Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry Picture Vocabulary - Periodic Table
Uploaded by
api-2545145130 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3K views32 pagesChemical Family the vertical columns on the Periodic Table, also known as Groups, where elements with similar properties are placed. Alkali Metal Any of the univalent elements belonging to Group 1a of the Periodic Table. Noble Gas Any of the elements found in Group 8a of the Periodic Table; each have the s and p sublevels of their outermost energy level filled.
Original Description:
Original Title
chemistry picture vocabulary- periodic table
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentChemical Family the vertical columns on the Periodic Table, also known as Groups, where elements with similar properties are placed. Alkali Metal Any of the univalent elements belonging to Group 1a of the Periodic Table. Noble Gas Any of the elements found in Group 8a of the Periodic Table; each have the s and p sublevels of their outermost energy level filled.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3K views32 pagesChemistry Picture Vocabulary - Periodic Table
Uploaded by
api-254514513Chemical Family the vertical columns on the Periodic Table, also known as Groups, where elements with similar properties are placed. Alkali Metal Any of the univalent elements belonging to Group 1a of the Periodic Table. Noble Gas Any of the elements found in Group 8a of the Periodic Table; each have the s and p sublevels of their outermost energy level filled.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 32
The Periodic Table
Picture Vocabulary
Chemistry
Alkali Metal
Any of the univalent elements belonging to
Group 1A of the Periodic Table.
Alkaline Earth Metal
Any of the bivalent metals belonging to
Group 2A of the Periodic Table.
Halogen
Any of the electronegative non-metallic
elements in Group 7A of the Periodic Table.
Inner Transition Elements
An element in the lanthanide and actinide series that is
characterized by the addition of electrons to f orbitals.
Noble Gas
Any of the elements found in Group 8A of the Periodic
Table; each have the s and p sublevels of their outermost
energy level filled.
Transition Elements
The B Group elements (3-12) found on the
Periodic Table, also known as transition metals.
Chemical Family
The vertical columns on the Periodic Table, also known
as Groups, where elements with similar properties are
placed.
Atomic Number
The number of protons found in the nucleus of
an element, represented by the letter Z.
Proton
A positively-charged subatomic particle of the
nucleus of an atom and contributes to the mass
of the atom.
Neutron
A subatomic particle of the nucleus of an atom
that is without charge and contributes to the mass
of an atom.
Electron
A negatively-charged subatomic particle of the
electron cloud; involved in the formation of
chemical bonds.
Nucleus
The tiny, very dense, positively-charged region in
the center of an atom; made up of protons and
neutrons.
Valence Electrons
The electrons in the outermost energy level of an
atom that influence how an element will react with
other substances.
Groups
The columns on a Periodic Table that arrange the
elements by the number of electrons that are in the
outside shell.
Periods
The rows in a Periodic Table that classify the
elements by the number of atomic shells.
Metals
Most elements are metals, typically solid, shiny,
malleable, and a good conductor of heat and electricity.
Non-metals
Elements typically not shiny, usually a gas or brittle solid,
not malleable, and a poor conductor of heat and
electricity.
Metalloids
Elements that have properties of both metals and nonmetals; sometimes referred to as semiconductors.
Chemical Symbol
A 1 to 2 letter representation of a specific
element, sometimes referred to as an atomic
symbol.
Periodic Trends
Picture Vocabulary
Chemistry
Atomic Radii
The distance between the nucleus of an atom to the
outermost electron orbital, usually measured in
nanometers.
Ionic Radii
The radius of either a positive or
a negative ion found in an ionic crystal.
Electronegativity
Within a molecule, it is the ability of an atom in
that molecule to attract electron pairs to itself.
Ionization Energy
The energy required to remove one electron from a
neutral atom of an element in the gaseous state.
Ion
Atoms (or groups of atoms) that have an electrical
charge due to a different number of protons and
electrons.
Neutral
Having no electrical charge.
Energy Level
Regions around the nucleus of an atom
where electrons may be found.
Shielding Effect
An effect that occurs as the inner electron shells of an
atom shield the valence electrons in the outer
electron shells from the positive pull of the nucleus.
Periodicity
The quality or state of being periodic,
or occurring at regular intervals.
Cation
Any atom or group of atoms with a positive charge.
Anion
Any atom or group of atoms with a negative
charge.
You might also like
- Classification of The ElementsDocument17 pagesClassification of The ElementsNoor Mohammad NofaerNo ratings yet
- 2013 The Periodic TableDocument90 pages2013 The Periodic Tableapi-266061131No ratings yet
- 3.1 Org, Clssify and Trend PeriodicDocument87 pages3.1 Org, Clssify and Trend PeriodicSylvia AnggraeniNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY - Science Notes For End of Year 9 AssessmentDocument7 pagesCHEMISTRY - Science Notes For End of Year 9 AssessmentJenny Davidson100% (1)
- 04.protection of 33KV Feeder.Document16 pages04.protection of 33KV Feeder.gnpr_10106080No ratings yet
- Periodic Table TrendsDocument22 pagesPeriodic Table TrendsLoraine CastroNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For Periodic Table TESTDocument19 pagesStudy Guide For Periodic Table TESTHarani ThillainathanNo ratings yet
- Methods For Assessing The Stability of Slopes During Earthquakes-A Retrospective 1Document3 pagesMethods For Assessing The Stability of Slopes During Earthquakes-A Retrospective 1ilijarskNo ratings yet
- Design & Fabrication of a Cost-Effective Agricultural DroneDocument57 pagesDesign & Fabrication of a Cost-Effective Agricultural DroneFatima Nasir R:29No ratings yet
- About The Periodic Table of The ElementsDocument11 pagesAbout The Periodic Table of The ElementsKal El Dadi100% (2)
- Facilities Assignment 1-2-2015Document2 pagesFacilities Assignment 1-2-2015Xnort G. Xwest0% (1)
- FMDS0129Document49 pagesFMDS0129hhNo ratings yet
- Operational Guidelines For VlsfoDocument2 pagesOperational Guidelines For VlsfoИгорьNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Elements: ObjectivesDocument5 pagesAtoms and Elements: ObjectivesAngel RingorNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of ElementsDocument58 pagesPeriodic Table of ElementsMichelle Casayuran - RegalaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry in Action Note PackageDocument21 pagesChemistry in Action Note Packageapi-235471411No ratings yet
- Chapter Notes - Chapter 14 Chemical Periodicity Goals: To Gain An Understanding ofDocument5 pagesChapter Notes - Chapter 14 Chemical Periodicity Goals: To Gain An Understanding ofAryyama JanaNo ratings yet
- Atoms Molecules and IonsDocument3 pagesAtoms Molecules and Ionsapi-304350501No ratings yet
- The Periodic Table of Elements: Chemistry Lec 3Document11 pagesThe Periodic Table of Elements: Chemistry Lec 3المونتاج الاخيرNo ratings yet
- Pearson Chemistry Chapter 6 Flashcards - QuizletDocument5 pagesPearson Chemistry Chapter 6 Flashcards - Quizletأستغفرالله واتوب اليهNo ratings yet
- Modern Periodic TableDocument8 pagesModern Periodic TableSabbir HossainNo ratings yet
- MODERN PERIODIC TABLEDocument4 pagesMODERN PERIODIC TABLENabil Abdullah0% (1)
- Modern Periodic TableDocument8 pagesModern Periodic Tablemixing hubNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PDFDocument3 pagesChemistry PDFSukfcNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table PowerpointDocument26 pagesPeriodic Table PowerpointCindy De Guzman TandocNo ratings yet
- LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET-CHEM 1 q1 Week 7Document20 pagesLEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET-CHEM 1 q1 Week 7Jhude JosephNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3.1: Chapter 3: Periodicity - GlossaryDocument4 pagesWorksheet 3.1: Chapter 3: Periodicity - GlossaryNeha KabraNo ratings yet
- ES III Midterm Module 6 WK 6Document5 pagesES III Midterm Module 6 WK 6Oct Toberey MendozaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and The Periodic TableDocument46 pagesAtomic Structure and The Periodic TableJonathan CasillaNo ratings yet
- UMs topic list for end of year examination 2023Document4 pagesUMs topic list for end of year examination 2023sevebv2No ratings yet
- Periodic Table PropertiesDocument18 pagesPeriodic Table PropertiesDragana ModestyNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Periodic Table and Bonding AeDocument24 pagesUnit 6 Periodic Table and Bonding AeRomu RaiNo ratings yet
- Periodic PropertiesDocument19 pagesPeriodic Propertiesnamannn555No ratings yet
- Dr. Ram Manohar Lohiya P. G. College: Modern Periodic TableDocument19 pagesDr. Ram Manohar Lohiya P. G. College: Modern Periodic TableDeepraj Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Electronic Structure and PeriodicityDocument10 pagesChapter 4 - Electronic Structure and PeriodicityAbrienne CaprichoNo ratings yet
- CHM 122 - 2016 - grp1-4 PDFDocument89 pagesCHM 122 - 2016 - grp1-4 PDFGlory UsoroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Study Guide The Periodic Table Section 1Document2 pagesChapter 4 Study Guide The Periodic Table Section 1SyfensNo ratings yet
- Electronic Structure Notes by Aung Kyaw SwarDocument9 pagesElectronic Structure Notes by Aung Kyaw Swarေအာင္ ေက်ာ္ စြာNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Atoms and MatterDocument44 pagesChapter 2-Atoms and MatterNajma AqilahNo ratings yet
- كتابDocument187 pagesكتابdalyrazan60No ratings yet
- 2 2 1 NotesDocument7 pages2 2 1 Notesapi-369706779No ratings yet
- The Periodic Table MP2020Document21 pagesThe Periodic Table MP2020Nathan TvascorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document49 pagesChapter 13Purani SevalingamNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Trends and Element PropertiesDocument4 pagesPeriodic Table Trends and Element PropertiesSANDEEP SINGHNo ratings yet
- Lesson - The Periodic TableDocument4 pagesLesson - The Periodic TableramyaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument1 pagePeriodic Classification of ElementsMoninaRoseTeNo ratings yet
- Chemical PeriodicityDocument9 pagesChemical PeriodicityCorine CaracasNo ratings yet
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Class 11 Notes Chemistry Chapter 3Document12 pagesClassification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Class 11 Notes Chemistry Chapter 3Bijay SchoolNo ratings yet
- The Periodic TableDocument33 pagesThe Periodic TableIra MunirahNo ratings yet
- Periodic ClassificationDocument36 pagesPeriodic ClassificationSHAIK YASMINNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table ExplainedDocument24 pagesPeriodic Table Explainedchristian jay pilarNo ratings yet
- Demarcation of Periodic Table BlocksDocument4 pagesDemarcation of Periodic Table BlocksRana Irfan100% (1)
- AQA Level 1/2 Certificate in Chemistry - IGCSE' (Draft) - Atoms and BondingDocument3 pagesAQA Level 1/2 Certificate in Chemistry - IGCSE' (Draft) - Atoms and BondingFarahAlAsaadNo ratings yet
- Elements, Groups, Properties of Periodic TableDocument23 pagesElements, Groups, Properties of Periodic TableStephNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument27 pagesChemistryErica LeNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table: Oakland Schools Chemistry Resource UnitDocument42 pagesPeriodic Table: Oakland Schools Chemistry Resource UnitAnum TauqirNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document12 pagesWeek 2Oseni MuibaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table - Study NotesDocument19 pagesPeriodic Table - Study NotesTamoghna DeyNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Periodic Relations Among ElementsDocument21 pages2.0 Periodic Relations Among Elementsparkinsondilys7No ratings yet
- Elements of the Periodic TableDocument60 pagesElements of the Periodic TableruchitlpatelNo ratings yet
- Grade-11 Chemistry Definitions CollectionDocument65 pagesGrade-11 Chemistry Definitions CollectionMoun Lynn Sythu100% (3)
- Periodic Table 3Document26 pagesPeriodic Table 3anirban82inNo ratings yet
- CHEM 2 - Module 2 Periodic Table of ElementsDocument4 pagesCHEM 2 - Module 2 Periodic Table of ElementsMicah BlazaNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Group 2Document15 pagesGen Chem Group 2Dharwin Nhicko FriasNo ratings yet
- 6th Six Weeks - Aca Chem 16-17 CalendarDocument1 page6th Six Weeks - Aca Chem 16-17 Calendarapi-254514513No ratings yet
- Acid-Base Indicator Lab MakeupDocument2 pagesAcid-Base Indicator Lab Makeupapi-254514513No ratings yet
- Water ArticleDocument6 pagesWater Articleapi-254514513No ratings yet
- Ion ReferenceDocument2 pagesIon Referenceapi-254514513No ratings yet
- 4th Six Weeks - Aca Chem 16-17 Calendar Evens - EditedDocument1 page4th Six Weeks - Aca Chem 16-17 Calendar Evens - Editedapi-254514513No ratings yet
- Oths Academic Chemistry Syllabus 16-17 Ready To OrderDocument6 pagesOths Academic Chemistry Syllabus 16-17 Ready To Orderapi-254514513No ratings yet
- 3rd Six Weeks - Aca Chem 16-17 Calendar EvensDocument1 page3rd Six Weeks - Aca Chem 16-17 Calendar Evensapi-254514513No ratings yet
- 2nd Six Weeks - Aca Chem 16-17 Calendar EvensDocument1 page2nd Six Weeks - Aca Chem 16-17 Calendar Evensapi-254514513No ratings yet
- Ut Quest Info Sheet Ready To OrderDocument6 pagesUt Quest Info Sheet Ready To Orderapi-254514513No ratings yet
- 5th Six Weeks - Aca Chem 16-17 Calendar EvensDocument1 page5th Six Weeks - Aca Chem 16-17 Calendar Evensapi-254514513No ratings yet
- Element List 2016-2017 With Ptable On BackDocument2 pagesElement List 2016-2017 With Ptable On Backapi-254514513No ratings yet
- Cornell Notes TemplateDocument1 pageCornell Notes Templateapi-254514513No ratings yet
- 1st Six Weeks - Aca Chem 16-17 Calendar Evens - 3 Monday TestsDocument1 page1st Six Weeks - Aca Chem 16-17 Calendar Evens - 3 Monday Testsapi-254514513No ratings yet
- 6th Six Weeks Calendar 15-16 UpdatedDocument1 page6th Six Weeks Calendar 15-16 Updatedapi-254514513No ratings yet
- Quest Online Homework InformationDocument1 pageQuest Online Homework Informationapi-254514513No ratings yet
- Chemistry Picture Vocabulary - MolesDocument8 pagesChemistry Picture Vocabulary - Molesapi-254514513No ratings yet
- Instructional Calendar 2016-2017Document1 pageInstructional Calendar 2016-2017api-254514513No ratings yet
- Chemistry Picture Vocabulary - SolutionsDocument28 pagesChemistry Picture Vocabulary - Solutionsapi-254514513No ratings yet
- Chemistry Picture Vocabulary - ThermochemDocument14 pagesChemistry Picture Vocabulary - Thermochemapi-254514513No ratings yet
- Equipment Lab MakeupDocument1 pageEquipment Lab Makeupapi-254514513No ratings yet
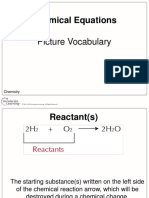
- Chemistry Picture Vocabulary - Chemical ReactionsDocument16 pagesChemistry Picture Vocabulary - Chemical Reactionsapi-254514513No ratings yet
- Chemistry Picture Vocabulary - ElectronsDocument18 pagesChemistry Picture Vocabulary - Electronsapi-254514513No ratings yet
- Chemistry Picture Vocabulary - BondingDocument35 pagesChemistry Picture Vocabulary - Bondingapi-2545145130% (1)
- Chemistry Picture Vocabulary - StoichDocument9 pagesChemistry Picture Vocabulary - Stoichapi-254514513No ratings yet
- Chemistry Picture Vocabulary - Gas LawsDocument23 pagesChemistry Picture Vocabulary - Gas Lawsapi-254514513No ratings yet
- Chemistry Picture Vocabulary - NuclearDocument15 pagesChemistry Picture Vocabulary - Nuclearapi-254514513No ratings yet
- Chemistry Picture Vocabulary - Atomic TheoryDocument5 pagesChemistry Picture Vocabulary - Atomic Theoryapi-254514513No ratings yet
- R8557B KCGGDocument178 pagesR8557B KCGGRinda_RaynaNo ratings yet
- Ex - No: 4 Integrator and Differentiator Using Fpaa DateDocument4 pagesEx - No: 4 Integrator and Differentiator Using Fpaa DatechandraprabhaNo ratings yet
- Baidu - LeetCodeDocument2 pagesBaidu - LeetCodeSivareddyNo ratings yet
- Meeting 5: Data Warehouses and SQL Query OptimizationDocument4 pagesMeeting 5: Data Warehouses and SQL Query Optimizationzvipev1050% (2)
- QAF10A200S TheTimkenCompany 2DSalesDrawing 03 06 2023Document1 pageQAF10A200S TheTimkenCompany 2DSalesDrawing 03 06 2023LeroyNo ratings yet
- Reboilers and VaporizersDocument20 pagesReboilers and Vaporizers58 - Darshan ShahNo ratings yet
- Efficiency Evaluation of The Ejector Cooling Cycle PDFDocument18 pagesEfficiency Evaluation of The Ejector Cooling Cycle PDFzoom_999No ratings yet
- M.E. Comm. SystemsDocument105 pagesM.E. Comm. SystemsShobana SNo ratings yet
- Craig Vaughan CHPTR 07Document44 pagesCraig Vaughan CHPTR 07Jorge CananeaNo ratings yet
- Synology DS718 Plus Data Sheet EnuDocument6 pagesSynology DS718 Plus Data Sheet EnuSteve AttwoodNo ratings yet
- Bab 8Document29 pagesBab 8Nurul AmirahNo ratings yet
- MITRES 6 002S08 Chapter2Document87 pagesMITRES 6 002S08 Chapter2shalvinNo ratings yet
- PDF Solution Manual For Gas Turbine Theory 6th Edition Saravanamuttoo Rogers CompressDocument7 pagesPDF Solution Manual For Gas Turbine Theory 6th Edition Saravanamuttoo Rogers CompressErickson Brayner MarBerNo ratings yet
- FTP FUNCTION MODULE in ABAPDocument8 pagesFTP FUNCTION MODULE in ABAPAdriano PermanaNo ratings yet
- NewsDocument26 pagesNewsMaria Jose Soliz OportoNo ratings yet
- Reliability EngineeringDocument9 pagesReliability Engineeringnvaradharajan1971No ratings yet
- Instrumentation Design UTHMDocument5 pagesInstrumentation Design UTHMAnis AzwaNo ratings yet
- View DsilDocument16 pagesView DsilneepolionNo ratings yet
- 0001981572-JAR Resources in JNLP File Are Not Signed by Same CertificateDocument13 pages0001981572-JAR Resources in JNLP File Are Not Signed by Same CertificateAnonymous AZGp1KNo ratings yet
- 08 Candelaria Punta Del Cobre IOCG Deposits PDFDocument27 pages08 Candelaria Punta Del Cobre IOCG Deposits PDFDiego Morales DíazNo ratings yet
- Instrument Resume OIL and GAS.Document3 pagesInstrument Resume OIL and GAS.RTI PLACEMENT CELLNo ratings yet
- Solvent based printing inks applicationsDocument34 pagesSolvent based printing inks applicationsAmna liaquatNo ratings yet
- Microstation V8I Accudraw Basics: Bentley Institute Course GuideDocument80 pagesMicrostation V8I Accudraw Basics: Bentley Institute Course Guideh_eijy2743No ratings yet
- College of Information Technology Dmmmsu-Mluc City of San FernandoDocument9 pagesCollege of Information Technology Dmmmsu-Mluc City of San FernandoZoilo BagtangNo ratings yet