Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ASVAB Mechanical Comprehension Practice Test 4
Uploaded by
ASVABTestBankCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ASVAB Mechanical Comprehension Practice Test 4
Uploaded by
ASVABTestBankCopyright:
Available Formats
ASVAB Practice Test | ASVAB Test Bank
ASVAB Mechanical Comprehension Practice Test
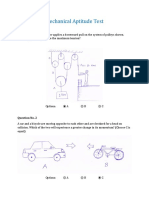
If A = 7 ft. and the green box weighs 10 lbs. what is the torque acting on the A side of this lever?
35 ft. lb.
1 ft. lb.
70 ft. lb.
140 ft. lb.
Which of the following is not a scalar quantity?
Length
Mass
Electric Charge
Force
What is the pressure of a water tank that measures 20 ft. square by 17 ft. deep?
106.1 psi
2.7 psi
1060.8 psi
26.5 psi
This image represents what configuration of pulley?
Movable
Block and Tackle
Simple
Fixed
If this lever is in equilibrium with an effort force of 15 ft. lb. at the blue arrow and a resistance force of 3 ft. lb. at the green box, what is its mechanical advantage?
0.8
0.2
0.05
0.1
Solutions
If A = 7 ft. and the green box weighs 10 lbs. what is the torque acting on the A side of this lever?
35 ft. lb.
1 ft. lb.
70 ft. lb.
140 ft. lb.
SOLUTION
For a lever, torque is weight x distance from the fulcrum which, in this case, is: 10 x 7 = 70 ft. lb.
Which of the following is not a scalar quantity?
Length
Mass
Electric Charge
Force
SOLUTION
A vector quantity has at least two forces at work against an object to cause movement while a scalar quantity has only one force at work. Scalar quantities have magnitude while vector quantities have magnitude and direction. Vector quantities include: velocity, force, momentum, spin, displacement. Scalar quantities include: speed, work, length, area, mass, energy, electric charge.
What is the pressure of a water tank that measures 20 ft. square by 17 ft. deep?
106.1 psi
2.7 psi
1060.8 psi
26.5 psi
SOLUTION
Pressure is equal to force per unit area or F . For water, F = w d where w is the weight of water and d its depth. Water weighs 62.4 F=wd
lb. so: ft.3 A
= 62.4
lb. ft.3
17ft.=1060.8
lb. ft.2
The area (A) of the pool is 20ft.20ft.= 400ft.2 so:
1060.8
lb.
P= F A
400 ft.2
ft.2
= 2.7 psi
This image represents what configuration of pulley?
Movable
Block and Tackle
Simple
Fixed
SOLUTION
A fixed pulley changes the direction of the effort but does not multiply effort. A movable pulley multiplies effort but does not change the direction of the effort. A block and tackle is a combination of one or more fixed and movable pulleys and both multiplies effort and changes the direction of the effort.
If this lever is in equilibrium with an effort force of 15 ft. lb. at the blue arrow and a resistance force of 3 ft. lb. at the green box, what is its mechanical advantage?
0.8
0.2
0.05
0.1
SOLUTION
Mechanical advantage (MA) is the ratio by which effort force relates to resistance force. If both forces are known, calculating MA is simply a matter of dividing resistance force by effort force: MA = Fr / Fe = 3 ft. / 15 ft. = 0.2 In this case, the mechanical advantage is less than one meaning that each unit of effort force results in just 0.2 units of resistance force. However, a third class lever like this isn't designed to multiply force like a first class lever. A third class lever is designed to multiply distance and speed at the resistance at a sacrifice of force at the resistance. Different lever styles have different purposes and multiply forces in different ways.
This sample test is from the ASVAB Test Bank Get unlimited unique online ASVAB practice tests at www.asvabtestbank.com
You might also like
- ASVAB Mechanical Comprehension Practice Test 2Document8 pagesASVAB Mechanical Comprehension Practice Test 2ASVABTestBank100% (1)
- ASVAB Mechanical Comprehension Practice Test 3Document8 pagesASVAB Mechanical Comprehension Practice Test 3ASVABTestBankNo ratings yet
- All in OneDocument65 pagesAll in OneSamuel AdamuNo ratings yet
- Media and Information LiteracyDocument31 pagesMedia and Information LiteracyLukman AndalNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Reasoning TestsDocument14 pagesMechanical Reasoning TestsNguyễn Huy Bình100% (2)
- Mechanical Aptitude & Spatial Relations Practice QuestionsFrom EverandMechanical Aptitude & Spatial Relations Practice QuestionsNo ratings yet
- ASVAB Electronics Information Practice Test 3Document5 pagesASVAB Electronics Information Practice Test 3ASVABTestBank100% (1)
- ASVAB General Science Practice Test 2Document5 pagesASVAB General Science Practice Test 2ASVABTestBank100% (1)
- Mechanical Spatial 222222222222Document236 pagesMechanical Spatial 222222222222destaw100% (2)
- ASVAB Mechanical Comprehension Practice Test 5Document5 pagesASVAB Mechanical Comprehension Practice Test 5ASVABTestBankNo ratings yet
- ASVAB Paragraph Comprehension Practice Test 4Document8 pagesASVAB Paragraph Comprehension Practice Test 4ASVABTestBank100% (1)
- ASVAB Mechanical Comprehension Practice Test 1Document5 pagesASVAB Mechanical Comprehension Practice Test 1ASVABTestBankNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Aptitude AnswersDocument8 pagesMechanical Aptitude Answerssurenthar100% (2)
- ASVAB General Science Practice Test 4Document5 pagesASVAB General Science Practice Test 4ASVABTestBankNo ratings yet
- 14 Mechanical Tests ExplainedDocument8 pages14 Mechanical Tests ExplainedSudip Sural0% (1)
- Mechanical Aptitude Test 080609Document63 pagesMechanical Aptitude Test 080609Soonyam100% (11)
- NTS Quantitative ReasoningDocument5 pagesNTS Quantitative Reasoningaftab awan100% (1)
- Mechanical AbilityDocument6 pagesMechanical AbilityMichelle Van Amenamen89% (9)
- Mechanical AptitudeDocument25 pagesMechanical AptitudedestawNo ratings yet
- Verbal Reasoning Tests Volume 2 DownloadDocument362 pagesVerbal Reasoning Tests Volume 2 DownloadAhmed FathyNo ratings yet
- Preparation Guide For Mechanical Reasoning TestsDocument4 pagesPreparation Guide For Mechanical Reasoning TestschevypickupNo ratings yet
- ASVAB Electronics Information Practice Test 4Document5 pagesASVAB Electronics Information Practice Test 4ASVABTestBankNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Aptitude TestDocument82 pagesMechanical Aptitude TestContinuous Improvement Projects100% (1)
- GSE Abstract Reasoning Test 3 - QuestionDocument9 pagesGSE Abstract Reasoning Test 3 - QuestionChidiebere Samuel OkogwuNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Reasoning ReviewDocument7 pagesMechanical Reasoning Reviewking gh100% (3)
- Levers, Pulleys, Gears and Springs: Examples of Questions on Basic Mechanical ConceptsDocument6 pagesLevers, Pulleys, Gears and Springs: Examples of Questions on Basic Mechanical ConceptsTewodros AbateNo ratings yet
- Apprenticeship Readiness Test No AnswersDocument16 pagesApprenticeship Readiness Test No AnswersMagendran MunisamyNo ratings yet
- Aptitude Testing BookletDocument11 pagesAptitude Testing BookletkunjapNo ratings yet
- Spatial Ability: Mechanical Aptitude TestsDocument46 pagesSpatial Ability: Mechanical Aptitude Testsrofiq100% (1)
- VST - Practice Booklet - 2016Document28 pagesVST - Practice Booklet - 2016stanley100% (1)
- Mechanical Aptitude QuestionsDocument4 pagesMechanical Aptitude Questionsgiridharadhayalan1267% (3)
- Analytical ReasoningDocument33 pagesAnalytical ReasoningrpramkmrNo ratings yet
- TCS 70 Patterns With SolutionsDocument43 pagesTCS 70 Patterns With SolutionsChandrakant PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- ASVAB Paragraph Comprehension Practice Test 5Document10 pagesASVAB Paragraph Comprehension Practice Test 5ASVABTestBank100% (1)
- ASVAB Shop Information Practice Test 2Document5 pagesASVAB Shop Information Practice Test 2ASVABTestBankNo ratings yet
- ASVAB Extra Sample Test 1Document84 pagesASVAB Extra Sample Test 1Al LeachNo ratings yet
- TCS QUESTION PAPER SET-1 ANALYZEDDocument10 pagesTCS QUESTION PAPER SET-1 ANALYZEDkarthikalam12.901235No ratings yet
- ASVAB Paragraph Comprehension Practice Test 2Document9 pagesASVAB Paragraph Comprehension Practice Test 2ASVABTestBank100% (2)
- Visual ReasoningDocument12 pagesVisual ReasoningsamdhathriNo ratings yet
- Mechanical, Spatial & Abstract ReasoningFrom EverandMechanical, Spatial & Abstract ReasoningRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Miller Analogies Practice Test 07Document3 pagesMiller Analogies Practice Test 07Ferrer BenedickNo ratings yet
- Sample Mechanical Reasoning TestDocument3 pagesSample Mechanical Reasoning Testkyloz100% (1)
- Mechanical Aptitude TestDocument5 pagesMechanical Aptitude TestPrabhjot Singh Sahi100% (5)
- 加拿大数学十年级 (高一) 省考模拟试题A PDFDocument38 pages加拿大数学十年级 (高一) 省考模拟试题A PDFTommyNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Advantage of Gears Explained in 40 StepsDocument20 pagesMechanical Advantage of Gears Explained in 40 StepsHamza-ur- RehmanNo ratings yet
- GAT General Practice TestDocument11 pagesGAT General Practice Testfameansari100% (1)
- Mechanical ComprehensionDocument14 pagesMechanical Comprehensiondanielhealy100% (6)
- Definite Integral (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandDefinite Integral (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Mechanical AbilityDocument25 pagesMechanical AbilityRonald Donor92% (13)
- AP Statistics Practice Test on Normal DistributionsDocument5 pagesAP Statistics Practice Test on Normal DistributionssnarkjazzoNo ratings yet
- Gremath Set08-1Document48 pagesGremath Set08-1api-3801230No ratings yet
- Aptitude Nonverbal REasoningDocument141 pagesAptitude Nonverbal REasoningbhar4tp100% (1)
- Inductive Reasoning Test1 SolutionsDocument11 pagesInductive Reasoning Test1 SolutionsSoonyamNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelDocument28 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelJason YapNo ratings yet
- 2010physics JJCDocument60 pages2010physics JJCcindySfyNo ratings yet
- 9702 s08 QP 1Document20 pages9702 s08 QP 1Pathmanathan NadesonNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Loadings: Prismatic BarDocument7 pagesFundamental Loadings: Prismatic BarAGEGTAMNo ratings yet
- Announcements: Today's ObjectivesDocument24 pagesAnnouncements: Today's ObjectivesLuke Ook ChoiNo ratings yet
- Physics 20 21Document23 pagesPhysics 20 21CarolusBorromeusWisnuNo ratings yet
- HWSteel StructureDocument18 pagesHWSteel StructureMohsinNo ratings yet
- ASVAB Electronics Information Practice Test 5Document5 pagesASVAB Electronics Information Practice Test 5ASVABTestBankNo ratings yet
- ASVAB Electronics Information Practice Test 4Document5 pagesASVAB Electronics Information Practice Test 4ASVABTestBankNo ratings yet
- ASVAB Electronics Information Practice Test 2Document5 pagesASVAB Electronics Information Practice Test 2ASVABTestBankNo ratings yet
- ASVAB Shop Information Practice Test 3Document5 pagesASVAB Shop Information Practice Test 3ASVABTestBankNo ratings yet
- ASVAB Shop Information Practice Test 5Document6 pagesASVAB Shop Information Practice Test 5ASVABTestBankNo ratings yet
- ASVAB Electronics Information Practice Test 1Document5 pagesASVAB Electronics Information Practice Test 1ASVABTestBankNo ratings yet
- ASVAB Electronics Information Practice Test 3Document5 pagesASVAB Electronics Information Practice Test 3ASVABTestBank100% (1)
- ASVAB Shop Information Practice Test 2Document5 pagesASVAB Shop Information Practice Test 2ASVABTestBankNo ratings yet
- ASVAB Paragraph Comprehension Practice Test 1Document8 pagesASVAB Paragraph Comprehension Practice Test 1ASVABTestBankNo ratings yet
- ASVAB Paragraph Comprehension Practice Test 3Document9 pagesASVAB Paragraph Comprehension Practice Test 3ASVABTestBank100% (1)
- ASVAB Paragraph Comprehension Practice Test 4Document8 pagesASVAB Paragraph Comprehension Practice Test 4ASVABTestBank100% (1)
- ASVAB Paragraph Comprehension Practice Test 2Document9 pagesASVAB Paragraph Comprehension Practice Test 2ASVABTestBank100% (2)
- ASVAB General Science Practice Test 1Document5 pagesASVAB General Science Practice Test 1ASVABTestBankNo ratings yet
- ASVAB Paragraph Comprehension Practice Test 5Document10 pagesASVAB Paragraph Comprehension Practice Test 5ASVABTestBank100% (1)
- ASVAB Arithmetic Reasoning Practice Test 3Document5 pagesASVAB Arithmetic Reasoning Practice Test 3ASVABTestBankNo ratings yet
- ASVAB Mechanical Comprehension Practice Test 5Document5 pagesASVAB Mechanical Comprehension Practice Test 5ASVABTestBankNo ratings yet
- ASVAB Mechanical Comprehension Practice Test 1Document5 pagesASVAB Mechanical Comprehension Practice Test 1ASVABTestBankNo ratings yet
- ASVAB Arithmetic Reasoning Practice Test 4Document5 pagesASVAB Arithmetic Reasoning Practice Test 4ASVABTestBank0% (1)
- ASVAB General Science Practice Test 4Document5 pagesASVAB General Science Practice Test 4ASVABTestBankNo ratings yet
- ASVAB General Science Practice Test 5Document5 pagesASVAB General Science Practice Test 5ASVABTestBank100% (1)
- ASVAB General Science Practice Test 3Document5 pagesASVAB General Science Practice Test 3ASVABTestBankNo ratings yet
- ASVAB Arithmetic Reasoning Practice Test 5Document6 pagesASVAB Arithmetic Reasoning Practice Test 5ASVABTestBankNo ratings yet
- ASVAB General Science Practice Test 2Document5 pagesASVAB General Science Practice Test 2ASVABTestBank100% (1)
- ASVAB Arithmetic Reasoning Practice Test 2Document6 pagesASVAB Arithmetic Reasoning Practice Test 2ASVABTestBankNo ratings yet
- ASVAB Arithmetic Reasoning Practice Test 1Document7 pagesASVAB Arithmetic Reasoning Practice Test 1ASVABTestBank100% (2)
- ASVAB Word Knowledge Practice Test 2Document5 pagesASVAB Word Knowledge Practice Test 2ASVABTestBankNo ratings yet
- ASVAB Word Knowledge Practice Test 5Document5 pagesASVAB Word Knowledge Practice Test 5ASVABTestBankNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Course Code: 4300001: Page 1 of 10Document10 pagesMathematics Course Code: 4300001: Page 1 of 10jigarNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICS-Physics 9Document25 pagesINTRODUCTION TO PHYSICS-Physics 9Onur YavuzcetinNo ratings yet
- Tut Fsurf V80R2.0 EngDocument61 pagesTut Fsurf V80R2.0 EngJavier Federico AllendeNo ratings yet
- Dynamic stiffness parameters better predict fluid instabilityDocument6 pagesDynamic stiffness parameters better predict fluid instabilitysalkan_rahmanovic810No ratings yet
- Presentation About Edge DetectionDocument23 pagesPresentation About Edge DetectionUvasre SundarNo ratings yet
- Tugas 1 - VektorDocument5 pagesTugas 1 - VektorDiva Mustika Takhiyah divamustika.2021No ratings yet
- Advanced Physics Nick Lucid Jan 2023Document529 pagesAdvanced Physics Nick Lucid Jan 2023Khashayar KhavariNo ratings yet
- Orthogonal Curvilinear Coordinate SystemsDocument78 pagesOrthogonal Curvilinear Coordinate SystemsJorge ReyesNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes Class 11 Chapter 4 Motion in A Plane Part 1Document8 pagesPhysics Notes Class 11 Chapter 4 Motion in A Plane Part 1ShashankAnil50% (2)
- Analysis of Complex Statistical Variables into Principal ComponentsDocument25 pagesAnalysis of Complex Statistical Variables into Principal ComponentsAhhhhhhhNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument40 pagesProjectile MotionTrilok AkhaniNo ratings yet
- Physics 71Document9 pagesPhysics 71nik-koNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument345 pagesPhysicsjoanthanbiederman100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Engineering MechanicsDocument19 pagesFundamentals of Engineering MechanicsayingbaNo ratings yet
- Motion in PlaneDocument20 pagesMotion in PlanekartikthedashingNo ratings yet
- IB MTHHL 2007oxfordtx 12VctrTechDocument17 pagesIB MTHHL 2007oxfordtx 12VctrTechKinkei ChooNo ratings yet
- 5 - 6 - Intersection of Plane Ad Lines and AnglesDocument11 pages5 - 6 - Intersection of Plane Ad Lines and AnglesSudibyo GunawanNo ratings yet
- FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF RIGID BODY MECHANICSDocument14 pagesFUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF RIGID BODY MECHANICSTarvesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Step-by-step guide to Principal Component Analysis (PCADocument7 pagesStep-by-step guide to Principal Component Analysis (PCAVaibhav YadavNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument288 pagesUntitledBaishali SurNo ratings yet
- PHYS 1100 Vector SolutionsDocument13 pagesPHYS 1100 Vector SolutionsAlameenNo ratings yet
- New Syllabus Mathematics 3 & 4 (6Th Edition) Specific Instructional Objectives (Sios) For Normal (Academic) LevelDocument7 pagesNew Syllabus Mathematics 3 & 4 (6Th Edition) Specific Instructional Objectives (Sios) For Normal (Academic) LevelVincents Genesius EvansNo ratings yet
- Ste Adv Phys q1 Las 1 9Document46 pagesSte Adv Phys q1 Las 1 9KonichiwichiNo ratings yet
- Vectors Practice Questions NameDocument1 pageVectors Practice Questions NameEngr Muhammad MubeenNo ratings yet
- Book Short Ans 1 FSC Physics Text Book Part 1Document31 pagesBook Short Ans 1 FSC Physics Text Book Part 1Adnan Ali50% (2)
- Mathematics concepts under 40 charsDocument52 pagesMathematics concepts under 40 charsSaishi XiongNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Syllabus 10-12Document37 pagesMathematics Syllabus 10-12Edwin DayakarNo ratings yet
- Calculate Moment of a Force About Lines and AxesDocument29 pagesCalculate Moment of a Force About Lines and AxesHannahSamonteNo ratings yet
- Isu Module Subject: CE 223 and Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDocument17 pagesIsu Module Subject: CE 223 and Dynamics of Rigid BodieseysNo ratings yet
- CS602 Midterm Objective (MCQ'Z) Solved With Reference: by Well Wisher (Aqua Leo)Document12 pagesCS602 Midterm Objective (MCQ'Z) Solved With Reference: by Well Wisher (Aqua Leo)blanooba231No ratings yet