Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sample of Rapid Development Methods Exam (Dec 2009) - UK University BSC Final Year
Uploaded by
TDiscoverOriginal Title
Copyright
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Sample of Rapid Development Methods Exam (Dec 2009) - UK University BSC Final Year
Uploaded by
TDiscoverCopyright:
EXAMINATION PAPER:
ACADEMIC SESSION 2009/2010
Campus School Department Level TITLE OF PAPER COURSE CODE Date and Time BAHRAIN GREECE KENYA MALAYSIA MALAWI MYANMAR SAUDI ARABIA SRI LANKA SYRIA TRINIDAD ZAMBIA VIETNAM
Maritime Greenwich Computing and Mathematical Sciences Information System and Multimedia Three Rapid Development Methods COMP1487 Wednesday 2nd Dec 2009 (2 hours) 15:00 15:00 16:00 18:30 14:00 15:30 16:00 18:30 14:00 09:30 15:00 17:30 BOTSWANA HONG KONG LONDON MALTA MAURITIUS RWANDA SINGAPORE SOUTH AFRICA TANZANIA UAE BANGLADESH 15:00 18:30 13:00 14:00 18:00 14:00 17:30 15:00 16:00 17:00 18:30
You MUST answer question 1 which is worth 40 marks Answer TWO questions from the remaining THREE questions, questions 2 to 4 which are worth 30 marks each. If you answer all THREE questions from questions 2 to 4, marks will ONLY be awarded for your TWO best answers. CALCULATORS AND ELECTRONIC DEVICES ARE NOT PERMITTED
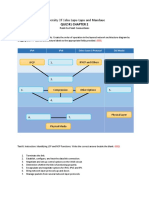
FINAL SECTION A COMPULSORY 1. It is claimed that DSDM, which provides a complete framework for building and maintaining RAD systems, is now the de facto standard for RAD projects in the UK. (Stapleton, 2003).
a) Critically discuss the DSDM philosophy and rationale, identifying and explaining the main principles on which it is based.
[30 marks] b) Why is the implementation phase of the DSDM framework iterative? [10 marks]
Rapid Development Methods COMP1487 Page 2 of 3
FINAL SECTION B Answer any TWO questions 2. a) Identify the four core techniques that are defined in the DSDM framework and describe each one. [15 marks] b) For the techniques that you identified in part a) identify how and where these techniques are used in the DSDM framework and critically evaluate the benefits of using each technique. [15 marks]
3. Clearly identify and explain the following roles and responsibilities of personnel within a DSDM project. a) b) c) d) Project Manager Technical co-ordinator Scribe [5 marks] Developer & Senior Developer [10 marks] [10 marks]
[5 marks]
4. The DSDM principle that active user involvement is imperative means that Facilitated Workshops, sometimes called Joint Application Developments (JAD), are used a great deal. The DSDM Consortium (2003) considers that the definition, preparation, execution and reporting of a facilitated workshop can be viewed as a sub-process within an overall project and stresses the importance of their use in almost all stages of the framework. a) Clearly identify the different types of Facilitated Workshops that can be used to good effect and show where within the framework they would be used? [20 marks] b) Explain briefly the purpose and the expected outcome of each workshop you identified in part a). [10 marks] Rapid Development Methods COMP1487 Page 3 of 3
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Sample of Rapid Development Methods Exam (June 2010) - UK University BSC Final YearDocument3 pagesSample of Rapid Development Methods Exam (June 2010) - UK University BSC Final YearTDiscoverNo ratings yet
- Urgent Animal Welfare CrisisDocument4 pagesUrgent Animal Welfare CrisisTDiscoverNo ratings yet
- Sample of Object Oriented Software Development Exam (June 2009) - UK University BSC Final YearDocument6 pagesSample of Object Oriented Software Development Exam (June 2009) - UK University BSC Final YearTDiscoverNo ratings yet
- Sample of Object Oriented Software Development Exam (Dec 2007) - UK University BSC Final YearDocument7 pagesSample of Object Oriented Software Development Exam (Dec 2007) - UK University BSC Final YearTDiscoverNo ratings yet
- COMP1487 December 2008Document3 pagesCOMP1487 December 2008Doggysperms DoggyspermNo ratings yet
- Sample of Object Oriented Software Development Exam (June 2007) - UK University BSC Final YearDocument8 pagesSample of Object Oriented Software Development Exam (June 2007) - UK University BSC Final YearTDiscoverNo ratings yet
- Sample of Object Oriented Software Development Exam (June 2010) - UK University BSC Final YearDocument4 pagesSample of Object Oriented Software Development Exam (June 2010) - UK University BSC Final YearTDiscoverNo ratings yet
- Sample of Rapid Development Methods Exam (June 2009) - UK University BSC Final YearDocument4 pagesSample of Rapid Development Methods Exam (June 2009) - UK University BSC Final YearTDiscoverNo ratings yet
- Sample of Object Oriented Software Development Exam (Dec 2010) - UK University BSC Final YearDocument6 pagesSample of Object Oriented Software Development Exam (Dec 2010) - UK University BSC Final YearTDiscoverNo ratings yet
- Sample of Object Oriented Software Development Exam (Dec 2009) - UK University BSC Final YearDocument6 pagesSample of Object Oriented Software Development Exam (Dec 2009) - UK University BSC Final YearTDiscoverNo ratings yet
- Sample of Object Oriented Software Development Exam (2007/2008) - UK University BSC Final YearDocument14 pagesSample of Object Oriented Software Development Exam (2007/2008) - UK University BSC Final YearTDiscoverNo ratings yet
- Sample of Object Oriented Software Development Exam (Dec 2008) - UK University BSC Final YearDocument6 pagesSample of Object Oriented Software Development Exam (Dec 2008) - UK University BSC Final YearTDiscoverNo ratings yet
- Web Engineering Exam June 2010 - UK University BSC Final YearDocument4 pagesWeb Engineering Exam June 2010 - UK University BSC Final YearTDiscoverNo ratings yet
- Web Engineering Exam December 2010 - UK University BSC Final YearDocument3 pagesWeb Engineering Exam December 2010 - UK University BSC Final YearTDiscoverNo ratings yet
- Sample of Web Engineering Exam (Dec 2008) - UK University BSC Final YearDocument6 pagesSample of Web Engineering Exam (Dec 2008) - UK University BSC Final YearTDiscoverNo ratings yet
- Web Engineering Exam June 2009 - UK University BSC Final YearDocument7 pagesWeb Engineering Exam June 2009 - UK University BSC Final YearTDiscoverNo ratings yet
- Sample of Web Engineering Exam (June 2008) - UK University BSC Final YearDocument6 pagesSample of Web Engineering Exam (June 2008) - UK University BSC Final YearTDiscoverNo ratings yet
- Web Engineering Exam December 2009 - UK University BSC Final YearDocument3 pagesWeb Engineering Exam December 2009 - UK University BSC Final YearTDiscoverNo ratings yet
- Sample of Web Engineering Exam (Dec 2007) - UK University BSC Final YearDocument7 pagesSample of Web Engineering Exam (Dec 2007) - UK University BSC Final YearTDiscoverNo ratings yet
- Sample of Web Engineering Exam (May 2007) - UK University BSC Final YearDocument8 pagesSample of Web Engineering Exam (May 2007) - UK University BSC Final YearTDiscoverNo ratings yet
- Database Design and Implementation Exam December 2010 - UK University BSC Final YearDocument9 pagesDatabase Design and Implementation Exam December 2010 - UK University BSC Final YearTDiscoverNo ratings yet
- Sample of Web Engineering Exam (Dec 2006) - UK University BSC Final YearDocument9 pagesSample of Web Engineering Exam (Dec 2006) - UK University BSC Final YearTDiscoverNo ratings yet
- Database Design and Implementation Exam December 2009 - UK University BSC Final YearDocument9 pagesDatabase Design and Implementation Exam December 2009 - UK University BSC Final YearTDiscoverNo ratings yet
- Information Systems Management Exam December 2010 - UK University BSC Final YearDocument3 pagesInformation Systems Management Exam December 2010 - UK University BSC Final YearTDiscover100% (1)
- Database Design and Implementation Exam June 2010 - UK University BSC Final YearDocument10 pagesDatabase Design and Implementation Exam June 2010 - UK University BSC Final YearTDiscoverNo ratings yet
- Database Design and Implementation Exam June 2008 - UK University BSC Final YearDocument9 pagesDatabase Design and Implementation Exam June 2008 - UK University BSC Final YearTDiscoverNo ratings yet
- Information Systems Management Exam June 2010 - UK University BSC Final YearDocument3 pagesInformation Systems Management Exam June 2010 - UK University BSC Final YearTDiscoverNo ratings yet
- Database Design and Implementation Exam June 2009 - UK University BSC Final YearDocument7 pagesDatabase Design and Implementation Exam June 2009 - UK University BSC Final YearTDiscoverNo ratings yet
- Database Design and Implementation Exam December 2008 - UK University BSC Final YearDocument7 pagesDatabase Design and Implementation Exam December 2008 - UK University BSC Final YearTDiscoverNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Doli SQLDocument102 pagesDoli SQLChebbi MedNo ratings yet
- Certification Authorities Software Team (CAST) Position Paper CAST-2Document7 pagesCertification Authorities Software Team (CAST) Position Paper CAST-2VIJAYPUTRANo ratings yet
- Xappo FacuateDocument3 pagesXappo FacuateKhushboo DurkiyaNo ratings yet
- Map of Cascade Head RegionDocument1 pageMap of Cascade Head RegionStatesman JournalNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual: Digital System DesignDocument37 pagesLaboratory Manual: Digital System DesignArshad RasheedNo ratings yet
- Roles On Agile Teams: From Small To Large Teams: SearchDocument5 pagesRoles On Agile Teams: From Small To Large Teams: SearchKrishna PandeyNo ratings yet
- Frequent Itemset MiningDocument58 pagesFrequent Itemset MiningMesut ErkekliNo ratings yet
- Accounting Controls and ProcessesDocument31 pagesAccounting Controls and Processesnavie VNo ratings yet
- RBT Knowledge DimensionDocument3 pagesRBT Knowledge Dimension5cr1bdNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument11 pagesCase StudyAbinaya Sathya0% (1)
- Java Login Web Service: Part 4Document2 pagesJava Login Web Service: Part 4Lethal11100% (1)
- ReleaseNotes Freelance 2016 USDocument56 pagesReleaseNotes Freelance 2016 USradzinger065No ratings yet
- Thermal Analysis of Computer Motherboards using Digital Holographic InterferometryDocument1 pageThermal Analysis of Computer Motherboards using Digital Holographic InterferometryBoby ThomasNo ratings yet
- Raspberry Pi Guide: What is Raspberry Pi and How to Set it UpDocument18 pagesRaspberry Pi Guide: What is Raspberry Pi and How to Set it UpTrung NguyenNo ratings yet
- Excel ResearchDocument11 pagesExcel Researchjanjan eresoNo ratings yet
- Spark TuningDocument26 pagesSpark TuningajquinonespNo ratings yet
- Literature Review: Digital Payment System in IndiaDocument8 pagesLiterature Review: Digital Payment System in IndiaAkshay Thampi0% (1)
- OOP - Case StudyDocument84 pagesOOP - Case StudyEmilSNo ratings yet
- Frame Element PDFDocument7 pagesFrame Element PDFUnknow UnknowNo ratings yet
- OracleDocument103 pagesOracleanon_571993096No ratings yet
- Ccna Chapter 2 Point-To-PointDocument3 pagesCcna Chapter 2 Point-To-PointVerlin Grace CabalhugNo ratings yet
- 250 - U MarelDocument16 pages250 - U MareldicaveNo ratings yet
- 2015 Term 3 Theory Form 2Document7 pages2015 Term 3 Theory Form 2Teyemensah KubiNo ratings yet
- C If Else StatementDocument11 pagesC If Else StatementKiran KalyaniNo ratings yet
- SENTIMENT ANALYSIS ON TWEETSDocument2 pagesSENTIMENT ANALYSIS ON TWEETSvikibytesNo ratings yet
- Sap Scripts Tutorial PDFDocument89 pagesSap Scripts Tutorial PDFdamljanovic100% (2)
- 70-411 R2 Test Bank Lesson 16Document11 pages70-411 R2 Test Bank Lesson 16Mazaher MohamedaliNo ratings yet
- Ioannou Web Ch7Document63 pagesIoannou Web Ch7Yasemin BarutcuNo ratings yet
- AM TOGAF Quick Reference Charts PDFDocument21 pagesAM TOGAF Quick Reference Charts PDFKrishna Marconi100% (1)
- Using Calbr WKB 919 03252003 9430Document550 pagesUsing Calbr WKB 919 03252003 9430Aparna Tiwari100% (1)