Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acids, Derivatives and Nitriles
Uploaded by
Luqman HakimOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acids, Derivatives and Nitriles
Uploaded by
Luqman HakimCopyright:
Available Formats
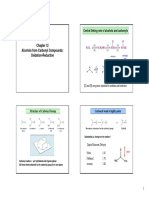
Carboxylic acid and derivatives
Structure of Carboxylic acid
O C R
H
124o 125o
O C
111
o
RCOOH
OH
106o
H O
Geometry : approximately planar
C : sp2 hybridised, nearly trigonal bond angles
OH is also in this plane eclipsed with C=O
Carboxylic acid and derivatives
Resonance of carboxylic acid
major
very minor
minor
Carboxylic acid and derivatives
Properties of carboxylic acid
1. Bp :
* higher than ROH, RCOR, RCHO of similar MW
2. Mp :
* > 8 C atoms are generally solids * Double bonds lower the mp
3. Solubility :
* very soluble in ROH / quite soluble in non-polar solvents * 1-4 C atoms are miscible with water * RCOO-Na+ quite soluble in water (ionic)
Carboxylic acid and derivatives
4. Acidity
* * * *
H Cl H
chloroacetic acid pKa = 2.86
weaker acid than mineral acids more acidic than ROH Electronegative substituent increases the acidity substituent effect depends on the number & distance from C=O
O H O Cl
dichloroacetic acid pKa = 1.26
H C C H Cl C C O H
O Cl
Cl C Cl
O C O H
acetic acid pKa = 4.74
trichloroacetic acid pKa = 0.64
Cl H CH3
Cl CH CH2
O C O H CH3 CH2
Cl
O CH C O
2-chlorobutanoic acid pKa = 2.86
CH2 CH2
CH2
4-chlorobutanoic acid pKa = 4.52
3-chlorobutanoic acid pKa = 4.05
Carboxylic acid and derivatives
Some important carboxylic acid
Acetic acid - vinegar and other foods, solvent, catalyst & reagent for synthesis
Fatty acids - fats and oils
Benzoic acid - drugs, preservatives
Adipic acid - to make nylon 66
Phthalic acid - to make polyesters
Carboxylic acid and derivatives
Synthesis of carboxylic acid
1. Oxidation of primary ROH and RCHO
2. Oxidative cleavage of alkenes and alkynes
3. Oxidation of substituted alkylbenzenes
[O] : hot KMnO4 ; hot chromic acid
R COOH
[O] H2O, 95C
Carboxylic acid and derivatives
4. Hydrolysis
a) Nitriles
b) Acid chloride d) Ester
c) Acid anhydride e) Amide
5. Carboxylation of Grignard reagents
i. CO2 ii. H3O+
R O OH
RMgX
Carboxylic acid and derivatives
Reaction of carboxylic acids
nucleophilic acyl substitution
one nucleophile replaces another on the acyl carbon
takes place under basic or acidic conditions
i. addition
ii. elimination
O R C Nuc Y
Nuc:
O R
O C Nuc + :Y
Carboxylic acid and derivatives
1. Conversion to ester
O R C OH
1. NaOH 2. R'X R'OH HCl
R
React with alcohols Eliminated water acid catalyse Fisher Esterification
O C OR'
OR'
Limited to primary alkyl halide (SN2)
Limited to simple alcohol
Carboxylic acid and derivatives
2. Conversion to Amides (direct synthesis to amide)
O heat >100 C amide
o
O NH 2
R NH + R' C
OH
+ R
H2O
3. Conversion to Acid Halides
O
SOCl2
Cl
OH
PBr3
Br
Carboxylic acid and derivatives
4. Conversion to Acid Anhydrides
O
R O O
OH
R'
Cl
800C
R'
OH
R'
R'
Carboxylic acid and derivatives
5. Reduction of carboxylic acids
i. LiAlH4 primary alcohol : strong reducing agent (non-selective)
O C ii) H3O
+
CH2
OH
i) LiAlH4
CH2 CH2 OH
ii. BH3 - primary alcohol (gives selectivity)
O C OH (or B2H6) BH3.THF CH3 O C CH2OH
CH3
Carboxylic acid and derivatives
Carboxylic acid derivatives
Derivatives : compounds with FGs that can be converted to carboxylic acids by simple acidic or basic hydrolysis
Acyl group is bonded to electronegative atom (heteroatoms)
O O R' R C OR' R R C O O O C NH2
Cl
Acid chloride Acid anhydride
Ester
Amide
reaction type nucleophilic acyl substitution
Carboxylic acid and derivatives
Acid chloride
O R C X
O O Acid anhydride R C O C R'
Ester
R C
O OR'
Amide
R
O C NH2
reactivity of the derivatives decreases as the LG becomes more basic
Carboxylic acid and derivatives
Acid chloride
:
see RCOOH reaction
Synthesis :
O C NR'2 R' O C NHR'
Reaction
1. hydrolysis 2. alcoholysis 3. aminolysis
NH2
R'
R'2NH R'NH2
R'
4. reduction
R'
OR'
R'OH
O C R Cl
NH3
O H H
Py
H2O
1. LiAlH4 2. H3O
+
1. LiAlH4
C R' H
R'
OH
2. H3O
C R' OH
Carboxylic acid and derivatives
5. Reaction with organometallic reagents
Grignard reagent
O
RMgX 1. RMgX
R R
OH
Cl
ether 2. H3O
R R R
Gilman reagent
O C R Cu R' R' R O C R'
Cl
Li+R'2Cu Ether
+ R'Cu Ketone
6. Conversion to acid anhydride (See RCOOH reaction)
Carboxylic acid and derivatives
Acid anhydride
:
see RCOOH reaction
Synthesis :
O R' C NH2
Reaction
alcoholysis
aminolysis
R'
OR'
R'OH NH3
O O C R' O R C
H H
R'
H2O
OH
[R] LiAlH4
hydrolysis
H3O
R'
LiAlH4
H
H3O+
R'
OH
Carboxylic acid and derivatives
Ester
:
see RCOOH and ROCl reaction
Synthesis :
O R' C NH2
Reaction
hydrolysis
R'
aminolysis
OH
H2O NH3
O C OR
H+ / OH[R]
O
+
H R' C
R'
LiAlH4 H3O
LiAlH4
H
H3O+
R'
OH
Carboxylic acid and derivatives
Amide
: see RCOOH, ROCl, RCOOCOR and RCOOR reaction :
H
hydrolysis
Synthesis
Reaction
O R'
-
R'
OH
C H
NH 2
H / OH
O R' C
H2O
LiAlH 4
[R]
NH 2
Nitrile
O R
C : sp hybridised Geometry : planar C-N : polar bond undergo nucleophilic addition reactions
RCN
C N R C OH
NuR
Nu C
+ -
Products Imine anion
Nitrile
Synthesis
1. From 1 alkyl halide
RCH2Br SN2
Na+ CN-
RCH2CN
2. Dehydration of 1 amide
SOCl2 or
NH2
R POCl3
CN
Nitrile
Reaction
H R H NH2
reduction
H3O+
LiAlH4 H2O
R NH2 O
H2O
H+ / OHR
O OH
H+ / OHhydrolysis O R R'
* See preparation of RCOOH
1. R'MgX 2. H3O+
Grignard reagent
Nitrile
N R R N C H
LiAlH4,
H C
2-
LiAlH4, ether H2O
ether Dianion Imine anion
H R C
H NH2
R R C R'
R'MgX
H2O
R O C R'
+ NH3
You might also like
- Synthesis of Drug - 2Document44 pagesSynthesis of Drug - 2'Nurirjawati ElRuri KawangNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes On AlcoholsDocument13 pagesRevision Notes On AlcoholsMuredzwa MuzendaNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Ethers and PhenolsDocument45 pagesAlcohols, Ethers and Phenolsshivam08No ratings yet
- Undergraduate organic reactions summaryDocument41 pagesUndergraduate organic reactions summaryKathyNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidDocument21 pagesCarboxylic AcidShalsabila NHNo ratings yet
- Chemsheets AS 1138 (Free Radical Substitution 2)Document2 pagesChemsheets AS 1138 (Free Radical Substitution 2)Yashkur Al-ShahwaniNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidDocument37 pagesCarboxylic Acidaman2611994_1920111580% (5)
- 12 Chemistry Keypoints Revision Questions Chapter 12Document20 pages12 Chemistry Keypoints Revision Questions Chapter 12sangam patraNo ratings yet
- Orgo Reaction SheetDocument9 pagesOrgo Reaction SheetKyle Broflovski100% (1)
- Microsoft PowerPoint - Aldehydes and KetonesDocument24 pagesMicrosoft PowerPoint - Aldehydes and KetonesAR LazagaNo ratings yet
- CHEM 215 F12 Chapter 13 Notes UMICHDocument13 pagesCHEM 215 F12 Chapter 13 Notes UMICHRoxanne IlaganNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Alcohols: Organic Chemistry, 7Document53 pagesReactions of Alcohols: Organic Chemistry, 7haha_le12100% (1)
- Carboxylic Acids: Structures, Nomenclature and ReactionsDocument41 pagesCarboxylic Acids: Structures, Nomenclature and ReactionsSazzad TanimNo ratings yet
- Naming Chemical Compounds WorksheetDocument4 pagesNaming Chemical Compounds WorksheetSam Jo100% (1)
- Chemistry AlcoholsDocument44 pagesChemistry AlcoholsSayan Kumar KhanNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonsDocument5 pagesHydrocarbonsClaire Danes Tabamo DagalaNo ratings yet
- Org Chem Alcohol Mechanisms From JasperseDocument22 pagesOrg Chem Alcohol Mechanisms From JasperseChloe JazminesNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidsDocument26 pagesCarboxylic Acidsapi-3734333100% (1)
- A Review of Organic Reactions and Reagents For Chemistry 551Document38 pagesA Review of Organic Reactions and Reagents For Chemistry 551Cris WRNo ratings yet
- Xii CH-7 Synopsis Chemistry CCWSDocument10 pagesXii CH-7 Synopsis Chemistry CCWSTanmay RawatNo ratings yet
- R-Cooh, R-Co H,: À Ant À VinegarDocument43 pagesR-Cooh, R-Co H,: À Ant À VinegarArvin MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl SubstitutionDocument30 pagesCarboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl SubstitutionSudrajatNo ratings yet
- Chem 121 Carbonyl CompsDocument36 pagesChem 121 Carbonyl CompsAbubakarNo ratings yet
- Org 13 PDFDocument40 pagesOrg 13 PDFrichardchan001No ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds: Aldehydes and KetonesDocument9 pagesCarbonyl Compounds: Aldehydes and KetonesCamille AdleNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds Aldehydes and KetonesDocument62 pagesCarbonyl Compounds Aldehydes and KetonesSubhabrata MabhaiNo ratings yet
- Aliphatic Organic SynthesisDocument30 pagesAliphatic Organic SynthesisrationalwikiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 NotesDocument43 pagesChapter 21 NotesTiffany YehNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid 13-02-2019Document29 pagesCarboxylic Acid 13-02-2019Sania KhanNo ratings yet
- Che 176 Carboxylic Acids-2Document67 pagesChe 176 Carboxylic Acids-2BalogunNo ratings yet
- Ch7Summary AlcoholDocument6 pagesCh7Summary AlcoholdanielmahsaNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids: Structure, Reactivity and DerivativesDocument73 pagesCarboxylic Acids: Structure, Reactivity and DerivativesNizarNo ratings yet
- Functional Group Transformation NotebookDocument78 pagesFunctional Group Transformation NotebookchedhedNo ratings yet
- AminesphenolsDocument15 pagesAminesphenolsSivakumar PonnusamyNo ratings yet
- 4.5 Carbonyl CompoundsDocument30 pages4.5 Carbonyl CompoundsimaniceguyNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles CH 20modifiedDocument35 pagesLec 2 Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles CH 20modifiedpolinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20: Introduction To Carbonyl Chemistry Organometallic Reagents Oxidation and ReductionDocument41 pagesChapter 20: Introduction To Carbonyl Chemistry Organometallic Reagents Oxidation and ReductionRavi JaiswalNo ratings yet
- McMurry 7e Ch19-23 Notes 5-29-07Document55 pagesMcMurry 7e Ch19-23 Notes 5-29-07Kay BradyNo ratings yet
- PPT Alcohol JadiDocument60 pagesPPT Alcohol JadiBudi AbutNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Properties of Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers and EpoxidesDocument14 pagesPreparation and Properties of Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers and Epoxidesitsleochandu21No ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and Their DerivativesDocument22 pagesCarboxylic Acids and Their DerivativesEugene OkpanteyNo ratings yet
- Aldehid Keton 08Document48 pagesAldehid Keton 08Priagung SetyawanNo ratings yet
- DerivativesDocument58 pagesDerivativesravi_balaskarNo ratings yet
- Alkanes: Methods of PreparationDocument16 pagesAlkanes: Methods of PreparationayushNo ratings yet
- Alcohols and Ethers CHM457Document51 pagesAlcohols and Ethers CHM457AIMAN IMAN SHAIFUDDINNo ratings yet
- Alcohols From Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation-Reduction: Central Linking Role of Alcohols and CarbonylsDocument12 pagesAlcohols From Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation-Reduction: Central Linking Role of Alcohols and CarbonylsAmihanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17Document35 pagesChapter 17Mohammed FarhanNo ratings yet
- ReductionDocument7 pagesReductionPranayNo ratings yet
- Pdf-Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument159 pagesPdf-Haloalkanes and HaloarenesOmkar Singh Shekhawat100% (2)
- Carboxylic Acid DerivativesDocument38 pagesCarboxylic Acid DerivativesshaikmguNo ratings yet
- Alcohol and PhenolDocument117 pagesAlcohol and Phenolsulihah12100% (2)
- Carboxylic AcidsDocument3 pagesCarboxylic AcidsDian Agus SetyawatiNo ratings yet
- MOC Alcohol RXN Map PDFDocument2 pagesMOC Alcohol RXN Map PDFNickOoPandeyNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Alcohol: Oxidation ReductionDocument18 pagesReactions of Alcohol: Oxidation ReductioncikguhafidzuddinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 SlidesDocument63 pagesChapter 8 SlidespoojaNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Carboxylic Acids 1. Oxidation of Primary AlcoholsDocument6 pagesSynthesis of Carboxylic Acids 1. Oxidation of Primary AlcoholsjlventiganNo ratings yet
- Word Problems in Organic ChemistryDocument70 pagesWord Problems in Organic ChemistryreghuuchihaNo ratings yet
- 202004032240234952abha Carbonyl Compounds PDFDocument14 pages202004032240234952abha Carbonyl Compounds PDFSrikeshav BNo ratings yet
- Organic 6 CDocument26 pagesOrganic 6 CDr.Rajarshi PatelNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument19 pagesAldehydes and KetonesVaibhav TarkasbandNo ratings yet
- Alcoholes 3Document47 pagesAlcoholes 3Дана ЧилибаеваNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document45 pagesChapter 7Wai Kwong ChiuNo ratings yet
- Change - Piezoelectric Technology ReviewDocument35 pagesChange - Piezoelectric Technology ReviewRajesh GoudNo ratings yet
- Reaxys Anonymous 20121108 002529 577Document11 pagesReaxys Anonymous 20121108 002529 577Luqman HakimNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 17 Chemical Equilibria 1Document128 pagesCHAPTER 17 Chemical Equilibria 1Luqman HakimNo ratings yet
- APA Style: American Psychological AssociationDocument24 pagesAPA Style: American Psychological AssociationLuqman HakimNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 9 DiodesDocument2 pagesKuliah 9 DiodesLuqman HakimNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document8 pagesLecture 1Luqman HakimNo ratings yet
- 03 - 01 - Curriculum Design of POC-II - III SemDocument6 pages03 - 01 - Curriculum Design of POC-II - III SemAtolkar AkshayNo ratings yet
- Moles Formulae Equations QuestionsDocument148 pagesMoles Formulae Equations QuestionsShifa RizwanNo ratings yet
- FórmulasDocument13 pagesFórmulasramichemNo ratings yet
- 95 Important Trends of Inorganic Chemistry for NEET 2021Document23 pages95 Important Trends of Inorganic Chemistry for NEET 2021NithinNo ratings yet
- Acid Ionic EqulbrmDocument21 pagesAcid Ionic EqulbrmsheenajerryNo ratings yet
- EXPE9Document8 pagesEXPE9K-yanVehraaYomomaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24 - Chemistry of Coordination CompoundsDocument15 pagesChapter 24 - Chemistry of Coordination CompoundsBarnishikha BoruahNo ratings yet
- Everything About Alkynes - Q&ADocument22 pagesEverything About Alkynes - Q&AJoostGoNo ratings yet
- Structure and conformation of lanthanide thiocyanate complexesDocument11 pagesStructure and conformation of lanthanide thiocyanate complexesadri_didinNo ratings yet
- KGianan Stem12 Chemistry1 (Chapter 3)Document6 pagesKGianan Stem12 Chemistry1 (Chapter 3)Kyle GiananNo ratings yet
- Modern Theories of Acids & Bases: The Arrhenius and Bronsted-Lowry TheoriesDocument48 pagesModern Theories of Acids & Bases: The Arrhenius and Bronsted-Lowry TheoriesAgung PratamaNo ratings yet
- What Is A CarbohydrateDocument2 pagesWhat Is A CarbohydrateChermona DanielNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Module 3 FinalDocument7 pagesChemistry Module 3 Finalangelo aquinoNo ratings yet
- SeparationsDocument8 pagesSeparationsHidayat KesumaNo ratings yet
- 27 Alcohol Phenol Ether Formula Sheets Getmarks AppDocument15 pages27 Alcohol Phenol Ether Formula Sheets Getmarks AppFLASH FFNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange Regeneration MethodsDocument9 pagesIon Exchange Regeneration MethodsarufatoNo ratings yet
- Alkali Metals and Halogens WorksheetDocument4 pagesAlkali Metals and Halogens Worksheetwebsite webNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Relative Strengths of Acids and BasesDocument1 pageFactors Affecting Relative Strengths of Acids and BasesRSL80% (5)
- MCQ - Coordination CompoundsDocument20 pagesMCQ - Coordination Compoundstharoonsays100% (1)
- Nitrogen and Its CompoundsDocument4 pagesNitrogen and Its Compoundssayma_akhter5074No ratings yet
- Appendix - Chemical Test, Routes of SynthesisDocument11 pagesAppendix - Chemical Test, Routes of Synthesisgoi_pin100% (4)
- Identification of ions in toothpasteDocument19 pagesIdentification of ions in toothpasteAKSHAY JAINNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl SubstitutionDocument107 pagesChapter 19 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl SubstitutionHani ShamsedeenNo ratings yet
- Biology 12 Biological Molecules Review KEYDocument5 pagesBiology 12 Biological Molecules Review KEYFeras TarawnehNo ratings yet
- CHEM1920 Lecture 10Document22 pagesCHEM1920 Lecture 10Kahelia CampbellNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acid Imp Questions Paper 4 SolutionsDocument5 pagesAldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acid Imp Questions Paper 4 SolutionsheartworkbylakshitaNo ratings yet