Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Icapp
Uploaded by
Surya TejaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Icapp
Uploaded by
Surya TejaCopyright:
Available Formats
ACE
Engineering College
Ankushapur(V), Ghatkesar(M), R.R.Dist - 501 301 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING III B.Tech I Sem. (EEE)
IC APPLICATIONS
I - UNIT Assignment 1. (a) Broadly classify the integrated circuits for a wide range of applications. (b) What is a practical Op-amp? Draw its equivalent circuit. (c) In an Op-amp, V2 = 0 (inverting terminal input). What is the voltage at V1 (non-inverting terminal input) for an output of 5V if AOL = 50000. 2. (a) List various advantages of IC technology over discrete component implementation. (b) Distinguish between differential mode and common mode operations of differential amplifier. 3. (a) Explain the terms: i. CMRR. ii. PSRR. iii. Thermal drift. iv. Inverting configuration of Op-Amp. v. Input offset voltage (b) What is a voltage follower? What are its features and applications? 4. (a) Draw the circuit diagram and explain the operation of an inverting amplifier, obtain the expression for closed loop voltage gain. (b) Derive the output voltage of an Op-amp based differential amplifier. 5. (a) Obtain the frequency response of an op-amp using suitable mathematical expressions. (b) How fast can the output of an op-amp change by 10V if its slew rate is 1V / S? 6. (a) Discuss D.C. characteristics of op-amp in detail. (b) The input signal Vi to an op-amp is 0.04 Sin 1.13 X 105t is to be amplified to the maximum extent. How much maximum gain can be had by using op-amp, with slew rate of 0.4 V/Sec.
II - UNIT Assignment
1. (a) Derive the expression for the frequency of the output of an astable multivibrator. (b) Design a averaging amplifier circuit to provide a gain 5 for 4 input signals of same frequency. 2. (b) What is a sample and hold circuit? Why is it needed? With neat circuit diagram, describe the operation of an Op-amp based sample and hold circuit. (b) What do you mean by sampling? 3. (a) Draw the circuit for converting a sinusoidal ware form into a square wave and into a series of pulses, one per cycle and explain. (b) Design a subtractor in non inverting configuration. 4. (a) What is an instrumentation amplifier? What are the basic requirements of a good instrumentation amplifier.
(b) Design an instrumentation amplifier whose gain can be varied continuously over the range 1 A 1000 use 100 k potentiometer. 5. (a) Draw the circuit and explain the operation of instrumentation amplifier using transducer bridge. Derive the expression for its output voltage. (b) What are the applications of instrumentation amplifier? Explain. 6. (a) Explain how the averaging circuit can be derived from the summer. (c) Design the op-amp circuit which can give the output as V0 = 2 V1 - 3 V2 + 4V3 - 5V4 7. (a) Explain the operation of zero crossing detector using Op-amps. (b) Design a differentiator using Op-amp to differentiate an input signal that varies in frequency from 1 KHz to 10 KHz. 8. (a) Explain with a neat circuit diagram the working of voltage to current converter with floating load and grounded. (b) Design a circuit to convert a 4 mA to 20mA input current to 0V to 10V output voltage. The circuit is powered from 15V regulated supplies. (Assume necessary data)
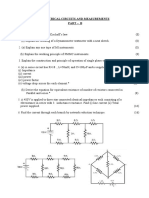
III - UNIT Assignment 1. (a) Explain the operation of RC phase shift oscillator using op-amp and derive the expression for frequency of oscillations. (b) Design the wien bridge oscillator circuit to have output frequency of 10 KHz. 2. (a) Draw the circuit diagram of a triangular wave generator using a comparator and integrator. Explain its operation by referring to the output waveform. (b) Design an RC phase shift oscillator for 300 Hz frequency using IC 741 and 15 volt power supplies. Assume necessary component values. Suggest a method to reduce the output voltage swing to 6:5 volts 3. (a) Explain the frequency responses of all types of filters. (b) Figure 1 below shows the first order Butterworth LPF that uses RC network, calculate the gain if the filter is a function of frequency. Give gain magnitude and phase angle equations. 4. (a) Draw the basic circuit of wien bridge oscillator and explain its operation. Also derive the expression for frequency of oscillation. (b) Design a second order low pass filter at a higher cut off frequency of 2KHz. 5. (a) Derive the expression for frequency of VCO and list important specifications of 566 VCO IC. (b) Define the conditions on the feedback circuit of an amplifier to convert it in to an oscillator. 6. (a) Design a I order wide band- reject having fH=200 Hz and fL =1 kHz, having the pass band gain of 2 each. Assume necessary data. (b) Draw the first order low-pass Butterworth filter and analyze the same by deriving the gain and phase angle equation. 7. (a)Write short notes on the operation of Quadrature oscillator. (b) In the figure 2 given below if the integrator components are R1=120 K and C1 = 0.01 F, R3= 6.8 K , R2= 1.2K , determine i. Peak-to-peak triangular output amplitude. ii. The frequency of triangular wave.
Figure 1
Figure 2
IV - UNIT Assignment 1. (a) Draw and explain the functional block diagram of IC 555. (b) Explain the functioning of 555 in Monostable configuration. 2. (a) Explain how astable mode of 555 can be modified to get a square wave generator. (b) Design a 555 based square wave generator to produce a symmetrical square wave of 1 KHz. If VCC = 12V. Draw the voltage across timing capacitor and the output. 3. (a) Describe the 555 timer (i) Monostable multivibrator application in Pulse Width Modulation. (ii) Astable multivibrator application in FSK generator. (b) A 555 timer is configured to run in astable mode with R1 = 20K and R2 = 8Kand C = 0.1uf. Determine the output frequency and duty cycle. 4. (a) Design an astable multivibrator using 555 timer to produce a square wave of 2 KHz frequency and 70% duty cycle. Draw the circuit with all component values. (b) Explain how a PLL is used as a frequency multiplier. 5. (a) Explain the role of the basic building blocks of PLL. (b) Determine the DC control voltage vc at lock if signal frequency fs = 10 KHz, VCO free running frequency is 10.66 KHz and the voltage to frequency transfer coefficient of VCO is 6600 Hz / V. 6. (a) Draw the schematic circuit diagram of the following and explain their working. i. Analog phase detector. ii. VCO. Derive necessary expressions. (b) What is their role in PLL? Explain. 7. (a) Describe how frequency division and multiplication can be achieved using a Phase Locked Loop. (b) Draw the circuit of a PLL AM detector and explain its operation.
IV - UNIT Assignment 1. (a) Draw and explain the functional block diagram of IC 555. (b) Explain the functioning of 555 in Monostable configuration.
2. (a) Explain how astable mode of 555 can be modified to get a square wave generator. (b) Design a 555 based square wave generator to produce a symmetrical square wave of 1 KHz. If VCC = 12V. Draw the voltage across timing capacitor and the output. 3. (a) Describe the 555 timer (i) Monostable multivibrator application in Pulse Width Modulation. (ii) Astable multivibrator application in FSK generator. (b) A 555 timer is configured to run in astable mode with R1 = 20K and R2 = 8Kand C = 0.1uf. Determine the output frequency and duty cycle. 4. (a) Design an astable multivibrator using 555 timer to produce a square wave of 2 KHz frequency and 70% duty cycle. Draw the circuit with all component values.
5. (a) Explain the role of the basic building blocks of PLL. (b) Define the following terms with reference to PLL. i. Lock range. ii. Capture range. iii. Pull-in-time.
V - UNIT Assignment 1. (a) Explain the operation of flash A/D converter. (b) Explain how dual slope A/D converter provides noise rejection. (c) If the maximum output voltage of a 7-bit D/A converter is 25.4V. What is the smallest change in the output as the binary count increases. 2. (a) What are the sources of errors in DAC? Explain. (b) The digital input for a 4-bit DAC is 0110 calculate its final output voltage. (c) Draw and explain the block diagram of IC 1408. 3. (a) Compare flash, dual slope and successive approximation register type ADCs. (b) Find out step size and analog output for 4-bit R-2R laddar DAC when input is 0100 and 1100. Assume Vref = +5V. 4. (a) Explain Functional diagram of successive approximation ADC (b) Explain counter type A/D converter. 5. (a) The basic step of a 16-bit DAC is 10.3 mV. If 0000000000000000 represents 0V, what output is produced if the input is 1101101111111111? (b) Calculate the values of the LSB, MSB and full scale output for an 32 bit DAC for the 0 to 20V. 6. Write short note on: (a) R-2R Ladder DAC
(b) inverted R-2R Ladder.
7. (a) Explain the operation of a multiplying DAC and mention its applications. (b) List out various types of D/A converter and A/D converters and compare their merits and demerits.
VI - UNIT Assignment 1. (a)Explain the following terms: (a) VOL(max) (b) VOH(min) (c) VIL(max) (d) VIH(min) (b) Explain with neat diagram interfacing of TTL gate and CMOS gates.
2. (a) Explain the classification of integrated circuits (b) Sketch TTL NAND Gate and explain its working (c) Sketch TTL NOR Gate and explain its working. 3. (a) Sketch CMOS NAND Gate and explain its working (b) Sketch CMOS NOR Gate and explain its working. 4. (a) What is a transmission gate ? Explain with the help of neat diagram. (b) Explain why two totem pole outputs can't be tied together. (c) With neat circuit explain the concept of open collector O/P with pull-up resistor. 5. (a) Design a CMOS transistor circuit that has the functional behavior F(Z) = (A + B)(B + C). (b) Explain sinking current and sourcing current of TTL output? Which of the above parameters decide the fan out and how? 6. (a) Draw the circuit of a Totem-pole TTL NAND gate ? What is the purpose of using a diode at the output stage? Explain its operation and verify the truth table. (b) When do we use open-collector TTL gate? (c) Which is the fastest logic gate and why?
VII - UNIT Assignment 1. Design and Explain 4- line to 16 line decoder with 74138. 2. (a) Design 4:1 Mux with logic diagram and symbolic representation. (b) Convert the binary numbers to gray codes using Ex- OR gates (a) 1001 (b) 11001111 (c) 10000001 (d) 10011 3. (a) Draw the logic diagram of 74x283 IC and explain the operation? (b) Write short notes on BCD to binary converter? 4. (a) Design a 3 input 5 outputt multiplexer? Write the truth table and draw the logic diagram. (b) Write short notes on full subtractor. 5. (a) Give the logic diagram of 74x147 and explain its truth table? (b) Write short notes on half subtractor? 6. (a) Design a 2-bit comparator using logic gates and draw its logic diagram (b) Explain BCD to 7-segment decoder with the help of a truth table.
VIII - UNIT Assignment
1. (a) Explain with neat sketch how four bits 1110 are serially entered into the shift register. (b) Explain with neat sketch how four bits 1110 are serially shifted out of the shift register. 2. (a) Draw the circuit diagram, function table and logic symbol of a D latch with a control signal (b) Draw and explain the working of RS and clocked RS flip flops 3. Differentiate between Asynchronous counter and synchronous counter? Design a 4-bit counter in synchronous mode 4. (a) Design and explain 4-bit parallel-in and serial-out shift register (b) Distinguish between latch and flip-flop
5. (a) Draw and explain the working of 4-bit UP/DOWN synchronous counter. (b) Write short notes on edge triggered and level triggered flip flops
You might also like
- Aprilmay 2009Document8 pagesAprilmay 2009Viswa ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- 9A04502 Linear IC ApplicationsDocument4 pages9A04502 Linear IC ApplicationssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- EDC PapersDocument3 pagesEDC Papersmandalapu91No ratings yet
- 9A04502 Linear IC ApplicationsDocument4 pages9A04502 Linear IC ApplicationssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Linear and Digital Ic ApplicatonsDocument4 pagesLinear and Digital Ic ApplicatonsViswa ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- DC Machine Theory and Transformer PrinciplesDocument32 pagesDC Machine Theory and Transformer PrinciplesPolireddi Gopala KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Module-Wise Eln QBDocument5 pagesModule-Wise Eln QBRashmi SamantNo ratings yet
- Aprilmay 2007Document7 pagesAprilmay 2007Viswa ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- BEEE Important Questions 16 MarksDocument5 pagesBEEE Important Questions 16 Marksaeroheroz25% (4)
- EdcDocument3 pagesEdcSandy RonaldoNo ratings yet
- EC6404-Linear Integrated Circuits Question BankDocument7 pagesEC6404-Linear Integrated Circuits Question BankkundaviNo ratings yet
- Graph Sheets May Be Supplied On Demand: Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesGraph Sheets May Be Supplied On Demand: Page 1 of 2sarang acNo ratings yet
- LDICA 10M QuestionsDocument2 pagesLDICA 10M Questionsdeepa reddyNo ratings yet
- Edlc May 2008Document1 pageEdlc May 2008SwapnilDashputeNo ratings yet
- Acfrogbgmnwmqv4eglpe8ygzrbxirecy6hxc7fg45hsevhgoh6wxmviowc6bl5i4dec Gj2idfp z0mw1bfxcr Kxa6nwwhmlbs1hhdnwzs-Htw5pxgkui9kgl6kd1y-Btfyixjksoz8eazqclksDocument2 pagesAcfrogbgmnwmqv4eglpe8ygzrbxirecy6hxc7fg45hsevhgoh6wxmviowc6bl5i4dec Gj2idfp z0mw1bfxcr Kxa6nwwhmlbs1hhdnwzs-Htw5pxgkui9kgl6kd1y-Btfyixjksoz8eazqclksNithiya MaharajanNo ratings yet
- LIC - Question BankDocument8 pagesLIC - Question Banksriramraghu4_6423936No ratings yet
- Jntuworld: R07 Set No. 2Document5 pagesJntuworld: R07 Set No. 2Kasarla Shiva SjNo ratings yet
- Anna University Ec2251: Electronic Circuits Ii Sem / Year: Iv/ Ii QUESTION BANK - 2012 EditionDocument9 pagesAnna University Ec2251: Electronic Circuits Ii Sem / Year: Iv/ Ii QUESTION BANK - 2012 EditionJoseph AntoNo ratings yet
- Linear Integrated Circuits and Applications Question BankDocument10 pagesLinear Integrated Circuits and Applications Question BankAyyar KandasamyNo ratings yet
- Answer Any Two Full Questions, Each Carries 15 Marks.: Reg No.: - NameDocument2 pagesAnswer Any Two Full Questions, Each Carries 15 Marks.: Reg No.: - Namesheena mNo ratings yet
- Multi-Stage Amplifiers and Feedback CircuitsDocument5 pagesMulti-Stage Amplifiers and Feedback CircuitsChandra SekharNo ratings yet
- Answer ALL QuestionsDocument2 pagesAnswer ALL QuestionsShobana SureshNo ratings yet
- LIC Important QuestionsDocument2 pagesLIC Important QuestionsRahul RNo ratings yet
- PSG College of Technology, Coimbatore - 641 004 Semester Examinations, SemesterDocument2 pagesPSG College of Technology, Coimbatore - 641 004 Semester Examinations, SemesterAravindh AadhityaNo ratings yet
- 2020 11 04SupplementaryCS207CS207 H Ktu QbankDocument3 pages2020 11 04SupplementaryCS207CS207 H Ktu QbankpittalasureshNo ratings yet
- RA 9A04402 Electronic Circuit AnalysisDocument1 pageRA 9A04402 Electronic Circuit AnalysissivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Question Bank: Unit - I Electrical Circuits and MeasurementsDocument6 pagesQuestion Bank: Unit - I Electrical Circuits and MeasurementsEthan Emmanuel ClintonNo ratings yet
- 08.304 Electronic Circuits (R F) : C (Sat)Document2 pages08.304 Electronic Circuits (R F) : C (Sat)akhilarajNo ratings yet
- Edlc Dec2007Document1 pageEdlc Dec2007SwapnilDashputeNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Que NewDocument3 pages1st Year Que Newbalusasi_skgNo ratings yet
- Anna University Microwave Question PapersDocument9 pagesAnna University Microwave Question PapersDeepak100% (2)
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document0 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Manoj DNo ratings yet
- Ect301 Linear Integrated Circuits, December 2022Document2 pagesEct301 Linear Integrated Circuits, December 2022Dinil DhananjayanNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 3Document2 pagesSample Paper 3saiganesh_49No ratings yet
- June July 2017 PDFDocument2 pagesJune July 2017 PDFmabhatNo ratings yet
- Ee 2254 Lic Int - 3Document2 pagesEe 2254 Lic Int - 3Ryan MillerNo ratings yet
- QP Eee 22 May2010 LdicaDocument6 pagesQP Eee 22 May2010 LdicaHari PrasadNo ratings yet
- EC 6404 exam questions cover op-amps, filters, convertersDocument5 pagesEC 6404 exam questions cover op-amps, filters, convertersVigneswaran VigneshNo ratings yet
- 1 Electronic Devices and Circuits - Main Jan 2017Document3 pages1 Electronic Devices and Circuits - Main Jan 2017Akash RoboticsNo ratings yet
- DC Machines and Electrical Drives Exam QuestionsDocument2 pagesDC Machines and Electrical Drives Exam QuestionsJangoNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics - 102409025108 - 1Document7 pagesPower Electronics - 102409025108 - 1Herbert DeepakNo ratings yet
- Eet205 Analog Electronics, December 2021Document3 pagesEet205 Analog Electronics, December 2021Midun RamkumarNo ratings yet
- Answer Any Two Full Questions, Each Carries 15 Marks.: Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesAnswer Any Two Full Questions, Each Carries 15 Marks.: Page 1 of 2sheena mNo ratings yet
- BEEE Important Questions 16 MarksDocument6 pagesBEEE Important Questions 16 MarkskrishnandrkNo ratings yet
- Linear IC Applications Exam QuestionsDocument2 pagesLinear IC Applications Exam Questionssaiganesh_49No ratings yet
- Electronics: June/July, 2010Document7 pagesElectronics: June/July, 2010Prasad C MNo ratings yet
- r05221002 Linear Ic ApplicationsDocument7 pagesr05221002 Linear Ic ApplicationsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- B.E./B.Tech. Degree Examinations Electronics and Communication Engineering Question PaperDocument3 pagesB.E./B.Tech. Degree Examinations Electronics and Communication Engineering Question PaperGOJAN ECENo ratings yet
- rr310404 Linear Ic ApplicationsDocument8 pagesrr310404 Linear Ic ApplicationsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Linear and Digital Ic Applications RRDocument8 pagesLinear and Digital Ic Applications RRNizam Institute of Engineering and Technology LibraryNo ratings yet
- PULSE AND DIGITAL CIRCUITS ASSIGNMENTDocument4 pagesPULSE AND DIGITAL CIRCUITS ASSIGNMENTathomeNo ratings yet
- LIC Question Bank 2021 - LevelsDocument12 pagesLIC Question Bank 2021 - LevelsPavan ParthikNo ratings yet
- Edc 7Document8 pagesEdc 729viswa12100% (1)
- B. Tech: Roll NoDocument5 pagesB. Tech: Roll NoRavindra KumarNo ratings yet
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)From EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)No ratings yet
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsFrom EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsNo ratings yet
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorFrom Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNo ratings yet
- Heterojunction Bipolar Transistors for Circuit Design: Microwave Modeling and Parameter ExtractionFrom EverandHeterojunction Bipolar Transistors for Circuit Design: Microwave Modeling and Parameter ExtractionNo ratings yet
- Discovering Knowledge in Data An Introduction To Data Mining (1 To 60)Document60 pagesDiscovering Knowledge in Data An Introduction To Data Mining (1 To 60)Surya TejaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Writing Case AnalysesDocument3 pagesGuidelines For Writing Case AnalysesSurya TejaNo ratings yet
- Profile Evaluation Technique by MSinUSDocument9 pagesProfile Evaluation Technique by MSinUSSurya TejaNo ratings yet
- Deregulated Power System: Presented byDocument21 pagesDeregulated Power System: Presented bySurya TejaNo ratings yet
- Mpu 2312Document15 pagesMpu 2312Sherly TanNo ratings yet
- Jesd8 15aDocument22 pagesJesd8 15aSridhar PonnurangamNo ratings yet
- HVAC Master Validation PlanDocument51 pagesHVAC Master Validation Plannavas197293% (30)
- 3d Control Sphere Edge and Face StudyDocument4 pages3d Control Sphere Edge and Face Studydjbroussard100% (2)
- Consumers ' Usage and Adoption of E-Pharmacy in India: Mallika SrivastavaDocument16 pagesConsumers ' Usage and Adoption of E-Pharmacy in India: Mallika SrivastavaSundaravel ElangovanNo ratings yet
- UD150L-40E Ope M501-E053GDocument164 pagesUD150L-40E Ope M501-E053GMahmoud Mady100% (3)
- Mobile ApplicationDocument2 pagesMobile Applicationdarebusi1No ratings yet
- October 2009 Centeral Aucland, Royal Forest and Bird Protecton Society NewsletterDocument8 pagesOctober 2009 Centeral Aucland, Royal Forest and Bird Protecton Society NewsletterRoyal Forest and Bird Protecton SocietyNo ratings yet
- Mounting InstructionDocument1 pageMounting InstructionAkshay GargNo ratings yet
- eHMI tool download and install guideDocument19 pageseHMI tool download and install guideNam Vũ0% (1)
- Analyze and Design Sewer and Stormwater Systems with SewerGEMSDocument18 pagesAnalyze and Design Sewer and Stormwater Systems with SewerGEMSBoni ClydeNo ratings yet
- Alternate Tuning Guide: Bill SetharesDocument96 pagesAlternate Tuning Guide: Bill SetharesPedro de CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Iphoneos 31Document159 pagesIphoneos 31Ivan VeBoNo ratings yet
- Pulse Width ModulationDocument13 pagesPulse Width Modulationhimanshu jainNo ratings yet
- Evil Days of Luckless JohnDocument5 pagesEvil Days of Luckless JohnadikressNo ratings yet
- C4 ISRchapterDocument16 pagesC4 ISRchapterSerkan KalaycıNo ratings yet
- Managerial EconomicsDocument3 pagesManagerial EconomicsGuruKPONo ratings yet
- Typical T Intersection On Rural Local Road With Left Turn LanesDocument1 pageTypical T Intersection On Rural Local Road With Left Turn Lanesahmed.almakawyNo ratings yet
- Rubric 5th GradeDocument2 pagesRubric 5th GradeAlbert SantosNo ratings yet
- Bengali (Code No - 005) COURSE Structure Class - Ix (2020 - 21Document11 pagesBengali (Code No - 005) COURSE Structure Class - Ix (2020 - 21Břîšťỹ ÃhmęđNo ratings yet
- LegoDocument30 pagesLegomzai2003No ratings yet
- Uses and Soxhlet Extraction of Apigenin From Parsley Petroselinum CrispumDocument6 pagesUses and Soxhlet Extraction of Apigenin From Parsley Petroselinum CrispumEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Kaydon Dry Gas SealDocument12 pagesKaydon Dry Gas Sealxsi666No ratings yet
- Service Manual: Precision SeriesDocument32 pagesService Manual: Precision SeriesMoises ShenteNo ratings yet
- Lab StoryDocument21 pagesLab StoryAbdul QadirNo ratings yet
- Kate Elizabeth Bokan-Smith ThesisDocument262 pagesKate Elizabeth Bokan-Smith ThesisOlyaGumenNo ratings yet
- Indian Standard: Pla Ing and Design of Drainage IN Irrigation Projects - GuidelinesDocument7 pagesIndian Standard: Pla Ing and Design of Drainage IN Irrigation Projects - GuidelinesGolak PattanaikNo ratings yet
- Inventory ControlDocument26 pagesInventory ControlhajarawNo ratings yet
- Desana Texts and ContextsDocument601 pagesDesana Texts and ContextsdavidizanagiNo ratings yet
- Uniform-Section Disk Spring AnalysisDocument10 pagesUniform-Section Disk Spring Analysischristos032No ratings yet