Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bioavailability and pharmacokinetics practice problems
Uploaded by
Linh PhamOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bioavailability and pharmacokinetics practice problems
Uploaded by
Linh PhamCopyright:
Available Formats
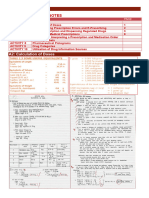
BIOAVAILABILITY PHARMACOKINETICS PRACTICE PROBLEMS 1. If the bioavailability factor (F) for a 100-mg tablet of a drug is 0.
70 compared with the bioavailability factor of 1.0 for an injection of the same drug, how many milliliters of the injection containing 40 mg/mL would be considered bioequivalent to the tablet? 2. If 5 mL of an elixir containing 2 mg/mL of a drug is bioequivalent to a 15 mg tablet having a bioavailability factor of 0.60, what is the bioavailability factor of the elixir? 3. If 500 mg of a drug are administered orally and 300 mg are absorbed into the circulation, calculate the bioavailability factor (F). 4. A drug is 40% bioavailable by the oral route and 58% bioavailable by the transdermal route. If a patient is taking a 2.5 mg oral dose twice a day and is switched to the counterpart 2% ointment, how many grams of the ointment should be administered to provide the equivalent dose of the drug? 5. A drug used to treat asthma is 55% bioavailable as 5mg tablets. If a patient is switched to the inhalant form of the drug, which is 87% bioavailable, how many metered 500-g sprays should the patient administer every 12 hours to receive an equivalent drug dose? 6. If a 6-mg dose of a drug is administered intravenously and produces a blood concentration of 0.4 g/mL, calculate its apparent volume of distribution. 7. If at equilibrium, two thirds of the amount of a drug substance in the blood is bound is bound to protein, what would be the alpha () value of the drug? 8. The alpha () value for a drug in the blood is 0.90, equating to 0.55 ng/mL. What is the concentration of total drug in the blood? 9. A patient received an intravenous dose of 10 mg of a drug. A blood sample was drawn and it contained 40g/100 mL. Calculate the apparent volume of distribution? 10. The volume of distribution for a drug was found to be 10 liters with a blood level concentration of 2 g/mL. Calculate the total amount of drug present in the patient? 11. Calculate the elimination rate constant for a drug having an elimination half-life of 1.7 hours? 12. What percentage of an originally administered intravenous dose of a drug remains in the body following three half-lives?
PRACTICE PROBLEMS
8162013
13. If 100 mg of a drug are administered intravenously, and the resultant drug plasma concentration is determined to be 2.5 g/mL, calculate the apparent volume of distribution? 14. If the dose of 1g of a drug is administered intravenously to a patient and the drug plasma concentration is determined to be 65 g/mL, calculate the apparent volume of distribution? 15. The volume of distribution for chlordiazepoxide has been determined to be 34 liters. Calculate the expected drug plasma concentration of the drug in micrograms per deciliter, immediately after an intravenous dose of 5 mg. 16. In normal subjects, blood makes up about 7% of body weight. A) Calculate the approximate blood volume in liters, for a man weighing 70 kg. B) If the drug ZANTAC reached peak blood levels of about 500ng/mL, 2 to 3 hours after an oral dose, calculate the total amount of the drug, in milligrams, in the blood of the patient described in (A) when peak blood levels are achieved.
PRACTICE PROBLEMS
8162013
You might also like
- Module 1 Lesson 2 Spectrometric CalculationsDocument40 pagesModule 1 Lesson 2 Spectrometric CalculationsVeronica DeldioNo ratings yet
- (Dispensing 1 Laboratory) Review NotesDocument12 pages(Dispensing 1 Laboratory) Review NotesZen HeartNo ratings yet
- The PrescriptionDocument86 pagesThe PrescriptionChristine Arrabis100% (3)
- Statement of Principle Self-Care Including Self-Medication - The Professional Role of The PharmacistDocument5 pagesStatement of Principle Self-Care Including Self-Medication - The Professional Role of The PharmacistAprilia R. Permatasari0% (1)
- Activity #3Document9 pagesActivity #3PrincessNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Prescription and Medication OrderDocument30 pagesLesson 1 Prescription and Medication OrderAngelica GomezNo ratings yet
- The Philippine Pharmacy Act: RA 10918 Submitted By: Emerald Shaine P. SamozaDocument49 pagesThe Philippine Pharmacy Act: RA 10918 Submitted By: Emerald Shaine P. Samozaemerald shaine samozaNo ratings yet
- Community Pharmacy InternshipDocument8 pagesCommunity Pharmacy InternshipKenny TuanNo ratings yet
- Calculate Pharmaceutical FormulasDocument28 pagesCalculate Pharmaceutical FormulasKatie Wilson100% (3)
- Stroke and HypertensionDocument4 pagesStroke and HypertensionKhessie Laye Garcia JacintoNo ratings yet
- List of Prescription AbbreviationsDocument5 pagesList of Prescription Abbreviationsrandatag100% (1)
- Pharmacy Orientation PPP211: Introduction To The Pharmacy Profession and The Future of The PharmacistDocument27 pagesPharmacy Orientation PPP211: Introduction To The Pharmacy Profession and The Future of The PharmacistJape GarridoNo ratings yet
- Intern Drug ListDocument5 pagesIntern Drug ListKenette Diane CantubaNo ratings yet
- Hospital Documentation ActivityDocument4 pagesHospital Documentation ActivityJANNIE BELLE RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Jurisprudence ManualDocument12 pagesPharmaceutical Jurisprudence ManualSlark SlarkNo ratings yet
- Wine Production ProcessDocument2 pagesWine Production ProcessJanice Malafu De GuiaNo ratings yet
- Patient Medication Profile and CounselingDocument56 pagesPatient Medication Profile and CounselingMeimei QueNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy Informatics Laboratory Activity 14Document1 pagePharmacy Informatics Laboratory Activity 14April Mergelle LapuzNo ratings yet
- Perspectives in PharmacyDocument7 pagesPerspectives in Pharmacygizelle mae pasiolNo ratings yet
- Lab09 Therapy4 IronDeficiencyDocument5 pagesLab09 Therapy4 IronDeficiencyHayna Rose100% (1)
- Group 5 Pdis211 Lab E1Document22 pagesGroup 5 Pdis211 Lab E1Mikaela Kean JoseNo ratings yet
- BREX S Microbiology and Public Health Reviewer CompleteDocument30 pagesBREX S Microbiology and Public Health Reviewer CompleteLeonibel GhloeNo ratings yet
- B Pharmaceutical ChemistryDocument29 pagesB Pharmaceutical ChemistryZllison Mae Teodoro MangabatNo ratings yet
- Superintendent and Supervising Pharmacists Guidance On RolesDocument3 pagesSuperintendent and Supervising Pharmacists Guidance On RolessefrounfNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Organic MedicinalsDocument7 pagesModule 1 Organic MedicinalsMARIA FREDIJEAN CARIÑONo ratings yet
- Household Poisnous MaterialsDocument4 pagesHousehold Poisnous MaterialsTarfha AbduhalimNo ratings yet
- Pharm 231: Hospital Pharmacy: Iii. Medication ProfileDocument3 pagesPharm 231: Hospital Pharmacy: Iii. Medication ProfileTESORO Zeus DavidNo ratings yet
- Pharm CalculationsDocument35 pagesPharm CalculationsHuma Hameed DogarNo ratings yet
- Survey Research GuideDocument6 pagesSurvey Research GuideMarie Eloise BugayongNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms, Drug Delivery Systems and Medical Devices Pharm 201L Name:Tallod, Emerson John L. Group:11 Year/Section:Q2A Final RatingDocument7 pagesPharmaceutical Dosage Forms, Drug Delivery Systems and Medical Devices Pharm 201L Name:Tallod, Emerson John L. Group:11 Year/Section:Q2A Final RatingJames AzurinNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For CV and Respiratory DrugsDocument9 pagesReviewer For CV and Respiratory Drugsprinz1mendezNo ratings yet
- Clinical Toxicology GuideDocument70 pagesClinical Toxicology GuideJerson Aizpuro SuplementoNo ratings yet
- Legal Pharm Course OutlineDocument69 pagesLegal Pharm Course OutlineLysa VeeNo ratings yet
- Pro TaminaDocument2 pagesPro TaminaArcenciel26No ratings yet
- IV Drug IncompatibilitiesDocument29 pagesIV Drug IncompatibilitiesMichael Freudiger100% (2)
- Dispensing AnsDocument197 pagesDispensing AnsPrincess Ronsable100% (1)
- ACTIVITY-3 (1) WT VariationDocument4 pagesACTIVITY-3 (1) WT VariationdavenNo ratings yet
- Comp&Disp 3Document14 pagesComp&Disp 3kakak zea100% (1)
- Powder PharmaceuticsDocument58 pagesPowder PharmaceuticskishnapraveenNo ratings yet
- Activity 7 Calculations Involved in Parenteral Therapy: University of Santo TomasDocument3 pagesActivity 7 Calculations Involved in Parenteral Therapy: University of Santo TomasJANNIE BELLE RODRIGUEZ100% (1)
- Introduction To Pharmacy PracticeDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Pharmacy PracticeRai Waqas100% (1)
- Pharmacist Role in ADR MDocument9 pagesPharmacist Role in ADR Mimran moopansNo ratings yet
- Community Pharmacy Intern Exercises5-9Document6 pagesCommunity Pharmacy Intern Exercises5-9Joslin RozNo ratings yet
- Bioavailability and BioequivalenceDocument56 pagesBioavailability and Bioequivalenceنور الهدى100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Final ProductDocument9 pagesChapter 1 Final ProductJay Cabahug JugarNo ratings yet
- Sources of Drug InformationDocument36 pagesSources of Drug InformationCristine ChubiboNo ratings yet
- Republic Act 3720Document16 pagesRepublic Act 3720Kyle Tan DomingoNo ratings yet
- BiopharmaceuticsDocument13 pagesBiopharmaceuticsAngeli Marie PadillaNo ratings yet
- Ama Namin by Barbie Dumlao SatbDocument8 pagesAma Namin by Barbie Dumlao SatbLou Andrae G. SantosNo ratings yet
- Solid Dosage FormsDocument4 pagesSolid Dosage Formscofodike1No ratings yet
- Rational Use of DrugsDocument2 pagesRational Use of DrugsRajan Manandhar ShambhavNo ratings yet
- Toxicology Course Outline - CompletedDocument4 pagesToxicology Course Outline - Completedtpetronellah mandishona100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical Calculations VIOLET PACOPDocument41 pagesPharmaceutical Calculations VIOLET PACOPSan DarraNo ratings yet
- INPI Module 1 PDFDocument39 pagesINPI Module 1 PDFlevi pinedaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual Pharmaceutics Ii Laboratory Manual Cum Logbook 3 1 2 - PHT Level VDocument66 pagesLaboratory Manual Pharmaceutics Ii Laboratory Manual Cum Logbook 3 1 2 - PHT Level VTIVIYAH THEVAR 1017No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document27 pagesChapter 6yeshi janexo100% (1)
- Activity 7 DISPENSING PRICE With AnswersDocument3 pagesActivity 7 DISPENSING PRICE With AnswersChristine DelmendoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacognosy Activity Carbohydrates Different Types of Starch PowderDocument4 pagesPharmacognosy Activity Carbohydrates Different Types of Starch PowderArlene FortezaNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Drug Toxicity: Proceedings of the Third International Pharmacological MeetingFrom EverandMechanisms of Drug Toxicity: Proceedings of the Third International Pharmacological MeetingH. RaškováNo ratings yet
- Chem410Cancer1 PDFDocument6 pagesChem410Cancer1 PDFLinh PhamNo ratings yet
- Counseling Week 4 LabsDocument1 pageCounseling Week 4 LabsLinh PhamNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument19 pagesEnzymesLinh PhamNo ratings yet
- Secundum Artem: Send This Completed Form in For CE Credit Today!Document6 pagesSecundum Artem: Send This Completed Form in For CE Credit Today!randatagNo ratings yet
- Rectal SuppositoriesDocument6 pagesRectal SuppositoriesLinh PhamNo ratings yet
- Preparing For PandemicDocument3 pagesPreparing For PandemicLinh PhamNo ratings yet
- Analytical ChemistryDocument2 pagesAnalytical ChemistryLinh PhamNo ratings yet
- PPM Action Plan - 13 - 01 - 2022Document128 pagesPPM Action Plan - 13 - 01 - 2022whoosh2008No ratings yet
- What Is Compounding?: and How Can It Benefit Me?Document32 pagesWhat Is Compounding?: and How Can It Benefit Me?Nike Moore0% (1)
- Nima ReportDocument81 pagesNima ReportNima MuraleedharanNo ratings yet
- Principles of Antimicrobial PrescribingDocument38 pagesPrinciples of Antimicrobial Prescribingioana antonesiNo ratings yet
- Speakers List: Arencibia Quality Compliance Associates Independent ConsultantDocument7 pagesSpeakers List: Arencibia Quality Compliance Associates Independent ConsultantIcee SinlapasertNo ratings yet
- Drug Reduction List 112006Document21 pagesDrug Reduction List 112006Pruthvish PatelNo ratings yet
- Novel Drugs 2022 Ce Update HandoutDocument10 pagesNovel Drugs 2022 Ce Update Handoutapi-661456802No ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical LicensingDocument13 pagesPharmaceutical Licensingkumari astha rupaliNo ratings yet
- Fentanyl NeomedDocument3 pagesFentanyl NeomedmuarifNo ratings yet
- The Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940 and Rules, 1945Document177 pagesThe Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940 and Rules, 1945Bhaskar Chaurasia100% (3)
- At The Pharmacy British English Teacher Ver2Document6 pagesAt The Pharmacy British English Teacher Ver2Manuel Alfaro PumarinoNo ratings yet
- Details of Projects B Pharm and M Pharm Final YearDocument19 pagesDetails of Projects B Pharm and M Pharm Final YearRitesh GangoleNo ratings yet
- Non ComplianceDocument29 pagesNon ComplianceFaraz Qurban Rajper100% (2)
- Pharmacokinetics: of OphthalmicDocument4 pagesPharmacokinetics: of OphthalmicWina Siska Purnama BurmanNo ratings yet
- Lista Me Cmimet CIF Dhe EXW Te BarnaveDocument1,070 pagesLista Me Cmimet CIF Dhe EXW Te BarnaveAgron Spahija100% (1)
- Bedaquiline TB PDFDocument2 pagesBedaquiline TB PDFHana Fauzyyah HanifinNo ratings yet
- Abdullah M. Kharbosh, B.SC., PharmDocument27 pagesAbdullah M. Kharbosh, B.SC., PharmsrirampharmaNo ratings yet
- Digital Hospital BrochureDocument11 pagesDigital Hospital BrochuresyonaNo ratings yet
- Dishman Carbogen Amcis LTD: Company BackgroundDocument3 pagesDishman Carbogen Amcis LTD: Company BackgroundKhush GosraniNo ratings yet
- National List of Essential Medicines of India 2011Document123 pagesNational List of Essential Medicines of India 2011Gopal KarvaNo ratings yet
- ANDA Filing and Refuse To Receive Issues: Johnny Young, M.A.L.ADocument39 pagesANDA Filing and Refuse To Receive Issues: Johnny Young, M.A.L.AJoe Luis Villa MedinaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Mosbys Pharmacy Technician 5th Edition Karen Davis Anthony GuerraDocument12 pagesTest Bank For Mosbys Pharmacy Technician 5th Edition Karen Davis Anthony GuerrachokydeplorerbxeNo ratings yet
- AstraZeneca, Merck, Ofthalmi and other pharmaceutical products listDocument4 pagesAstraZeneca, Merck, Ofthalmi and other pharmaceutical products listcloris gilNo ratings yet
- Birthdays List JuneDocument14 pagesBirthdays List JuneRamanjaneyulu ReddyNo ratings yet
- Omnicell-HealthTrust Overview BrochureDocument8 pagesOmnicell-HealthTrust Overview BrochuregurbaxeeshNo ratings yet
- Drugs and Drug Development StagesDocument50 pagesDrugs and Drug Development StagesmotlhankanalaronaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledEllen LarocoNo ratings yet
- Drug Registration Guidance Document DRGD - Second Edition Revised - July 2019Document710 pagesDrug Registration Guidance Document DRGD - Second Edition Revised - July 2019Revathy ThandapaniNo ratings yet
- Food and Drug Interactions NotesDocument8 pagesFood and Drug Interactions NotesSUDHEER SNo ratings yet
- Contoh Implementasi Fmea Dalam Pelayanan FarmasiDocument13 pagesContoh Implementasi Fmea Dalam Pelayanan FarmasiSuroso RidhoNo ratings yet