Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exp-5 Impact Test
Uploaded by
Hanamant HunashikattiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exp-5 Impact Test
Uploaded by
Hanamant HunashikattiCopyright:
Available Formats
CIVIL ENGINEERING VIRTUAL LABORATORY
EXPERIMENT: 5 IMPACT TEST
STRENGTH OF MATERIALS
AIM:
To determine the Impact toughness (strain energy) through Izod test and Charpy test
THEORY:
In a impact test a specially prepared notched specimen is fractured by a single blow from a heavy hammer and energy required being a measure of resistance to impact. Impact load is produced by a swinging of an impact weight W (hammer) from a height h. Release of the weight from the height h swings the weight through the arc of a circle, which strikes the specimen to fracture at the notch (fig.. Kinetic energy of the hammer at the time of impact is mv2 /2, which is equal to the relativ e potential energy of the hammer before its release. (mgh),where m is the mass of the hammer and v
2 gh is its tangential velocity at impact, g
less.
is gravitational acceleration (9.806 m/s2) and h is the height through which hammer falls. Impact velocity will be 5.126 m/s or slightly
Here it is interesting to note that height through which hammer drops determines the velocity and height and mass of a hammer combined determine the energy. Energy used can be measured from the scale given. The difference between potential energies is the fracture energy. In test machine this value indicated by the pointer on the scale. If the scale is calibrated in energy units, marks on the scale should be drawn keeping in view angle of fall () and angle of rise (. Height h1 and h2 equals,
h1
R (1 cos ) and h2
(1 cos )
With the increase or decrease in values, gap between marks on scale showing energy also increase or decrease. This can be seen from the attached scale with any impact machine. Energy used in fracturing the specimen can be obtained approximately as Wh1Wh2 This energy value called impact toughness or impact value, which will be measured, per unit area at the notch.
EXPERIMENT: 5
IMPACT TEST
SoM-CEVL
Izod introduced Izod test in 1903. Test is as per the IS: 1598 Charpy introduced Charpy test in 1909. Test is as per the IS: 1499.
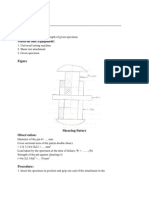
a. Izod test Specimen and equipment 1. Impact testing machine.(fig.3) 2. Specimen and v notch is shown in the fig.4. Size of the specimen is 10mm X 10mm X 7 5mm Mounting of the specimen: Specimen is clamped to act as vertical cantilever with the notch on tension side. Direction of blow of hammer is shown in fig. (). Direction of blow is shown i n fig
EXPERIMENT: 5
IMPACT TEST
SoM-CEVL
EXPERIMENT: 5
IMPACT TEST
SoM-CEVL
PROCEDURE:
1. Measure the dimensions of a specimen. Also, measure the dimensions of the notch. 2. Raise the hammer and note down initial reading from the dial, which will be energy to be used to fracture the specimen. 3. Place the specimen for test and see that it is placed center with respect to hammer. Che ck the position of notch. 4. Release the hammer and note the final reading. Difference between the initial and final r eading will give the actual energy required to fracture the Specimen. 5. Repeat the test for specimens of other materials. 6. Compute the energy of rupture of each specimen.
OBSERVATION:
Initial and final reading of the dial. Result Strain energy of given specimen is
b. Charpy test Specimen and equipment: 1. Impact testing machine. (Fig.6) 2. U notch is cut across the middle of one face as shown in (fig.5).
EXPERIMENT: 5
IMPACT TEST
SoM-CEVL
Mounting of specimen Specimen is tested as a beam supported at each end (fig.7). Hammer is allowed to hit t hen specimen at the opposite face behind the notch.
EXPERIMENT: 5 Figure.7
IMPACT TEST
SoM-CEVL
Procedure 1. Measure the dimensions of a specimen. Also, measure the dimensions of The notch. 2. Raise the hammer and note down initial reading from the dial, which will be energy to be used to fracture the specimen. 3. Place the specimen for test and see that it is placed center with respect to hammer. Che ck the position of notch. 4. Release the hammer and note the final reading. Difference between the initial and final r eading will give the actual energy required to fracture the Specimen. 5. Repeat the test for specimens of other materials. 6. Compute the energy of rupture of each specimen.
OBSERVATION:
Initial and final reading of the dial. Result Strain energy of given specimen is
EXPERIMENT: 5
IMPACT TEST PART 2 ANIMATION STEPS
SoM-CEVL
EXPERIMENT: 5
IMPACT TEST PART 3 VIRTUAL LAB FRAME
SoM-CEVL
You might also like
- Impact IzodDocument6 pagesImpact IzodTanu RdNo ratings yet
- Impact Test Machine CalculationsDocument6 pagesImpact Test Machine CalculationsSoumadipta SenNo ratings yet
- Som Manual-2013 RegDocument26 pagesSom Manual-2013 RegsugunavidiyadarNo ratings yet
- FM and SM Lab ManualDocument87 pagesFM and SM Lab ManualGeorge OliverNo ratings yet
- btech3rd-CE SOM LAB MANUALDocument21 pagesbtech3rd-CE SOM LAB MANUALvkmstp2005No ratings yet
- MEC 222 EXP-Lab-SOMDocument69 pagesMEC 222 EXP-Lab-SOMAbhijeeth NagarajNo ratings yet
- WH - WHDocument5 pagesWH - WHAfia S HameedNo ratings yet
- Charpy Impact Test ExplainedDocument4 pagesCharpy Impact Test ExplainedBaibhav MohantyNo ratings yet
- ImpactNotes With ResultsDocument5 pagesImpactNotes With Resultsاحمد الشلمانيNo ratings yet
- Impact Test LOAYDocument6 pagesImpact Test LOAYBin IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Torsion Test Experiment 2Document5 pagesTorsion Test Experiment 2Ryan Hasnan HNo ratings yet
- Torsion Test Experiment 2Document5 pagesTorsion Test Experiment 2Ryan Hasnan HNo ratings yet
- Experi M E N T NO - 6: Brown Hills College of Engineering and Technology Som Lab FileDocument21 pagesExperi M E N T NO - 6: Brown Hills College of Engineering and Technology Som Lab FileAtul GaurNo ratings yet
- Impact Testing Machine ExperimentDocument4 pagesImpact Testing Machine Experimentmuna222No ratings yet
- Strength of Materials Lab. Manual: Production EngineeringDocument16 pagesStrength of Materials Lab. Manual: Production EngineeringSudhakar SenganNo ratings yet
- Ce 2010 - Experiment 05Document5 pagesCe 2010 - Experiment 05Minhajul IslamNo ratings yet
- Material Testing LabDocument79 pagesMaterial Testing LabBrijesh VermaNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materia Lab Manual UET, LahoreDocument14 pagesStrength of Materia Lab Manual UET, LahoreRizwan Khurram100% (3)
- Am LabDocument22 pagesAm LabJayavel123No ratings yet
- Lab Manual: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument19 pagesLab Manual: Department of Mechanical Engineeringhydromec_indiaNo ratings yet
- Impact Testing of MaterialsDocument4 pagesImpact Testing of MaterialsYogiNo ratings yet
- Charpy Impact TestDocument4 pagesCharpy Impact TestRao MaazNo ratings yet
- MOM Lab Manuals OrigionalDocument95 pagesMOM Lab Manuals OrigionalMansoob BukhariNo ratings yet
- Rotating Fatigue PDFDocument2 pagesRotating Fatigue PDFMia FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Measure bending moment with loadsDocument9 pagesMeasure bending moment with loadsOmar Arabi0% (1)
- SM Lab ManualsDocument27 pagesSM Lab ManualspraveenampilliNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1 Impact Strength of A MaterialDocument7 pagesExperiment No. 1 Impact Strength of A MaterialMansoob Bukhari100% (1)
- Experiment:-To Determine The Tensile Properties of Given Material. Theory:-The Tensile Test Consists of Clamping One and of The Specimen and AnDocument11 pagesExperiment:-To Determine The Tensile Properties of Given Material. Theory:-The Tensile Test Consists of Clamping One and of The Specimen and AnGurmeet MehmaNo ratings yet
- Fatigue SomDocument13 pagesFatigue SomOmed HajiNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis With Strain Gage Measurements: Experiment 1Document7 pagesStructural Analysis With Strain Gage Measurements: Experiment 1Yılmaz GürpınarNo ratings yet
- CE 6315 Strength of Materials LabDocument33 pagesCE 6315 Strength of Materials LabSenthil SelvamNo ratings yet
- Charpy Impact Test - Lab ReportDocument18 pagesCharpy Impact Test - Lab ReportChitra Nadia100% (1)
- Impact Test Lab ManualDocument7 pagesImpact Test Lab ManualYap Khong LeongNo ratings yet
- Bending Moment Lab ReportDocument8 pagesBending Moment Lab ReportMihir Ashar0% (1)
- Exp 7Document20 pagesExp 7Jad Antonios JelwanNo ratings yet
- Standard Tension TestDocument12 pagesStandard Tension TestStephen Mirdo50% (2)
- Laboratory Manual: MEC259 Unified Mechanical Engineering IIDocument35 pagesLaboratory Manual: MEC259 Unified Mechanical Engineering IIHimanshu Kumar Raut100% (2)
- Mild Steel Tensile Test ResultsDocument30 pagesMild Steel Tensile Test ResultsDipesh GugaleNo ratings yet
- Complete Impact Test PDFDocument9 pagesComplete Impact Test PDFKalKatu MaLam86% (22)
- Impact - Test and Fracture TestDocument14 pagesImpact - Test and Fracture TestMinh Tam CaoNo ratings yet
- AE 451A Experiments in Aerospace Engineering IiiDocument11 pagesAE 451A Experiments in Aerospace Engineering IiiKeshav KantNo ratings yet
- Charpy TestDocument3 pagesCharpy TestSunil ChincholikarNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials Lab Manual: 1. Tension Test On MS Bar and HYSD BarsDocument61 pagesStrength of Materials Lab Manual: 1. Tension Test On MS Bar and HYSD Barsswe_maniNo ratings yet
- ME150 CharpyDocument10 pagesME150 Charpyahmet şahinNo ratings yet
- Strength of Material Experiment 3 (Torsion Test)Document20 pagesStrength of Material Experiment 3 (Torsion Test)Atikah Mohd57% (7)
- Exp-4 Torsion TestDocument5 pagesExp-4 Torsion TestDinesh BajajNo ratings yet
- Tension Test on Mild Steel RodDocument38 pagesTension Test on Mild Steel RodSathis KumarNo ratings yet
- Impact TestDocument4 pagesImpact TestmanmathkNo ratings yet
- Fatigue Failure Due To Variable LoadingDocument13 pagesFatigue Failure Due To Variable Loadingsrinivas kappagantulaNo ratings yet
- Modul 3 Strain Measurement v2 PDFDocument11 pagesModul 3 Strain Measurement v2 PDFFachrudin HanafiNo ratings yet
- Torsion New +Document6 pagesTorsion New +احمد الشلمانيNo ratings yet
- Principles of Mechanical Engineering Lab ReportDocument13 pagesPrinciples of Mechanical Engineering Lab ReportJohn kamandaNo ratings yet
- Testing of MaterialsDocument37 pagesTesting of MaterialsSethu ramNo ratings yet
- Ijaz ReportDocument15 pagesIjaz ReportEngineer AnasNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document7 pagesExperiment 1waseemjuttNo ratings yet
- Som Lab ManualDocument33 pagesSom Lab ManualRakheeb BashaNo ratings yet
- Unified Mechanical Engineering Lab-2Document38 pagesUnified Mechanical Engineering Lab-2sharmashnNo ratings yet
- Mos Lab Manual PDFDocument34 pagesMos Lab Manual PDFs.rihanaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 (A) : Izod Pendulum Impact Resistance TestDocument4 pagesExperiment 5 (A) : Izod Pendulum Impact Resistance Testnikhil jaiswalNo ratings yet
- Environmental EngineeringDocument17 pagesEnvironmental EngineeringHanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- Brochure FinalDocument2 pagesBrochure FinalHanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- Accident AnalysisDocument137 pagesAccident AnalysisHanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- BBD Site & Soil ReadingDocument24 pagesBBD Site & Soil ReadingHanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- First Infn. BrochureDocument2 pagesFirst Infn. BrochureHanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- KLE Engg.Document2 pagesKLE Engg.Hanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- IA B.E Civil Semester4 DivisionADocument3 pagesIA B.E Civil Semester4 DivisionAHanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5-Sedimentation and Flocculation (Part 2)Document21 pagesLecture 5-Sedimentation and Flocculation (Part 2)Harold Taylor100% (1)
- Foundation Analysis - COURSE CONTENTDocument3 pagesFoundation Analysis - COURSE CONTENTHanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- Mercury Systems2Document1 pageMercury Systems2Hanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- Kle - Dr.M.S.S.Sheshagiri Collage of Engineering and Technology, BelagaviDocument1 pageKle - Dr.M.S.S.Sheshagiri Collage of Engineering and Technology, BelagaviHanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- Schedule (Pavement Evaluation and Rehabilitation) Day 1: 7 Sep 2017 Time Theme SpeakerDocument1 pageSchedule (Pavement Evaluation and Rehabilitation) Day 1: 7 Sep 2017 Time Theme SpeakerHanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- RDocument60 pagesRHanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- Kle. Dr.M.S.Shesgiri College of Engineering & Technology: Automatic Road Analyzer (Aran)Document1 pageKle. Dr.M.S.Shesgiri College of Engineering & Technology: Automatic Road Analyzer (Aran)Hanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- TH THDocument2 pagesTH THHanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- Charimath BLGM Model - PDF 2Document1 pageCharimath BLGM Model - PDF 2Hanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- 2) PART - B (Abstract)Document1 page2) PART - B (Abstract)Hanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- 02 KLE, BelagaviDocument6 pages02 KLE, BelagaviHanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- Light Weight DefelctometerDocument1 pageLight Weight DefelctometerHanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- LetterDocument1 pageLetterHanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- InvitationDocument2 pagesInvitationHanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- First Infn. BrochureDocument2 pagesFirst Infn. BrochureHanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- Base Isolation EdditedDocument64 pagesBase Isolation EdditedHanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- HRTC Training Attendance Report for Civil Engineering StudentsDocument1 pageHRTC Training Attendance Report for Civil Engineering StudentsHanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- Mtech Transportation EngineeringDocument5 pagesMtech Transportation EngineeringHanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- Pavement Evaluation Workshop InvitationDocument1 pagePavement Evaluation Workshop InvitationHanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- Parameter Sensitive Analysis of F 2016 International Journal of Pavement ResDocument7 pagesParameter Sensitive Analysis of F 2016 International Journal of Pavement ResHanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- FEM Analysis of Pavement Linear and Non Linear PDFDocument6 pagesFEM Analysis of Pavement Linear and Non Linear PDFHanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- Numerical Modeling of Geogrid Reinforced Flexible Pave 2016 Construction andDocument17 pagesNumerical Modeling of Geogrid Reinforced Flexible Pave 2016 Construction andHanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Modeling and Parametric Analysis of Visc 2017 Construction AnDocument13 pagesFinite Element Modeling and Parametric Analysis of Visc 2017 Construction AnHanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- Thermal Conductivity GuideDocument181 pagesThermal Conductivity GuideAl BNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Part1 Static AnalysisDocument11 pagesSimulation of Part1 Static AnalysisFahmi FahreziNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Semiconductor Devices: Betty Lise Anderson - Richard L. AndersonDocument52 pagesFundamentals of Semiconductor Devices: Betty Lise Anderson - Richard L. Andersonfourier76No ratings yet
- Review of Fluid Review of Fluid MechanicsDocument40 pagesReview of Fluid Review of Fluid MechanicsNebiyou KorraNo ratings yet
- Vijay Gupta - Elements of Heat and Mass Transfer-New Age International Pub (2020)Document565 pagesVijay Gupta - Elements of Heat and Mass Transfer-New Age International Pub (2020)Mustapha MellalNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Introduction To FoundationDocument73 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To FoundationKerwin BadmanNo ratings yet
- Turbine: The Effect of Friction On The Joule CycleDocument13 pagesTurbine: The Effect of Friction On The Joule CycleGeorge AniborNo ratings yet
- A RANS-based Analysis Ool For Ducted Propeller Systems in Open Water ConditionDocument23 pagesA RANS-based Analysis Ool For Ducted Propeller Systems in Open Water ConditionLeonardo Duarte MilfontNo ratings yet
- SteamWhirl PhenomenaDocument6 pagesSteamWhirl PhenomenaAle MilicNo ratings yet
- OSA-06-Vibration Fatigue Analysis of Sheet Metal Mahindra2wheelerDocument11 pagesOSA-06-Vibration Fatigue Analysis of Sheet Metal Mahindra2wheelerikramishereNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics of A Human BodyDocument13 pagesThermodynamics of A Human BodyJuan Carlos Cahuasquí IntriagoNo ratings yet
- Steam SilencerDocument3 pagesSteam SilencerAntonio Perez100% (1)
- Non-Reciprocal Phase TransitionsDocument23 pagesNon-Reciprocal Phase TransitionsYongzheng SunNo ratings yet
- 5.0 PressureDocument82 pages5.0 PressureKalkien CtNo ratings yet
- Human Levers and Equilibrium ConceptsDocument27 pagesHuman Levers and Equilibrium ConceptsLeighton JamesNo ratings yet
- Wrinkle of FoilDocument48 pagesWrinkle of FoilLuận NgôNo ratings yet
- D2105Document6 pagesD2105Mario LunaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Construction and DesignDocument5 pagesModule 3 Construction and DesignDhimas Surya Negara100% (1)
- Kramer Steven PDFDocument32 pagesKramer Steven PDFFurkan YılmazNo ratings yet
- Concept: Defining ConstraintsDocument3 pagesConcept: Defining ConstraintsPraveen SreedharanNo ratings yet
- Locking of Hene Laser Modes Induced by Synchronous Intracavity ModulationDocument3 pagesLocking of Hene Laser Modes Induced by Synchronous Intracavity ModulationMohamad paidarNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter SoundDocument8 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Chapter SoundVaibhav SinhaNo ratings yet
- Forces and friction problems for inclined planesDocument5 pagesForces and friction problems for inclined planesbasakranjan0% (1)
- Fluids 2015 QuestionsDocument7 pagesFluids 2015 QuestionsFaisal Al QadriNo ratings yet
- MMPD Advance MathematicsDocument45 pagesMMPD Advance Mathematicsmayuresh_6767No ratings yet
- Week 8 ModifiedDocument3 pagesWeek 8 ModifiedNirmal KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 and 15 HomeworkDocument29 pagesChapter 14 and 15 HomeworkFatboy91100% (4)
- Chapter 1 - Mece5104 - Mechanical VibrationDocument22 pagesChapter 1 - Mece5104 - Mechanical VibrationCedricNo ratings yet
- Thermal-hydraulic performance of turbulent flow in corrugated tubesDocument24 pagesThermal-hydraulic performance of turbulent flow in corrugated tubeschaib benchaibNo ratings yet
- Example 2 - Bending TestDocument10 pagesExample 2 - Bending TestMuhd Fauzan IbrahimNo ratings yet