Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan
Uploaded by
Sheng GosepOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Care Plan
Uploaded by
Sheng GosepCopyright:
Available Formats
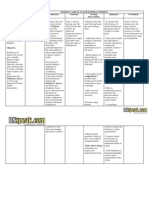
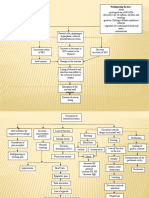
NURSING CARE PLAN ASSESSMENT Subjective: Nahihirapan akong kumain as verbalized by the patient.
Objective: Body weight: 20 % below BMI Pale mucus membrane Poor muscle tone Decrease appetite. Weight: 49 kgs. Height: 54 NURSING DIAGNOSIS Imbalance Nutrition: Less than body requirement related to inability to ingest foods. SCIENTIFIC EXPLANATION PLANNING After 2 months of nursing intervention the client will: 1. Progressively gain weight towards desired goals. 2. Weight within normal range for height and weight. 3. Consume adequate nourishment. 4. Be free of signs of malnutrition. INTEVENTION Monitor vital signs. Determine the ability to chew, swallow and tolerate food. Assess weight, age, and body build. Note total daily intake. Assist in developing individualized regimen. Provide diet modifications. (moderate protein, increase calories) RATIONALE For baseline data. EVALUATION
Provides comparative baseline. To reveal changes that should be made in clients dietary intake. To correct and control underlying factors.
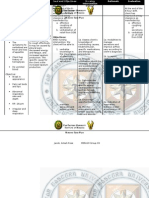
ASSESSMENT Subjective: Hirap akong huminga as verbalized by the patient. Objective: Dyspnea. Cyanosis. RR=24 cpm Capillary refill= 3 secs With 02 inhalation via nasal cannula 2 LPM. Easy fatigability. Use of accessory muscles for breathing.
NURSING DIAGNOSIS Ineffective airway clearance related to decreased ability to cough and swallow secondary to muscle weakness.
SCIENTIFIC EXPLANATION
PLANNING After 1 hour of nursing intervention the client will be able to:
INTEVENTION
RATIONALE
EVALUATION
Monitor vital signs. For baseline data. Assess for airway obstruction. Monitor respiratory patterns. 1. Maintain in patent Position the client airway at all to optimized times. respiration. 2. Identify and avoid Elevate the head of To take advantage specific factors the bed or change of gravity that inhibit position every 2 decreasing effective airway hours. pressure on the clearance. Encourage deepdiaphragm. breathing and coughing exercises. Give expectorants/ bronchodilators as ordered. Observe signs of To assess changes respiratory distress. and to note complications.
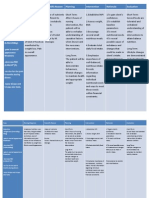
ASSESSMENT Subjective: Nanghihina ako, konting galaw o lakad lang mdali akong mpagod as verbalized by the patient. Objective: Limited range of motion. Limited ability to perform gross fine/ motor skills. Difficulty turning. Slow and uncoordinated movement. Muscle strength=2/5
NURSING DIAGNOSIS Impaired Physical Mobility related to neuromuscular impairment.
SCIENTIFIC EXPLANATION
PLANNING After 2 months of nursing intervention the client will be able to: 1. Perform activity independently in ADLs such as: Grooming Feeding Ambulating Communicating Toileting. 2. Demonstrate techniques that enable resumption of activities. 3. Maintain position of function and skin integrity. 4. Maintain in normal or increase strength.
INTEVENTION Monitor vital signs. Determine degree of immobility. Assist client to reposition self every 2 hours. Assist in doing passive assistive range of motion exercises to all extremities. Schedule activities with adequate rest periods during the day. Assist client to learn safety measures. Keep side rails up and bed in low position.
RATIONALE For baseline data. To assess functional ability. To promote optimal level of function and prevent complications. To reduce fatigue.
EVALUATION
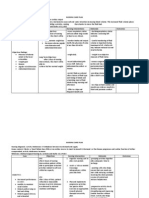
ASSESSMENT Subjective: Nahihirapan akong ngumuya at lumunok as verbalized by the patient. Objective: Dysphagia. Difficulty of chewing. Unable to consume the meal served. Record current weight.
NURSING DIAGNOSIS Impaired swallowing related to neuromuscular impairment.
SCIENTIFIC EXPLANATION
PLANNING After 2 months of nursing intervention the client will be able to: 1.
INTEVENTION Monitor vital signs. Assess sensoryperceptual status.
RATIONALE For baseline data. To assess contributing factors and degree of impairment.
EVALUATION
Evaluate ability to swallow using crushed ice or small sips of water. Identify individual factors that can precipitate aspiration. Raise head to 90 degree angle with head in anatomic alignment and slightly flexed forward during feeding. Position patient on the unaffected side when feeding. Encourage rest To minimize period before fatigue. meals. Allow ample time for eating.
You might also like
- Essentials of Internal MedicineDocument832 pagesEssentials of Internal MedicineEmanuelMC100% (74)
- LaryngitisDocument24 pagesLaryngitisfatihahannisahumaira100% (1)
- DM Care PlanDocument9 pagesDM Care PlanHarish Kumar KumawatNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDocument3 pagesRespiratory and Circulatory SystemsJeffrey Costan100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for a Diabetic Patient with Dehydration and FatigueDocument9 pagesNursing Care Plan for a Diabetic Patient with Dehydration and FatigueDanica Salinas100% (1)
- Anatomy Supertable PDFDocument14 pagesAnatomy Supertable PDFAlex Ondevilla100% (1)
- Diabetes Mellitus NCPDocument7 pagesDiabetes Mellitus NCPjfgnzls182892% (12)
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPAbbie TantengcoNo ratings yet
- Self Care DeficitDocument4 pagesSelf Care DeficitEllaine RamirezNo ratings yet
- MI Chest Pain AssessmentDocument5 pagesMI Chest Pain AssessmentDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaNo ratings yet
- NGT Enteral Feeding CareDocument8 pagesNGT Enteral Feeding CareSheng GosepNo ratings yet
- NGT Enteral Feeding CareDocument8 pagesNGT Enteral Feeding CareSheng GosepNo ratings yet
- Intermittent Fasting For Women: A Beginner’s Transformation Made EasyFrom EverandIntermittent Fasting For Women: A Beginner’s Transformation Made EasyNo ratings yet
- Cha 24 Tortora Respiratory SystemDocument12 pagesCha 24 Tortora Respiratory Systemsrinivas ceoNo ratings yet
- Optional (AEMT), Optional (Paramedic)Document76 pagesOptional (AEMT), Optional (Paramedic)Mark ReinhardtNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPbjhilarioNo ratings yet
- Enteral Feeding Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesEnteral Feeding Nursing Care PlanCyrus De Asis93% (15)
- NCLEX Questions PulmDocument27 pagesNCLEX Questions PulmAnthony Hawley100% (2)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 pagesNursing Care PlanGinel Laquiores100% (1)
- Drug Study and NCP!Document8 pagesDrug Study and NCP!Abegail Abaygar100% (1)
- ARDS Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument49 pagesARDS Respiratory Distress Syndromesonam yadav67% (3)
- Diabetic patient wound careDocument7 pagesDiabetic patient wound careMichael Anthony Cardenas Macaballug67% (3)
- NCP and Problems FinalDocument8 pagesNCP and Problems FinalRina CebreroNo ratings yet
- 1) Nursing Careplan For FeverDocument9 pages1) Nursing Careplan For FeverY. Beatrice AbigailNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans for Pancreatitis PatientDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plans for Pancreatitis PatientClaire Alcantara50% (2)
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPAbegail Abaygar100% (1)
- Care of neonate on ventilatorDocument7 pagesCare of neonate on ventilatorAmy LalringhluaniNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For FallDocument20 pagesNCP Risk For FallRen Ren Determinado86% (7)
- NCPDocument1 pageNCPAlynna ValbuenaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 NotesDocument5 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Type 2 NotesAimee Kaye DetablanNo ratings yet
- NCP (Fatigue)Document1 pageNCP (Fatigue)student_019100% (1)
- NCP ImbalancedDocument7 pagesNCP ImbalancedSasha FongNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument9 pagesNursing Care PlanjmichaelaNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationKatrina Ponce86% (7)
- GastroenteritisDocument8 pagesGastroenteritistanlimdania100% (3)
- NCP FinalDocument18 pagesNCP FinalJessica Medina100% (1)
- NCP For MGDocument1 pageNCP For MGSandra MedinaNo ratings yet
- CBT Sample MCQs - Source Royal Marsden ANSWERSDocument16 pagesCBT Sample MCQs - Source Royal Marsden ANSWERSarchana100% (6)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanCristina L. JaysonNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPBeverLyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans for Stroke PtDocument13 pagesNursing Care Plans for Stroke PtJuls Flares SycaycoNo ratings yet
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDocument3 pagesNCP Activity Intolerancekeiii_21No ratings yet
- NCPDocument8 pagesNCPJose Benit DelacruzNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument10 pagesNCPNefre Dayap DarrocaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesNursing Care PlantinnnnnnnnnnnnnNo ratings yet
- Actual NCPDocument2 pagesActual NCPbaki0146No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyHennah ReblandoNo ratings yet
- NCP FinalDocument7 pagesNCP FinalAkira MizukamiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis: Fatigue related to decreased muscular strengthDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis: Fatigue related to decreased muscular strengthAna Ramos LopezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument6 pagesNursing Care PlansTwobee Kriz LeghidNo ratings yet
- Dermatomyositis NCPDocument3 pagesDermatomyositis NCPMakki MarcosNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationLean Ashly Tuddao Macarubbo0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan (CASE STUDY DENGUE)Document10 pagesNursing Care Plan (CASE STUDY DENGUE)NiooleNo ratings yet
- Assessment Data Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Data Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationCrystelle MonaresNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJoey PolicarNo ratings yet
- Subjective Cues: Short Term GoalDocument2 pagesSubjective Cues: Short Term GoalcarissagacutnoNo ratings yet
- Managing Diabetes and RisksDocument8 pagesManaging Diabetes and RisksChristopher LontocNo ratings yet
- Imblanced NutritionDocument2 pagesImblanced NutritionCristina L. JaysonNo ratings yet
- NCP Nursing Diagnosis: Activity IntoleranceDocument4 pagesNCP Nursing Diagnosis: Activity IntoleranceAngelica Orbase BelmonteNo ratings yet
- Ix. Nursing Care Plan: Asessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesIx. Nursing Care Plan: Asessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationemman_russelNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer ChemotherapyDocument6 pagesCervical Cancer ChemotherapyTheeya Quigao0% (1)
- NCPDocument10 pagesNCPannamargie07No ratings yet
- 5ncp AnemiaDocument8 pages5ncp Anemiabeverly_domingoNo ratings yet
- R: This Provides Baseline Measurement For Future Evaluation and Guides TherapyDocument4 pagesR: This Provides Baseline Measurement For Future Evaluation and Guides TherapyTyron ChuaNo ratings yet
- NCP For Impaired MobilityDocument4 pagesNCP For Impaired MobilityBettinaFernandoNo ratings yet
- NCP GrandcaseDocument5 pagesNCP GrandcaseSaima BataloNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care ManagementDocument40 pagesNursing Care ManagementɱΘΟθ CuasitoNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Nursing Care Plan for CVA, DM, HypertensionDocument3 pagesConcept Map Nursing Care Plan for CVA, DM, HypertensionFranklin A. Salaum III0% (2)
- Nourish A Comprehensive Guide to Healthy Eating and Sustainable LivingFrom EverandNourish A Comprehensive Guide to Healthy Eating and Sustainable LivingNo ratings yet
- Viii. Drug Study: Drug Action Indications Containdications Side / Adverse Reactions Nursing ConsiderationDocument18 pagesViii. Drug Study: Drug Action Indications Containdications Side / Adverse Reactions Nursing ConsiderationSheng GosepNo ratings yet
- Myasthemia GravisDocument11 pagesMyasthemia GravisSheng GosepNo ratings yet
- Gastroenteritis OverviewDocument5 pagesGastroenteritis OverviewSheng GosepNo ratings yet
- Hydralazine hydrochloride: Antihypertensive drug generic name, brand name, indications, adverse effectsDocument1 pageHydralazine hydrochloride: Antihypertensive drug generic name, brand name, indications, adverse effectsSheng Gosep100% (3)
- Anatomy of The Central Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesAnatomy of The Central Nervous SystemSheng GosepNo ratings yet
- Vitamin K3 Drug Generic Name, Brand, Uses, Side EffectsDocument2 pagesVitamin K3 Drug Generic Name, Brand, Uses, Side EffectsSheng GosepNo ratings yet
- Facts About Myasthenia GravisDocument14 pagesFacts About Myasthenia GravisSheng GosepNo ratings yet
- Personality Development NotesDocument11 pagesPersonality Development Notesvasantha_btechNo ratings yet
- Invasive Ductal Carcinoma: Group 13 ADocument3 pagesInvasive Ductal Carcinoma: Group 13 ASheng GosepNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure: Marvick F. Galima RNDocument42 pagesHeart Failure: Marvick F. Galima RNSheng GosepNo ratings yet
- Bpud, PathoDocument2 pagesBpud, PathoSheng GosepNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To GeriatricsDocument45 pages1.introduction To Geriatricsbookstore wormNo ratings yet
- Understanding How Density Affects Weight in Different MediumsDocument72 pagesUnderstanding How Density Affects Weight in Different MediumsJiaYing WinNo ratings yet
- Home Based CareDocument34 pagesHome Based CaremewselectionsNo ratings yet
- 03 - Diffuse Pulmonary NodulesDocument13 pages03 - Diffuse Pulmonary NodulesOmar Guerrero Soto100% (1)
- Lore BookDocument131 pagesLore BookMárcio Machado Ribeiro (Jamesfoxbr)No ratings yet
- Hand Out 2 NCM 103 PrelimDocument3 pagesHand Out 2 NCM 103 PrelimLouisa Marie MirandaNo ratings yet
- Management of Respiratory Failure Ventilator.17Document9 pagesManagement of Respiratory Failure Ventilator.17Margarida ReisNo ratings yet
- Prone VentilationDocument20 pagesProne VentilationdeepaksolarNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Ventilation Troubleshooting Skill Respiratory Therapy COVID 19 Toolkit - 070420Document8 pagesMechanical Ventilation Troubleshooting Skill Respiratory Therapy COVID 19 Toolkit - 070420Sirgut TesfayeNo ratings yet
- BSC Nursing SyllDocument218 pagesBSC Nursing SyllKiran KhasaNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Biology (SBI 3U1) Name: - Unit: Internal Systems Lab: Virtual Fetal Pig Dissection DateDocument3 pagesGrade 11 Biology (SBI 3U1) Name: - Unit: Internal Systems Lab: Virtual Fetal Pig Dissection DateSydney Drizis [Student]No ratings yet
- Broncho Ect As IsDocument28 pagesBroncho Ect As Ismeaza rorisaNo ratings yet
- Airway Clearance. Physiology, Pharmacology, Techniques, and Practice - Rubin, Hess 2007Document5 pagesAirway Clearance. Physiology, Pharmacology, Techniques, and Practice - Rubin, Hess 2007Maxi BoniniNo ratings yet
- Review in Science Circulatory System PulmonaryDocument3 pagesReview in Science Circulatory System PulmonaryElvie Jane P. MolatoNo ratings yet
- ASPEN Nutrition Support During Prone PositionDocument5 pagesASPEN Nutrition Support During Prone PositionAlimah YasminNo ratings yet
- The Anesthesia Gas MachineDocument28 pagesThe Anesthesia Gas MachineBianca RotaruNo ratings yet
- Course Outline For 125:355, Physiological Systems For Biomedical EngineersDocument2 pagesCourse Outline For 125:355, Physiological Systems For Biomedical EngineersbillNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Gas Exchange in HumansDocument4 pagesCH 11 Gas Exchange in HumansPranitha RaviNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired Gas ExchangeAlliah MayoNo ratings yet
- Apnea Testing For The Determination of Brain Death A Systematic Scoping ReviewDocument13 pagesApnea Testing For The Determination of Brain Death A Systematic Scoping Reviewrisna sariNo ratings yet