Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Foundation and Its Role
Uploaded by
Sneha AnbalaganOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Foundation and Its Role
Uploaded by
Sneha AnbalaganCopyright:
Available Formats
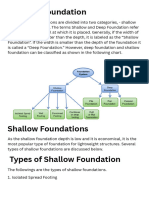
UNIT 5 DESIGN OF FOUNDATIONS 1. What is foundation and its role?
? The lowest artificially prepared parts of the structures which are in direct contact with the ground is known as foundation or substructure. Its role is to transmit the loads of the structures to the ground. The soil ground on which the foundations rest is called the foundation bed or foundation soil and it ultimately bears the load and interacts with the foundations of buildings. The lowermost portion of the foundation which is in direct contact with the sub-soil is called the footing. 2. Define bearing capacity of soil? Bearing capacity is the capacity of soil to support the loads applied to the ground. The bearing capacity of soil is the maximum average contact pressure between the foundation and the soil which should not produce shear failure in the soil. Ultimate bearing capacity is the theoretical maximum pressure which can be supported without failure; Allowable bearing capacity is the ultimate bearing capacity divided by a factor of safety. Sometimes, on soft soil sites, large settlements may occur under loaded foundations without actual shear failure occurring; in such cases, the allowable bearing capacity is based on the maximum allowable settlement. There are three modes of failure that limit bearing capacity: they include
general shear failure, local shear failure, punching shear failure. 3. Under what situation pile foundation is preferred? They are preferred in case soft/silty/clayey type of soils. As in such case of soils going for normal foundations may not be possible either from economical point of view or may not be possible at all in case we want to construct near seashore etc., these are the foundations which transfer load to greater depths, where there is strong strata / load reaching that point is minimal.
4. What is pile and pile cap? PILE:
Pile is a type of foundation, used in case soft/silty/clayey type of soils. which transfer load to greater depths, where there is strong strata / load reaching that point is minimal. These are pipe shaped, different types of pile foundations exist.
PILE CAP: A pile cap is a thick concrete mat that rests on concrete or timber piles that have been driven into soft or unstable ground to provide a suitable stable foundation. It usually forms part of the foundation of a building, typically a multi-storey building, structure or support base for heavy equipment. (OR) pile cap is a reinforced or mass concrete connecting beam cast around the head of a group of piles enabling it to act as a single unit to support the imposed load 5. Functions of pile cap. To distribute a single load equally over the pile group and thus over a greater area of bearing potential, To laterally stabilise individual piles thus increasing overall stability of the group. And To provide the necessary combined resistance to stresses set up by the superstructure and/or ground movement.
Pile caps are thick slabs used to tie a group of piles together to support and transmit column loads to the piles.
6. Different types of foundation. The following are types of reinforced concrete foundations, the particular type being chosen depending on the magnitude and disposition of the structural loads, and the bearing capacity of the ground.
a) Individual Footings: Individual footing are generally square and support a central column. Rectangular footings can be used when the space is restricted in one direction.
Individual footings of circular and other
shapes can also be used. b) Combined Footings: Combined footings become necessary where the external columns of the structure are close to the boundry of an existing structure and also where the footings of individual columns overlap one another. Such foundations (supporting more than one column/pedestal or a continuous wall) shall be proportioned to resist the design loads and individual reactions, in accordance with appropriate design requirements.
c) Raft foundation: This is where you have concrete spread around your building from the base of foundation all through to the german floor/oversite
concrete/ground floor slab. It is mainly used in areas where the soil are sandy and loose, you spend more on this than the other previous two most of the time. It is also recommended in waterlogged areas but with buildings of less storeys It has a ground beam which shuts out from the foundation base and is also attached to the ground floor slab to form a network of concrete embedded round the building space. The ground beam are usually from 600mm to 1200mm for low buildings.
d) Strip foundation: This is the most common type, it is mainly used where you have strong soil base and non-waterlogged areas. Most small buildings of just a floor are constructed with this type of foundation . The depth of the foundation could be from 600mm to 1200mm mostly for small scale buildings . When the soil is excavated, a level at which the concrete will settle evenly is established, then concrete is poured this may be from 150mm(6) thick to 450mm(18) thick depending also on building after that block is set round the trenches at the center of foundation ,the foundation usually follows the block lines. The blocks are then layed to d.p.c level before another concrete is poured on top, this is the german or oversite concrete. This type seems to be the cheapest.
e) Pile foundation: The most expensive and the strongest type of foundation, this requires specialist engineering to do. The soil are bored deep down the earth and filled with concrete to be able to support loads of multistory building on top. Most skyscrapers are constructed with this foundation type, a waterlogged area of high building may also require this. It is the costliest hence it is used for high rise building mostly.
7 . What is pile cut-off level? The "cut-off level" is the measurement at which the piles are cut to make them all of even height.
You might also like
- Aircraft Gas Turbine Tecnology by IRWINE TREAGER PDFDocument684 pagesAircraft Gas Turbine Tecnology by IRWINE TREAGER PDFJai Deep87% (67)
- Hollywood Game Plan 20 Page Sample PDFDocument20 pagesHollywood Game Plan 20 Page Sample PDFMichael Wiese Productions0% (1)
- 021SAACK Burner Operating Instructions PDFDocument136 pages021SAACK Burner Operating Instructions PDFmekidmu tadesse100% (1)
- American Woodworker No 171 April-May 2014Document76 pagesAmerican Woodworker No 171 April-May 2014Darius White75% (4)
- SMChap 018Document32 pagesSMChap 018testbank100% (8)
- FoundationDocument34 pagesFoundationEdmund ChuiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 22 PDFDocument5 pagesAssignment 22 PDFsayan mukherjeeNo ratings yet
- ADVANCED RC DESIGN AND PRESTRESSED CONCRETE STRUCTURESDocument195 pagesADVANCED RC DESIGN AND PRESTRESSED CONCRETE STRUCTURESJaya RamNo ratings yet
- BWT Septron Line 31-61 Rev01!08!05-18 Opm enDocument56 pagesBWT Septron Line 31-61 Rev01!08!05-18 Opm enDavide Grioni100% (1)
- Research of William Wells at HarvardDocument10 pagesResearch of William Wells at HarvardARGHA MANNANo ratings yet
- Effects of War On EconomyDocument7 pagesEffects of War On Economyapi-3721555100% (1)
- CH 4 FoundationDocument43 pagesCH 4 FoundationEyoatem Teferi100% (1)
- FoundationDocument53 pagesFoundationLorence OmbaoNo ratings yet
- Isolated FootingDocument12 pagesIsolated FootingSyed AzmathNo ratings yet
- Concept PaperDocument4 pagesConcept PaperAbigail67% (3)
- Essay About Reinforced Concrete Design: Rizal Technological UniversityDocument6 pagesEssay About Reinforced Concrete Design: Rizal Technological UniversityEjay EmpleoNo ratings yet
- SOIL SCIENCE FUNDAMENTALSDocument13 pagesSOIL SCIENCE FUNDAMENTALSXDXDXDNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument40 pagesResearch PaperSalauddinAnsariNo ratings yet
- Structural Framing SystemDocument20 pagesStructural Framing SystemOdee EbitaNo ratings yet
- Eccentricconnectionsinsteelstructure 151210011806Document33 pagesEccentricconnectionsinsteelstructure 151210011806Manjunath TontanalNo ratings yet
- Introduction in Steel DesignDocument18 pagesIntroduction in Steel DesignJade Carillo100% (1)
- Types of FoundationDocument28 pagesTypes of FoundationraniepaulNo ratings yet
- Staircase Design and Load DistributionDocument9 pagesStaircase Design and Load DistributionRuzengulalebih ZEta's-ListikNo ratings yet
- Structural Engineer Role & RequirementsDocument4 pagesStructural Engineer Role & RequirementsDikshit GoelNo ratings yet
- Design in Reinforced Concrete: Prepared By: M.N.M Azeem Iqrah B.SC - Eng (Hons), C&G (Gdip)Document66 pagesDesign in Reinforced Concrete: Prepared By: M.N.M Azeem Iqrah B.SC - Eng (Hons), C&G (Gdip)rashmiNo ratings yet
- Seatwork 1 Types of Structures & Loads PDFDocument6 pagesSeatwork 1 Types of Structures & Loads PDFhhhhNo ratings yet
- Chapter (4 Retaining Wall)Document28 pagesChapter (4 Retaining Wall)Henok YalewNo ratings yet
- STAAD - Pro Notes 1Document11 pagesSTAAD - Pro Notes 1Tashi DorjeNo ratings yet
- Joint DesignDocument44 pagesJoint DesignMuhammad ImranNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2-Flexural Analysis of BeamsDocument15 pagesLesson 2-Flexural Analysis of Beamsnelson christopher servidaNo ratings yet
- Embankment ConstructionDocument25 pagesEmbankment ConstructionVikalp AwasthiNo ratings yet
- Failure of Short Columns Case Study PrepDocument17 pagesFailure of Short Columns Case Study PrepAsdar AzisNo ratings yet
- Floor SystemDocument14 pagesFloor SystemCJ Ong100% (1)
- Synopses of LecturesDocument9 pagesSynopses of LecturesadasdNo ratings yet
- 14 - (Columns) Design of Sections of Columns (2016)Document79 pages14 - (Columns) Design of Sections of Columns (2016)Nadeem HassoonNo ratings yet
- Normal and Tangential Components of AccelerationDocument8 pagesNormal and Tangential Components of AccelerationihtishamqabidNo ratings yet
- Design of Deck For COMPLEX Concrete BridgeDocument75 pagesDesign of Deck For COMPLEX Concrete BridgeJunaid AminNo ratings yet
- Steel vs. Concrete MaterialDocument3 pagesSteel vs. Concrete MaterialGerald YasonNo ratings yet
- Steel DOS 1Document107 pagesSteel DOS 1MazharYasinNo ratings yet
- Design of Concrete Beam StructuresDocument26 pagesDesign of Concrete Beam StructuresVRKVRK10No ratings yet
- What Are Different Types of FootingsDocument4 pagesWhat Are Different Types of FootingsSonamTiwariNo ratings yet
- KIOT Building Construction LectureDocument26 pagesKIOT Building Construction Lecturebini1221No ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics I.handoutDocument114 pagesSoil Mechanics I.handoutZeleke Taimu100% (1)
- Prestressed IntroductionDocument39 pagesPrestressed IntroductionAndri Azhari WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- Moment Distribution Method: BY Dr. Mahdi DamghaniDocument39 pagesMoment Distribution Method: BY Dr. Mahdi DamghaniallahmahdialiNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Slabs Design GuideDocument282 pagesReinforced Concrete Slabs Design GuideEVER GUZMAN BALCASNo ratings yet
- Construction Material and Methods in AfghanDocument54 pagesConstruction Material and Methods in AfghanVictor394100% (1)
- Unit-I - Limit State Method Concept and Design of Beams: 1. MaterialsDocument7 pagesUnit-I - Limit State Method Concept and Design of Beams: 1. MaterialsYAZHININo ratings yet
- Aspects of Connection in Steel FramesDocument50 pagesAspects of Connection in Steel FramesChai Weng100% (2)
- Slab DesignDocument53 pagesSlab DesignRhyckayen AENo ratings yet
- Industrial Building Design FactorsDocument59 pagesIndustrial Building Design FactorsPhuong ThaoNo ratings yet
- 3-Bearing Pressure and Bearing CapacityDocument62 pages3-Bearing Pressure and Bearing CapacityAli Arat100% (1)
- Earthworks in Buildings PDFDocument21 pagesEarthworks in Buildings PDFCristel BurayagNo ratings yet
- MECHANICS OF MATERIALS: BUCKLING AND COLUMN STABILITYDocument51 pagesMECHANICS OF MATERIALS: BUCKLING AND COLUMN STABILITYtyo13No ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Steel and Concrete ConstructionDocument5 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Steel and Concrete Constructionmjrobust05No ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Design Lecture OverviewDocument22 pagesReinforced Concrete Design Lecture OverviewGreg LoncaricNo ratings yet
- CV332-Lecture - 4 (Soil Shear Strength)Document17 pagesCV332-Lecture - 4 (Soil Shear Strength)Muhammad Umar Tariq100% (1)
- RC-SEODocument200 pagesRC-SEOMeverlyn RoqueroNo ratings yet
- Floor Systems in Multistory BuildingsDocument25 pagesFloor Systems in Multistory Buildingsمحمد. إخوانNo ratings yet
- Basics of Civil Engineering Cv0121 Unit 3 1Document139 pagesBasics of Civil Engineering Cv0121 Unit 3 1Hanish Manikanta100% (1)
- Chapter 7 BoltDocument38 pagesChapter 7 BoltRamesh P KoiralaNo ratings yet
- Ce 132 - Geotechnical Engineering 2: Mindanao State University Fatima, General Santos City PhilippinesDocument28 pagesCe 132 - Geotechnical Engineering 2: Mindanao State University Fatima, General Santos City PhilippinesAngelica Curambao100% (1)
- Design of Concrete Structures - I Question PaperDocument3 pagesDesign of Concrete Structures - I Question PaperSourav Sil50% (2)
- FOUNDATIONDocument40 pagesFOUNDATIONOl MackNo ratings yet
- BCE Lecture 9Document11 pagesBCE Lecture 9MurgaNo ratings yet
- Types of FoundationDocument16 pagesTypes of Foundationbgsy76fgy6No ratings yet
- Types of Foundation and Their UsesDocument3 pagesTypes of Foundation and Their UsessherrysherryNo ratings yet
- Robin Engine EH722 DS 7010Document29 pagesRobin Engine EH722 DS 7010yewlimNo ratings yet
- Country Profile - NigerDocument1 pageCountry Profile - Nigernana kayNo ratings yet
- Putri KartikaDocument17 pagesPutri KartikaRamotSilabanNo ratings yet
- Roll Covering Letter LathiaDocument6 pagesRoll Covering Letter LathiaPankaj PandeyNo ratings yet
- Type of PoemDocument10 pagesType of PoemYovita SpookieNo ratings yet
- Diferencias Gas LP y Gas Natural: Adminigas, S.A. de C.VDocument2 pagesDiferencias Gas LP y Gas Natural: Adminigas, S.A. de C.VMarco Antonio Zelada HurtadoNo ratings yet
- Network Theory - BASICS - : By: Mr. Vinod SalunkheDocument17 pagesNetwork Theory - BASICS - : By: Mr. Vinod Salunkhevinod SALUNKHENo ratings yet
- Fuather, That Smid Govern-: Such Time As It May Deem Proper: TeDocument18 pagesFuather, That Smid Govern-: Such Time As It May Deem Proper: Tencwazzy100% (1)
- Expose Anglais TelephoneDocument6 pagesExpose Anglais TelephoneAlexis SoméNo ratings yet
- PSAII Final EXAMDocument15 pagesPSAII Final EXAMdaveadeNo ratings yet
- Issue 189Document38 pagesIssue 189Oncampus.net100% (1)
- Edexcel A2 Biology 6BI06Document7 pagesEdexcel A2 Biology 6BI06abhayNo ratings yet
- Ericsson 3G Chapter 5 (Service Integrity) - WCDMA RAN OptDocument61 pagesEricsson 3G Chapter 5 (Service Integrity) - WCDMA RAN OptMehmet Can KahramanNo ratings yet
- Galley cleaning hazards and controlsDocument9 pagesGalley cleaning hazards and controlsRosalie RosalesNo ratings yet
- Audi A3 Quick Reference Guide: Adjusting Front SeatsDocument4 pagesAudi A3 Quick Reference Guide: Adjusting Front SeatsgordonjairoNo ratings yet
- OV2640DSDocument43 pagesOV2640DSLuis Alberto MNo ratings yet
- An RNA Vaccine Drives Expansion and Efficacy of claudin-CAR-T Cells Against Solid TumorsDocument9 pagesAn RNA Vaccine Drives Expansion and Efficacy of claudin-CAR-T Cells Against Solid TumorsYusuf DemirNo ratings yet
- Plants Life Cycles and PartsDocument5 pagesPlants Life Cycles and PartsseemaNo ratings yet
- MMH Dan StoringDocument13 pagesMMH Dan Storingfilza100% (1)
- Rev F AvantaPure Logix 268 Owners Manual 3-31-09Document46 pagesRev F AvantaPure Logix 268 Owners Manual 3-31-09intermountainwaterNo ratings yet
- Module 2 What It Means To Be AI FirstDocument85 pagesModule 2 What It Means To Be AI FirstSantiago Ariel Bustos YagueNo ratings yet
- What Is Chemical EngineeringDocument4 pagesWhat Is Chemical EngineeringgersonNo ratings yet