Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HSDPA Code Resource Allocation Methods
Uploaded by
excaliburslvOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HSDPA Code Resource Allocation Methods
Uploaded by
excaliburslvCopyright:
Available Formats
HSDPA Code Resource Allocation
Channelization codes are constant resource consisting of the following three parts 1. channelization codes for HS-PDSCH 2. channelization codes for Common channels and HS-SCCH 3. channelization codes for DPCH The resources are reserved for the common channels and the HS-SCCH. The parameter of the codes reserved for the HS-SCCH can be configured. The codes of the HS-PDSCH physical channel can be allocated in three ways :
Static HSDPA code Allocation
Static HS-PDSCH code allocation spreading factor = 16 allocate continuously
Static HS-SCCH code allocation Spreading factor = 128 allocate with common channel
RNC Controlled dynamic allocation
In the RNC-controlled dynamic allocation, the RNC adjusts the reserved HSPDSCH codes according to the real-time usage status of the codes Configure the maximum and minimum numbers of codes available for HS-PDSCH on the RNC LMT. The codes between the two parameters are called shared codes The RNC periodically monitors how the code resource is used and decides to extend or reduce the codes reserved for the HS-PDSCH
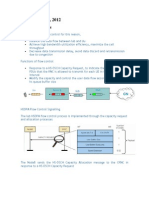
When allocating the code resource triggered by radio link setup or radio link deletion, the RNC will extend the codes reserved for the HS-PDSCH if the following cases are fulfilled: If in cell's code tree there is at least one code can be reserved and this code's SF is equal to or less than the Cell SF reserved threshold, NodeB will try to increase HS-PDSCH code number Among shared codes, the code which neighbors to the reserved codes for the HSPDSCH is idle, which can be attained by reshuffling the cell code resource
the solid represent the occupied codes and the circles represent the idle codes Reducing the Codes Reserved for HS-PDSCH When allocating the code resources triggered by radio link setup, the RNC will reallocate one of the shared codes reserved for HS-PDSCH to DPCH if the minimum SF among free codes is larger than the Cell SF reserved threshold. The code number of the reallocated code should be the minimum.
the solid represent the occupied codes and the circles represent the idle codes The code number for HS-SCCH is parameter sets the number of HS-SCCH codes available in a cell and can be set from 1 to 15 Parameter Alocate code mode can used to choose the mode of allocating HSPDSCH codes in the RNC, there are two mode, static and dynamic The number of HS-PDSCH codes available in cell can be added from 1 - 15 codes, and only when allocate code mode is set to manual. If the allocate code mode is set to automatic, the parameter maximum number of HS-PDSCH codes in a cell can set.
NodeB - Controlled dynamic allocation
NodeB-controlled dynamic allocation allows the NodeB to use the HS-PDSCH codes that are statically allocated by the RNC. Besides, the NodeB can dynamically allocate the idle codes of the current cell to the HS-PDSCH channel The NodeB periodically detects the SF16 codes apart from the RNC-allocated HSPDSCH codes every 2 ms. If the codes or sub-codes are allocated by the RNC to the DCH or common channels, they are identified as occupied. Otherwise, they are identified as unoccupied. Therefore, the HS-PDSCH codes available for the HS-PDSCH channel include the codes allocated by the RNC and those consecutive and unoccupied SF16 codes NodeB-controlled dynamic allocation For example, if the RNC allocates five codes to the NodeB, that is, No.11 to 15 SF16 codes are allocated to the HS-PDSCH. Suppose in a 2 ms TTI, No. 0 to 5 SF16 codes are allocated to the DCH and common channels. No. 0 to 5 SF16 codes are occupied. Therefore, in the current TTI, the HS-PDSCH can use No. 6 to 15 SF16 codes If the DCH codes allocated by the RNC are temporarily occupied by the HS-PDSCH during the setup of radio links, the NBAP message returned to the RNC indicates that the radio link is set up successfully. From the next 2 ms TTI, the HS-PDSCH no longer uses these codes until they are released from the DCH
by ajusady
You might also like
- Keysign N Scales PDFDocument19 pagesKeysign N Scales PDFRuf MNo ratings yet
- Protel DXP BeginnersDocument38 pagesProtel DXP BeginnersandreskapazNo ratings yet
- Learn basic Mirpuri phrases and vocabularyDocument9 pagesLearn basic Mirpuri phrases and vocabularyInder M NagiNo ratings yet
- Proto AlgonquianDocument5 pagesProto Algonquianlibrary364No ratings yet
- Rare Yoga Part 3Document13 pagesRare Yoga Part 3VikasNo ratings yet
- 37222090-Huawei-WCDMA-HSDPA-Parameters Huawei)Document68 pages37222090-Huawei-WCDMA-HSDPA-Parameters Huawei)Faizal Jamaludeen100% (2)
- GSM Channel & TRX Mapping: 1 BTS, 3 Cells, 4 TRX/CellDocument2 pagesGSM Channel & TRX Mapping: 1 BTS, 3 Cells, 4 TRX/Cellexcaliburslv92% (12)
- 03 - Importing GPEHDocument6 pages03 - Importing GPEHmitmap123No ratings yet
- Communicating Data Through ChartsDocument38 pagesCommunicating Data Through ChartsTrevor Warren100% (2)
- For HSDPA Maximum Cell ThroughputDocument3 pagesFor HSDPA Maximum Cell ThroughputLeonardo CamiloNo ratings yet
- TCH Drop Analysis: Change & ObserveDocument8 pagesTCH Drop Analysis: Change & ObserveLenny MajawNo ratings yet
- COMMSCOPE ActiveantennaDocument18 pagesCOMMSCOPE ActiveantennaGaurav Raghuvanshi100% (1)
- Channel Elements Usage MonitoringDocument10 pagesChannel Elements Usage MonitoringdudulzsNo ratings yet
- 3G UL-DL Capacity Monitoring V1.0Document55 pages3G UL-DL Capacity Monitoring V1.0Denmark Wilson100% (1)
- Link Budget Calculation Example For UMTSDocument5 pagesLink Budget Calculation Example For UMTSexcaliburslvNo ratings yet
- Link Budget Calculation Example For UMTSDocument5 pagesLink Budget Calculation Example For UMTSexcaliburslvNo ratings yet
- Lingoda ClassDocument28 pagesLingoda ClassGareth GriffithsNo ratings yet
- How To Improve Code and DL Power Congestion - HuaweiDocument12 pagesHow To Improve Code and DL Power Congestion - HuaweiSandeepNo ratings yet
- Activating HSDPA 15 CodesDocument2 pagesActivating HSDPA 15 Codesdjemai cherguiNo ratings yet
- Huawei Proposes Code Optimization to Reduce Network CongestionDocument15 pagesHuawei Proposes Code Optimization to Reduce Network CongestionSandeepNo ratings yet
- CE Cong Issue Troubleshooting Step and Guidence - Good RefDocument6 pagesCE Cong Issue Troubleshooting Step and Guidence - Good RefKurnia Chris Pradana WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- CountersDocument36 pagesCountersShejin RaghavanNo ratings yet
- Direct HS-DSCH To DCH Switch NokiaDocument3 pagesDirect HS-DSCH To DCH Switch NokiazeroNo ratings yet
- Initial Tuning and OptimizationDocument34 pagesInitial Tuning and OptimizationNicolas AttisNo ratings yet
- Layered Paging in Idle ModeDocument2 pagesLayered Paging in Idle Modemoses100% (1)
- Solution For IUB CongestionDocument1 pageSolution For IUB CongestionJason Payne100% (1)
- NSN - WCDMA - HS Throughput Improvement PDFDocument8 pagesNSN - WCDMA - HS Throughput Improvement PDFraghavendra1595No ratings yet
- GSM - UMTS Cell Reselection & HandoverDocument11 pagesGSM - UMTS Cell Reselection & Handovercool_virginboyNo ratings yet
- 3g Huawei NoteDocument28 pages3g Huawei NotehendraNo ratings yet
- Huawei 3G Parameter Setting Guideline V2.1: Huawei RNP/RNO TeamDocument11 pagesHuawei 3G Parameter Setting Guideline V2.1: Huawei RNP/RNO TeamemilsonacruzNo ratings yet
- Radio Network Accessibility (NBH) : SN Kpi Uom GranularityDocument158 pagesRadio Network Accessibility (NBH) : SN Kpi Uom GranularityNikan AminiNo ratings yet
- Load SharingDocument6 pagesLoad SharingDana YasserNo ratings yet
- User Experience Improvement For Lightly Loaded Cells (RAN18.1 - 01)Document165 pagesUser Experience Improvement For Lightly Loaded Cells (RAN18.1 - 01)Abdel SbeitiNo ratings yet
- GBO - 024 - E1 - 1 2G-3G Cell Reselection & Handover-39Document39 pagesGBO - 024 - E1 - 1 2G-3G Cell Reselection & Handover-39Clive Mangwiro100% (1)
- RRCDocument1 pageRRCAlselawi AhmadNo ratings yet
- CSFBSRBRate ParameterDocument4 pagesCSFBSRBRate Parameterawansn1984No ratings yet
- Huawei ParametersDocument52 pagesHuawei ParametersalemuNo ratings yet
- Packet Scheduler OptimisationDocument9 pagesPacket Scheduler OptimisationArmenayvNo ratings yet
- High Speed DL FachDocument23 pagesHigh Speed DL FachSumon Kumar BiswasNo ratings yet
- LTE throughput counters by network sectionDocument6 pagesLTE throughput counters by network sectionvishalkavi18No ratings yet
- RN31672EN30GLA1 - RANPAR Combined - Parameter - Configuration - v1.0 - RU40Document38 pagesRN31672EN30GLA1 - RANPAR Combined - Parameter - Configuration - v1.0 - RU40khanhnam0509No ratings yet
- 3G Parameter Template RU30 T-Mobile v3Document63 pages3G Parameter Template RU30 T-Mobile v3ArhamNo ratings yet
- Idle Mode StrategyDocument13 pagesIdle Mode StrategyMahmoud Anshasi100% (1)
- Huawei Parameters v60 v18c01b071 090607Document905 pagesHuawei Parameters v60 v18c01b071 090607wijayadny0% (1)
- 2G-Ericsson Counter SummaryDocument4 pages2G-Ericsson Counter Summarykhurramsh3100% (1)
- Multi-RAT 2G parameter functions for QSI, FDDQMIN, FDDQOFF, FDDQMINOFF and FDDRSCPMINDocument2 pagesMulti-RAT 2G parameter functions for QSI, FDDQMIN, FDDQOFF, FDDQMINOFF and FDDRSCPMINTariq MuhammadNo ratings yet
- 3g Optimization v2 PDFDocument50 pages3g Optimization v2 PDFPutri Dorotea TouorNo ratings yet
- Timeslot (2G) Vs CE (3G)Document5 pagesTimeslot (2G) Vs CE (3G)Raman Bal100% (10)
- 3G LayeringDocument12 pages3G LayeringTina HidayatNo ratings yet
- CS Call Drop Counter: 1. Relationship of Different CountersDocument4 pagesCS Call Drop Counter: 1. Relationship of Different Countersarupsaha81100% (1)
- ALARM DefinitionsDocument2 pagesALARM DefinitionsbasswardNo ratings yet
- Eul ParametersDocument2 pagesEul Parametersnassr_ismailNo ratings yet
- Random Access Channel in 3GDocument9 pagesRandom Access Channel in 3GkisvishalNo ratings yet
- Mute CallDocument12 pagesMute CallAnonymous zMWwN7aYNo ratings yet
- DL Enhanced Cell - FachDocument2 pagesDL Enhanced Cell - FachMuhammad RizkiNo ratings yet
- Low CSSR 3GDocument3 pagesLow CSSR 3GKhoa Duy NguyenNo ratings yet
- ISHO Parameter SettingDocument10 pagesISHO Parameter Settingzc_eeNo ratings yet
- RN3158 RANKPI Training: Radio Access BearerDocument77 pagesRN3158 RANKPI Training: Radio Access BearerAliNSNNo ratings yet
- Optimize Dual Band Network PerformanceDocument24 pagesOptimize Dual Band Network PerformanceJim RamosNo ratings yet
- Scrambling Code PlanningDocument1 pageScrambling Code PlanningMahesh B Kadam100% (1)
- UMTS Multi Carrier Strategy and Configuration 20100622Document44 pagesUMTS Multi Carrier Strategy and Configuration 20100622arupsaha81No ratings yet
- Cross-Layer Resource Allocation in Wireless Communications: Techniques and Models from PHY and MAC Layer InteractionFrom EverandCross-Layer Resource Allocation in Wireless Communications: Techniques and Models from PHY and MAC Layer InteractionNo ratings yet
- CAMEL: Intelligent Networks for the GSM, GPRS and UMTS NetworkFrom EverandCAMEL: Intelligent Networks for the GSM, GPRS and UMTS NetworkRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- HSDPA Code Resource Allocation Methods for Static, RNC, and NodeB ControlDocument4 pagesHSDPA Code Resource Allocation Methods for Static, RNC, and NodeB ControlNguyenDucTaiNo ratings yet
- Code Optimization Suggestions: Security LevelDocument15 pagesCode Optimization Suggestions: Security LevelSandeepNo ratings yet
- Hsdpa Code AllocationDocument2 pagesHsdpa Code AllocationShejin RaghavanNo ratings yet
- HS-PDSCH Technical SpecificationsDocument2 pagesHS-PDSCH Technical Specificationsronics123No ratings yet
- 12 Wcdma Hsdpa RRM and ParametersDocument67 pages12 Wcdma Hsdpa RRM and ParameterskltowerNo ratings yet
- Ebooks 7400130 enDocument51 pagesEbooks 7400130 enexcaliburslvNo ratings yet
- AISG ES-RAB V 2.1.0Document21 pagesAISG ES-RAB V 2.1.0excaliburslvNo ratings yet
- JVC Roku TV Spec LT-43MAW595Document1 pageJVC Roku TV Spec LT-43MAW595excaliburslvNo ratings yet
- Zap08007 AnrDocument9 pagesZap08007 AnrexcaliburslvNo ratings yet
- Oracle Fast Formula 11iDocument206 pagesOracle Fast Formula 11iAvinash100% (11)
- Customer Information Antenna Characteristics With Clamps V3Document2 pagesCustomer Information Antenna Characteristics With Clamps V3excaliburslvNo ratings yet
- 64 QamDocument3 pages64 QamexcaliburslvNo ratings yet
- Channel Mapping in UMTSDocument4 pagesChannel Mapping in UMTSexcaliburslvNo ratings yet
- HSDPA Flow Control for Bandwidth EfficiencyDocument2 pagesHSDPA Flow Control for Bandwidth EfficiencyexcaliburslvNo ratings yet
- UMTS Link Budget Basic ParameterDocument7 pagesUMTS Link Budget Basic ParameterexcaliburslvNo ratings yet
- EGPRS 2 Evolution Reach Maximum 1.2 MbpsDocument4 pagesEGPRS 2 Evolution Reach Maximum 1.2 MbpsexcaliburslvNo ratings yet
- Energy Consumption On Smart PhoneDocument2 pagesEnergy Consumption On Smart PhoneexcaliburslvNo ratings yet
- PA Aplications UMTSDocument6 pagesPA Aplications UMTSexcaliburslvNo ratings yet
- Policy in UMTS IEEE NetworkDocument17 pagesPolicy in UMTS IEEE NetworkexcaliburslvNo ratings yet
- 900mhz RefarmingDocument3 pages900mhz RefarmingrejreyesNo ratings yet
- Understanding HSDPADocument3 pagesUnderstanding HSDPAMohamed MoujtabaNo ratings yet
- 900mhz RefarmingDocument3 pages900mhz RefarmingrejreyesNo ratings yet
- Oracle Fast Formula 11iDocument206 pagesOracle Fast Formula 11iAvinash100% (11)
- Expressing - About To - With - Jiuyao - Chinese Grammar Wiki PDFDocument2 pagesExpressing - About To - With - Jiuyao - Chinese Grammar Wiki PDFMILKII TubeNo ratings yet
- Radamel Falcao GarcíaDocument4 pagesRadamel Falcao GarcíaEliud ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Design BooksDocument3 pagesDesign BooksAnuja shNo ratings yet
- Meeting people in ITDocument8 pagesMeeting people in ITDavid ValenzNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work - P2Document7 pagesScheme of Work - P2Glory At ร.ร.กลอรี่No ratings yet
- 2 Mathematics For Social Science-1-1Document58 pages2 Mathematics For Social Science-1-1ሀበሻ EntertainmentNo ratings yet
- New Benchmark Instances For The Capacitated Vehicle Routing ProblemDocument32 pagesNew Benchmark Instances For The Capacitated Vehicle Routing ProblemAditya RestuajiNo ratings yet
- Multicon User Manual: Revision: TDocument99 pagesMulticon User Manual: Revision: TRaj BenNo ratings yet
- Once There Were Wolves - AnalysisDocument5 pagesOnce There Were Wolves - AnalysisДаниела ИсаевичNo ratings yet
- Ghana Communication Tech University English Course OutlineDocument6 pagesGhana Communication Tech University English Course Outlineshalil hamidNo ratings yet
- Dictionary Skills Review: List 1 List 2Document2 pagesDictionary Skills Review: List 1 List 2Louise YongcoNo ratings yet
- Philippine LiteratureDocument2 pagesPhilippine LiteratureSuzzayne ButengNo ratings yet
- The Notebook Interface: Wolfram Mathematica (Usually Termed Mathematica) Is A Modern Technical Computing SystemDocument9 pagesThe Notebook Interface: Wolfram Mathematica (Usually Termed Mathematica) Is A Modern Technical Computing SystemDeenNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 Lesson 4 Grade 8Document3 pagesQuarter 2 Lesson 4 Grade 8JAHMAE ARTIAGANo ratings yet
- Group Persuasive Speech Evaluation Form: The Introduction Is EffectiveDocument1 pageGroup Persuasive Speech Evaluation Form: The Introduction Is EffectivePrateekNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Number Theory Notes Anwar Khan PDFDocument110 pagesAlgebraic Number Theory Notes Anwar Khan PDFSikandar KhanNo ratings yet
- Noman Ul Haq - Galileo-Goes-to-Jail-and-Other-Myths-about-Science-and-ReligionDocument8 pagesNoman Ul Haq - Galileo-Goes-to-Jail-and-Other-Myths-about-Science-and-ReligionHuzaifa AliNo ratings yet
- Paths, Rechability and Connectedness (Lecture Notes)Document10 pagesPaths, Rechability and Connectedness (Lecture Notes)YASH PRAJAPATINo ratings yet
- Abaqus, How Can I Use An Output Temperature in Next Job?: More Questions, Even More AnswersDocument3 pagesAbaqus, How Can I Use An Output Temperature in Next Job?: More Questions, Even More AnswersJA KNo ratings yet
- SSD Buying Guide ListDocument18 pagesSSD Buying Guide Listriski arrixki2No ratings yet
- Quick Start Guide - DSE4520 MKII Multi-LanguageDocument37 pagesQuick Start Guide - DSE4520 MKII Multi-LanguageCJCONSTANTENo ratings yet
- ISI - Sequence and SeriesDocument44 pagesISI - Sequence and SeriesRajarshiNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD System VariablesDocument92 pagesAutoCAD System VariablesganeshprabhuNo ratings yet
- Moog Animatics SmartMotor DevelopersGuide Manual enDocument948 pagesMoog Animatics SmartMotor DevelopersGuide Manual enAsh KetchumNo ratings yet