Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hemorrhoids (Final Draft)
Uploaded by
Orville VillaceteOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hemorrhoids (Final Draft)
Uploaded by
Orville VillaceteCopyright:
Available Formats
SOUTHEAST ASIAN COLLEGE INC. 6 N. Ramirez St.
Quezon City
In Partial Fulfillment in RLE
Case Study Hemorrhoids: Grade III
Presented by: Castro, Jemi Myca Correa, Reinz Lui Queral, Alyssa Marie Raquiza, Bianca Yvonne Reyes, Frances Diane Sabiniano, Tharlene May Sapungan, Maria Moriel Subido, Christine Tamondong, Hanzel Faye Tible, Darleen Kaye Villacete, Orville
BSN S31-Group 4 Surgery Ward United Doctors Medical Center Quezon City
I.
Introduction
This case is of Patient L who was diagnosed with Internal Hemorrhoids Grade III. She was diagnosed with Internal Hemorrhoids Grade III which means that hemorrhoids bleed and prolapsed with straining and required manual effort for replacement into the anal canal. Hemorrhoids are swollen and inflamed veins around the anus or in the lower rectum. The rectum is the last part of the large intestine leading to the anus. The anus is the opening at the end of the digestive tract where bowel contents leave the body. External hemorrhoids are located under the skin around the anus. Internal hemorrhoids develop in the lower rectum. Internal hemorrhoids may protrude, or prolapsed, through the anus. Most prolapsed hemorrhoids shrink back inside the rectum on their own. Severely prolapsed hemorrhoids may protrude permanently and require treatment. We chose this case for us to extend and improve our knowledge and understanding with regards to the causes, effects, complications, signs and symptoms, and nursing implications for hemorrhoids for us to be able to attain a comprehensive and thorough learning experience with regards to our study that would benefit not only us but also the readers and for the patients that we will be catering in the future with such kind of disease. This case study is important because it imparts knowledge regarding the complication in having hemorrhoids. We, as students will benefit from this study as we reviewed the anatomy and physiology, pathophysiology and studied nursing interventions for this case. Patients and also readers will gain knowledge regarding awareness or learn preventions, treatments and management to such diagnosis. The scopes of this study are people who are suffering and diagnosed from hemorrhoids. This case presentation will attempt to cover and discuss the disease process and present condition of the patient. This case presentation will be limited only to the patients verbalizations, laboratory reports, signs and symptoms as evidenced by and observed from the patient.
II.
Patients Profile NAME: Ms. L AGE: 36 years old BIRTH DAY: April 26, 1975 BIRTH PLACE: Rizal SEX: Female RELIGION: Roman Catholic CIVIL STATUS: Single ADDRESS: Mandaluyong City DATE ADMITTED: May 22, 2011 CHIEF COMPLAINT: Anal Pain with Bleeding
III.
Theoretical Framework
IDA JEAN ORLANDOS DYNAMIC NURSE-PATIENT RELATIONSHIP According to Orlandos theory, the role of the nurse is to find out and meet the patients need. This function of professional nursing is achieved by immediately responsing to patients concerns. We used Orlandos theory in the case of our patient. The day after the surgery, we found out that the patient was not able to void though he had a full bladder. A straight catheter was inserted to the patient and health teachings were advice. Pain was noted as well as fear to defecate was observed to the client. Hot Sitz Bath was done to relive patients discomfort. It is a disciplined professional response of the nurse to carry out physicians order and provide comfort to the patient as well as assisting patients need. We used these principles in caring our patient and achieving satisfaction of both part.
IV.
Nursing History
History of Present Illness It was year 1999 when the patient started to experience constipation. She consulted the physician and was advice to take medications. Upon taking these medications, the patient was still constipated. Almost every year tried to see a doctor and was still given medications. 5 years prior to admission, patient noticed mass, protruding anal opening which was spontaneously reddening and accompanied by occasional pain on defecation. 4 months prior to admission, the patient noticed an increased in size of the mass, still with bleeding, persistence of signs and symptoms, prompted consult and was advice for surgery. The patient was admitted on May 22, and was undergone surgery on May 23. Past Medial History ( - ) previous hospitalization Family Medical History ( + ) hypertension mother side and brother Personal and Social History ( - ) smoker ( - ) alcohol drinker ( + ) allergy to ibuprofen
V.
Course in the Ward
On the first day, we received the patient lying flat on bed, conscious and coherent with ongoing IVF D5LR1L x 31gtts/min at 900 cc level and infusing well. The patient underwent proctoscopy with hemorrhoidectomy under RA-SAB. It was our first encounter with our patient so we introduced ourselves and established rapport. We took VS and plotted it on TPR sheet and on the patients chart. The patient complained of pain so we administered paracetamol as ordered by the physician. Also, hot sitz bath was done. We monitored intake and output. On the second day, we received patient lying on bed, conscious and coherent. We took her VS and plotted it on the TPR and patients chart. Problem with urinary retention was encountered. Straight catheterization was done and drained 1250cc. Celecoxib 200mg/tab BID was given. Hot sitz bath was increased to 4 times a day. We monitored intake and output. On the third day, we received patient sitting on bed, conscious and coherent. We took her VS and plotted it on TPR and patientd chart. Celecoxib 200mg/tab BID was given and Fibrosine 1 sachet q6 was given. Hot sitz bath was done. She was able to defecate. We monitored intake and output. On the fourth day, the patient was discharged and was advised to increase fluid intake and increase in fiber diet. Continue celecoxib 200 mg/cap 2x a day. Follow up schedule in May 28,2011.
VI. Gordons Functional Pattern A. NUTRITIONAL AND METABOLIC PATTERN BEFORE DURING Ms. Ls typical daily food She still eats any foods intake is more on meat that she wants but she and she seldom eats was advised by the fish and vegetables. She doctor to eat more only eats vegetables vegetables that are rich like pechay and in fibers and to increase broccoli. She prefers her fluid intake. water than soda. Her daily fluid intake is less than 1L per day. She is allergic to any food that has preservatives.
ANALYSIS Before, she only eats meat most of the time. Now, she was advised to increase her vegetable diet that is rich in fiber and to increase her fluid intake as well.
B. ELIMINATION PATTERN BEFORE Whenever Ms L. is constipated, she defecates every other day and feels pain during defecation. Her stool is usually hard in consistency with presence of blood during defecation. She takes dulcolax to achieve normal elimination. She urinates normally and dont feel pain during urination. DURING She wasnt able to defecate for couple of days after surgery because she was afraid to push. But she was able to defecate on the day before she was discharged. On the day of post-op, she had urinary retention. Around 1:30 am of the next day, straight catheterization was done and drained 1250cc. By then, her urination went back to normal. ANALYSIS Theres still presence of blood during defecation. She experienced urinary retention because of the post op pain.
C. ACTIVITY AND EXERCISE PATTERN BEFORE She works in an office and sits for the whole shift (8hrs). She goes to work the whole weekdays. She performs DURING During hospitalization, she took a sick leave from work. She walks only when she needs to go to the bathroom to ANALYSIS Before, she does sports and goes to work. During confinement, her activities were limited.
warm up exercises for 5-10 minutes and she plays tennis 4x a week. During her day off, she finishes her laundry and she goes to the mall.
urinate. But most of the time she lays down in bed and seldom sits on the chair. She watches TV for entertainment.
D. SLEEP-REST PATTERN BEFORE Her normal sleep usually takes 8 hours of sleep and feels energetic and satisfied for the the day. She usually sleeps early at night and wakes up early for work. She doesnt have any problem in falling asleep. She takes a nap in the afternoon. DURING During confinement, she couldnt sleep well. She keeps on waking up every 2-3 hours because of pain. She watches TV to help her fall to sleep. ANALYSIS Before, she falls to sleep easily and gets enough sleep. Now, she is having a hard time to fall asleep because of the discomfort that was brought by pain.
E. COGNITIVE-PERCEPTUAL PATTERN BEFORE Ms. L can read and write. She doesnt have any problem in speaking, hearing and sight. She has no changes on her memories and she always find easy ways in learning. DURING Ms. L can still read and write. She doesnt have any problem in speaking, hearing and sight. There are still no changes at all on her memories and she finds easy ways in learning. ANALYSIS There are no difficulties on reading, hearing, speaking, and writing.
F. SELF-PERCEPTION AND SELF CONCEPT BEFORE DURING She sees herself equal She still found herself to others. She expresses equal to others. She still ANALYSIS Theres no change on her perception and goal
herself by telling what she feels, going out with others and sharing what she has. For the next five year, her goal is to have her own house and lot by working so hard.
expresses herself by in life. telling what she feels, going out with others and sharing what she has. Her goal is still to have her own house and lot someday.
G. ROLE-RELATIONSHIP PATTERN BEFORE Ms. L has a good relationship with her boss and co-worker. Together with her siblings, she also supports any financial problems in their family. Shes the one who plans for their family gathering like swimming. DURING Shes with her two sisters during her confinement. She also visited by her coworkers. She still supports the financial needs of the family. ANALYSIS On her confinement, shes with her boss, coworkers and two sisters. She supports the financial needs of the family.
H. SEXUALITY-REPRODUCTIVE PATTERN BEFORE Since the patient is single, she doesnt engage in sexual activity and dont use contraceptives. Her menstruation was started when she was 18 years old. Her last menstruation period was on the last week of april. Every time she has her menstruation she suffers from dysmenorrhea. DURING She still not engages in sexual activity and not using contraceptives. ANALYSIS Theres no change on her sexual activities.
I. COPING-STRESS TOLERANCE PATTERN
BEFORE For the past 5 years, she was suffering from hemorrhoid that gives her stress including her work. To relieve those stresses, she plays tennis. Sometimes she asks for advice from her family.
DURING After surgery, she feels more comfortable about her condition.
ANALYSIS Her stress was lessened because she underwent hemorrhoidectomy.
J. VALUE BELIEF PATTERN BEFORE Ms. L believes that a healthy person should have a healthy lifestyle. Every Sunday, she goes to church. DURING ANALYSIS Ms. L still believes that a Theres no change on healthy person should what she believes in have a healthy lifestyle life. like eating variety of foods. She still prays to God.
BEFORE Every year Ms. L goes to her physician for check up. She performs breast self examination every month. She doesnt smoke and drink.
DURING She perceives to have a healthy life.
ANALYSIS Theres no change at all on her health perception.
K. HEALTH
PERCEPTION AND HEALTH MANAGEMENT PATTERN
VII.
Physical Assessment Area to assess Normal Findings Abnormal Findings
ANTHROPOMETRIC MEASUREMENT POSTURE RANGE OF MOTION
VITAL SIGNS
SKIN
HAIR
NAILS
HEAD
WEIGHT: 43 LBS. HEIGHT: 52 ft. In standing position, the torso and head are upright. Normal range of motion Inability to voluntarily and comfortable move a joint in the directions and to the degrees that are consider normal. TEMPPERATURE: 36 DEGREES CELSIUS PULSE RATE: 78 bpm RESPIRATORY RATE: 18 cpm BLOOD PRESSURE: 90/60 mmHg Skin is smooth and has a normal skin color. Moisture: Skin is dry, with a minimal perspiration. When skin is released it rapidly returns to its original contour. Hair varies from dark black to pale blonde. The hair is equally distributed on all the areas of the body. Nails are normally having a pink cast and have a capillary refill within 2-3 seconds. The shape and configuration of nails are smooth and slightly rounded to flat. The textures of the nails base are firm upon palpation. The scalp is normally shiny, intact and without
any lesions. The head is normocephalic and symmetrical. The skull is smooth, nontender, and without masses or depressions.
The facial features should be symmetrical. The face is slightly oval in shape with no edema, or involuntary movements. EYES Has normal visual acuity of 20/20. EYELIDS The eyelids appear symmetrically. CORNEA The corneal surface was moist and shiny without discharges. IRIS The iris is smooth and without apparent vascularity. PUPIL The pupil is deep black, round and of equal diameter ranging from 26mm. LENS The lenses are transparent. VOICE WHISPER TEST The patient should be able to repeat words whispered from a distance of 2 feet. EXTERNAL EAR The color is matching the color of the rest of the patients skin and is positioned centrally and is proportion to the head. The patient doesnt complain pain or tenderness during palpation. NOSE Located at the midline of the face and is without swelling, bleeding, lesions and masses. Each nostril is patent. No evidence of swelling around the nose and eyes. The lips and membranes are pinkish and have no lesions or inflammation. The tongue is in the midline of the tongue. Have 32 teeth, which should be white with smooth edges, in proper
FACE
The external nose is swollen and has an incision on right side of the nose.
LIPS TONGUE TEETH
The lips are dry.
VIII. Laboratory Examinations URINALYSIS Date: May 28, 2011 Age/Sex: 36/Female Color Transparency pH (rection) Specific Gravity Sugar Albumin Bile MICROSCOPIC EXAMINATION Amorphous Urates Amorphous Phosphates Epithelial cells Renal cells Mucous threads Bacteria Crystals: Calcium Oxalate Uric Acid Triple Phosphate BLOOD CHEMISTRY Date: May 19, 2011 Age/Sex: 36/Female Procedure: sgpt/alt Conventional Unit Fasting Blood 60-110 mg/dL Sugar Creatinine 0.60-1.13 mg/dL Sgpt (alt) 0-31 U/L Rare/lpf Few Rare Few Few Result Light Yellow Clear 6.0 1.010 Negative Negative SI Unit Straw-dark Yellow Clear 4.6-6.5 1.010 1.015 Negative Negative
Result 82.24 0.63 26.00
SI Unit 3.33-6.11 mmol/L 53.04-99.89 umol/L 0-31 u/L
Result 4.56 55.69 26.00
HEMATOLOGY Date: May 20, 2011 Procedure: CBC with APC (actual platelet count) Normal Hemoglobin 123.153 g/dL Hematocrit 0.35-0.44 WBC Count 5-10 x 10/L Platelet Count 150-400 x 10/L Segmenters 0.50-0.70 Lymphocytes 0.25-0.35 Mixed Cells Eosinophil 0.00-0.05 Monocyte 0.00-0.07 Stabs 0.01-0.05 HEMATOLOGY Date: May 20, 2011 Procedure: Prothrombin time Pts Count Control Count % Activity XRAY Date: May 18, 2011 Procedure: X-ray Chest PA REMARKS: Lung Field clear Heart is not enlarged Diaphragm & Sulci intact Bony Thorax is unremarkable Result 12.5 secs 12 secs 85 %
Result 122 0.39 6.1 249 0.61 0.29 0.02 0.05 0.03
Normal Values 10-13 secs 10-13 secs 70-120%
PATHOLOGY Date: May 25, 2011 Procedure: Surgical Pathology report Specimen: Hemmorhoid Tissue Exam Requested: 1st Histopath Procedure: Proctohemorrhoidectomy Clinical Diagnosis: Internal Hemorrhoids Grade III Gross Findings: It is labeled hemorrhoids consists of (2) irregular pieces of rubbery tissue ranging from 0.5 x 0.5 x 0.3 cm to 2.7 x 1.0 x 1.0 cm. The outer surfaces are partly covered pink-tan to gray-tan convoluted mucosa & skin with focal red black, ragged areas. Sections reveal red-tan, finely granular surface. Representative sections are taken in (2) cassettes & labeled B (3-4). Microscopic Findings: Microscopy done Diagnosis: Mixed Hemorrhoidal Varices, anorectal tissue (Proctohemorrhoidectomhy)
IX.
Anatomy and Physiology
Anus the end-point of the digestive system. Itcontains sweat and oil glands, hair follicles, as well as many nerve endings, which make it very sensitive to pain and erotic stimulation. Anal opening is an ovalopening located about an inch in front of the spine. When closed, the anus is about an inch incircumference Anal crypt the depression between rectal columns that encloses networks of veins that, when inflamed, are called hemorrhoids. Internal sphincter muscle of anus A smooth muscle ring formed by an increase of the circular fibers of the rectum, situated at the upper end of the anal canal. External sphincter muscle that circles the anus it can stretch to about five times the size. Internal sphincter muscle - controls the passage of stool in the elimination process Dentate line is a line which divides the upper 2/3s and lower 1/3 of the anal canal. Developmentally, this line represents the hindgut-proctodeum junction. ring of tissue fold arranged in zigzag or sawtooth pattern Rectum approximately six inches long, with folds called the valvesof Houston. Valves of houston serve as shelves where thefeces rest between bowel movements. When the stoolbecomes heavy, the valve presses against the rectal wall,which results in the "the call of nature" signal or the urge todefecate.
XI.
Nursing Care Management
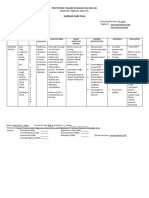
Nursing Problem Cues Subjective: Sobran g sakit ng puwet ko hindi ko na kaya. As verbaliz ed by the patient. Pain scale of 8/10 accordin g to the patient.
Nursing diagnos is Acute Pain related to Surgical Procedur e.
Nursing Objectives GOAL: After 30 minutes of nursing interventions, the patient will: Verbalized pain as tolerated. Demonstra te use of relaxation skills and diversional activities, as indicated for individual situation. Follow prescribed pharmacol ogical regimen.
Nursing Intervention INDEPENDENT: Assessed patients pain. Monitored vital signs. Used pain rating scale appropriate for age. Provided comfort measures( e.g . quiet environment) Encouraged use of relaxation technique such as deep breathing exercise or listening to slow music. Encouraged diversional activities (watching
Rationale
Evaluation
To help determine the intensity of the pain. Usually altered in acute pain. Pain is subjective experience and cannot be felt by others. Promote non pharmacological pain management. Reduce tension.
After 30 minutes of nursing intervention, the patient: Verbalized pain as relieved. Demonstra ted use of relaxation skills and diversional activities, as indicated for individual situation. Followed prescribed pharmacol ogical regimen.
Objective: Facial grimace Irritabilit y Guardin g behavior
Distract attention.
Nursing Cues Subjective: -hindi ako maihi as verbalized by the client. Objective: -Bladder distention -Absence of bladder output
Nursing Diagnosis Acute urinary retention related to regional anesthesia and post-op pain
Nursing Objectives Goal: After 4 hours of nursing interventio n, the patient will be able to void normally
Nursing Intervention Assess the patient if her bladder is distended Ascertain whether client has sensation of bladder fullness and determine level of discomfort Determine if there has been significant urine output in the last 6-8 hours Note recent amount/typ e of fluid intake Drain
Rationale
Evaluatio n To verify if After 4 shes hours of suffering nursing from interventio bladder n, the distention client was able to Sensation of void discomfort normally can vary, depending on underlying cause of retention To monitor the normal urine output from the last 6-8 hours To monitor the normal urine output Reference are mixed as to need
bladder with straight catheter per agency protocol
for fractional drainage in increments of 200mL at a time to prevent possibility of bladder spasm, syncope/ hypotension
Nursing Problem Cues Subjective: Hindi ako makatulog ng maayos kasi hindi ako kumportable. As verbalized by the patient. Objective: -Restlessness -Irritability
Nursing diagnosis Sleep Deprivation related to Prolonged Discomfort
Nursing Objectives
Nursing Intervention
Rationale
Evaluation
GOAL: INDEPENDENT: After 8 hours of Assessed nursing causative/contri interventions, the buting factors. patient will be Determined able to: clients usual sleep pattern Identify and individual expectations. appropriate Suggested interventio abstaining from ns to daytime naps. promote sleep. Report improveme nt in sleep pattern. Instructed in relaxation techniques, music therapy, and meditation. Provided calm, quiet environment and manage controllable sleep disrupting factors such as noise, light, room temperature.
Identify factors that are interfering with sleep. Provide comparative baseline. Because they impair ability to sleep at night. Decrease tension, prepare rest/sleep.
After 8 hours of nursing intervention, the patient: Identified individual appropria te interventi ons to promote sleep. Reported improve ment in sleep pattern.
Reduce stimulation so client can relax.
Reduce pain to
DEPENDENT: Administered pain reliever. COLLABORATIVE: Discussed effective ageappropriate bedtime rituals (e.g. reading, listening to music).
promote a better sleep. Enhance clients ability to fall asleep.
Nursing Cues
Nursing Diagnosis
Nursing Objectives
Nursing Intervention
Rationale
Evaluation
Subjective: Fear related to Nadudumi ako surgical incision pero natatakot ako umiri baka lalong sumakit ang opera ko as verbalized by the client.
Goal: After 8 hours of nursing intervention the patient will eliminate or reduce feelings of apprehension and tension and reduce disabling feelings of fear
Establish rapport on the client Monitor the vital signs Convey acceptanc e of the patients perceptio n of fear to encourag e open communic ation regarding the source of fear Use calm, reassurin g approach Encourag e an attitude of realistic hope as a way of dealing
To establish trust and cooperati on on the client To obtain baseline data To open the mind of the patient regarding her fear
After 8 hours of nursing intervention the patient was able to reduce her fear
To promote a smooth communic ation. To help the patient to overcome her fear
To relax the mind
with feelings of helplessn ess Use relaxation technique like music to reduce attention on fear Administe r medicatio n such as fibrosine Encourag e the client to increase oral fluid intake and high fiber diet
of the patient regarding her fear
This facilitate easy expulsion of the fecal matter
Nursing Problem Cues
Nursing diagnos is
Nursing Objectives
Nursing Intervention
Rationale
Evaluation
Objective: Surgical Incision on the anal part
Risk for Infection related to Surgical Procedu res
GOAL: After 8 hours of nursing interventions, the patient will: Verbalized understan ding of individual risk factors. Identify interventi ons to prevent/re duce risk for infection.
INDEPENDENT: Stressed proper hand hygiene by all caregivers. Observed for localized signs of infection at the surgical incision.
Reduce risk of crosscontaminatio n.
After 8 hours of nursing intervention, the patient: Verbalized understan ding of individual risk factors. Identified interventio ns to prevent/re duce risk for infection.
DEPENDENT: Administered/monitor ed medication regimen and note clients response.
Determine effectiveness of therapy/pres ence of side effects.
XII.
Drug Study Drug Actions Competitively blocks the effects of histamine at H1-receptor sites, has atropine-like, anti-pruritic, and sedative effects. Indications Relief of symptoms associated with perennial and seasonal allergic rhinitis; vasomotor rhinitis, allergic conjunctiviti s, mild; amelioratio n of allergic reactions to blood or plasma. Side Effects Dizziness anorexia, nausea, urinary retention. Nursing Intervention Give drug with food if GI upset occurs. Advice patient to take the drug only as prescribed. Report difficulty of breathing, hallucinatio ns, tremors, loss of coordinatio n, or unusual bleeding.
Generic Name: Diphenhydramin e Hydrochloride Brand Name: Benadryl Classification/s: Antihistamine Dosage/Route/Frequ ency: 250mg/tablet P.O TID
Drug Generic Brand: Nalbuphine Hydrochloride Brand Name: Nubain Classification/s: Opioid agonistantagonist analgesic Dosage/Route/Freq uency: 10mg IM
Action Acts as an agonist specific opioid receptors in the CNS to produce analgesia and sedation but also acts to cause hallucinations and is an antagonist at mu receptors.
Indication Relief of moderate to severe pain. Preoperative analgesia, as a supplement to surgical anesthesia.
Side Effects Sedation, dizziness, hallucinations, nausea, vomiting, respiratory depression, bitter taste.
NursingInterventi on Report severe nausea, vomiting, palpitations, shortness of breath or difficulty breathing.
Drug Generic Brand: Fibrosine Brand Name: Fibromil Classification/s: Laxatives Dosage/Route/Freq uency: 1 sachet P.O q6
Actions Acts directly on the bowels, stimulating the bowel muscles to cause a bowel movement.
Indications Fiber supplement to maintain regularity of bowel movement. Chronic constipation
Side Effects Excessive bowel activity, weakness, dizziness, abdominal cramps.
Nursing Intervention Give with meals if GI upset occur. Report if severe nausea, vomiting or stomach pain occurs.
Name of the Drug Generic: Domperidone Brand: Motilium Classification: GIT Regulators, Antiflatulents& AntiInflammatories / Antiem etics Dosage: 1 tab Q6 2 doses
Action Domperidone is a peripheral dopaminereceptor blocker. It increases esophageal peristalsis, lower esophageal sphincter pressure, gastric motility and peristalsis, thus facilitating gastric emptying and decreasing small bowel transit time.
Indication For manageme nt of dyspepsia, heartburn, epigastric pain, nausea, and vomiting.
Contraindicatio n Hypersensitivity. GI haemorrhage, obstruction and perforation, patients with prolactin releasing pituitary hormone, nausea and vomiting.
Adverse Effects Drowsiness; constipation or diarrhoea, decreased libido, skin rash, itch. Potentially Fatal: Convulsions, cardiac arrest, Seizures
Nursing Consideratio n Assess for GI complaints: Nausea, vomiting, anorexia, constipation, abdominal distention before and after administration Assess for pain Assess for change in bowel habits
Name of the Drug Generic: Mg Hydroxide + Al Hydroxide Kremil-S Brand: Mylanta Classification: Antiulcer agents, antacids Dosage: 1Tab Q8
Action -For the symptomatic relief of hyperacidity associated with peptic ulcer, gastritis, esophagitis, and dyspepsia -as supplement to H2-blockers or proton pump inhibitors for the rapid relief of ulcer symptoms. -as an antiflatulent to alleviate the symptoms of gassiness, including postoperative gas pain, associated with hyperacidity. osteomalacia.
Contraindicati on Diarrhea or -patients with constipation renal failure may occur to -partial patients taking intestinal antacids obstruction, containing Mg & appendicitis, Al. The fecal impaction, following occur gastric outlet rarely: Due to obstruction, and Al(OH)3: constipation Proximal -phosphate myopathy; depletion and encephalopathy low serum & dementia phosphate, may occur in osteomalacia patient w/ renal failure; intestinal obstruction; fecal impaction;
Indication
Adverse Effects Diarrhea or constipation may occur in patients taking antacids containing magnesium and aluminum.
Nursing Consideration Give atleast 2 hrs apart from other medication. Do not take longer than 2 wks unless directed by the physician. For peptic ulcer take 1 and 3 hrs after meals and at bedtime for 4-6 wks. Chew tablets thoroughly, followed with the glass of water; shake suspensions well.
Name of the Drug Generic: Celecoxib Brand: Celebrex Classification: Nonsteroidal AntiInflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) Dosage: 200mg/cap BID
Action It inhibits prostaglandin synthesis by selectively inhibiting cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2). Relieves pain and inflammation
Indication Management of acute pain
Contraindicati on Contraindicated with allergies to sulfonamides, celecoxib, NSAIDs, or aspirin; Significant renal impairment
Adverse Effects CNS: dizziness, drowsiness, headache, insomnia, fatigue GI: nausea, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, flatulence, dry mouth, Hematologic: decreased hemoglobin or hematocrit
Nursing Consideration Assess patients range of motion, degree of swelling, and pain in affected joints before and periodically throughout therapy. Assess patient for allergy to sulfonamides, aspirin, or NSAIDS. Patients with these allergies should not receive celecoxib. May be administered without regard to meals. Instruct patient to take celecoxib exactly as directed. Do not take more than prescribed dose. Increasing doses does not appear to
increase effectiveness. Advise patient to notify health care professional promptly if signs or symptoms of GI toxicity (abdominal pain, black stools), skin rash, unexplained weight gain, edema occurs. Patient should discontinue celecoxib and notify health care professional if signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity (nausea, fatigue, lethargy, pruritus, jaundice, upper right quadrant tenderness, flulike symptoms) occur.
Name of the Drug Generic: Acetaminophen Brand: Paracetamol Classification: antipyretics, nonopioid analgesics
Action Inhibits the synthesis of prostaglandin s that may serve as mediators of pain and fever, primarily in the CNS
Indication Mild Pain Fever
Contraindicati on Hypersensitivity to drug
Adverse Effects Hema: hemolytic anemia, Hepa:jaundice Metabolic: hypoG GI:HEPATIC FAILURE, HEPATOTOXICIT Y (overdose) GU:renal failure (high doses/chronic use). Derm: rash, urticaria
Nursing Consideration BEFORE: ~ Advise parents or caregivers to check concentrations of liquid preparations. Errors have resulted in serious liver damage. ~ Assess fever; note presence of associated signs (diaphoresis, tachycardia, and malaise). DURING: ~ Adults should not take acetaminophen longer than 10 days and children not longer than 5 days unless directed by health care professional.
~ Advise mother or caregiver to take medication exactly as directed and not to take more than the recommended amount. AFTER: ~ Advise patient to consult health care professional if discomfort or fever is not relieved by routine doses of this drug or if fever is greater than 39.5C (103F) or lasts longer than 3 day
XIII. Discharge Planning Medication Continue taking medicines as prescribed at the right dose, time, frequency, and route (Celecoxib 200mg/capsule twice a day for pain [PRN]) Exercise Diet Encouraged to follow recommended diet Encouraged to increase fiber in diet and increase fluid intake Advised the patient to go to the church every weekends to uplift of spiritual health Encourage patient to participate in desired religious activities Encouraged patient to exercise regularly Encouraged to get enough rest and sleep Advised patient to stay in clean, safe and comfortable place Instructed the patient to seek medical aid in the nearest health center for continuing health care Encouraged to follow treatment regimen Instructed the patient to continue hot sitz bath every 6hours The patient is instructed about the importance of an adequate oral intake and of maintaining bowel and urinary tract function The patient should resume activities gradually The patient is reminded about following appointment in May 28,2011 Out-patient follow-up
Treatment
Health Teaching
Spiritual Counseling
You might also like
- VentilationDocument92 pagesVentilationRobert Nixon100% (1)
- Revised Case Report - HemorrhoidsDocument47 pagesRevised Case Report - Hemorrhoidschristina_love08100% (2)
- Hemorrhoidectomy Case StudyDocument19 pagesHemorrhoidectomy Case StudyJoyJoy Tabada CalunsagNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Indirect Inguinal Hernia (R)Document71 pagesCase Study of Indirect Inguinal Hernia (R)Mary Grace Mas100% (1)
- Hemorrhoids Pathophysiology and TreatmentDocument4 pagesHemorrhoids Pathophysiology and TreatmentBianca Freya Porral100% (4)
- HemorrhoidsDocument25 pagesHemorrhoidsHazel Joyce MoletaNo ratings yet
- Case Study HemorrhoidsDocument4 pagesCase Study HemorrhoidsTeanu Jose Gabrillo TamayoNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic GastritisDocument17 pagesAcute and Chronic GastritisIndah Nur PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation HemorrhoidDocument20 pagesCase Presentation HemorrhoidawalrmdhnNo ratings yet
- Appendectomy CSDocument30 pagesAppendectomy CSMASIINo ratings yet
- AppendicitisDocument17 pagesAppendicitisAhmed Halaby100% (1)
- Ugib Case StudyDocument33 pagesUgib Case StudyRosemarie Cunanan Grifoni100% (1)
- Project Report On Air FilterDocument5 pagesProject Report On Air FilterEIRI Board of Consultants and PublishersNo ratings yet
- Case DiscussionDocument8 pagesCase DiscussionAishwarya BharathNo ratings yet
- Otitis Media - CSDocument14 pagesOtitis Media - CSMASII100% (3)
- Case Study of HypospadiaDocument19 pagesCase Study of Hypospadiagaylenice100% (10)
- Indirect Inguinal Hernia FINALDocument6 pagesIndirect Inguinal Hernia FINALJonalyn TumanguilNo ratings yet
- Patient Biodata for Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)/TITLEDocument31 pagesPatient Biodata for Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)/TITLEpreet kaur100% (2)
- Nursing Case Study Acute GastroDocument8 pagesNursing Case Study Acute GastroEdilyn BalicaoNo ratings yet
- Grand Case NP 1 Laparoscopic CholecystectomyDocument21 pagesGrand Case NP 1 Laparoscopic CholecystectomyFarida Paula R. SevillaNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Dengue FeverDocument76 pagesCase Study On Dengue FeverMary Rose Silva Gargar0% (1)
- Healthcare Financing in IndiADocument86 pagesHealthcare Financing in IndiAGeet Sheil67% (3)
- Consider Recycled Water PDFDocument0 pagesConsider Recycled Water PDFAnonymous 1XHScfCINo ratings yet
- Supplier Assessment Report-Shenzhen Illuman Photoelectronic Co., LTDDocument29 pagesSupplier Assessment Report-Shenzhen Illuman Photoelectronic Co., LTDAdam Andrew OngNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Bilateral NephrolithiasisDocument85 pagesCase Study On Bilateral NephrolithiasisShoixi ⎝⓿⏝⓿⎠100% (1)
- CASE PRESENTATION On PNEUMONIADocument41 pagesCASE PRESENTATION On PNEUMONIARodney Reyes100% (1)
- Dengue Case StudyDocument23 pagesDengue Case Studycutie_0023No ratings yet
- A Case PresentationDocument50 pagesA Case PresentationAnaleah MalayaoNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument29 pagesCase StudyGerome ValderamaNo ratings yet
- Case Study Stomach CancerDocument2 pagesCase Study Stomach CancerJoseNo ratings yet
- 06wk48 - CSSR Improvement Fach Power Trial Phase II - VDF UKDocument19 pages06wk48 - CSSR Improvement Fach Power Trial Phase II - VDF UKsyedNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis Case StudyDocument51 pagesCholelithiasis Case StudyANCHAL SHARMANo ratings yet
- Course in The WardDocument12 pagesCourse in The WardBunzay GelineNo ratings yet
- CHOLECYSTITIS CASE STUDY Version 2.0Document57 pagesCHOLECYSTITIS CASE STUDY Version 2.0Gabriel Arch100% (1)
- Acute Appendicitis - CSDocument29 pagesAcute Appendicitis - CSMASIINo ratings yet
- Hypospadia CompletedDocument92 pagesHypospadia Completedgideon A. owusu100% (1)
- PdaDocument43 pagesPdaSandy ShahNo ratings yet
- Special Power of AttorneyDocument1 pageSpecial Power of AttorneyOrville VillaceteNo ratings yet
- Acute PyelonephritisDocument53 pagesAcute Pyelonephritiseeymee100% (1)
- Case Study On Gastric Outlet ObstructionDocument37 pagesCase Study On Gastric Outlet ObstructionJunayed Safar Mahmud100% (4)
- HerniaDocument6 pagesHerniahani alzo3bi100% (7)
- Appendectomy Case StudyDocument16 pagesAppendectomy Case StudyMahmoud Al Abed100% (1)
- External HemorrhoidsDocument61 pagesExternal HemorrhoidsitsmeayaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy &physiology JaundiceDocument2 pagesAnatomy &physiology JaundiceHCX dghhqNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation - Acute Otits MediaDocument31 pagesCase Presentation - Acute Otits MediaJean nicole Garibay0% (1)
- Pancreatic CancerDocument15 pagesPancreatic CancerMutiana Muspita JeliNo ratings yet
- NCP PryllDocument6 pagesNCP PryllpjcolitaNo ratings yet
- Discharge Plan For Dengue Fever 1Document4 pagesDischarge Plan For Dengue Fever 1Cecille Ursua0% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Peptic UlcerDocument16 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Peptic UlcerDrNarayan KR100% (8)
- Case Study Pleural EffusionDocument4 pagesCase Study Pleural EffusionKhristine Anne FabayNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment On GERD PatientDocument8 pagesPhysical Assessment On GERD PatientRobert Medina100% (1)
- Case Plan On Diarrhoea (Medical Surgical Nursing)Document15 pagesCase Plan On Diarrhoea (Medical Surgical Nursing)kamini ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Iloilo Doctors' College Case Study on PneumoniaDocument38 pagesIloilo Doctors' College Case Study on PneumoniaLuna JadeNo ratings yet
- Acute Gastroenteritis in Paediatrics 1Document43 pagesAcute Gastroenteritis in Paediatrics 1Imran FaisalNo ratings yet
- A Case Study In:: Hirschsprung DiseaseDocument18 pagesA Case Study In:: Hirschsprung DiseaseJaimie La PenaNo ratings yet
- Case Study On LeukemiaDocument33 pagesCase Study On LeukemiaBhupesh PatidarNo ratings yet
- CASE REPORT Rhinitis AlergyDocument36 pagesCASE REPORT Rhinitis AlergySiti MunirahNo ratings yet
- Case Study FistulectomyDocument94 pagesCase Study FistulectomyQuolette Constante80% (5)
- Hydronephrosis Fred LuceDocument69 pagesHydronephrosis Fred LuceKMNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of AppendixDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of AppendixKandilanapumapaso SapusongbawattaoNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis Case StudyDocument13 pagesAppendicitis Case StudyMelanie Agaran Bautista100% (1)
- Case StudyDocument33 pagesCase StudySarah GatuzNo ratings yet
- Case Study Dengue FeverDocument4 pagesCase Study Dengue FeverGerard Guevarra0% (1)
- CHOLECYSTOLITHIASISDocument77 pagesCHOLECYSTOLITHIASISMarkie ArqueroNo ratings yet
- Case Study On FCBDDocument38 pagesCase Study On FCBDKwinutskie LiteratoNo ratings yet
- Inflammation Gall Bladder Cholelithiasis Cystic Duct Inspissation Bile StasisDocument12 pagesInflammation Gall Bladder Cholelithiasis Cystic Duct Inspissation Bile StasisAndrew Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Calculus CholecystitisDocument48 pagesCalculus CholecystitisEdderlyn LamarcaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument5 pagesDiabetes MellitusOrville VillaceteNo ratings yet
- Varicoceles Are A Relatively Common ConditionDocument1 pageVaricoceles Are A Relatively Common ConditionOrville VillaceteNo ratings yet
- 2 TheoriesDocument5 pages2 TheoriesOrville VillaceteNo ratings yet
- Cultural Rituals of Pregnancy in KoreaDocument2 pagesCultural Rituals of Pregnancy in KoreaOrville VillaceteNo ratings yet
- MAPEH 2 SBC 2nd Quarterly AssesmentDocument5 pagesMAPEH 2 SBC 2nd Quarterly AssesmentReshiele FalconNo ratings yet
- Catálogo SEDIVERDocument32 pagesCatálogo SEDIVEREnver Rojas DiazNo ratings yet
- Ielts Band Score 7Document2 pagesIelts Band Score 7Subhan Iain IINo ratings yet
- CWK-IDD-009-CC-2020: Reference Checking Consent and Authorization Form Candidate's Full NameDocument1 pageCWK-IDD-009-CC-2020: Reference Checking Consent and Authorization Form Candidate's Full NamePopa Alina-ManuelaNo ratings yet
- Secondary AssessmentsDocument12 pagesSecondary Assessmentsapi-338389967No ratings yet
- DOC023.97.80076 - 3ed Sensores ORPDocument148 pagesDOC023.97.80076 - 3ed Sensores ORPAlejandroNo ratings yet
- Company Law AssignmentDocument5 pagesCompany Law AssignmentABISHEK SRIRAM S 17BLA1008No ratings yet
- Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale. Detection of Postnatal Depression. Development of The 10-ItemDocument6 pagesEdinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale. Detection of Postnatal Depression. Development of The 10-ItemKyze LQNo ratings yet
- Solucionario. Advanced Level.Document68 pagesSolucionario. Advanced Level.Christian Delgado RamosNo ratings yet
- Jamec Air FittingsDocument18 pagesJamec Air Fittingsgoeez1No ratings yet
- Fischer FBN II BoltDocument5 pagesFischer FBN II BoltJaga NathNo ratings yet
- Atomic and Molecular PhysicsDocument28 pagesAtomic and Molecular PhysicsAvinash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Honda PCX150Document137 pagesHonda PCX150Akchu KadNo ratings yet
- Requirement & Other Requirement: 2.311 Procedure For Accessing Applicable LegalDocument2 pagesRequirement & Other Requirement: 2.311 Procedure For Accessing Applicable Legalkirandevi1981No ratings yet
- Cell Biology & BiochemistryDocument320 pagesCell Biology & BiochemistryVai SanNo ratings yet
- Amaryllidaceae Family Guide with Endemic Philippine SpeciesDocument28 pagesAmaryllidaceae Family Guide with Endemic Philippine SpeciesMa-anJaneDiamos100% (1)
- Bio ViberDocument7 pagesBio ViberMarco BuntNo ratings yet
- 4 6051111060339957657Document361 pages4 6051111060339957657Oviedo OviedoNo ratings yet
- Causes of Failure of Earth DamsDocument11 pagesCauses of Failure of Earth DamsThéoneste NSANZIMFURANo ratings yet
- Versidrain 150: Green RoofDocument2 pagesVersidrain 150: Green RoofMichael Tiu TorresNo ratings yet
- SSMT ConplanDocument2 pagesSSMT ConplanJeffrey VillangcaNo ratings yet
- SafewayDocument70 pagesSafewayhampshireiiiNo ratings yet
- Climate Change and Global Warming and Its Impact On BangladeshDocument7 pagesClimate Change and Global Warming and Its Impact On BangladeshAminulHoqueNo ratings yet
- Steroids ActivityDocument1 pageSteroids Activityfaqed ilzakiraNo ratings yet