Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MM 11
Uploaded by
Somasekhar Chowdary KakaralaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MM 11
Uploaded by
Somasekhar Chowdary KakaralaCopyright:
Available Formats
To get more please visit: www.creativeworld9.blogspot.
com
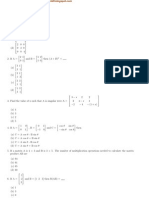
1. The matrix (a) Nilpotent (b) Skew-symmetric (c) Involutary (d) Orthogonal 2. (AB)1 = (a) B 1 A1 (b) (BA)1 (c) B 1 A1 (d) A1 B 1 3. (AB)T = (a) (A + B)T (b) AT B T (c) AT B T (d) B T AT 4. If A is a square matrix such that AAT = I then the value of AT A is (a) A (b) A2 (c) A 1 (d) I 5. If Amn and Bpq are two matrices state the conditions for the existence of AB (a) n=p (b) n<p (c) n>p (d) n = p 6. A square matrix is said to upper triangular matrix if (a) aij = 0, i = j (b) aij = 1 , i = j (c) aij = 0 , i < j (d) aij = 0 , i > j 7. If A is a zero matrix then R(A) = (a) 0 (b) 2 (c) 1 (d) 3 8. A matrix is multiplied with a non - singular matrix then the rank of the matrix is (a) remaining same (b) zero (c) order of the matrix (d) one 9. If every minor of order r of a matrix A is zero, then rank of A is (a) less than or equal to r (b) less than r (c) equal to r (d) greater than r 10. The system 2x + y + z = 0 , x + y + 3z = 0 and 4x + 3y +z = 0 has non trivial solution then (a) = 6 (b) = 6 (c) = 8 (d) = 8 11. X is a characteristic root of A if and only if there exists (a) unit vector (b) Zero vector (c) Non zero vector (d) Negative vector 0 0 12. The sum of the eigen values of A = 2 (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) 3 0 0 0 0 13. The eigen vector of the matrix 0 0 (a) ( 0, 0, 0 ) (b) ( 0, 0, k ) (c) ( k1 , k2 , k3 ) (d) ( k1 , k2 , 0 ) 14. If A and B one two non - singular matrics then the matrics AB and BA have the eigen values (a) dierent (b) of A (c) same (d) may or may not be the same 15. If is an eigen value of an orthogonal matrix, then 1/ is also its (a) real vector (b) eigen value (c) complex vector (d) eigen vector 16. By Cayley Hamilton theorem, matrix A = (a) A2 - 7A + 6 = 0 (b) A2 - 7A - 2 = 0 (c) A2 - 7A - 6 = 0 (d) A2 - 7A+ 2 = 0 17. The characteristic equation of the square matrix A = (a) (b) (c) (d)
1 13 1 13 1 13 1 13
28 16
49 28
is a
matrix
vector such that A X = X
1 2 0 5 is 4 0
a 0 a = 0, for the eigen value =0 is 0
5 4 1 2
, satises its characteristic equation. Which is
2 7
3 4
is 2 + 2 + 13 = 0, then A1 is
4 7
3 2
4 3 7 2 4 7 3 2
4 3 7 2 4 3 5 0 0 1 1 0 0 5 1 2 then the diagonal matrix D =
18. If A = (a) (b) (c) (d)
1 0 0 1 5 0 0 1
19. If the characteristic equation of A is 3 - 11 2 - 4 +1 = 0 then A4 = (a) -11A3 4A2 + A (b) 11A3 4A2 + A (c) 11A3 + 4A2 - A (d) 11A3 4A2 - A 20. The matrix B which diagonalises A is (a) modal (b) symmetric (c) spectral (d) Orthogonal matix.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Mass of Jupiter From Observations of Galilean SatellitesDocument7 pagesThe Mass of Jupiter From Observations of Galilean Satellitesanon-232673No ratings yet
- Resonance Magazine, 1st January 1996Document108 pagesResonance Magazine, 1st January 1996Kiran Kumar KuppaNo ratings yet
- MM 47Document1 pageMM 47Somasekhar Chowdary KakaralaNo ratings yet
- MM 48Document1 pageMM 48Somasekhar Chowdary KakaralaNo ratings yet
- MM 46Document1 pageMM 46Somasekhar Chowdary KakaralaNo ratings yet
- MM 49Document1 pageMM 49Somasekhar Chowdary KakaralaNo ratings yet
- MM 44Document1 pageMM 44Somasekhar Chowdary KakaralaNo ratings yet
- MM 3Document1 pageMM 3Somasekhar Chowdary KakaralaNo ratings yet
- MM 43Document1 pageMM 43Somasekhar Chowdary KakaralaNo ratings yet
- MM 43keyDocument1 pageMM 43keySomasekhar Chowdary KakaralaNo ratings yet
- MM 39Document1 pageMM 39Somasekhar Chowdary KakaralaNo ratings yet
- MM 45Document1 pageMM 45Somasekhar Chowdary KakaralaNo ratings yet
- MM 41Document1 pageMM 41Somasekhar Chowdary KakaralaNo ratings yet
- MM 42Document1 pageMM 42Somasekhar Chowdary KakaralaNo ratings yet
- MM 38Document1 pageMM 38Somasekhar Chowdary KakaralaNo ratings yet
- MM 35Document1 pageMM 35Somasekhar Chowdary KakaralaNo ratings yet
- MM 36Document1 pageMM 36Somasekhar Chowdary KakaralaNo ratings yet
- MM 35keyDocument1 pageMM 35keySomasekhar Chowdary KakaralaNo ratings yet
- MM 5Document1 pageMM 5Somasekhar Chowdary KakaralaNo ratings yet
- MM 37Document1 pageMM 37Somasekhar Chowdary KakaralaNo ratings yet
- MM 31Document1 pageMM 31Somasekhar Chowdary KakaralaNo ratings yet
- MM 33keyDocument1 pageMM 33keySomasekhar Chowdary KakaralaNo ratings yet
- MM 34Document1 pageMM 34Somasekhar Chowdary KakaralaNo ratings yet
- MM 27keyDocument1 pageMM 27keySomasekhar Chowdary KakaralaNo ratings yet
- MM 25keyDocument1 pageMM 25keySomasekhar Chowdary KakaralaNo ratings yet
- MM 19Document1 pageMM 19Somasekhar Chowdary KakaralaNo ratings yet
- MM 30Document1 pageMM 30Somasekhar Chowdary KakaralaNo ratings yet
- MM 28Document1 pageMM 28Somasekhar Chowdary KakaralaNo ratings yet
- MM 29Document1 pageMM 29Somasekhar Chowdary KakaralaNo ratings yet
- MM 25Document1 pageMM 25Somasekhar Chowdary KakaralaNo ratings yet
- MM 23keyDocument1 pageMM 23keySomasekhar Chowdary KakaralaNo ratings yet
- MM 24Document1 pageMM 24Somasekhar Chowdary KakaralaNo ratings yet
- 6 Social Sciecne SP 16 17 Sa1Document3 pages6 Social Sciecne SP 16 17 Sa1abhay vermaNo ratings yet
- Physicalscience12 q2 Mod4 Einstein S Theory of Relativity v4Document50 pagesPhysicalscience12 q2 Mod4 Einstein S Theory of Relativity v4UNKNOWNNo ratings yet
- "The Question Concerning Technology" by Martin HeideggerDocument4 pages"The Question Concerning Technology" by Martin HeideggerFranzelle JaictenNo ratings yet
- Sepharial - The Forecast 6 (49p)Document49 pagesSepharial - The Forecast 6 (49p)royNo ratings yet
- W40k - Dark HeresySector OverviewDocument9 pagesW40k - Dark HeresySector OverviewSotiris PetrotzoglisNo ratings yet
- Earth Sun Moon Worksheet Homework ResourcesDocument4 pagesEarth Sun Moon Worksheet Homework Resourcesafeuspaoh100% (1)
- The Blue Mountains UFO Research Club Newsletter - August 2011Document17 pagesThe Blue Mountains UFO Research Club Newsletter - August 2011Rex and Heather GilroyNo ratings yet
- Test Ray OpticsDocument2 pagesTest Ray OpticsShivam Jaggi0% (1)
- Nine Seeds PDFDocument1 pageNine Seeds PDFprinces242No ratings yet
- Plan and Conduct A Passage and Determine Position Revisi 2Document2 pagesPlan and Conduct A Passage and Determine Position Revisi 2Rio Arya50% (4)
- Year 9 Physics Midterm Home WorkDocument3 pagesYear 9 Physics Midterm Home Workyuhitsabby10No ratings yet
- Our Creators Cosmos by Neal A. MaxwellDocument7 pagesOur Creators Cosmos by Neal A. MaxwellBJ Spurlock100% (1)
- Drops of Jupiter KoorDocument6 pagesDrops of Jupiter KoorFrank KokNo ratings yet
- Spacecraft Attitude Determinatio PDFDocument23 pagesSpacecraft Attitude Determinatio PDFAlee K. ObeidNo ratings yet
- Hebrew Astrology in Byzantine Southern Italy PDFDocument33 pagesHebrew Astrology in Byzantine Southern Italy PDFkorrg1234100% (1)
- Jupiter and IoDocument3 pagesJupiter and IoNI�A VICTORIA BARLANNo ratings yet
- VenusDocument2 pagesVenusYhamNo ratings yet
- Astro Consultant Shri Nathulal Vyas BhilwaraDocument1 pageAstro Consultant Shri Nathulal Vyas Bhilwaranakulyadav7No ratings yet
- L15 PDFDocument15 pagesL15 PDFlesNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Hyperspectral Image Analysis: A Powerful Remote Sensing TechnologyDocument13 pagesIntroduction to Hyperspectral Image Analysis: A Powerful Remote Sensing TechnologyFanakiri AsaNo ratings yet
- PPSC MCQSDocument230 pagesPPSC MCQSfameansari63% (8)
- KarakDocument12 pagesKarakSandeep Kumar0% (1)
- SWd20 Rule BookDocument178 pagesSWd20 Rule BookRyan CloutierNo ratings yet
- Gamma Ray: 1 History of DiscoveryDocument12 pagesGamma Ray: 1 History of DiscoveryDhanmeet KaurNo ratings yet
- Ud11t1201 Navigation III DNSDocument2 pagesUd11t1201 Navigation III DNSB1038 Swaroop NairNo ratings yet
- Wave Practice 2Document24 pagesWave Practice 2Soyoko U.No ratings yet
- Se-Heon Oh, Lister Staveley-Smith, Kristine Spekkens, Peter Kamphuis & B Arbel S. KoribalskiDocument46 pagesSe-Heon Oh, Lister Staveley-Smith, Kristine Spekkens, Peter Kamphuis & B Arbel S. KoribalskiIanjamasimanana RogerNo ratings yet