Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Problem Set2 Dynamics
Uploaded by
Sonrim JunioOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Problem Set2 Dynamics
Uploaded by
Sonrim JunioCopyright:
Available Formats
engineering mechanics | dynamics
PROBLEM SET 2
5. A ball is thrown vertically upward from a point on a bridge located
135 ft above the water. Knowing that it strikes the water 4 sec after release, determine (a) the velocity of the ball upon release, (b) the velocity of the ball as it strikes the water. ( a. 30.65 ft/sec, b. 98.15 ft/sec )
1. A stone is dropped down a well and 5 seconds later the sound of the
splash is heard. If the velocity of sound is 1120 ft per sec, what is the depth of the well? ( 353.31 ft )
6. Ball A is released from rest at a height of 40 ft at the same time that a
second ball B is thrown upward 5 ft from the ground. If the balls pass one another at a height of 20 ft, determine the speed at which ball B was thrown upward.
2. A stone is thrown vertically upward from the ground with a velocity
of 48.3 ft per sec. One second later another stone is thrown vertically upward with a velocity of 96.6 ft per sec. How far above from the ground will the stones be at the same level? ( 36.064 ft )
3. Two automobiles A and B are approaching each other in adjacent
highway lanes. At t = 0, A and B are 0.62 mi apart, their speeds are v A = 68 mi/h and v B = 39 mi/hr, and are at points P and Q, respectively. Knowing that A passes point Q 40 sec after B was there and that B passes point P 42 sec after A was there, determine (a) the uniform accelerations of A and B, (b) when the vehicles pass each other, (c) the speed of B at that time.
7. Two automobiles A and B are traveling in the same direction in 4. A motorcyclist at A is traveling at 60 ft/s when he wishes to pass the
truck T which is traveling at a constant speed of 60 ft/s. To do so the motorcyclist accelerates at 6 ft/ s2 until reaching a maximum speed of 85 ft/s. If he then maintains this speed, determine the time needed for him to reach a point 100 ft in front of the truck. adjacent highway lanes. Automobile B is stopped when it is passed by A, which travels at a constant speed of 36 km/hr. Two seconds later automobile B starts and accelerates at a constant rate of 1.5 m/s2. Determine (a) the time when and where B will overtake A, (b) the speed of B at that time. ( a. 15.1 s, b. 22.65 m/s )
8. Two automobiles A and B are traveling in the same direction in
adjacent lanes and are stopped at a traffic signal. As the signal turns green, automobile A accelerates at a constant rate of 2 m/s2. Two seconds later, automobile B stars and accelerates at a constant speed of 3.6 m/s2. Determine (a) when and where B will overtake A, (b) the speed of each automobile at that time. (a) 7.85 s, 61.7 m; (b) v A = 15.71 m/s, v B = 21.1 m/s.
9. A police officer in a patrol car parked in a 70 km/h speed zone
observes a passing automobile traveling at a slow, constant speed.
Believing that the driver of the automobile might be intoxicated, the officer starts his car, accelerates to 90 km/h in 8 sec, and, maintaining a constant velocity of 90 km/h, overtakes the motorist 42 sec after the automobile passed him. Knowing that 18 sec elapsed before the officer began pursuing the motorist, determine (a) the distance the officer traveled before overtaking the motorist, (b) the motorists speed. (a. 0.5 km, b. 42.9 km/hr)
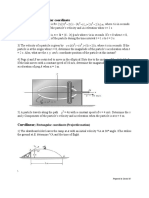
10. The acceleration of slider A is defined by the relation
a = 2k k 2 v 2 , where
and v are expressed in m/s2 and m/s, respectively, and k is a constant. The system starts at s = 0.5 m with v = 0 m/s and t = 0. Knowing that s = 0.4 m when t = 0.2 s, determine the value of k .
12.
In a close harness race, horse 2 passes horse 1 at point A where the two velocities are v 2 = 7 m/s and v1 = 6.8 m/s. Horse 1 later passes horse 2 at point B and goes on to win the race at point C, 400 m from A. The elapsed times from A to C for horse 1 and horse 2 are t1 = 61.5 s and t 2 = 62 s, respectively. Assuming uniform accelerations for both horses between A and C, determine (a) the distance from A to B, (b) the position of horse 1 relative to horse 2 when horse 1 reaches the finish line C.
11.
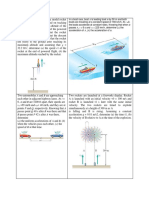
Two rockets are launched at a fireworks performance. Rocket A is launched with an initial velocity vO and rocket B is launched 4 sec later with the same initial velocity. The two rockets are timed to explode simultaneously at a height of 80 m, as A is falling and B is rising. Assuming constant acceleration g = 9.81 m/s2, determine (a) the initial velocity vO , (b) the velocity of B relative to A at the time of explosion.
You might also like
- 2003 Nissan Altima 2.5 Serivce Manual WTDocument6 pages2003 Nissan Altima 2.5 Serivce Manual WTAndy DellingerNo ratings yet
- API Piping PlanDocument109 pagesAPI Piping PlanSakthikumar ChandrasekaranNo ratings yet
- Lighting and ShadingDocument44 pagesLighting and Shadingpalaniappan_pandianNo ratings yet
- Selected Problems in Physics with AnswersFrom EverandSelected Problems in Physics with AnswersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Problems in Soil Mechanics and Foundation EngineeringDocument172 pagesProblems in Soil Mechanics and Foundation EngineeringCharilyn Echeverre100% (16)
- Kinematics Subjective Problems-SP-NPJC I-Jun 13Document11 pagesKinematics Subjective Problems-SP-NPJC I-Jun 13Mohit GargNo ratings yet
- DynamicsDocument10 pagesDynamicsJan Roald Buemia Triumfante32% (25)
- Rotary Drum SpecsDocument16 pagesRotary Drum SpecsArrianne Jaye MataNo ratings yet
- Zhang2014.Numerical Investigation On Factors For Deep-Seated Slope Stability of StoneDocument10 pagesZhang2014.Numerical Investigation On Factors For Deep-Seated Slope Stability of Stonejose monteNo ratings yet
- Dynamics 1 Solved ProblemsDocument5 pagesDynamics 1 Solved ProblemsIkie YuNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For College Physics 8th EditionDocument24 pagesTest Bank For College Physics 8th EditionAlbert Ascher100% (34)
- Mod 2 QuestionsDocument49 pagesMod 2 Questionscyder100% (1)
- Kinematics Worksheet 1Document4 pagesKinematics Worksheet 1CesarNo ratings yet
- Problem Set On DynamicsDocument40 pagesProblem Set On DynamicsMa. Socorro Angela LlavoresNo ratings yet
- Unit I Rectilinear and Curvilinear Motion ProblemsDocument4 pagesUnit I Rectilinear and Curvilinear Motion ProblemsmanojNo ratings yet
- Es-26 PS2 (2023)Document2 pagesEs-26 PS2 (2023)Guenivere SanchezNo ratings yet
- Prob Set 2Document2 pagesProb Set 2salvadortobitoNo ratings yet
- Physics Mechanics 1D Motion KinematicsDocument2 pagesPhysics Mechanics 1D Motion KinematicsSuman SinghNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Particles ProblemsDocument9 pagesKinematics of Particles ProblemsNadlor Gasco OzausNo ratings yet
- Revision On Motion: SI UnitsDocument6 pagesRevision On Motion: SI UnitsYoussef SalemNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document3 pagesAssignment 5Garvit GargNo ratings yet
- Homework 2Document2 pagesHomework 2MoH mAdNo ratings yet
- FDocument2 pagesFtrucy-dollNo ratings yet
- Curvilinear Rectangular Coordinate: T J+ K M, Where T Is in SecondsDocument4 pagesCurvilinear Rectangular Coordinate: T J+ K M, Where T Is in Secondsdaniel hambissaNo ratings yet
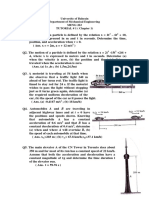
- University of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 1 (Chapter 1)Document3 pagesUniversity of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 1 (Chapter 1)Vivin MathewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - WorksheetDocument11 pagesChapter 2 - WorksheetHenokNo ratings yet
- Mech PsetDocument7 pagesMech PsetJomel JazminNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For College Physics 8th EditionDocument24 pagesTest Bank For College Physics 8th EditionlouisadonaldlwrNo ratings yet
- Inbound 4435889675498454681Document1 pageInbound 4435889675498454681keepersilent2No ratings yet
- Rectilinear Motion: Variable AccelerationDocument11 pagesRectilinear Motion: Variable AccelerationKavita DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Dynamics 1 - HandoutsDocument8 pagesDynamics 1 - HandoutsRomeoNo ratings yet
- Physics Pre-AP One Dimensional MotionDocument2 pagesPhysics Pre-AP One Dimensional MotionJohnCarloTigue100% (1)
- Repaso de Problemas de Temas 8 y 9Document5 pagesRepaso de Problemas de Temas 8 y 9Slow ECFNo ratings yet
- Worksheet I - Kinematics of ParticlesDocument7 pagesWorksheet I - Kinematics of ParticlesAdnan ShafiNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper2Document2 pagesPhysics Paper2atul narkhedeNo ratings yet
- 1D Worksheet PDFDocument2 pages1D Worksheet PDFGenesis ValerioNo ratings yet
- Kinematics P ME KNM 04 08Document3 pagesKinematics P ME KNM 04 08Raghav MishraNo ratings yet
- Ch.3 Linear Motion (WS2)Document2 pagesCh.3 Linear Motion (WS2)TreeiciclesNo ratings yet
- Problem Set No. 3 Speed, Velocity, Acceleration Word Count: 38Document14 pagesProblem Set No. 3 Speed, Velocity, Acceleration Word Count: 38Arazo, Oliver B.No ratings yet
- Assignment (Kinematics) : X 4t+5t MetreDocument1 pageAssignment (Kinematics) : X 4t+5t MetreGurleen KaurNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document3 pagesCH 02Mohammed Abdul MajidNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument4 pagesProblem SetJULLIANA VILORIANo ratings yet
- ENG105 Engineering Dynamics Tutorial 02: 100km/hr and VDocument1 pageENG105 Engineering Dynamics Tutorial 02: 100km/hr and VmanoliNo ratings yet
- Problem-Set-Part-1-AnswerDocument17 pagesProblem-Set-Part-1-AnswerVince MarananNo ratings yet
- 3 Kinematics-1Document3 pages3 Kinematics-1arunpatel32No ratings yet
- Relative Motion Problems and SolutionsDocument5 pagesRelative Motion Problems and SolutionsAtulNo ratings yet
- Solution Activity No.1Document7 pagesSolution Activity No.1Shaft SandaeNo ratings yet
- PSET DRB FRDocument8 pagesPSET DRB FRKATHLEEN JOY DE CASTRONo ratings yet
- Phy 1Document50 pagesPhy 1Garlapati Srinivasa Rao100% (1)
- 1-D Kinematics Review PacketDocument7 pages1-D Kinematics Review PacketXaxxa1571% (7)
- Tutorial 2Document5 pagesTutorial 2Vivin MathewNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1: Dynamic Physics Problems/TITLEDocument3 pagesProblem Set 1: Dynamic Physics Problems/TITLEpeneNo ratings yet
- Uniform Motion (SUVT) QuestionsDocument2 pagesUniform Motion (SUVT) QuestionsmjdaihmohammedNo ratings yet
- JjoDocument3 pagesJjoAnonymous DJuu65GNo ratings yet
- DPP 7 Kinematics RelativemotioninOne DimensionDocument2 pagesDPP 7 Kinematics RelativemotioninOne DimensionGoutam PhysicsloverNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document1 pageProblem Set 1Niño John JaymeNo ratings yet
- Constant Acceleration Horizontal MotionDocument2 pagesConstant Acceleration Horizontal Motion7644c6xg6gNo ratings yet
- 21Document3 pages21harshanauocNo ratings yet
- Physics 71 1 Long Sample ExamDocument4 pagesPhysics 71 1 Long Sample ExamManna Pinto100% (1)
- Train Speed ChapterDocument6 pagesTrain Speed ChapterAnuj PaudelNo ratings yet
- HomeworkDocument3 pagesHomeworkUriel CadenaNo ratings yet
- 00worksheets GrammarDocument1 page00worksheets GrammarSara Alvarez MenendezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Velocity and Acceleration: Method 1 in The Fi RST 3 Minutes The Average Velocity IsDocument4 pagesChapter 1: Velocity and Acceleration: Method 1 in The Fi RST 3 Minutes The Average Velocity IsAnuj PaudelNo ratings yet
- Exam I Redo 2010Document1 pageExam I Redo 2010Benjamin FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Task #5 (Hermo)Document4 pagesTask #5 (Hermo)KATHLEEN MAE HERMONo ratings yet
- Lewis Structures: Molecular Structure and BondingDocument83 pagesLewis Structures: Molecular Structure and Bondingحني اسفيانيNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To ME, AME, MSNT)Document2 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To ME, AME, MSNT)Asheesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Som & DmeDocument2 pagesSom & DmeSurulivelrajantNo ratings yet
- Separation of HCl-H2SO4 by MDDocument7 pagesSeparation of HCl-H2SO4 by MDKuldeep BhattNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0921452617305768 MainDocument5 pages1 s2.0 S0921452617305768 MainpovNo ratings yet
- Dynamic of Billboard Thin PlateDocument6 pagesDynamic of Billboard Thin PlateJoseph Cloyd LamberteNo ratings yet
- Wireless Power Transfer DeviceDocument65 pagesWireless Power Transfer DevicebhagathnagarNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Vector Algebra: 1.1.1 ScalarsDocument7 pages1.1 Vector Algebra: 1.1.1 ScalarsreachsudhirNo ratings yet
- Iit-Jee-Neet-Weekly Test SeriesDocument5 pagesIit-Jee-Neet-Weekly Test SeriesICSE HubNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange Chromatography Separates ProteinsDocument3 pagesIon Exchange Chromatography Separates ProteinsAdeliza MortallaNo ratings yet
- SsssDocument17 pagesSsssPhysicsNo ratings yet
- Using Jmol To Help Students Better Understand Fluxional ProcessesDocument1 pageUsing Jmol To Help Students Better Understand Fluxional Processesdevy ridaNo ratings yet
- Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University Hyderabad M.Tech II Semester Examinations Structural Dynamics QuestionsDocument3 pagesJawaharlal Nehru Technological University Hyderabad M.Tech II Semester Examinations Structural Dynamics QuestionsFrank JohnNo ratings yet
- Dcmotors601 0241Document42 pagesDcmotors601 0241Afrida Fazira MNo ratings yet
- Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions of Alkyl HalidesDocument36 pagesNucleophilic Substitution Reactions of Alkyl HalidesmaulidyaNo ratings yet
- Laplace TableDocument2 pagesLaplace TableosmanfıratNo ratings yet
- 3001 Machine Design Elements SampleDocument14 pages3001 Machine Design Elements SampleCGD ReviewNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt 18 19 XII Phy Study Package 5 SET 2 Chapter 1Document36 pagesCLS Aipmt 18 19 XII Phy Study Package 5 SET 2 Chapter 1Adil Ahmed83% (12)
- L1B16Document6 pagesL1B16HanTeongNo ratings yet
- 08 Contour IntegrationvhdhdDocument14 pages08 Contour IntegrationvhdhdxhfakqaawuorgxbwneNo ratings yet
- Air Crew Radiation Exposure - An OverviewDocument8 pagesAir Crew Radiation Exposure - An OverviewStarxteelNo ratings yet
- Cryogenics IntroductionDocument26 pagesCryogenics Introductionsenior high100% (1)