Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Amphibole: Amphibole in Metabasic Rock
Uploaded by
vasokosmOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Amphibole: Amphibole in Metabasic Rock
Uploaded by
vasokosmCopyright:
Available Formats
22/5/13
Amphibole
Return to introduction
Amphibole
Mineral structure: Chain silicate Common mineral in Granites, Diorites, Metabasics, Calc-silicates Rock-forming minerals associated with Amphibole: Plagioclase Metabasic rocks may contain large amounts of amphibole at moderate grades = Amphibolites.
Amphibole in Metabasic rock
Analyser out Analyser in
Key optical features of amphibole in thin section: Green (more rarely Brown, Colourless or Blue) Two cleavages (intersect at 120 o ) Pleochroic Moderate interference colours Inclined extinction (typically <30o ) Common minerals that might be confused with amphibole and may occur in similar rocks: Biotite (One cleavage, straight extinction), Chlorite (Green, low interference colours) Pyroxene (Two cleavages at 90 o , higher extinction angle, typically paler coloured) Common alteration product: Chlorite (pale green). Commonly replaces: Clinopyroxene Analyser out
web2.ges.gla.ac.uk/~minerals/Amphibole.htm
1/5
22/5/13
Amphibole
Complete or partial alteration at lower temperature associated with influx of fluids
Amphibole shape
Amphibole forms typically well-shaped crystals in rocks with abundant quartz or plagioclase. Ideal crystal forms are elongate with diamond-shaped or stretched hexagon cross section. In rocks with abundant Fe-Mg silicates amphibole typically is equant Amphibole in granite Analyer out Amphibole in Calc-silicate
Amphibole in Gneiss Analyser out
Amphibole in contact metabasic
Amphibole colours and composition (images with analyser out)
Glaucophane (blue-mauve-colurless) Actinolite (blue green green)
web2.ges.gla.ac.uk/~minerals/Amphibole.htm
2/5
22/5/13
Amphibole
Tremolite (colourless)
Hornblende (green brown)
Hornblende (brown)
Note: Different amphibole compositions associated with different rock types and conditions Glaucophane - Na-rich found stable at low T and high P (blueschists) Tremolite - Mg-rich found in metamorphosed carbonates and peridotites Actinolite Fe-rich stable at moderate T (moderate T metamorphic rocks) Hornblende Fe-Al-rich stable at high T (igneous rocks and high T metamorphic rocks) Typically paler amphiboles contain less Fe and more Mg
Amphibole pleochroism in amphibolite
Analyser out Stage rotated by 90 o
web2.ges.gla.ac.uk/~minerals/Amphibole.htm
3/5
22/5/13
Amphibole
Note: Regional metamorphism may cause elongate amphiboles to align in similar orientation. However amphibole-rich rocks rarely contain a strong cleavage in comparison to mica-rich lithologies.
Cleavage in Amphibole
Amphibole has two cleavages running parallel to the length of the crystal. Thus elongate sections through amphibole crystals show a single cleavage, cross sections show two cleavages intersecting at 120 o . Note: grains showing two well-developed cleavages may be tricky to find All images with analyser out
Inclined extinction in Amphibole
Tremolite in a calcite marble Analyser in Analyser in
web2.ges.gla.ac.uk/~minerals/Amphibole.htm
4/5
22/5/13
Amphibole
Actinolite in a metabasic rock Analyser out Analyser in
Note: extinction angles measured in elongate crystals typically <30o Twinned amphibole in granite Analyser in
Note: twinning in amphiboles is relatively unusual.
Take the Amphibole test Return to top Return to introduction
web2.ges.gla.ac.uk/~minerals/Amphibole.htm
5/5
You might also like
- Tyre ReportDocument19 pagesTyre ReportZachary HuffmanNo ratings yet
- AP621 Lect02 DiffractionDocument117 pagesAP621 Lect02 DiffractionHassanNo ratings yet
- 1097-1136 Metallogenic Provinces in An Evolving Geodynamic FrameworkDocument40 pages1097-1136 Metallogenic Provinces in An Evolving Geodynamic FrameworkLYNAMARICELA83No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Differential EquationsDocument27 pagesChapter 1 - Differential EquationsAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint Presentation 1Document34 pagesPowerPoint Presentation 1Tamani MoyoNo ratings yet
- Agilent Vacuum Training GuideDocument27 pagesAgilent Vacuum Training GuidesinytellsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 07 G278 2007 Optical IndicatrixDocument27 pagesLecture 07 G278 2007 Optical IndicatrixAaqib AliNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulics Proceedings of 26th InternationalDocument601 pagesFluid Mechanics and Hydraulics Proceedings of 26th InternationalSwan Zay AungNo ratings yet
- Biomarkers: PetroleumDocument13 pagesBiomarkers: PetroleumMohamed HaboNo ratings yet
- Gamma Scanning TechniqueDocument26 pagesGamma Scanning TechniqueWillykateKairu75% (4)
- US Army Radio Wave Propagation and AntennasDocument186 pagesUS Army Radio Wave Propagation and Antennaswa4gvt5044100% (1)
- Dimension Stone: The Latest Trends in Exploration and Production TechnologyDocument36 pagesDimension Stone: The Latest Trends in Exploration and Production Technologytkujun9636No ratings yet
- P1 (Intro) & P2Document38 pagesP1 (Intro) & P2Khana Rizki MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Disaster readiness risk assessmentDocument2 pagesDisaster readiness risk assessmentMary Ann Tolibao100% (5)
- Minerals Engineering: Duncan M. Smythe, Annegret Lombard, Louis L. CoetzeeDocument10 pagesMinerals Engineering: Duncan M. Smythe, Annegret Lombard, Louis L. Coetzeefaouzi rachidNo ratings yet
- B. Pesic - Electrometallurgy Review PDFDocument44 pagesB. Pesic - Electrometallurgy Review PDFAna Luisa Garnica Salgado100% (1)
- Hydrogen Permeability and Integrity of Hydrogen Transfer PipelinesDocument52 pagesHydrogen Permeability and Integrity of Hydrogen Transfer PipelineslaercioudescNo ratings yet
- Smart Street Light System Table of ContentsDocument27 pagesSmart Street Light System Table of ContentsMuhammad Solahuddin100% (2)
- Forming Mineral AtlasDocument44 pagesForming Mineral AtlasDaneel OliwanNo ratings yet
- Tornos 2015 Geoquimica CLAMDocument37 pagesTornos 2015 Geoquimica CLAMGabriel CarreñoNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Linear Control (PDFDrive)Document401 pagesFundamentals of Linear Control (PDFDrive)hajibaNo ratings yet
- Petrogenesis of Eclogites: M.Sc. Semester IIDocument15 pagesPetrogenesis of Eclogites: M.Sc. Semester IIDanis Khan100% (1)
- Practicaldistillationcontrol 140307141500 Phpapp01Document549 pagesPracticaldistillationcontrol 140307141500 Phpapp01syedmuhammadtariqueNo ratings yet
- Detachment Fault Related MineralizationDocument5 pagesDetachment Fault Related MineralizationFatah. RNo ratings yet
- Isotropic and Anisotropic MineralsDocument53 pagesIsotropic and Anisotropic MineralsGermán Rosano100% (2)
- Overview of Mineral Processing Methods: August 2015Document14 pagesOverview of Mineral Processing Methods: August 2015Zanele MbathaNo ratings yet
- Lead Anodes for Copper ElectrowinningDocument28 pagesLead Anodes for Copper Electrowinningvictor perez villegasNo ratings yet
- Metamorphism - Introduction: Metamorphism - All Solid-State Changes in A Rock's Composition and Fabric OccurringDocument55 pagesMetamorphism - Introduction: Metamorphism - All Solid-State Changes in A Rock's Composition and Fabric OccurringAvinash Upadhyay100% (1)
- Combination of Ion Exchange and Solvent Extraction Versus Solvent Extraction, A Technical-Economical ComparisonDocument14 pagesCombination of Ion Exchange and Solvent Extraction Versus Solvent Extraction, A Technical-Economical ComparisonJordan GonzalezNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Chemical Classification of Common Volcanic RocksDocument26 pagesA Guide to Chemical Classification of Common Volcanic RocksPepeeJh VaargasNo ratings yet
- 02-MIPR-421-Mineral Processing MethodologiesDocument39 pages02-MIPR-421-Mineral Processing MethodologiesGomeh Damien Mtonga100% (1)
- Mineral ProcessingDocument10 pagesMineral ProcessingMahmoud MahmoudmNo ratings yet
- Basarab Nicolescu, The Relationship Between Complex Thinking and TransdisciplinarityDocument17 pagesBasarab Nicolescu, The Relationship Between Complex Thinking and TransdisciplinarityBasarab Nicolescu100% (2)
- Amphiboles PDFDocument3 pagesAmphiboles PDFMaria Martha SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Graphitisation Cast IronDocument28 pagesGraphitisation Cast IronKurnia BijaksanaNo ratings yet
- Reflected 13Document17 pagesReflected 13TriePrasetyoWibowoNo ratings yet
- Amphibole (Shanki)Document32 pagesAmphibole (Shanki)debasish mahantaNo ratings yet
- Mineral IdentificationDocument17 pagesMineral IdentificationSandeep MeenaNo ratings yet
- GS - 104 Elementary Petrology Lecture Outline Structure of Metamorphic RocksDocument27 pagesGS - 104 Elementary Petrology Lecture Outline Structure of Metamorphic RocksSakaouth HossainNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Bentonite Clay PDFDocument6 pagesCharacterization of Bentonite Clay PDFHafiz Mudaser AhmadNo ratings yet
- Major and Minor Elements GeochemistryDocument7 pagesMajor and Minor Elements GeochemistryShah FahadNo ratings yet
- Banded Iron Formations (BIF) - Ancient Rock Layers Rich in IronDocument2 pagesBanded Iron Formations (BIF) - Ancient Rock Layers Rich in IronAlexandru StefanNo ratings yet
- Geochemistry of Metamorphic RocksDocument5 pagesGeochemistry of Metamorphic RocksGaddaf Ayub100% (2)
- Queen's University - Mining Engineering - ListDocument3 pagesQueen's University - Mining Engineering - ListNitinkiet103No ratings yet
- The Serpentine Mineral GroupDocument3 pagesThe Serpentine Mineral GroupYudhi PrawiraNo ratings yet
- Magmatic DifferentiationDocument6 pagesMagmatic DifferentiationEbenezerSherlockAyiteyNo ratings yet
- Geologic Map of AfricaDocument1 pageGeologic Map of Africaall_togetherNo ratings yet
- Genesis of KupferschieferDocument15 pagesGenesis of KupferschieferMaricela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Kimberlite - Mantle-Derived Igneous Rock Source of DiamondsDocument3 pagesKimberlite - Mantle-Derived Igneous Rock Source of DiamondsWWW.1580.L0GN.CFNo ratings yet
- Igneous Rock TexturesDocument5 pagesIgneous Rock Texturesapi-3808551No ratings yet
- Classification of Igneous RockDocument32 pagesClassification of Igneous RockNitesh-02100% (1)
- Magway (Magwe) RegionDocument3 pagesMagway (Magwe) RegionmyatNo ratings yet
- Application of Major and Trace ElementDocument29 pagesApplication of Major and Trace ElementkowsilaxNo ratings yet
- Cleavage (Geology) : Structural Geology Petrology MetamorphismDocument4 pagesCleavage (Geology) : Structural Geology Petrology MetamorphismNehaNo ratings yet
- Examination of Copper Electrowinning Smoothing Agents. Part I: A ReviewDocument7 pagesExamination of Copper Electrowinning Smoothing Agents. Part I: A ReviewHelen HuancaNo ratings yet
- MineralExplorationDocument16 pagesMineralExplorationJuan AgungNo ratings yet
- Maceral Characteristics and Vitrinite Reflectance PDFDocument12 pagesMaceral Characteristics and Vitrinite Reflectance PDFWahyu Probo AnantoNo ratings yet
- MigmatitesDocument3 pagesMigmatitessalvepramod99No ratings yet
- Mapping Mineral Systems With SWIRDocument45 pagesMapping Mineral Systems With SWIRHugo Poma FernándezNo ratings yet
- USGS Wentworth Grain Size ChartDocument1 pageUSGS Wentworth Grain Size Chartetchplain100% (1)
- MINERALOGY Lectureslides PDFDocument63 pagesMINERALOGY Lectureslides PDFSuman TimalsinaNo ratings yet
- Electron and Positron Spectroscopies in Materials Science and Engineering: Materials Science and TechnologyFrom EverandElectron and Positron Spectroscopies in Materials Science and Engineering: Materials Science and TechnologyOtto BuckNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature, Concepts and Classification of Oreshoots in Vein DepositsDocument20 pagesNomenclature, Concepts and Classification of Oreshoots in Vein DepositsAngel Salas ColcaNo ratings yet
- Rge 12129Document10 pagesRge 12129edwinNo ratings yet
- As 2856.3-2000 Coal Petrography Method For Microscopical Determination of The Reflectance of Coal MaceralsDocument7 pagesAs 2856.3-2000 Coal Petrography Method For Microscopical Determination of The Reflectance of Coal MaceralsSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- ORE MICROSCOPY APPLICATIONSDocument25 pagesORE MICROSCOPY APPLICATIONSRobert UribeNo ratings yet
- Paul Ramdohr (Auth.) - The Ore Minerals and Their Intergrowths-Elsevier (1969) - 641-656-9Document1 pagePaul Ramdohr (Auth.) - The Ore Minerals and Their Intergrowths-Elsevier (1969) - 641-656-9zetadoc um.sem1.2020No ratings yet
- Atlas of Zircon TextureDocument32 pagesAtlas of Zircon TexturemiarangocNo ratings yet
- Volcaniclastic Sediments - Composition, Classification and DiagenesisDocument45 pagesVolcaniclastic Sediments - Composition, Classification and DiagenesisDavid A. Cuéllar100% (3)
- Logger For Core RocksDocument19 pagesLogger For Core RocksVanesaRodriguezRojasNo ratings yet
- Clays and Clay Minerals: Proceedings of the Fourteenth National Conference, Berkeley, CaliforniaFrom EverandClays and Clay Minerals: Proceedings of the Fourteenth National Conference, Berkeley, CaliforniaS. W. BaileyNo ratings yet
- Grammar TargetsDocument2 pagesGrammar TargetsvasokosmNo ratings yet
- GTW Israel Sponsorship AgreementDocument3 pagesGTW Israel Sponsorship AgreementvasokosmNo ratings yet
- Ex.2 Cosmic B1Document1 pageEx.2 Cosmic B1vasokosmNo ratings yet
- Grammar PrepositionsDocument1 pageGrammar PrepositionsvasokosmNo ratings yet
- ECCE 2013 SampleAnsSheetDocument2 pagesECCE 2013 SampleAnsSheetPanagiotis MoragiannisNo ratings yet
- Ex.1 Cosmic B1Document1 pageEx.1 Cosmic B1vasokosmNo ratings yet
- Measuring Wind Speed with the Beaufort ScaleDocument2 pagesMeasuring Wind Speed with the Beaufort ScalevasokosmNo ratings yet
- ThoukididisDocument1 pageThoukididisvasokosmNo ratings yet
- Cook and travel !!! - Απρίλιος 2012 syntagh kourouDocument1 pageCook and travel !!! - Απρίλιος 2012 syntagh kourouvasokosmNo ratings yet
- AdidaktoDocument1 pageAdidaktovasokosmNo ratings yet
- Emeina EdwDocument1 pageEmeina EdwvasokosmNo ratings yet
- Listening Activity 1SBDocument1 pageListening Activity 1SBvasokosmNo ratings yet
- Umnos Eis Tin EleftheriaDocument1 pageUmnos Eis Tin EleftheriavasokosmNo ratings yet
- ThoukididisDocument1 pageThoukididisvasokosmNo ratings yet
- CrepesDocument1 pageCrepesvasokosmNo ratings yet
- Epidote: Epidote in Calc-SilicateDocument3 pagesEpidote: Epidote in Calc-SilicatevasokosmNo ratings yet
- PancakesDocument1 pagePancakesvasokosmNo ratings yet
- Askiseis MathimatikwnDocument2 pagesAskiseis MathimatikwnvasokosmNo ratings yet
- K-Feldspar: K-Feldspar (With Plagioclase Inclusion) in Granite and SimpleDocument4 pagesK-Feldspar: K-Feldspar (With Plagioclase Inclusion) in Granite and SimplevasokosmNo ratings yet
- Cordier It eDocument4 pagesCordier It evasokosmNo ratings yet
- Chlo RiteDocument5 pagesChlo RitevasokosmNo ratings yet
- Minerals Down The Microscope On MoodleDocument7 pagesMinerals Down The Microscope On MoodlevasokosmNo ratings yet
- Quartz in SchistDocument4 pagesQuartz in SchistvasokosmNo ratings yet
- Pla Gio ClaseDocument5 pagesPla Gio ClasevasokosmNo ratings yet
- Muscovite Mineral Structure and Optical PropertiesDocument4 pagesMuscovite Mineral Structure and Optical PropertiesvasokosmNo ratings yet
- Basalt Mineral PyroxeneDocument6 pagesBasalt Mineral Pyroxenevasokosm100% (2)
- Garnet Mineral Structure and Optical PropertiesDocument2 pagesGarnet Mineral Structure and Optical PropertiesvasokosmNo ratings yet
- A Taste of The Best - Vanilla Pudding CookiesDocument7 pagesA Taste of The Best - Vanilla Pudding CookiesvasokosmNo ratings yet
- CalciteDocument3 pagesCalcitevasokosmNo ratings yet
- Fusion Cross-Sections - 24 - 11 - 2020Document25 pagesFusion Cross-Sections - 24 - 11 - 2020Isaiah KimNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual Course Code Ece254 Course Title: Unified Electronics Laboratory-IDocument67 pagesLaboratory Manual Course Code Ece254 Course Title: Unified Electronics Laboratory-IKaran SainiNo ratings yet
- Physics 4 O LevelDocument3 pagesPhysics 4 O LevelChrispin Msofe100% (1)
- Homework 6 solutionsDocument3 pagesHomework 6 solutionsAntonio Abel Mejìa DìazNo ratings yet
- With Aerzen Turbos, Blowers and Compressors: Heat RecoveryDocument8 pagesWith Aerzen Turbos, Blowers and Compressors: Heat RecoveryBülent BulutNo ratings yet
- Radiation Heat Transfer: Chapter SevenDocument13 pagesRadiation Heat Transfer: Chapter SevenprasanthiNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Homework Solutions and CalculationsDocument4 pagesHeat Transfer Homework Solutions and CalculationsYELSI YAJAIRA QUICENO VILLANUEVANo ratings yet
- SHM & Elasticity: Ba C BC A Ba CDocument13 pagesSHM & Elasticity: Ba C BC A Ba CKrithikaNo ratings yet
- Foundation For MBR-flatDocument6 pagesFoundation For MBR-flatjatinNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 2 - Energy and MotionDocument7 pagesLab Report 2 - Energy and MotionDawood SulemanNo ratings yet
- Maths HL Topic 1Document2 pagesMaths HL Topic 1api-196197645No ratings yet
- INChO2012 Solution of Previous Year Question Papers of Indian National Chemistry Olympiad (INChO)Document9 pagesINChO2012 Solution of Previous Year Question Papers of Indian National Chemistry Olympiad (INChO)Akshay PandeyNo ratings yet
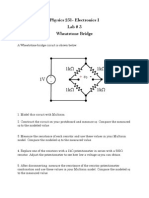
- Electronics I Lab #3 Wheatstone Bridge CircuitDocument4 pagesElectronics I Lab #3 Wheatstone Bridge Circuitmlj8753No ratings yet
- Car 66Document168 pagesCar 66DharmendraNo ratings yet
- Physics for Scientists and Engineers Introduction and Chapter 1 SummaryDocument20 pagesPhysics for Scientists and Engineers Introduction and Chapter 1 SummaryYana IshakNo ratings yet
- CmpE Degree RequirementsDocument3 pagesCmpE Degree RequirementsTrai TranNo ratings yet
- Cosmology, Physics and Philosophy: Benjamin Gal-OrDocument74 pagesCosmology, Physics and Philosophy: Benjamin Gal-Orapi-3835692No ratings yet