Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AE 221tutorial 1
Uploaded by
animeshkumarvermaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AE 221tutorial 1
Uploaded by
animeshkumarvermaCopyright:
Available Formats
AE221 Gas dynamics
(2012-13, II semester) Assignment 1
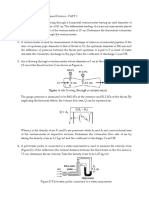
1. Calculate the divergence and curl of the velocity eld V = 3ti + xzj + ty2 k and comment about the compressible and rotational nature of the eld. 2. A velocity eld and density eld in Cartesian space is given as: V = L i and = Ktex L , where t L and K are constants having dimensions of length and density per time, respectively. Find the material derivative of the density . 3. A slow leak develops in a storage bottle and oxygen slowly leaks out. The volume of the bottle is 0.1 m3 and the diameter of the hole is 0.1 mm. The initial pressure is 10 MPa and the temperature is 20 C. The oxygen escapes through the hole according to the relation m = 0.04248 p ( TAe ), where m is mass ow rate (kg/s), p is the tank pressure (N/m2 ) and T is the tank temperature (K), Ae is area of the hole (m2 ). The constant 0.04248 is based on the gas constant and the ratio of specic heats of oxygen. Assuming that the temperature of the oxygen in the bottle does not change with time, determine the time it takes to reduce the pressure to one half of its initial value. 4. Fluid ows through constant area pipes as shown in Figure. Find the resultant force F. Assume ow in invicid.
5. Determine the force F required to push the at plate (see Figure) against the round air jet with a velocity of 10 cm/s. The air jet velocity is 100 cm/s, with a jet diameter of 5.0 cm. Air density is 1.2 kg/m3 .
6. Air enters a hand held hair dryer with a velocity of 3 m/s at a temperature of 20 C and a pressure of 101 kPa. Internal resistance heaters warm the air and it exits through an area of 20 cm2 with a velocity of 10 m/s at a temperature of 80 C. Assume that internal obstructions do not appreciably affect the pressure between inlet and exit and that heat transfer to the surroundings are negligible. Determine the power in kW needed to operate the hair dryer at steady state. 7. Air enters a compressor with a pressure of 100 kPa and a temperature 20 C; the mass ow rate is 0.25 kg/s. Compressed air is discharged from the compressor at 800 kPa and 50 C. Inlet and exit pipe diameters are 4.0 cm. Determine the exit velocity of the air at the compressor outlet and the compressor power required. Assume an adiabatic, steady, ow and that the air behaves as a perfect gas with constant specic heats; c p = 1.005 kJ/kg K and R = 0.287 kJ/kgK. 8. Air is adiabatically compressed from a pressure of 300 kPa and a temperature of 27 C to a pressure of 600 kPa and a temperature of 327 C. Is this compression actually possible?
1 of 1
You might also like
- Gas Dynamics TutorialDocument2 pagesGas Dynamics TutorialShubham MauryaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Worksheet 2Document8 pagesFluid Mechanics Worksheet 2anon_293092329No ratings yet
- Gas Dynamics Problem SheetDocument1 pageGas Dynamics Problem SheetMhamedNo ratings yet
- Fluid Properties (HW1)Document4 pagesFluid Properties (HW1)Jamiel CatapangNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Question Bank @Document6 pagesFluid Mechanics Question Bank @AnujNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document1 pageTutorial 1kiran aralikattiNo ratings yet
- Project BankDocument8 pagesProject BankVARUN SINGH SHEKHAWATNo ratings yet
- BN 1395749865 Heat TransferDocument5 pagesBN 1395749865 Heat TransferFrancis LopezNo ratings yet
- 9A14403 Fluid Mechanics & Heat TransferDocument8 pages9A14403 Fluid Mechanics & Heat TransfersivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- HT Practice QuestionsDocument3 pagesHT Practice QuestionsVivek SharmaNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument15 pagesPhysicssandrosteklegebre100% (1)
- Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow Engineering CalculationsDocument4 pagesHeat Transfer and Fluid Flow Engineering CalculationsAbhilash TilakNo ratings yet
- Isro Scientist Me 2020 Paper 80c39244Document20 pagesIsro Scientist Me 2020 Paper 80c39244Elsa PoirotNo ratings yet
- Gas dynamics assignment Mach numbers nozzlesDocument1 pageGas dynamics assignment Mach numbers nozzlesanimeshkumarvermaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2Venkitaraj K PNo ratings yet
- Me6604 Gas Dynamics and Jet PropulsionDocument8 pagesMe6604 Gas Dynamics and Jet PropulsionMohanraj SubramaniNo ratings yet
- Isentropic Flow - Area VariationDocument11 pagesIsentropic Flow - Area VariationMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document4 pagesSheet 1mohelg83No ratings yet
- ME6604 Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion TutorialDocument10 pagesME6604 Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion Tutorialshibin874141No ratings yet
- Problemas OrdinarioDocument10 pagesProblemas OrdinarioAngelo EdoraNo ratings yet
- Ammonia pipeline venting mass and mole fraction calculationsDocument14 pagesAmmonia pipeline venting mass and mole fraction calculationsSangetha Chelladorai0% (3)
- Fluid Mechanics AssignmentDocument11 pagesFluid Mechanics AssignmentAgnibha BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Problem Set: Lagrangian vs Eulerian DescriptionsDocument3 pagesFluid Mechanics Problem Set: Lagrangian vs Eulerian DescriptionsDeepika DeepuNo ratings yet
- Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion ConceptsDocument11 pagesGas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion Conceptschinnasamy76No ratings yet
- 054 - ME6604 Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion - Question Bank 2Document9 pages054 - ME6604 Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion - Question Bank 2JesnaNo ratings yet
- r5220303 Mechanics of FluidsDocument1 pager5220303 Mechanics of FluidsSaitheja SharmaNo ratings yet
- SP 1 Assignment 30 March 2022Document2 pagesSP 1 Assignment 30 March 2022ONKAR ARORA0% (1)
- FMDocument2 pagesFMepnaseefNo ratings yet
- CompressibleFlow PracticeProblemsDocument42 pagesCompressibleFlow PracticeProblemsGautam KadianNo ratings yet
- Tutorial4 6Document4 pagesTutorial4 6Chinmay JoshiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial-Sums DiffusionDocument11 pagesTutorial-Sums DiffusionHridyaAshokanNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2-Pressure DropDocument2 pagesSheet 2-Pressure Dropmohelg83No ratings yet
- Gas Dynamics Question BankDocument3 pagesGas Dynamics Question BankChanduNo ratings yet
- Che 4009 Transport Phenomena Assignment # 1Document7 pagesChe 4009 Transport Phenomena Assignment # 1Bao-Ngoc HoangNo ratings yet
- Takehome ActivityDocument5 pagesTakehome ActivityEdmond Yurag LLusalaNo ratings yet
- Flow Measurement Devices Part 2 Inc AnsDocument3 pagesFlow Measurement Devices Part 2 Inc AnsNeybilNo ratings yet
- Question Bank MechDocument5 pagesQuestion Bank MechSandeep MoreNo ratings yet
- ME2351-Gas Dynamics and Jet PropulsionDocument12 pagesME2351-Gas Dynamics and Jet PropulsionmayilsvhecNo ratings yet
- CH 3 AssignmentDocument3 pagesCH 3 AssignmentArpit PatelNo ratings yet
- Free Convection - with answersDocument17 pagesFree Convection - with answersKalpana meenaNo ratings yet
- r5220303 Mechanics of FluidsDocument1 pager5220303 Mechanics of FluidssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- CHE 111P Seatwork 1Document3 pagesCHE 111P Seatwork 1Dodjie MaestrecampoNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document4 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Ameer Hakeem Primus100% (1)
- AE5020 Gas Dynamics TutorialDocument4 pagesAE5020 Gas Dynamics Tutorialgokuler137No ratings yet
- 2nd Year - Fluid Mechanics 2 - SheetDocument3 pages2nd Year - Fluid Mechanics 2 - SheetAhmedTaha100% (1)
- IES-CONV-Mechanical Engineering-2002Document8 pagesIES-CONV-Mechanical Engineering-2002aditya_kumar_meNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - HMTDocument5 pagesQuestion Bank - HMTSUNDARAMAHALINGAM ANo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet (I, II, III, IV, V, VI) Group A & BDocument11 pagesTutorial Sheet (I, II, III, IV, V, VI) Group A & BVISHAL GUPTANo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1581164004643Document2 pagesOrca Share Media1581164004643Baby DarylNo ratings yet
- Cankaya University Thermodynamics Chapter 4 ExamplesDocument21 pagesCankaya University Thermodynamics Chapter 4 ExamplesCarlosCD17No ratings yet
- Che 222 Tutorial 2Document15 pagesChe 222 Tutorial 2naverfallNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document2 pagesSheet 1Syed Faisal Mohiuddin SharfiNo ratings yet
- 2021-Assignment-1 (Updated)Document2 pages2021-Assignment-1 (Updated)Rosario QFNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Problem Set 2 Compressible FlowDocument1 pageTutorial Problem Set 2 Compressible FlowBajajNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Assignment SolutionsDocument3 pagesThermodynamics Assignment SolutionsMohammad Nisar JavedNo ratings yet
- ME 411-Hw02-2018-1Document3 pagesME 411-Hw02-2018-1Harun SarıçamNo ratings yet
- 10 Useful Open Source Web Based File ManagersDocument1 page10 Useful Open Source Web Based File ManagersanimeshkumarvermaNo ratings yet
- ES490 Lecture - Notes 04Document55 pagesES490 Lecture - Notes 04animeshkumarvermaNo ratings yet
- IAS Recommendation Letter FormatDocument2 pagesIAS Recommendation Letter FormatAshwin RamanujamNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Structures DefinitionsDocument8 pagesAircraft Structures DefinitionsJerin CyriacNo ratings yet
- MTech Aerospace Structures Curriculum Syllabus 20130918Document6 pagesMTech Aerospace Structures Curriculum Syllabus 20130918Muralikrishnan GMNo ratings yet
- S Sukeshkumar@vssc - Gov.inDocument1 pageS Sukeshkumar@vssc - Gov.inanimeshkumarvermaNo ratings yet
- Sixth Semester Classes ScheduleDocument1 pageSixth Semester Classes ScheduleanimeshkumarvermaNo ratings yet
- HomeWork 1Document1 pageHomeWork 1animeshkumarvermaNo ratings yet
- Concrete Crack PropagationDocument5 pagesConcrete Crack PropagationanimeshkumarvermaNo ratings yet
- What is a prototypeDocument5 pagesWhat is a prototypeanimeshkumarvermaNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Structures Course OverviewDocument42 pagesAircraft Structures Course OverviewShwetha BhatNo ratings yet
- IIST PROJECT REPORT FORMATDocument8 pagesIIST PROJECT REPORT FORMATLee SweeneyNo ratings yet
- Sixth Semester Classes ScheduleDocument1 pageSixth Semester Classes ScheduleanimeshkumarvermaNo ratings yet
- AE BTech Syllabus 2011Document58 pagesAE BTech Syllabus 2011animeshkumarvermaNo ratings yet
- B.tech TimeTableDocument7 pagesB.tech TimeTableanimeshkumarvermaNo ratings yet
- How To Use The Hungarian AlgorithmDocument2 pagesHow To Use The Hungarian AlgorithmanimeshkumarvermaNo ratings yet
- Sixth Semester Classes ScheduleDocument1 pageSixth Semester Classes ScheduleanimeshkumarvermaNo ratings yet
- Latest Trends in MachiningDocument209 pagesLatest Trends in Machiningalexkr16661No ratings yet
- LC49-List of BooksDocument29 pagesLC49-List of BooksanimeshkumarvermaNo ratings yet
- AE BTech Syllabus 2011Document58 pagesAE BTech Syllabus 2011animeshkumarvermaNo ratings yet
- Our Wastewater Systems Overview - SA Water PDFDocument1 pageOur Wastewater Systems Overview - SA Water PDFanimeshkumarvermaNo ratings yet
- Workshop PDFDocument3 pagesWorkshop PDFanimeshkumarvermaNo ratings yet
- Value EnggDocument6 pagesValue EngganimeshkumarvermaNo ratings yet
- AE312 Assignment 1 PDFDocument1 pageAE312 Assignment 1 PDFanimeshkumarvermaNo ratings yet
- Springs PDFDocument7 pagesSprings PDFanimeshkumarvermaNo ratings yet
- IIST PROJECT REPORT FORMATDocument8 pagesIIST PROJECT REPORT FORMATLee SweeneyNo ratings yet
- AE 331 Lab Manual PDFDocument22 pagesAE 331 Lab Manual PDFanimeshkumarverma0% (1)
- Water Jet CutterDocument7 pagesWater Jet Cutteranimeshkumarverma100% (1)
- Voltage REgulationDocument8 pagesVoltage REgulationJacob CarterNo ratings yet
- 6 Semester Internship Evaluation CriteriaDocument1 page6 Semester Internship Evaluation CriteriaanimeshkumarvermaNo ratings yet
- SW GDLoader GettingStarted v3-0 enDocument41 pagesSW GDLoader GettingStarted v3-0 enEduardo QuispeNo ratings yet
- Proposal LayoutDocument11 pagesProposal Layoutadu g100% (1)
- Assessment of Knowledge, Attitude Andpractice Toward Sexually Transmitteddiseases in Boditi High School StudentsDocument56 pagesAssessment of Knowledge, Attitude Andpractice Toward Sexually Transmitteddiseases in Boditi High School StudentsMinlik-alew Dejenie88% (8)
- USAF Electronic Warfare (1945-5)Document295 pagesUSAF Electronic Warfare (1945-5)CAP History LibraryNo ratings yet
- 55fbb8b0dd37d Productive SkillDocument6 pages55fbb8b0dd37d Productive SkilldewiNo ratings yet
- Pagdaragdag (Adding) NG Bilang Na May 2-3 Digit Na Bilang Na May Multiples NG Sandaanan Antas 1Document5 pagesPagdaragdag (Adding) NG Bilang Na May 2-3 Digit Na Bilang Na May Multiples NG Sandaanan Antas 1Teresita Andaleon TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Read Me Slave 2.1Document7 pagesRead Me Slave 2.1Prasad VylaleNo ratings yet
- 2 - Thermal Analysis of Electric Machines (1788)Document70 pages2 - Thermal Analysis of Electric Machines (1788)Naveed IqbalNo ratings yet
- IBM's Corporate Service Corps: The Shift To A Globally Integrated EnterpriseDocument2 pagesIBM's Corporate Service Corps: The Shift To A Globally Integrated EnterprisePYXERA GlobalNo ratings yet
- The Four Humor Mechanisms 42710Document4 pagesThe Four Humor Mechanisms 42710Viorel100% (1)
- Question 1: Bezier Quadratic Curve Successive Linear Interpolation EquationDocument4 pagesQuestion 1: Bezier Quadratic Curve Successive Linear Interpolation Equationaushad3mNo ratings yet
- The Confidence Myth and What It Means To Your Career: by Tara MohrDocument4 pagesThe Confidence Myth and What It Means To Your Career: by Tara MohrdargeniNo ratings yet
- Struts HTML Checkbox enDocument4 pagesStruts HTML Checkbox enjudesahayarajNo ratings yet
- Soft Start - Altistart 48 - VX4G481Document2 pagesSoft Start - Altistart 48 - VX4G481the hawakNo ratings yet
- AbDocument13 pagesAbSk.Abdul NaveedNo ratings yet
- Impact of Social Media in Tourism MarketingDocument16 pagesImpact of Social Media in Tourism MarketingvidhyabalajiNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report On Satellite CommunicationDocument17 pagesSeminar Report On Satellite CommunicationHapi ER67% (6)
- Galletto 1250 User GuideDocument9 pagesGalletto 1250 User Guidesimcsimc1No ratings yet
- A Report On T&D by IbrahimDocument17 pagesA Report On T&D by IbrahimMohammed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Write Hello in The PDFDocument95 pagesWrite Hello in The PDFraghupulishettiNo ratings yet
- Differential Aptitude TestsDocument2 pagesDifferential Aptitude Testsiqrarifat50% (4)
- The Benefits of Radio Broadcasting As Perceived by The People in Rural AreasDocument10 pagesThe Benefits of Radio Broadcasting As Perceived by The People in Rural AreasMaeNo ratings yet
- Inami, Problem Other MindsDocument19 pagesInami, Problem Other MindsfortyrrNo ratings yet
- Damplas damp proof membranes CE Marked to EN 13967Document5 pagesDamplas damp proof membranes CE Marked to EN 13967Vikram MohanNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Vs Traditional ITDocument20 pagesCloud Computing Vs Traditional ITgarata_java100% (1)
- Analysis of PWM Nonlinearity in Non-Inverting Buck-Boost Power ConvertersDocument7 pagesAnalysis of PWM Nonlinearity in Non-Inverting Buck-Boost Power ConvertershamidmollaniaNo ratings yet
- SINGLE OPTION CORRECT ACCELERATIONDocument5 pagesSINGLE OPTION CORRECT ACCELERATIONShiva Ram Prasad PulagamNo ratings yet
- PESTEL Team Project (Group)Document9 pagesPESTEL Team Project (Group)Yadira Alvarado saavedraNo ratings yet
- Impact of K-Pop Music On The Academic PDocument29 pagesImpact of K-Pop Music On The Academic Pdave tayron paggao100% (1)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (48)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismFrom EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (500)
- The Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceFrom EverandThe Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (23)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1395)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishFrom EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsFrom EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (94)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (409)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeFrom EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNo ratings yet
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)From EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (155)
- In Search of Schrödinger’s Cat: Quantum Physics and RealityFrom EverandIn Search of Schrödinger’s Cat: Quantum Physics and RealityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (380)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldFrom EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Paradox: The Nine Greatest Enigmas in PhysicsFrom EverandParadox: The Nine Greatest Enigmas in PhysicsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (57)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceFrom EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityFrom EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (75)
- Starry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationFrom EverandStarry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (158)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseFrom EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- The Sounds of Life: How Digital Technology Is Bringing Us Closer to the Worlds of Animals and PlantsFrom EverandThe Sounds of Life: How Digital Technology Is Bringing Us Closer to the Worlds of Animals and PlantsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)