Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Advanced Smart Credential Cum Unique Identification and Recognition System. (Ascuirs)
Uploaded by
IAEME PublicationOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Advanced Smart Credential Cum Unique Identification and Recognition System. (Ascuirs)
Uploaded by
IAEME PublicationCopyright:
Available Formats
International Journal of INTERNATIONALComputer EngineeringCOMPUTER ENGINEERING JOURNAL OF and Technology (IJCET), ISSN 09766367(Print), ISSN 0976 6375(Online) Volume
e 4, Issue 1, January- February (2013), IAEME & TECHNOLOGY (IJCET)
ISSN 0976 6367(Print) ISSN 0976 6375(Online) Volume 4, Issue 1, January- February (2013), pp. 97-104 IAEME: www.iaeme.com/ijcet.asp Journal Impact Factor (2012): 3.9580 (Calculated by GISI) www.jifactor.com
IJCET
IAEME
ADVANCED SMART CREDENTIAL CUM UNIQUE IDENTIFICATION AND RECOGNITION SYSTEM. (ASCUIRS)
Mr.Lokesh S. Khedekar 1 , Dr.A.S.Alvi 2 PRMIT&R,Badnera,Amravati,India,lokeshkhedekar@gmail.com 1 PRMIT&R,Badnera,Amravati,India,abrar_alvi@rediffmail.com 2
ABSTRACT Today barcode system is very popular to identifying a unique product. Many organizations are using this technique for identifying a unique product. Tracking these items has historically been done by the use of bar-code technologies, which suffer from lack of efficiency, robustness, difficulty in automation, inability to have secure or dynamic data, etc., whereas the 2D Data matrix has the ability to overcome several of these limitations over barcode This paper presents a comparative basis for the Advanced Smart Credential cum Unique Identification and Recognition System via 2D Data matrix versus other technologies such as barcode and QR code. Keywords: Barcode, Data Matrix, Encoding, QR Code, SCUIRS. I. INTRODUCTION
This proposed paper is related with the implementation of a product that will combine the power of graphical representation and the power of random numbers and characters for a unique ID. Combination of both Unique ID and Unique image will help a user to identify the product from other products and store its information accordingly. ASCUIRS will not only give you a complete solution to product identification but can facilitate you with one more option. ASCUIRS will also act like a Security system. The basic idea behind the designing of ASCUIRS is to use the feature of Unique numbers combined with unique images and form a unique combination that will help in recognizing the product or a user or any item in inventory. 1.1 1.1.1 Existing Systems Barcode System
97
International Journal of Computer Engineering and Technology (IJCET), ISSN 09766367(Print), ISSN 0976 6375(Online) Volume 4, Issue 1, January- February (2013), IAEME
There are a variety of methods you can use to print BarCode [1]. We recommend the lowest cost alternative to get started a barcode font. Barcode fonts give you an inexpensive and flexible way to print labels quickly with high resolution and a low initial investment. The location barcode is important because the goal of the inventory system is to know not only what you have, but to be able to tell accurately where it all is. You can get creative with the location barcode. The first barcode was developed by Bernard Silver and Norman Joseph Woodland in the late 1940s and early 1950s. The first commercial use of barcodes was by the RCA/Kroger system installed in Cincinnati on the call of the National Association of Food Chains (NAFC). However it was not widely used until the Universal Product Code (UPC) [2] was introduced into America and adopted by the U.S. Supermarket Ad Hoc Committee. Todays barcodes have two forms: one dimensional (1D) barcode and two dimensional (2D) barcode [3][4]. The 1D barcodes use bars and gaps to encode identification information such as serial numbers. The 2D barcodes [5] consist of more complicated patterns and may encode up to 4K bytes of data. Figure 1 shows the 1D barcodes. Although 1D is the more prevalent barcode used in daily life.
Figure 1. 1D Barcode and 2D Barcode Figure 2 illustrates a basic barcode system. Barcodes are read or scanned by a barcode reader and the reader is connected to a computer. The operator has to physically align/point the barcode reader with/to the barcode to read the identification information. The software running on the computer processes the identification information picked up by the scanner. Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is usually used to control the scanner in more automated process such as production line. The primary scanning technology for barcode is LED (Light-Emitting Diode). More advanced scanning such as CCD (Charge-Coupled Device), Laser, and Imager are used in industry automatic processing.
Figure 2 Basic Barcode System 2D Barcode System
98
International Journal of Computer Engineering and Technology (IJCET), ISSN 09766367(Print), ISSN 0976 6375(Online) Volume 4, Issue 1, January- February (2013), IAEME
Barcodes can be printed from most printers. 1D barcodes usually have coded readable ID printed along with the barcode. Barcodes can be read by barcode scanners which we see at a typical Point of Sale (POS) in retail stores. The barcode can be printed from any black/white printer. Since the barcode can be directly printed on an object or on paper label, the cost for a barcode is typically less than 1 cent [6]. Disadvantage of Barcode System: Barcodes are graphic images featuring a series of lines or bars, of varying thickness, positioned parallel to each other in such a way that a scanner passed along the image will translate their thickness and spacing with relation to each other as a series of numbers or code. This code is then interpreted by customized software to produce pricing and stocking information in an effort to assist in the automation of the retail sales and stocking processes. It is a very efficient and effective system, but, like any other method of tracking inventory, it is not foolproof. Pricing Discrepancies and Scanning Problems When discounts apply to bar-coded merchandise, store employees may forget to code in the discount price. This, in turn, can lead to confusion and delays at the checkout counter, inconveniencing the customer, the checkout clerk, and other customers waiting in line. If a barcode can't be scanned, for any reason, the clerk must then read the corresponding numeric code and enter it manually. Because clerks have become used to scanning barcodes quickly and automatically, without any additional effort on their part, their lack of practice in manual code entries may potentially cause them to be slow and/or inaccurate in entering the information, further delaying the checkout process. Label Damage Barcodes that are printed on a torn section of packaging, or that have been smeared, smudged or otherwise damaged, will present additional scanning problems. If the corresponding numeric code is also illegible due to damage, the checkout process can be significantly delayed while another package of the same merchandise is located and brought to the checkout counter for scanning. Financial and Equipment Costs For businesses that are not already equipped for barcode checkout, the cost of the equipment necessary to implement the new system can be prohibitive. Other delays can occur in training employees to adapt to new equipment, and expensive printers must be purchased to print coded labels for any merchandise that doesn't come prepackaged with a barcode already on it. Dot matrix and ink jet printers, for example, are generally incapable of printing finelydetailed barcodes. 1.1.2 QR Code QR Code (abbreviated from Quick Response Code) is the trademark for a type of matrix barcode (or two-dimensional code) first designed for the automotive industry. The QR barcode [7] is a two dimensional symbol developed by Denso Wave in 1994. More recently, the system has become popular outside the industry due to its fast readability and large storage capacity compared to standard UPC barcodes. The code consists of black modules (square dots) arranged in a square pattern on a white background. The information encoded can be made up of four standardized kinds ("modes") of data (numeric, alphanumeric, byte/binary, Kanji), or through supported extensions, virtually any kind of data.
99
International Journal of Computer Engineering and Technology (IJCET), ISSN 09766367(Print), ISSN 0976 6375(Online) Volume 4, Issue 1, January- February (2013), IAEME
The code contains information in both the x-axis and y-axis, whereas traditional barcodes contain data in one direction only. The outer range is the quiet zone. The upper-left, upperright, and left bottom square areas of QR code [8] are used for position detection and pattern separators for positioning. Figure 3 depicts basic block diagram of QR Code scanning with any image capturing device.
Figure 3 QR Code Advantage of QR codes There is no need to write vital details down. A simple scan captures the desired information. QR Codes can be used to store addresses and URLs that can appear in magazines, on signs, buses, business cards or just about any product that users might need information about. Disadvantages of QR codes Users must be equipped with a camera phone and the correct reader software that can scan the image of the QR Code. Currently only Smartphones are technically equipped to do this. Many users that have mobile phones that have cameras are unable to get QR reading software for their phones. II. GENERAL STRUCTURE
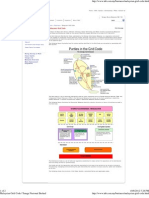
2-D bar code consists of a certain white and black geometric modules that alternately arrange in the vertical and horizontal directions according to certain rules see Figure, and it is a symbol with large capacity for storing information. As the 2-D bar code with smallest size in the world, data matrix code is widely applied to electronic product components. 2-Dbar code recognition technology shows great commercial value, and at present, most COTS (commercial of the shell) recognition algorithms are proprietary and protected by patents, so the 2-D bar code recognition technology is in a great demand for researching. Figure Data matrix structure shows the principle of a Data matrix barcode. The image shows an annotated Data matrix where the finder and synchronization patterns have been highlighted.
100
International Journal of Computer Engineering and Technology (IJCET), ISSN 09766367(Print), ISSN 0976 6375(Online) Volume 4, Issue 1, January- February (2013), IAEME
Figure 4.Data Matrix
III. PROBLEM DEFINITION
When user will store the product information the unique ID will be generated. This Unique ID will be Tier 1 identification for the product information. Entering this Unique ID as an Input to our Selective algorithm will generate a unique Image for that particular ID. This Unique image will act as Tier 2 identification for product information. This image will be hash mapped to the User Unique ID and both will be used to identify product information. When identifiers are used solely within a database, their generation should be left to the database itself. 3.1 ASCUIRS Working To generate a unique image from a unique ID and to map the image to a specific item in an inventory. When user will store information about a product or person a unique ID will be generated. This Unique ID will be Tier 1 identification for the User or Object. Entering this Unique ID as an Input to our Selective algorithm will generate a unique Image for that particular ID. This Unique image will act as Tier 2 identification for User or Object. This image will be hash mapped to the User Unique ID and both will be used to identify an object. Proposed Dataflow Diagram
3.2
Figure 5.Dataflow Diagram
101
International Journal of Computer Engineering and Technology (IJCET), ISSN 09766367(Print), ISSN 0976 6375(Online) Volume 4, Issue 1, January- February (2013), IAEME
GUI: Graphical User Interface will be used to gather information regarding the inventory from the user. GUI will consist of components to take inventory information and details from the user, components to save, edit, retrieve (searching) and delete the information. GUI will also contain a separate module for Unique ID (generated by the database and encrypted by selective algorithm) passing to generate an unique data matrix image. Selective algorithm for Unique ID encryption: This algorithm will be a modified version of 56 bit key DES algorithm. The selective algorithm will be used to encrypt the unique ID before been passed on for conversion into data matrix image. Selective algorithm for unique image The algorithm will encode the pre encrypted Unique ID and a data matrix will be generated that will be used for printing or publishing as required by the user. Storage of Unique ID: Database will store inventory information and details and a Unique ID will be generated and associated with every record. This Unique ID will act as Tier 1 identification for the record. Web server process and retrieval: A portal will be established which will contain the GUI and the entire process of storage of Data and retrieval along with data matrix image generation and publishing process. PROPOSED SYSTEM Web Portal:Web portal will contain a module that will take an input from the client which will be a data matrix image. Data inventory: Tables, relations related to items will be stored in data inventory. Data inventory is nothing but a set of tables that will contain records about items and its detailed information. Database: Information entered by the administrator will be stored in the database. This information will be stored in the form of a tuple. Each tuple will have a unique ID associated with it. Unique ID: This will be a 16 bit ID generated by the database (MySQL) and it will be used to identify the tuple in case of searching. Unique ID passed to (selective) algorithm: The algorithm will encrypt the Unique ID generated by database (MySQL). This encrypted key or string will be further passed on to another selective algorithm to create a unique image (i.e. Data Matrix image).
102
IV.
International Journal of Computer Engineering and Technology (IJCET), ISSN 09766367(Print), ISSN 0976 6375(Online) Volume 4, Issue 1, January- February (2013), IAEME
Unique image ready to publish: Unique image created by the selective algorithm can be either published or printed by the administrator. Capturing unique image: The image i.e. published or printed by the administrator can be captured by the user and sent back to the web portal through an HTTP response. Clipping: Since the captured image will vary in size, it needs to be clipped and exact Data Matrix needs to be extracted out of the captured image. Clipping will help to extract the exact image and pass it on to the web portal.
Figure 6.Proposed System.
103
International Journal of Computer Engineering and Technology (IJCET), ISSN 09766367(Print), ISSN 0976 6375(Online) Volume 4, Issue 1, January- February (2013), IAEME
Uploading of Image: An FTP request to the server will carry the clipped image that will be used to map with the database to find the related record or information. Sending information back to client: If mapping returns a record, then it will be sent back to the client (i.e. browser of phone or computer system) and this will complete the process. CONCLUSION
V.
Using this image through scanner or mobile phone camera we can decompile products information. The products information can be accessed anywhere if the database is stored and accessed through a web server. This ensures portability and security since the unique number will only be known to the organization. Organization will be using a unique image to access their product information or person or object. A new algorithm is proposed here which is a hybrid model for data hiding in data matrix and provides decoding algorithm which is independent of image orientation in any direction and de noising is one of the main advantages of this. It runs at 640480 resolution for real time scenarios. For practical implementation dimensions of data matrix image is 420420 includes finder pattern of 1010 ad size of squares is 2020.This proposed system provides an accuracy of 97.6%. REFERENCES [1] On The Creation of Automatic Identification and Data Capture Infrastructure via RFID Xiaoyong Su, Chi-Cheng Chu, B.S. Prabhu, RajitGadhUniversity of California, Los Angeles UCLA-WINMEC RFID Lab http://winmec.ucla.edu/rfid420 Westwood Plaza, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA 90095 [2] GS1 US, The Universal Product Code, http://www.uc-council.org/upc_background.html [3] Multi-color 2D datamatrix codeswith poorly readable colors Urka Bogataj1, Tadeja Muck, BrankaLozo ,Arjanaitnik. [4] YongyueYang ,Guang Zhu and Peng Wang, Reading system for 2D code based on machine vision, ICEMI ,2009 [5] Zhi Liu, HerongZhengWenting Cai, Research on Two- Dimensional code positioning approach based on Convex hull algorithm, International Conference on Digital Image Processing, 2009 [6] J. Abernethy, Widener Liberary: Book Identification Bar Codes & RFID, An Engineering Science 96 Report, M17, 1995, http://www.deas.harvard.edu/courses/es96/spring1995/barcodes_rfid/abernethy.html [7] Wen-Yuan Chen, Jing-Wein Wang; Nested image steganography scheme using QRbarcode technique Optical Engineering 48_5, 057004 _May 2009_Vol. 48(5). [8] Wakahara, Toshihiko; Yamamoto, Noriyasu; Image Processing of 2-Dimensional Barcode, Conference on Network-Based Information Systems (NBiS), 2011 14th International.
104
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Calculation of Induction Motor Starting Parameters Using MatlabDocument6 pagesCalculation of Induction Motor Starting Parameters Using MatlabДејан ПејовскиNo ratings yet
- Bop Test Info PDFDocument18 pagesBop Test Info PDFjairaso2950No ratings yet
- A Study On Talent Management and Its Impact On Employee Retention in Selected It Organizations in ChennaiDocument16 pagesA Study On Talent Management and Its Impact On Employee Retention in Selected It Organizations in ChennaiIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- BTech Seminar on MICROPILES: ADVANCED FOUNDATION ENGINEERINGDocument17 pagesBTech Seminar on MICROPILES: ADVANCED FOUNDATION ENGINEERINGTrudeep DaveNo ratings yet
- MagazineDocument34 pagesMagazineAhmed Khalil100% (1)
- BBU - Maintenance User GuideDocument578 pagesBBU - Maintenance User GuideSibte Hassan100% (2)
- Analyse The User Predilection On Gpay and Phonepe For Digital TransactionsDocument7 pagesAnalyse The User Predilection On Gpay and Phonepe For Digital TransactionsIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Determinants Affecting The User's Intention To Use Mobile Banking ApplicationsDocument8 pagesDeterminants Affecting The User's Intention To Use Mobile Banking ApplicationsIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Broad Unexposed Skills of Transgender EntrepreneursDocument8 pagesBroad Unexposed Skills of Transgender EntrepreneursIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- A Study On The Reasons For Transgender To Become EntrepreneursDocument7 pagesA Study On The Reasons For Transgender To Become EntrepreneursIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Impact of Emotional Intelligence On Human Resource Management Practices Among The Remote Working It EmployeesDocument10 pagesImpact of Emotional Intelligence On Human Resource Management Practices Among The Remote Working It EmployeesIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Influence of Talent Management Practices On Organizational Performance A Study With Reference To It Sector in ChennaiDocument16 pagesInfluence of Talent Management Practices On Organizational Performance A Study With Reference To It Sector in ChennaiIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Visualising Aging Parents & Their Close Carers Life Journey in Aging EconomyDocument4 pagesVisualising Aging Parents & Their Close Carers Life Journey in Aging EconomyIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Voice Based Atm For Visually Impaired Using ArduinoDocument7 pagesVoice Based Atm For Visually Impaired Using ArduinoIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- A Study of Various Types of Loans of Selected Public and Private Sector Banks With Reference To Npa in State HaryanaDocument9 pagesA Study of Various Types of Loans of Selected Public and Private Sector Banks With Reference To Npa in State HaryanaIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Analysis of Surface Roughness and White Later Thickness in Wire-Electric Discharge Turning Process Through Response Surface MethodologyDocument14 pagesModeling and Analysis of Surface Roughness and White Later Thickness in Wire-Electric Discharge Turning Process Through Response Surface MethodologyIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- A Study On The Impact of Organizational Culture On The Effectiveness of Performance Management Systems in Healthcare Organizations at ThanjavurDocument7 pagesA Study On The Impact of Organizational Culture On The Effectiveness of Performance Management Systems in Healthcare Organizations at ThanjavurIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Gandhi On Non-Violent PoliceDocument8 pagesGandhi On Non-Violent PoliceIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Attrition in The It Industry During Covid-19 Pandemic: Linking Emotional Intelligence and Talent Management ProcessesDocument15 pagesAttrition in The It Industry During Covid-19 Pandemic: Linking Emotional Intelligence and Talent Management ProcessesIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- A Multiple - Channel Queuing Models On Fuzzy EnvironmentDocument13 pagesA Multiple - Channel Queuing Models On Fuzzy EnvironmentIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Role of Social Entrepreneurship in Rural Development of India - Problems and ChallengesDocument18 pagesRole of Social Entrepreneurship in Rural Development of India - Problems and ChallengesIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF MECHANICAL AND TRIBOLOGICAL RELATION OF NYLON/BaSO4 POLYMER COMPOSITESDocument9 pagesEXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF MECHANICAL AND TRIBOLOGICAL RELATION OF NYLON/BaSO4 POLYMER COMPOSITESIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Moderating Effect of Job Satisfaction On Turnover Intention and Stress Burnout Among Employees in The Information Technology SectorDocument7 pagesModerating Effect of Job Satisfaction On Turnover Intention and Stress Burnout Among Employees in The Information Technology SectorIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- A Proficient Minimum-Routine Reliable Recovery Line Accumulation Scheme For Non-Deterministic Mobile Distributed FrameworksDocument10 pagesA Proficient Minimum-Routine Reliable Recovery Line Accumulation Scheme For Non-Deterministic Mobile Distributed FrameworksIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Application of Frugal Approach For Productivity Improvement - A Case Study of Mahindra and Mahindra LTDDocument19 pagesApplication of Frugal Approach For Productivity Improvement - A Case Study of Mahindra and Mahindra LTDIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Various Fuzzy Numbers and Their Various Ranking ApproachesDocument10 pagesVarious Fuzzy Numbers and Their Various Ranking ApproachesIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Financial Literacy On Investment Performance: The Mediating Effect of Big-Five Personality Traits ModelDocument9 pagesFinancial Literacy On Investment Performance: The Mediating Effect of Big-Five Personality Traits ModelIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Quality of Work-Life On Employee Retention and Job Satisfaction: The Moderating Role of Job PerformanceDocument7 pagesQuality of Work-Life On Employee Retention and Job Satisfaction: The Moderating Role of Job PerformanceIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Optimal Reconfiguration of Power Distribution Radial Network Using Hybrid Meta-Heuristic AlgorithmsDocument13 pagesOptimal Reconfiguration of Power Distribution Radial Network Using Hybrid Meta-Heuristic AlgorithmsIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Dealing With Recurrent Terminates in Orchestrated Reliable Recovery Line Accumulation Algorithms For Faulttolerant Mobile Distributed SystemsDocument8 pagesDealing With Recurrent Terminates in Orchestrated Reliable Recovery Line Accumulation Algorithms For Faulttolerant Mobile Distributed SystemsIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Self-Efficacy and Research Collaboration Towards Knowledge Sharing: The Moderating Effect of Employee CommitmentDocument8 pagesKnowledge Self-Efficacy and Research Collaboration Towards Knowledge Sharing: The Moderating Effect of Employee CommitmentIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Fuzzy Inference System Based Interline Power Flow Controller For Power System With Wind Energy Conversion System During Faulted ConditionsDocument13 pagesAnalysis of Fuzzy Inference System Based Interline Power Flow Controller For Power System With Wind Energy Conversion System During Faulted ConditionsIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Prediction of Average Total Project Duration Using Artificial Neural Networks, Fuzzy Logic, and Regression ModelsDocument13 pagesPrediction of Average Total Project Duration Using Artificial Neural Networks, Fuzzy Logic, and Regression ModelsIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Analysis On Machine Cell Recognition and Detaching From Neural SystemsDocument9 pagesAnalysis On Machine Cell Recognition and Detaching From Neural SystemsIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- A Review of Particle Swarm Optimization (Pso) AlgorithmDocument26 pagesA Review of Particle Swarm Optimization (Pso) AlgorithmIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Pundit Transducers - Operating Instructions - English - HighDocument8 pagesPundit Transducers - Operating Instructions - English - HighAayush JoshiNo ratings yet
- 20 Questions On Aircraft Asked in Indian Air Force InterviewDocument9 pages20 Questions On Aircraft Asked in Indian Air Force InterviewPreran PrasadNo ratings yet
- Liner Product Specification Sheet PDFDocument1 pageLiner Product Specification Sheet PDFsauravNo ratings yet
- Netsh Wlan Start HostednetworkDocument3 pagesNetsh Wlan Start HostednetworkM Nanda KumarNo ratings yet
- Virial Equation of State2Document46 pagesVirial Equation of State2ShainaBagonNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument8 pagesComputer Architecture - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaelcorinoNo ratings yet
- Kawasaki 4 Cylinder Hyperpack Installation ManualDocument8 pagesKawasaki 4 Cylinder Hyperpack Installation ManualJuan Carlos RojasNo ratings yet
- 32LS3400 KoreaDocument60 pages32LS3400 KoreaNightin VargheseNo ratings yet
- Tm500 Lte-A 3gpp Lte TestDocument8 pagesTm500 Lte-A 3gpp Lte TestSmith KumarNo ratings yet
- Bassett-jones-The Paradox of DiversityDocument8 pagesBassett-jones-The Paradox of DiversityKenneth WhitfieldNo ratings yet
- About The Business 1.1 Business Profile Positif CorporationDocument7 pagesAbout The Business 1.1 Business Profile Positif CorporationLinh DalanginNo ratings yet
- Cyberoam Quick Start Guide-50i-500iDocument8 pagesCyberoam Quick Start Guide-50i-500iPaul Anim AmpaduNo ratings yet
- Malaysia Grid CodeDocument2 pagesMalaysia Grid Codebee398No ratings yet
- Willy Chipeta Final Thesis 15-09-2016Document101 pagesWilly Chipeta Final Thesis 15-09-2016EddiemtongaNo ratings yet
- Modules Test ReportDocument4 pagesModules Test ReportprojectsNo ratings yet
- G-Series Pneumatic and Hydraulic Actuators: The Compact, Lightweight and Reliable SolutionDocument12 pagesG-Series Pneumatic and Hydraulic Actuators: The Compact, Lightweight and Reliable SolutionRoo Fa100% (1)
- 107-b00 - Manual OperacionDocument12 pages107-b00 - Manual OperacionJuan David Triana SalazarNo ratings yet
- He Likes TravelingDocument7 pagesHe Likes Travelingmesser3No ratings yet
- Dmr-Es10Eb Dmr-Es10Ec Dmr-Es10Eg Dmr-Es10Ep Dmr-Es10Ebl: DVD Video RecorderDocument71 pagesDmr-Es10Eb Dmr-Es10Ec Dmr-Es10Eg Dmr-Es10Ep Dmr-Es10Ebl: DVD Video RecorderWILIAM RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Pasundan United FC - Anggaran Dasar Dan Rumah Tangga Pasundan United FCDocument1,231 pagesPasundan United FC - Anggaran Dasar Dan Rumah Tangga Pasundan United FCdondo lambaNo ratings yet
- Twingo 3 & Clio 4Document10 pagesTwingo 3 & Clio 4Alexandre Le GrandNo ratings yet
- IV-series-fieldnetwork Field Network Um 442gb GB WW 1086-2Document114 pagesIV-series-fieldnetwork Field Network Um 442gb GB WW 1086-2azzszoNo ratings yet
- 1.1.3.4 Lab - Visualizing The Black HatsDocument3 pages1.1.3.4 Lab - Visualizing The Black HatsCordis CordisNo ratings yet
- R07 Set No. 2Document8 pagesR07 Set No. 2dileepNo ratings yet
- International Air Service Development at Boston Logan: June 7, 2012Document20 pagesInternational Air Service Development at Boston Logan: June 7, 2012chaouch.najehNo ratings yet