoryDocument74 pagesRotating Field TheoryKyambi MutiaNo ratings yet
- CH 4b Electromagnetic Induction - Key Examples 2022Document10 pagesCH 4b Electromagnetic Induction - Key Examples 2022andilenbNo ratings yet
- Development of Electromotive ForceDocument5 pagesDevelopment of Electromotive ForcesmhbNo ratings yet
- D.C. Generators: ChapterDocument34 pagesD.C. Generators: ChapterHuỳnh Thanh ThiệnNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines Lab March 16 UpdateDocument53 pagesElectrical Machines Lab March 16 Updatepeter vanderNo ratings yet
- Z-Learning 101 - Basics of Motors and Motor ControlsDocument44 pagesZ-Learning 101 - Basics of Motors and Motor ControlsridwantpNo ratings yet
- DC Machine FundamentalsDocument53 pagesDC Machine FundamentalsK04Anoushka TripathiNo ratings yet
- Information-No - 1 1 7-1Document12 pagesInformation-No - 1 1 7-1Black PearlNo ratings yet
- CH-2-DC MachineDocument83 pagesCH-2-DC MachineÙm ØrthøbøyNo ratings yet
- Turning Effect of A Current-Carrying Coil in A Magnetic FieldDocument0 pagesTurning Effect of A Current-Carrying Coil in A Magnetic FieldRizal SalasiahNo ratings yet
- Pid 2Document64 pagesPid 2RafaelNo ratings yet
- 5.0 DC Machines: Basic Electrical Engineering ELE 290Document20 pages5.0 DC Machines: Basic Electrical Engineering ELE 290Harizx SaufixNo ratings yet
- AC Induction Motor Principles in 40 CharactersDocument11 pagesAC Induction Motor Principles in 40 CharacterslifesvcksNo ratings yet
- DC Generator Ee301Document16 pagesDC Generator Ee301Fred S. RickNo ratings yet
- EEE20005 Week 6 7Document96 pagesEEE20005 Week 6 7ShelbyNo ratings yet
- SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR PHADocument15 pagesSYNCHRONOUS MOTOR PHA0004Prathamesh TayadeNo ratings yet
- Physics 12th AC Generator PDFDocument17 pagesPhysics 12th AC Generator PDFluckyNo ratings yet
- Physics 12th AC Generator PDFDocument17 pagesPhysics 12th AC Generator PDFlucky100% (2)
- EE-260 Lecture 14 To 16 AC MachineryDocument50 pagesEE-260 Lecture 14 To 16 AC MachineryRehan BasharatNo ratings yet
- Department of Electronics & Communication Course: Microcontroller Based System Design Course Code: ECE-358Document8 pagesDepartment of Electronics & Communication Course: Microcontroller Based System Design Course Code: ECE-358Varun SinghNo ratings yet
- Ac Generators: By:D.deepa Lakshmi 12 BDocument11 pagesAc Generators: By:D.deepa Lakshmi 12 BSharuk sNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument21 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectKarishma SharmaNo ratings yet
- Magnetism To Transformer (Pear) Set 1 (Question)Document10 pagesMagnetism To Transformer (Pear) Set 1 (Question)6C09 FUNG CHI LAMNo ratings yet
- ElectromagnetismDocument2 pagesElectromagnetismGauravNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Physics Chapter 3 - Teacher'sDocument17 pagesForm 5 Physics Chapter 3 - Teacher'sPavithiran80% (5)
- DC Machines2Document97 pagesDC Machines2Carlos VásquezNo ratings yet
- AC Generator: Working, Construction and ApplicationsDocument15 pagesAC Generator: Working, Construction and ApplicationsSPS KUSHWAHANo ratings yet
- Physics Word Document-2Document9 pagesPhysics Word Document-2shanmugapriyamanisadhu05No ratings yet
- Kayezelle Mendoza AC DC Lab4Document11 pagesKayezelle Mendoza AC DC Lab4Jaloyd MacalalagNo ratings yet
- EE-260 Lecture on Electro-Mechanical Systems and Induced TorqueDocument19 pagesEE-260 Lecture on Electro-Mechanical Systems and Induced TorqueJeff HardyNo ratings yet
- EM2 Lab 1Document6 pagesEM2 Lab 1Amit ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- A New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysFrom EverandA New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Solubility Rules: Checking UpDocument1 pageSolubility Rules: Checking UpReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of The ElementsDocument2 pagesPeriodic Table of The ElementsReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Calculate frequencies and energies of visible light wavelengthsDocument1 pageCalculate frequencies and energies of visible light wavelengthsReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Boiling Liquid Gas Added Condensation Gas Liquid Removed Evaporation Freezing Melting Deposition Gas Sublimation Solid VaporizationDocument1 pageBoiling Liquid Gas Added Condensation Gas Liquid Removed Evaporation Freezing Melting Deposition Gas Sublimation Solid VaporizationReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- For You To Do: Patterns and PredictionsDocument1 pageFor You To Do: Patterns and PredictionsReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table: ExampleDocument1 pageThe Periodic Table: ExampleReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- The Law of Definite Proportions: Checking UpDocument1 pageThe Law of Definite Proportions: Checking UpReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Copper 1083 2336 Mercury 357 Oxygen: Preparing For The Chapter ChallengeDocument1 pageCopper 1083 2336 Mercury 357 Oxygen: Preparing For The Chapter ChallengeReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- The Law of Definite Proportions: Checking UpDocument1 pageThe Law of Definite Proportions: Checking UpReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Volume and Mass of WaterDocument1 pageVolume and Mass of WaterReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Symbols For Some Elements: Movie Special EffectsDocument1 pageSymbols For Some Elements: Movie Special EffectsReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Freezing Point of Water, When Water Changes From A Liquid To A SolidDocument1 pageFreezing Point of Water, When Water Changes From A Liquid To A SolidReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Let Us Entertain You: (CM) (CM) 549 15 56 25 20 50 18 91 14 142Document1 pageLet Us Entertain You: (CM) (CM) 549 15 56 25 20 50 18 91 14 142Reeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Distance To Distance Current in Side of Area of Board (M) Squared Galvanometers (A) Square (CM) Square (CM)Document1 pageDistance To Distance Current in Side of Area of Board (M) Squared Galvanometers (A) Square (CM) Square (CM)Reeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Speed of The Car Relative To The Board: Activity 5 A Moving Frame of ReferenceDocument1 pageSpeed of The Car Relative To The Board: Activity 5 A Moving Frame of ReferenceReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Compare seat belt opinions by age groupDocument1 pageCompare seat belt opinions by age groupReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Inverse Square Relation Light Intensity DistanceDocument1 pageInverse Square Relation Light Intensity DistanceReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- CriteriaDocument1 pageCriteriaReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Newton's Second Law Explanation:: SafetyDocument1 pageNewton's Second Law Explanation:: SafetyReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Let Us Entertain YouDocument1 pageLet Us Entertain YouReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- How string length affects pitchDocument1 pageHow string length affects pitchReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- For You To Read Wave Vocabulary: Activity 1 Making WavesDocument2 pagesFor You To Read Wave Vocabulary: Activity 1 Making WavesReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Calculating Force to Stop an Object in a Short TimeDocument1 pageCalculating Force to Stop an Object in a Short TimeReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Making Waves ExperimentDocument1 pageMaking Waves ExperimentReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Reflecting On The Activity and The ChallengeDocument1 pageReflecting On The Activity and The ChallengeReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Let Us Entertain You: Amplitude Time For Pulse To Travel From One End To The Other Average Time SpeedDocument1 pageLet Us Entertain You: Amplitude Time For Pulse To Travel From One End To The Other Average Time SpeedReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- For You To Read Representing Motion Kilometers and Miles: SafetyDocument1 pageFor You To Read Representing Motion Kilometers and Miles: SafetyReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- CS_Ch2_Safety Measuring Response Time & Designing Car Safety DevicesDocument1 pageCS_Ch2_Safety Measuring Response Time & Designing Car Safety DevicesReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Common Lab TechniquesDocument6 pagesCommon Lab TechniquesQueen Alyana BernabeNo ratings yet
- Stc-12650 Fonte Itx Entrada 12vDocument3 pagesStc-12650 Fonte Itx Entrada 12vYung SangNo ratings yet
- IS - IEC 62271-1 (2007) - High-Voltage Switchgear and Controlgear, Part 1 - Common SpecificationsDocument2 pagesIS - IEC 62271-1 (2007) - High-Voltage Switchgear and Controlgear, Part 1 - Common SpecificationsAnand KumarNo ratings yet
- Coolplus-Ah1012t-Dc-100l-Air Oil Cooler/heat ExchangerDocument1 pageCoolplus-Ah1012t-Dc-100l-Air Oil Cooler/heat ExchangerCOOLPLUS OIL COOLERNo ratings yet
- The Probe Level Monitor: Instruction Manual PL-517 January 2001Document20 pagesThe Probe Level Monitor: Instruction Manual PL-517 January 2001horacio mondragon100% (1)
- 1 - Crude Oil Treatment - SeparationDocument85 pages1 - Crude Oil Treatment - SeparationHaider100% (12)
- Using Lasers to Control Lightning StrikesDocument3 pagesUsing Lasers to Control Lightning StrikesDhāraṇe KusalaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Geometry and PolarityDocument15 pagesMolecular Geometry and Polaritysincerely reverieNo ratings yet
- Bubble leak testing guide for detecting small leaksDocument5 pagesBubble leak testing guide for detecting small leaksMohanNo ratings yet
- Transformers definedDocument11 pagesTransformers definedAbdul BasitNo ratings yet
- DESIGN OF RETAINING WALL SESSIONDocument9 pagesDESIGN OF RETAINING WALL SESSIONFarah MujahidNo ratings yet
- 2019 Sec 4 Pure Chemistry SA2 Geylang MethodistDocument32 pages2019 Sec 4 Pure Chemistry SA2 Geylang MethodistErOn TaNNo ratings yet
- User Manual, S1 TITAN, Tracer 5, CTXDocument66 pagesUser Manual, S1 TITAN, Tracer 5, CTXCarcu TheodorNo ratings yet
- Sluice GateDocument24 pagesSluice GateEldhoThomas100% (1)
- Cayenne 5Document17 pagesCayenne 5Marcelo AndradeNo ratings yet
- Brochure Polypropylene Products Properties ENDocument20 pagesBrochure Polypropylene Products Properties ENMargaux PerrierNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 6: To Perform The Torsion Test and Determine The Modulus of Resilience of A Given SpecimenDocument8 pagesExperiment No 6: To Perform The Torsion Test and Determine The Modulus of Resilience of A Given SpecimenKhurram SattarNo ratings yet
- Automatic Side Stand For Two WheelerDocument84 pagesAutomatic Side Stand For Two Wheelercoolhari0825% (4)
- Question Phy 101Document19 pagesQuestion Phy 101Mohammed kashimNo ratings yet
- Review On Bivo Based Photoanodes For Photoelectrochemical Water Oxidation: The Main Influencing FactorsDocument18 pagesReview On Bivo Based Photoanodes For Photoelectrochemical Water Oxidation: The Main Influencing Factorsgta gtaNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document23 pagesCH 5Ahmed GadNo ratings yet
- Specific Gravity of Soil Solids Lab ReportDocument12 pagesSpecific Gravity of Soil Solids Lab ReportGeojanni PangibitanNo ratings yet
- Determining Dispersive Power of a PrismDocument4 pagesDetermining Dispersive Power of a Prismprayashkr sahaNo ratings yet
- 2019 04 18 Understanding The Aisc Direct Analysis Method of Design HandoutDocument85 pages2019 04 18 Understanding The Aisc Direct Analysis Method of Design Handoutcons2engNo ratings yet
- 2019 Higher Mathematics Paper 1 With SolutionsDocument9 pages2019 Higher Mathematics Paper 1 With SolutionsHassam SajidNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Unit TestDocument4 pagesPeriodic Table Unit Testapi-303120399No ratings yet
- Transfer Pump GBSDocument2 pagesTransfer Pump GBSsiddik.s2582100% (1)
- Useful Tips For Designing Thermal Insulation SystemsDocument25 pagesUseful Tips For Designing Thermal Insulation SystemsEddie FongNo ratings yet
- Sucker Rod Pumping Systems Design-Another Look (1981) PDFDocument13 pagesSucker Rod Pumping Systems Design-Another Look (1981) PDFMuhammad Yunaldi PrayogaNo ratings yet
- CGL Flame - Proof - MotorsDocument15 pagesCGL Flame - Proof - MotorspriteshNo ratings yet