Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tool Makers Microscope
Uploaded by
Anand BabuCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tool Makers Microscope
Uploaded by
Anand BabuCopyright:
Available Formats
QIS COLLEGE OF ENGG. & TECH.:ONGOLE,A.P.
METROLOGY LAB
MEASUREMENT OF LINEAR AND ANGULAR DIMENSIONS BY TOOL MAKERS MICROSCOPE
16
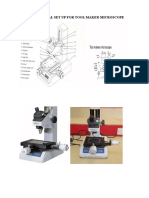
TOOL MAKERS MICROSCOPE
QIS COLLEGE OF ENGG. & TECH.:ONGOLE,A.P.
METROLOGY LAB
MEASUREMENT OF LINEAR AND ANGULAR DIMENSIONS BY TOOL MAKERS MICROSCOPE
AIM:
To measure the following parameters of threaded specimen of small magnitude: (1) Major Diameter (2) Minor Diameter (3) Pitch (4) Included angle
APPARATUS: Tool Makers Microscope THEORY:
Tool Makers Microscope is an optical device used to view and measure very fine details, shapes and dimensions on small and medium sized tools, dies, and work pieces. It is equipped with a glass table that is movable in two principal directions and can be read to 0.01 mm. Microscope is also equipped with a protractor to measure the angular dimensions. It is also equipped with surface illumination. Provision is available to adjust the height of the viewing head to get a sharp image of the object.
17
TOOL MAKERS MICROSCOPE
QIS COLLEGE OF ENGG. & TECH.:ONGOLE,A.P.
METROLOGY LAB
Screw thread is a helical ridge produced by forming a continuous helical groove of the uniform section on the external or internal surface of a cylinder or cone. A screw thread formed on a cylinder is known as straight or parallel. Screw thread, while the one formed on a cone or frustum of a cone is known as tapered screw thread. In the present experiment, parameters of a straight screw thread of small magnitude are measured. Parameters of small screws such as screws used in watches, electrical plugs, and toys cannot be measured using instruments like vernier calipers or micrometers. Unless they are magnified it is not possible to measure all the parameters. Some parameters of a straight screw thread are defined as follows:
Crest of a thread is defined as the prominent part of thread. Root of a thread is defined as the bottom of the groove between two flanks of thread. Flanks of thread are straight edges which connect the crest with the root. Angle of the thread also known as included angle is the angle between the flanks of the thread measured in axial plane. The pitch of a thread is the distance measured parallel to the axis of the thread, between corresponding points on adjacent thread forms in the same axial plane and on the same side of axis. 18
TOOL MAKERS MICROSCOPE
QIS COLLEGE OF ENGG. & TECH.:ONGOLE,A.P.
METROLOGY LAB
Major diameter is the diameter of an imaginary cylinder Co-axial with the screw which just touches the crests of an external thread or roots of an internal thread. Minor Diameter is the diameter of an imaginary cylinder co-axial with the screw which just touches the roots of an external thread or the crest of an internal thread
PROCEDURE:
1.
Determination of the major diameter: Keep the specimen on the glass table. Here the given specimen is a thread. Switch on the light to get the silhouette of the thread. Adjust the height of the viewing head until a sharp image appears. Adjust the cross line of the instrument as shown below.
Now note-down the reading of the Micrometer. Now move cross line in such a way that, horizontal cross line occupies other sides of the crests as shown in fig-2. Again note-down the reading of the Micrometer. Difference of the two readings gives the major diameter of the thread.
\ 19
TOOL MAKERS MICROSCOPE
QIS COLLEGE OF ENGG. & TECH.:ONGOLE,A.P.
METROLOGY LAB
2.
Determination of the Minor diameter:
After obtaining the sharp image of the Threaded specimen let the horizontal cross line touch all the root points as shown in fig-3. At this position take the micrometer reading adjust the micrometer in such a way that, same horizontal line touches the other side of the root paints as shown in fig-4. Again note-down the reading of the micrometer. Difference of the readings gives minor diameter.
3.
Determination of Pitch:
20
TOOL MAKERS MICROSCOPE
QIS COLLEGE OF ENGG. & TECH.:ONGOLE,A.P.
METROLOGY LAB
To measure pitch of the thread, align the centre of the cross lines at the peak of the crest as shown in the fig-5. At this position take the micrometer reading. Now move the micrometer in such a way that centre of the cross line align with the peak of the next thread as shown in for-6. Again note-down the reading of the micrometer. Difference of the two readings gives the pitch of the thread.
4.
Determination of the angle:
To measure the included angle of the thread coincide one of the lines of the cross lines with the flank of the thread as shown in the fig-7. Notedown the reading of the protractor. Now rotate the protractor in turn the cross lines in such a way that same line coincides with the opposite flank as shown in fig-8. Note-down the reading of the protractor. Difference of the two reading gives the included angle of the thread.
21
TOOL MAKERS MICROSCOPE
QIS COLLEGE OF ENGG. & TECH.:ONGOLE,A.P.
METROLOGY LAB
PRECAUTIONS: 1. Students are advised to take readings without any parallax error. 2. Lens must be properly adjusted to get a sharp image. 3. Move the Microscope table by gently holding micrometer thimble. RESULT:
22
TOOL MAKERS MICROSCOPE
You might also like
- Screw ThreadsDocument37 pagesScrew ThreadsOmkaar SinghNo ratings yet
- How To Use Micrometer On Microscopes: Biology 1Document7 pagesHow To Use Micrometer On Microscopes: Biology 1Rakeesh VeeraNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Measurements Laboratory Activity: Background InformationDocument4 pagesMicroscopic Measurements Laboratory Activity: Background InformationPaige EvansNo ratings yet
- Design of A Bearingless BLDC MotorDocument6 pagesDesign of A Bearingless BLDC MotorTien Dung TranNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 AntennaDocument27 pagesLesson 6 AntennaShylaja HalageriNo ratings yet
- Antennas & Their Associated PatternsDocument45 pagesAntennas & Their Associated PatternsTrần Châu ThôngNo ratings yet
- Tips for Capturing High-Quality Digital Microscope ImagesDocument4 pagesTips for Capturing High-Quality Digital Microscope ImagesAida LizethNo ratings yet
- Comparison MicoscopeDocument10 pagesComparison MicoscopeSwati V NairNo ratings yet
- Sinowon 3D Video Measuring Machine VMM-P Operation ManualDocument12 pagesSinowon 3D Video Measuring Machine VMM-P Operation ManualJohnny DaiNo ratings yet
- Olympus Microscope Maintenance Guide 2020Document12 pagesOlympus Microscope Maintenance Guide 2020csc palakkuttyNo ratings yet
- MPPT Algorithm Implementation for Solar Photovoltaic module using MicrocontrollerDocument3 pagesMPPT Algorithm Implementation for Solar Photovoltaic module using MicrocontrollerMazoon ButtNo ratings yet
- Screw Thread MeasurementDocument55 pagesScrew Thread MeasurementMadhuNo ratings yet
- Microscope: Greek Instrument Microscopy MicroscopicDocument9 pagesMicroscope: Greek Instrument Microscopy MicroscopicBrian Lester Llanos DeeNo ratings yet
- Radio Club G5RV Presentation 002Document25 pagesRadio Club G5RV Presentation 002golf1rvdNo ratings yet
- The DC Fast Charging Architecture For Implementing Vehicle-To-Grid Technology Within A Micro-GridDocument7 pagesThe DC Fast Charging Architecture For Implementing Vehicle-To-Grid Technology Within A Micro-GridIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Prof. Devang A Patel Mechanism Engineering Department SVIT VasadDocument24 pagesProf. Devang A Patel Mechanism Engineering Department SVIT VasadPavan Gandhi100% (1)
- Intellibox Basic Manual65060-01eDocument68 pagesIntellibox Basic Manual65060-01eΝίκος ΜπούλιαρηςNo ratings yet
- Smart Cities: A Review On Electric Vehicles: Technologies and ChallengesDocument33 pagesSmart Cities: A Review On Electric Vehicles: Technologies and ChallengesAhmad RabayaNo ratings yet
- Table of Contents Microscope ManualDocument39 pagesTable of Contents Microscope ManualAgus Salim DarmaNo ratings yet
- Tool Makers Microscope PPT - Siddhant SinghDocument15 pagesTool Makers Microscope PPT - Siddhant SinghSiddhant Singh100% (1)
- D STAR System IntroductionDocument6 pagesD STAR System IntroductionRu RickjamesNo ratings yet
- Quansheng Uv k5 Two Way RadioDocument12 pagesQuansheng Uv k5 Two Way Radioairbus75No ratings yet
- Inverted microscope for cell culture observationDocument7 pagesInverted microscope for cell culture observationRudra MouryaNo ratings yet
- Work Sharp Tool Sharpener WS2000Document31 pagesWork Sharp Tool Sharpener WS2000ottuserNo ratings yet
- What Is A Phase Contrast Microscope?Document10 pagesWhat Is A Phase Contrast Microscope?Alejandra NuñezNo ratings yet
- Ferrite Rod AntennaDocument15 pagesFerrite Rod AntennaRohan BharatiNo ratings yet
- Workshop Manual: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument82 pagesWorkshop Manual: Department of Mechanical Engineeringdoggie on streetNo ratings yet
- Vector Magnetic Potential of a Small Loop AntennaDocument12 pagesVector Magnetic Potential of a Small Loop Antennaalkesh.eng100% (1)
- C9 - GrindingDocument7 pagesC9 - GrindingHans PinonNo ratings yet
- Direct Sampling Software Define RadioDocument20 pagesDirect Sampling Software Define RadioGlen P YeldhoNo ratings yet
- Just Like Clockwork: A Clock Project ReportDocument8 pagesJust Like Clockwork: A Clock Project Reportapi-421395581No ratings yet
- AFIADORA DE BROCAS - Manual de InstruçãoDocument8 pagesAFIADORA DE BROCAS - Manual de InstruçãolccortesNo ratings yet
- Fresnel's BiprismDocument6 pagesFresnel's Biprismprateekjain010% (1)
- Engraving Tools Catalog: Quality Cutting Tools and Resharpening Service For The Engraving and Sign Making IndustriesDocument8 pagesEngraving Tools Catalog: Quality Cutting Tools and Resharpening Service For The Engraving and Sign Making IndustriesCristian FuentesNo ratings yet
- Lathe Alignment: by Tubal CainDocument7 pagesLathe Alignment: by Tubal CainmarkschooleyNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsDocument96 pagesElectronicsAnjan SenguptaNo ratings yet
- TOOL MAKING-Bench Work-Practical. Reference Notes For Engineers.Document84 pagesTOOL MAKING-Bench Work-Practical. Reference Notes For Engineers.Kamatar PbkamatarNo ratings yet
- Triangle Multi Drill HolderDocument43 pagesTriangle Multi Drill HolderSendhilNathan100% (1)
- Radar 2009 A - 9 Antennas 2Document70 pagesRadar 2009 A - 9 Antennas 2Sudhanshu VermaNo ratings yet
- Pc. Tap and Die Set: Operator'S ManualDocument8 pagesPc. Tap and Die Set: Operator'S Manualvirk_70No ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Nano AntennaDocument163 pagesAnalysis and Design of Nano AntennaSaidatul NorlyanaNo ratings yet
- Microscope: Eyepiece LensDocument16 pagesMicroscope: Eyepiece LensAireen Emada AsibNo ratings yet
- Gun Drill Sharpening Fixture - LIT-079Document2 pagesGun Drill Sharpening Fixture - LIT-079Ron Biggs100% (1)
- Analysis of a Thin Wire Circular Loop AntennaDocument11 pagesAnalysis of a Thin Wire Circular Loop AntennaSon Nguyen100% (1)
- Indexing and Dividing Head OperationsDocument55 pagesIndexing and Dividing Head OperationsShrinivas BhatNo ratings yet
- Solaredge Monitoring Portal User GuideDocument23 pagesSolaredge Monitoring Portal User GuidethegoodpatriotNo ratings yet
- GEARS FUNdaMENTALS of Design Topic 6 PDFDocument62 pagesGEARS FUNdaMENTALS of Design Topic 6 PDFCristina Andreea CrissyNo ratings yet
- Stacking Tool InstructionsDocument8 pagesStacking Tool InstructionsSonia SantamaríaNo ratings yet
- Laser MetrologyDocument41 pagesLaser MetrologyjennybunnyomgNo ratings yet
- Form Measurement GuideDocument68 pagesForm Measurement GuideRama SamyNo ratings yet
- Ham Radio NewsDocument22 pagesHam Radio NewsMorocotoedNo ratings yet
- 90-1 Rotary Table GuideDocument5 pages90-1 Rotary Table GuidehdquanNo ratings yet
- AO 820 Microtome PDFDocument8 pagesAO 820 Microtome PDFalmutazimNo ratings yet
- NL Maritime News 31-May-13Document5 pagesNL Maritime News 31-May-13vu2jabNo ratings yet
- NanoVNA-F V2 Quick Start Guide - For Firmware v0.1.0Document1 pageNanoVNA-F V2 Quick Start Guide - For Firmware v0.1.0Sasha PkhidenkoNo ratings yet
- Energybus Technical IntroductionDocument5 pagesEnergybus Technical Introductionhector acuñaNo ratings yet
- Design of Dual Reflector Cassegrain Feed System AntennaDocument4 pagesDesign of Dual Reflector Cassegrain Feed System Antennaseventhsensegroup100% (1)
- 1.tool Makers MicroscopeDocument7 pages1.tool Makers MicroscopeelavarasanNo ratings yet
- Measure Micrometers AccuratelyDocument10 pagesMeasure Micrometers AccuratelyBhargav DindukurthiNo ratings yet
- ScrewDocument20 pagesScrewIxora MyNo ratings yet
- Final DSY SUMER 21 TIME TABLEDocument1 pageFinal DSY SUMER 21 TIME TABLEAnand BabuNo ratings yet
- Dsy Iv Sem Load CalculationsDocument3 pagesDsy Iv Sem Load CalculationsAnand BabuNo ratings yet
- Tamer Samir Mahmoud Abdul Majeed - 2 - Introduction To CNC PDFDocument35 pagesTamer Samir Mahmoud Abdul Majeed - 2 - Introduction To CNC PDFdsathiyaNo ratings yet
- Study of Reduction Behaviour of Iron Ore Lumps A: BINAYAK MOHAPATRA (10504004) DHARANIDHAR PATRA (10504021)Document38 pagesStudy of Reduction Behaviour of Iron Ore Lumps A: BINAYAK MOHAPATRA (10504004) DHARANIDHAR PATRA (10504021)Anand BabuNo ratings yet
- Dsy M.tech Sumer 21 Time TableDocument1 pageDsy M.tech Sumer 21 Time TableAnand BabuNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledAnand BabuNo ratings yet
- Final M.TECH SUMER 21 TIME TABLEDocument1 pageFinal M.TECH SUMER 21 TIME TABLEAnand BabuNo ratings yet
- Wire EDM: Dielectric Liquid VoltageDocument12 pagesWire EDM: Dielectric Liquid VoltageAnand BabuNo ratings yet
- NodeDocument2 pagesNodeAnand BabuNo ratings yet
- Some Important Terms:: Isometric Axes, Lines and PlanesDocument10 pagesSome Important Terms:: Isometric Axes, Lines and PlanesAnand BabuNo ratings yet
- Thread MeasurementDocument5 pagesThread MeasurementAnand BabuNo ratings yet
- Metro Logy Lab ExperimentDocument1 pageMetro Logy Lab ExperimentAnand BabuNo ratings yet
- Rollers and Slip GaugesDocument6 pagesRollers and Slip GaugesAnand Babu50% (2)
- Profile ProjectorDocument6 pagesProfile ProjectorAnand Babu100% (1)
- Machine Tool TestingDocument9 pagesMachine Tool TestingAnand Babu70% (10)
- Measurement of Surface FinishDocument6 pagesMeasurement of Surface FinishAnand Babu100% (5)
- Gear MeasurementDocument5 pagesGear MeasurementAnand Babu100% (1)
- Study of Linear Measuring Instruments: Qis College of Engg. & Tech.:Ongole, A.P. Metrology LabDocument9 pagesStudy of Linear Measuring Instruments: Qis College of Engg. & Tech.:Ongole, A.P. Metrology LabAnand BabuNo ratings yet
- Metrology Lab ManualDocument1 pageMetrology Lab ManualAnand BabuNo ratings yet
- Work Power Energy JEE TestDocument6 pagesWork Power Energy JEE TestAman RolandNo ratings yet
- B 2000 (Ovsyannikov) Plasma DiagnosticsDocument590 pagesB 2000 (Ovsyannikov) Plasma Diagnosticsutente489133No ratings yet
- AC/A and CA/C ratiosDocument9 pagesAC/A and CA/C ratiosSesilia SekarbumiNo ratings yet
- RS Sensors CharacteristicsDocument24 pagesRS Sensors CharacteristicsKushana SaikirannNo ratings yet
- Optical Signal Distortion in FibersDocument48 pagesOptical Signal Distortion in FibersRoshan JayswalNo ratings yet
- 6.3 Gravitational Potential Energy and Gravitational PotentialDocument27 pages6.3 Gravitational Potential Energy and Gravitational PotentialSahra FadillahNo ratings yet
- Refractive ErrorsDocument15 pagesRefractive ErrorsMubasher 783No ratings yet
- Gauss's Law Explained in 24 Quick QuizzesDocument13 pagesGauss's Law Explained in 24 Quick QuizzesAr Yan100% (1)
- Visual AcuityDocument21 pagesVisual AcuityLynCapiliNo ratings yet
- Foundationsofphysics PDFDocument745 pagesFoundationsofphysics PDFBurnerTempBoiNo ratings yet
- 01 LL VoDocument47 pages01 LL VoHassanImranNo ratings yet
- Week 8Document11 pagesWeek 8yawahabNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS 71 - REVIEWERDocument33 pagesPHYSICS 71 - REVIEWERMarc Justin VergaraNo ratings yet
- Xenon Emerald 2.8 28 LDocument3 pagesXenon Emerald 2.8 28 LIlarion MogaNo ratings yet
- Radiative Heat Transfer: DR Ankit BansalDocument20 pagesRadiative Heat Transfer: DR Ankit Bansalvinay MurakambattuNo ratings yet
- PHY130 Exam#2 StudyGuideDocument2 pagesPHY130 Exam#2 StudyGuideSagar GogiaNo ratings yet
- Macro: Observations From Macro To MicroDocument4 pagesMacro: Observations From Macro To MicroClaudio DamascenoNo ratings yet
- XploRA One BrochureDocument2 pagesXploRA One Brochurejona_spNo ratings yet
- UNITED STATES PHYSICS TEAM AAPT Exam1-2014-2-2-SolutionsDocument24 pagesUNITED STATES PHYSICS TEAM AAPT Exam1-2014-2-2-SolutionsSaurabh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Light Refraction and Lenses (Autosaved)Document25 pagesLight Refraction and Lenses (Autosaved)fredNo ratings yet
- Sci W3 M3 PPT LightDocument23 pagesSci W3 M3 PPT LightJanice CrenciaNo ratings yet
- ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY - Two Mark Questions and AnswersDocument12 pagesELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY - Two Mark Questions and AnswersRavi Kannappan80% (5)
- Electromagnetic RadiationDocument5 pagesElectromagnetic Radiationprateek_goyal2091No ratings yet
- DPP 2 Motion in A Straight Line PDFDocument25 pagesDPP 2 Motion in A Straight Line PDFJoy Jonathan100% (1)
- Ghosh 1999Document8 pagesGhosh 1999rasyarifahNo ratings yet
- A Novel Technique For Measuring The Pulsewidth of Nanosecond Laser PulsesDocument4 pagesA Novel Technique For Measuring The Pulsewidth of Nanosecond Laser PulsesGindra WinaldiNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Shadows and Mirror ImagesDocument14 pagesThe Difference Between Shadows and Mirror ImagesDumalay Dcm Stella MarisNo ratings yet
- DPSS Laser Active ControlDocument5 pagesDPSS Laser Active Controlizham12No ratings yet
- Testbank Chapter13Document12 pagesTestbank Chapter13Doom RefugeNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 02Document3 pagesWorksheet 02Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet