Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hsab 2
Uploaded by
Mahesh Babu Sri0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageHard-Soft Acid-Base Theory (HSAB) Helps explain preference for Cversus O-alkylation. Hard Acids and Hard Bases react and bond!
Original Description:
Original Title
HSAB 2
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHard-Soft Acid-Base Theory (HSAB) Helps explain preference for Cversus O-alkylation. Hard Acids and Hard Bases react and bond!
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageHsab 2
Uploaded by
Mahesh Babu SriHard-Soft Acid-Base Theory (HSAB) Helps explain preference for Cversus O-alkylation. Hard Acids and Hard Bases react and bond!
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
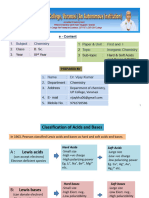
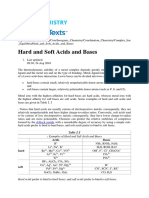
Hard-Soft Acid-Base Theory
(HSAB)
• Helps explain preference for C- versus O-alkylation
1) Hard Acids: high + charge, small, low polarizability,
electrostatically dominated bonding and reactivity.
-Examples: Na+, H+, Mg2+, R3SiX
2) Hard Bases: High electronegativity, small, low
polarizability, electrostatically dominated bonding and
reactivity
-Examples: F-, OR-, PO43-, R2O
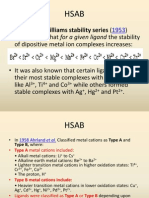
HSAB Theory (Continued)
3) Soft Acids: low + charge, large, high polarizability, covalent
chemistry (orbital controlled)
- Examples: Ag+, RHg+, Most C electrophiles (e.g., MeI).
4) Soft Bases: low electronegativity, large, polarizable, covalent
chemistry (orbital controlled)
- Examples: SR-, SR2, I-, carbon !-compounds
General Rule: Soft Acids and Soft Bases react and bond!
Hard Acids and Hard Bases react and bond!
You might also like
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Periodic Table with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Periodic Table with AnswersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Coordination ChemistryDocument33 pagesCoordination ChemistryGOVIND RANJAN80% (5)
- HSABDocument6 pagesHSABSuplab KumarNo ratings yet
- HSAB TheoryDocument3 pagesHSAB Theorykaran113No ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions - How Far and How FastDocument18 pagesChemical Reactions - How Far and How FastDoris GladiaNo ratings yet
- Hard-Soft Acid-Base (HSAB) TheoryDocument11 pagesHard-Soft Acid-Base (HSAB) Theorydarrenneoyoman0% (1)
- Acid Base Chemistry ShortDocument27 pagesAcid Base Chemistry ShortJianNo ratings yet
- HSAB Principle ExplainedDocument14 pagesHSAB Principle Explainedneha yarrapothuNo ratings yet
- Hard SoftDocument24 pagesHard SoftMuhammad FahmiNo ratings yet
- Lecture Wise Notes UNIT-3Document12 pagesLecture Wise Notes UNIT-3anuthakurNo ratings yet
- Hard and Soft Acids and Bases (HSAB) TheoryDocument4 pagesHard and Soft Acids and Bases (HSAB) TheoryRUFAS KANIKANTINo ratings yet
- CHB401A L 4 SL1 All 1Document15 pagesCHB401A L 4 SL1 All 1PrityyyNo ratings yet
- The Hard Soft (Lewis) Acid Base Principle: Type A Metal Cations IncludedDocument19 pagesThe Hard Soft (Lewis) Acid Base Principle: Type A Metal Cations IncludedIka SiswatiNo ratings yet
- Acid - Base Chemistry - ShortDocument27 pagesAcid - Base Chemistry - ShortSachin PatilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Acid –Base Chemistry: Theories and StrengthsDocument63 pagesChapter 6 Acid –Base Chemistry: Theories and StrengthsAlyssa BaltazarNo ratings yet
- 2013-2 Reactions and Properties of Lewis Acids and BasesDocument42 pages2013-2 Reactions and Properties of Lewis Acids and BasesTsabita AfaaninNo ratings yet
- HSAB Principle chemidtgdsdhsjresrebDocument19 pagesHSAB Principle chemidtgdsdhsjresrebiamkalash.vdNo ratings yet
- Hard Soft Acid Base TheoryDocument41 pagesHard Soft Acid Base TheoryChan MingxiaNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 - The HSAB PrincipleDocument28 pagesChap 1 - The HSAB PrincipleMuhamad FajarNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Theory GuideDocument34 pagesAcid-Base Theory GuideCeela PrwiraNo ratings yet
- HSAB Principles of Hard and Soft Acids and BasesDocument15 pagesHSAB Principles of Hard and Soft Acids and BasesDr. Md. Ehtesham Ul Hoque100% (2)
- Acid-Base and Lewis Concepts in Inorganic ChemistryDocument48 pagesAcid-Base and Lewis Concepts in Inorganic ChemistryChristian RV EscosarNo ratings yet
- Hard-Soft Acid-Base TheoryDocument5 pagesHard-Soft Acid-Base TheoryJherby TeodoroNo ratings yet
- Hard Soft Acid Base TheoryDocument41 pagesHard Soft Acid Base TheorythinhbuNo ratings yet
- HSAB Concept FDocument6 pagesHSAB Concept FGaurav 016No ratings yet
- Acid Base and Donor Acceptor ChemistryDocument73 pagesAcid Base and Donor Acceptor ChemistrybeaNo ratings yet
- HSAB Concept in Mineral OreDocument8 pagesHSAB Concept in Mineral OreKurnia NurfitriaNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument26 pagesAcids and BasesPravesh NiraulaNo ratings yet
- Hard and Soft Acids and Bases (Hsab)Document5 pagesHard and Soft Acids and Bases (Hsab)nolimitsjustfashionNo ratings yet
- HSABDocument16 pagesHSABYildiz Nazmi TyartaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Aufbau PrincipleDocument7 pagesChemistry: Aufbau PrincipleEmma HeNo ratings yet
- Hsab DPDocument20 pagesHsab DPShubham Baxla (CSEAIML23310662409:30)No ratings yet
- C31J OrganometalsDocument48 pagesC31J OrganometalsParas AliNo ratings yet
- Hard and Soft Acids and Bases: D-Block MetalsDocument2 pagesHard and Soft Acids and Bases: D-Block MetalsRoqyal RANo ratings yet
- Hard Soft AcidsDocument24 pagesHard Soft AcidsMaheshNo ratings yet
- Pearson's Classification of Lewis Acids and Lewis Bases Into Hard and Soft - Acids and BasesDocument5 pagesPearson's Classification of Lewis Acids and Lewis Bases Into Hard and Soft - Acids and BasesThantea ChhakchhuakNo ratings yet
- Hard and Soft Acids and Bases - RitterDocument3 pagesHard and Soft Acids and Bases - RitterNguyen Tri NguyenNo ratings yet
- CE/EN 520A - Soil Behavior and Its Role in Environmental ApplicationsDocument36 pagesCE/EN 520A - Soil Behavior and Its Role in Environmental Applicationstplain101No ratings yet
- 3.2 Periodic Trends - Chemical PropertiesDocument11 pages3.2 Periodic Trends - Chemical PropertiesAlisha TuliNo ratings yet
- Li MG OrganometallicsDocument62 pagesLi MG OrganometallicsArish AhmedNo ratings yet
- DSE Chem Last MinuteDocument61 pagesDSE Chem Last Minute何卓函No ratings yet
- Week7a - OrgChem1 - A-B Rxns in Org Chemistry - 2023Document18 pagesWeek7a - OrgChem1 - A-B Rxns in Org Chemistry - 2023happy cyenoNo ratings yet
- Hard and Soft Acids and BasesDocument17 pagesHard and Soft Acids and BasesSalmi Seprianti100% (2)
- Solubility Rule (Chemistry)Document1 pageSolubility Rule (Chemistry)Dela Cruz MTNo ratings yet
- B06 - Chemical Reactions and PH (Chapter 4 and 15) - MZD - PART 5Document17 pagesB06 - Chemical Reactions and PH (Chapter 4 and 15) - MZD - PART 5revabirla23No ratings yet
- Regolith Geochemistry: Factors Controlling Metal MobilityDocument53 pagesRegolith Geochemistry: Factors Controlling Metal MobilityChinox LokooNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument15 pagesAcids and Baseslebogang0% (1)
- Trace Elements and Isotopes in GeochemistryDocument38 pagesTrace Elements and Isotopes in GeochemistryJaor JnrNo ratings yet
- Naming Compounds PDFDocument18 pagesNaming Compounds PDFJohn Jade BasuelNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reviews: The Hard Acids Bases (HSAB) Principle and Organic ChemistryDocument20 pagesChemical Reviews: The Hard Acids Bases (HSAB) Principle and Organic ChemistryPinottoNo ratings yet
- Slides For Topic I by Prof. L SrinivasDocument42 pagesSlides For Topic I by Prof. L SrinivasKushNo ratings yet
- Kromatografi KolomDocument20 pagesKromatografi KolomRista Siti MaarniNo ratings yet
- Regolith Geochemistry FactorsDocument53 pagesRegolith Geochemistry FactorsmohammedalmasriNo ratings yet
- Inorganic HSAB 8apr2012Document29 pagesInorganic HSAB 8apr2012اردها نزواNo ratings yet
- Hard and Soft Acids and BasesDocument11 pagesHard and Soft Acids and Basesnoor uddinNo ratings yet
- Chemistry on Modified Oxide and Phosphate Surfaces: Fundamentals and ApplicationsFrom EverandChemistry on Modified Oxide and Phosphate Surfaces: Fundamentals and ApplicationsNo ratings yet