Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ethernet
Uploaded by
Riti NayyarCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ethernet
Uploaded by
Riti NayyarCopyright:
Available Formats
Ethernet ensures the position free data transfer over the network. It is the backbone of various types of networks.
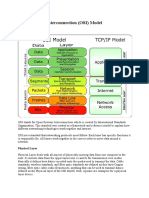
Early Ethernet ware 10 base T which supports a max speed of 10 mbps. Which when replaced by a faster network can support up to 100mbps. The last are gigabit Ethernet which supports a transfer rate upto 1gbps. It supports a speed upto 5 gbps. OSI reference application layer Presentation layer Session reciever layer Transport layer Network layer Data-link layer Physical layer The same damn thing on this side Network layer Data-link layer Physical layer sender
Data communications standard The basic objective of standardization was to create easy user interface & allow the software to fulfill the technical requirements of transmitting the data effectively. The standardization made the communication process easy & simple which can handle in a plug and play manner. An organization could change its data communication hardware w/o changing its programs or retraining the users & the user might not even realize that there had been a change in the hardware. Biz must
be able to implement the new technologies needed to stay competitive & gain strategic advantage w/o changing the programs. 2 of the first data communication models were IBMs (SNA) system network architecture and DECCs network architecture. These and other models were designed primarily to link their own hardware in response to the numerous vendor models, the ISO. The ISO developed the 7 layered open system OSI model to standardize the communication industry. The 7 layers of OSI describes what happens when a computer communicates with another computer. The model provides a set of standards that define a common language that 2 computers can talk to each other over a network. Protocols describe how the data are to be transferred between different parts of the model. Protocol is a communication language that computer networks use to communicate with each other. The first layer (physical layer) enables the electrical connections and signalling to take place. This layer is made up of tables such are twisted pair cables, fibre optic cables. All communication signals from higher level travel through the physical layer which helps in physical connectivity. The 2 nd layer (data link layer) is responsible for controlling the data stream between the sending & receiving nodes. Its job is to put the characters together into messages, check them for errors & start the transmission. It also checks to see whether the message arrives at its destination & initiates any necessary retransmission. The 3 rd layer (network layer) determines the physical pathway the data will take when they are communicated. This decision is based on network conditions, priorities of service etc. IP protocol (TCPIP) is the network layer. the 4 th layer (transport layer) is used to look for alternate routes for saving transmitted data in the event the network fails. It is also responsible for quality control of data received. A popular protocol used in transport layer is TCP. The 5th layer (session layer) initiates, maintains & terminates each session. It allows 2 applications to communicate across the network & is responsible for functions such as security, logging in & out, administration & the name recognition. The 6th layer (presentation layer) formats data so that they can be used by the application program or communication devices. It controls screen features such as blinking characters, reverse video, special data entry formats & graphics. It may also control encryption and other special file formatting. All control codes, special graphics & character sets reside in this layer. The operation of printers, plotters & other peripheral devices is also controlled by the software in this layer. The 7 th & the aapplication layer as the network application system & application programs reside in this layer & are directly controlled by the user. Each layer in this model performs a service for the layer above it. (connect the entire receiver part from above) - aplication transport
connect these bitches into a hierarchy ------------ network Host to network TCPIP model: the 4 layers (the application layer, the presentation layer & The session layer) are combined into 1 layer that is application layer. The transport & network layers remain as they are functionally as well. The data-link & physical layer are combined into 1 layer known as host to network. Copy table from palak
The various devices used in the physical layer: HUBS/repeaters: are simple devices that pass all traffic in both directions between the LAN sections. They are the connection components for different devices on the network (printer, fax machine etc). they link & operate at the physical layer of the OSI or TCIP reference model. The main function of the HUB is to amplify (adjust the timng signals) before transmitting them to other parts of the network. They forward every msg they receive to other sections of the LAN even though if it is not required by the nodes. There are 3 types of HUBS: passive, intelligent & switching. Bridges connect 2 LANs or 2 segments of the same LAN. They operate at the datalink layer of the OSI/TCPIP model. Bridges dont perform protocol conversion. In a large network, thye forward only those msgs which need to go to other segments of the network based on the IP address. Bridges are a combination of hardware & Software. Switches connect 2 or more LAN segments that uses the same data link& network protocol. They work at the data link layer of OSI/TCIP model. They connect several low speed LAN segments into backbone networks. They typically provide codes in multiples of 4. Reuters connect 2 or more LANs that use the same or different data link protocols but the same network protocol. The router operates at the network layer of the OSI/tCPIP model. One of the major features of the router is its capability of selecting the optimal network path to transmit the packets. to accomplish this task the router uses a routing table. It also possesses software which identifies the best rule to transmit the packet. They allow the logical separation of an internet work into many networks by using an addressing schemethat distinguishes between devices addresses at the data link layer & internet work addresses at the network layer. Routing systems use the internet work addresses to specify the network protocol packet & the routing tables for routing decisions. The difference between a
router & a bridge: a router processes only those messages that are specifically addressed to it. They also act as a firewall if implemented properly. Gateways are more complex than bridges or routers as they are the interfaces between 2 or more dissimilar networks. As shown in the diagram, gateway connects 2 different networks working on 2 different protocols, namely TCPIP for LAN & SNA for IBM mainframe computer. Gateway operates right through the network layer up to the application layer. They forward only those msgs that need to go to another network. They translate 1 network protocol into another, translates data formats & Opens sessions between application progs, thus overcoming both hardware & software incompatibilities.
Types of communication Simplex: in 1 direction (car radio, tv, keyboard) Half duplex: in 1 direction at a time (2 way radio) full duplex: in both directions (telephone)
internet, intranet, extranet internet is a universal network. It is a network of networks. It has universal ownership, available & accessible all the time from any part of the world. TCPIP protocol is the backbone of the internet. It is a public network. Intranet is a corporate internet meant for defined users of an organization. It is a pvt network created for the community of the organization which allow them to access organizations data & databases using the browser from anywhere at any time. It is a pvt computer network that uses internet technologies to securely share any part of an organizations info or operational info w/ its employees & users. It can be LAN based or WAN based depending upon how big the organizations network is. Well known internet protocols are used in the intranet such as HTTP, SMTP, FTP. Following are the characteristics of the intranet: 1. It allows users to share the data & work space which helps users to locate & view info faster as per authorization level. 2. It serves as a powerful communication tool within an org across various locations and across various projects. Extranet: it is an extended intranet. It is a pvt-to-pvt network between defined users & the stakeholders & organizations. Between 2 or more intranets using internet technologies.
Virtual pvt network wherein the public telecommunications infrastructure is used so that the organizations will not have to use leased lines.
You might also like
- Assignment 4Document10 pagesAssignment 4anil rajputNo ratings yet
- Communications Layers SummaryDocument7 pagesCommunications Layers SummaryKarthickmanikandan GNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Computer Networks and OSI ModelDocument16 pagesIntroduction to Computer Networks and OSI Modelnavya goneNo ratings yet
- Network Architectures: Layers of OSI Model and TCP/IP ModelDocument5 pagesNetwork Architectures: Layers of OSI Model and TCP/IP ModelLvly AngelNo ratings yet
- The Open System Interconnection Explain PDFDocument9 pagesThe Open System Interconnection Explain PDFruletriplexNo ratings yet
- OSI ModelDocument6 pagesOSI ModelmushahidNo ratings yet
- Network LabDocument8 pagesNetwork LabTanusri GhoshNo ratings yet
- Network Programming: MT-24C Assignment-1Document17 pagesNetwork Programming: MT-24C Assignment-1Inder2002No ratings yet
- 10ec71 NotesDocument129 pages10ec71 NotesMSAMHOURINo ratings yet
- 10ec71 - CCN - Notes PDFDocument127 pages10ec71 - CCN - Notes PDFRashmi Samant100% (2)
- P1: Discuss The Benefits and Constraints of Different Network Types and StandardsDocument8 pagesP1: Discuss The Benefits and Constraints of Different Network Types and StandardsSangam50% (2)
- Computer Networking Refers To Connected Computing Devices 222Document13 pagesComputer Networking Refers To Connected Computing Devices 222RAY COOLNo ratings yet
- The TCP/IP Protocol Architecture ExplainedDocument3 pagesThe TCP/IP Protocol Architecture ExplainedAmirtha Varshini100% (1)
- OSI Model ExplainedDocument8 pagesOSI Model ExplainedRenegade DiverNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Networking LayersDocument17 pagesIntroduction to Networking LayersSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Networking For PentestingDocument3 pagesNetworking For PentestingNana AdjeiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction Structure:: 1.0 ObjectivesDocument19 pagesUnit 1 Introduction Structure:: 1.0 ObjectivesMohamed HajiNo ratings yet
- General:: Ali Mohammed Hassn Muafa TC 08-19Document12 pagesGeneral:: Ali Mohammed Hassn Muafa TC 08-19saske969No ratings yet
- BSC Honours in Computer Science: Part 2 Semester 1: Kashuware Brilliant M198070 Mazonde Phyeciathy M190810Document16 pagesBSC Honours in Computer Science: Part 2 Semester 1: Kashuware Brilliant M198070 Mazonde Phyeciathy M190810Brilliant Billykash KashuwareNo ratings yet
- UNIT_IV[1]Document29 pagesUNIT_IV[1]Erwin VunguNo ratings yet
- What is TCP/IP? The basics of the TCP/IP protocol suiteDocument5 pagesWhat is TCP/IP? The basics of the TCP/IP protocol suiteNarayana MayyaNo ratings yet
- Network Support LayersDocument3 pagesNetwork Support LayersAbdelrhman AhmedNo ratings yet
- Omputer Engineering - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument20 pagesOmputer Engineering - WWW - Rgpvnotes.indeepak kushwahNo ratings yet
- First Assignment in CnsDocument7 pagesFirst Assignment in CnsAlcala, John Paul P.No ratings yet
- 1.0 The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) ModelDocument5 pages1.0 The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) Modelvickypatel_63873791100% (1)
- OSI ModelDocument32 pagesOSI ModelNathenael Yimer DametewNo ratings yet
- 1 STDocument60 pages1 STmayank barsenaNo ratings yet
- MOdel OSI NoteDocument7 pagesMOdel OSI NoteZulfadli HanaffiNo ratings yet
- OSI Model (Open Systems Interconnection) : NetworkDocument22 pagesOSI Model (Open Systems Interconnection) : NetworkStephen ChidhandaraNo ratings yet
- Capture All HTTP Packets by Using Wireshark and Try To Fetch All HTTP Usernames & PasswordsDocument38 pagesCapture All HTTP Packets by Using Wireshark and Try To Fetch All HTTP Usernames & PasswordsCandy AngelNo ratings yet
- OSI ModelDocument32 pagesOSI ModelBhanu Singh0% (1)
- TCP/IP Model ExplainedDocument14 pagesTCP/IP Model ExplainedLovepreet SinghNo ratings yet
- IPv4 Overview in 40 CharactersDocument24 pagesIPv4 Overview in 40 CharactersusamaNo ratings yet
- IT Notes Unit 5Document14 pagesIT Notes Unit 5Deepankar Anil KumarNo ratings yet
- Presentacion 8 PDFDocument18 pagesPresentacion 8 PDFJose Leonardo Simancas GarciaNo ratings yet
- OSI Model and TCPIPDocument12 pagesOSI Model and TCPIPSTONE POWERNo ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument5 pagesPDF DocumentBritney PitttersonNo ratings yet
- Name - Prajwal Ghale Roll On - NP000477 Section - B: Question No.1Document4 pagesName - Prajwal Ghale Roll On - NP000477 Section - B: Question No.1Prajwal GhalezNo ratings yet
- Network Protocols - TutorialspointDocument5 pagesNetwork Protocols - TutorialspointThusharika ThilakaratneNo ratings yet
- Networking QuestionsDocument4 pagesNetworking QuestionsShivanshu Kumar UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- OSI and TCP/IP Models ExplainedDocument5 pagesOSI and TCP/IP Models ExplainedCustomer CUstomerNo ratings yet
- Computer CommunicationDocument7 pagesComputer Communicationsaravanamuthaly1397No ratings yet
- Lab-2 Networking Basics: What Is A Network?Document6 pagesLab-2 Networking Basics: What Is A Network?Haidar MalikNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks:: OSI Reference ModelDocument11 pagesComputer Networks:: OSI Reference ModelMasterNo ratings yet
- Computer Communication Networks CCN NotesDocument127 pagesComputer Communication Networks CCN NotesVTU PRO100% (3)
- BSNLDocument14 pagesBSNLRavi SinghNo ratings yet
- TCP IP ApplicationsDocument10 pagesTCP IP ApplicationsJetesh DevgunNo ratings yet
- Cisco: Sritrusta SukaridhotoDocument34 pagesCisco: Sritrusta SukaridhotoAhmad SahalNo ratings yet
- Overview of Comp NWsDocument42 pagesOverview of Comp NWsfahana abdul vahabNo ratings yet
- TCP-IP Part-1Document38 pagesTCP-IP Part-1Aadya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyFrom EverandIntroduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Networking and The Osi ModelDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Networking and The Osi ModelJerald Pacheco JoseNo ratings yet
- IPv 4Document20 pagesIPv 42224 Momynul IslamNo ratings yet
- Is OSI ModelDocument7 pagesIs OSI ModelLena AudeNo ratings yet
- DNC 2113 - Network Programming Theory and Java OverviewDocument38 pagesDNC 2113 - Network Programming Theory and Java OverviewainnNo ratings yet
- Internetworking Models: Model Was Created by The International Organization ForDocument45 pagesInternetworking Models: Model Was Created by The International Organization Forkerya ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Osi Iso Tcp/Ip Netware Atm Sna Ss7: ComputerDocument7 pagesOsi Iso Tcp/Ip Netware Atm Sna Ss7: ComputerAmarbant Singh DNo ratings yet
- BASIC CONCEPT OF LAYERINGDocument11 pagesBASIC CONCEPT OF LAYERINGSneha SinghNo ratings yet
- OSI ModelDocument10 pagesOSI ModelJayalle PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1From EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Nabh Hvac OTDocument9 pagesNabh Hvac OTPrafulNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Philosophy LogicDocument68 pagesIntroduction To Philosophy LogicRiti Nayyar50% (2)
- Cooking MeasuresDocument4 pagesCooking MeasuresRiti NayyarNo ratings yet
- InfectionDocument3 pagesInfectionRiti NayyarNo ratings yet
- Intro To PhilosophyDocument1 pageIntro To PhilosophyRiti NayyarNo ratings yet
- Strategy ConceptsDocument14 pagesStrategy ConceptsRiti NayyarNo ratings yet
- Imp Spanish Verb ListDocument4 pagesImp Spanish Verb ListRiti NayyarNo ratings yet
- Spanish Weather Expressions GuideDocument4 pagesSpanish Weather Expressions GuideRiti NayyarNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument14 pagesStrategic ManagementRiti NayyarNo ratings yet
- Family Clothes Body Stationery - SpanishDocument2 pagesFamily Clothes Body Stationery - SpanishRiti NayyarNo ratings yet
- Cost of CapitalDocument26 pagesCost of CapitalRiti Nayyar100% (1)
- Human Resource PlanningDocument22 pagesHuman Resource PlanningRiti NayyarNo ratings yet
- Business Law - Class NotesDocument3 pagesBusiness Law - Class NotesRiti NayyarNo ratings yet
- FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT NotesDocument68 pagesFINANCIAL MANAGEMENT NotesSiddharth Singh91% (80)
- Organisational BehaviourDocument279 pagesOrganisational Behaviouranjanaindia3542100% (22)
- Lecture 3 - Techniques of Criminal InvestigationDocument11 pagesLecture 3 - Techniques of Criminal InvestigationRiti NayyarNo ratings yet
- Chap 017Document10 pagesChap 017Riti NayyarNo ratings yet
- CTR Ball JointDocument19 pagesCTR Ball JointTan JaiNo ratings yet
- Nokia CaseDocument28 pagesNokia CaseErykah Faith PerezNo ratings yet
- SBI Sample PaperDocument283 pagesSBI Sample Paperbeintouch1430% (1)
- MCQ Ch16solDocument4 pagesMCQ Ch16solandiswahlongwa870No ratings yet
- Lecture NotesDocument6 pagesLecture NotesRawlinsonNo ratings yet
- Flowmon Ads Enterprise Userguide enDocument82 pagesFlowmon Ads Enterprise Userguide ennagasatoNo ratings yet
- Applied Statics and Strength of Materials 6th Edition Ebook PDFDocument61 pagesApplied Statics and Strength of Materials 6th Edition Ebook PDFteri.sanborn87695% (44)
- A Princess of Mars Part 3Document4 pagesA Princess of Mars Part 3Sheila Inca100% (1)
- Guia de Usuario GPS Spectra SP80 PDFDocument118 pagesGuia de Usuario GPS Spectra SP80 PDFAlbrichs BennettNo ratings yet
- Three Comparison of Homoeopathic MedicinesDocument22 pagesThree Comparison of Homoeopathic MedicinesSayeed AhmadNo ratings yet
- Dolni VestoniceDocument34 pagesDolni VestoniceOlha PodufalovaNo ratings yet
- Critical Methodology Analysis: 360' Degree Feedback: Its Role in Employee DevelopmentDocument3 pagesCritical Methodology Analysis: 360' Degree Feedback: Its Role in Employee DevelopmentJatin KaushikNo ratings yet
- Technical specifications for JR3 multi-axis force-torque sensor modelsDocument1 pageTechnical specifications for JR3 multi-axis force-torque sensor modelsSAN JUAN BAUTISTANo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 6 Whole Numbers WorksheetDocument2 pagesCBSE Class 6 Whole Numbers WorksheetPriyaprasad PandaNo ratings yet
- Flexible Regression and Smoothing - Using GAMLSS in RDocument572 pagesFlexible Regression and Smoothing - Using GAMLSS in RDavid50% (2)
- Astm D7928 - 17Document25 pagesAstm D7928 - 17shosha100% (2)
- Mil STD 2154Document44 pagesMil STD 2154Muh SubhanNo ratings yet
- STS Prelim ExamDocument2 pagesSTS Prelim ExamMychie Lynne MayugaNo ratings yet
- GP Rating GSK Exit ExamDocument108 pagesGP Rating GSK Exit ExamMicle VM100% (4)
- Marshall Stability Test AnalysisDocument5 pagesMarshall Stability Test AnalysisZick Zickry50% (2)
- Gabinete STS Activity1Document2 pagesGabinete STS Activity1Anthony GabineteNo ratings yet
- New Hire WorkbookDocument40 pagesNew Hire WorkbookkNo ratings yet
- Product Data Sheet For CP 680-P and CP 680-M Cast-In Firestop Devices Technical Information ASSET DOC LOC 1540966Document1 pageProduct Data Sheet For CP 680-P and CP 680-M Cast-In Firestop Devices Technical Information ASSET DOC LOC 1540966shama093No ratings yet
- HP HP3-X11 Exam: A Composite Solution With Just One ClickDocument17 pagesHP HP3-X11 Exam: A Composite Solution With Just One ClicksunnyNo ratings yet
- SOP-for RecallDocument3 pagesSOP-for RecallNilove PervezNo ratings yet
- Technical Manual - C&C08 Digital Switching System Chapter 2 OverviewDocument19 pagesTechnical Manual - C&C08 Digital Switching System Chapter 2 OverviewSamuel100% (2)
- 7 Aleksandar VladimirovDocument6 pages7 Aleksandar VladimirovDante FilhoNo ratings yet
- Form Active Structure TypesDocument5 pagesForm Active Structure TypesShivanshu singh100% (1)
- Mpu 2312Document15 pagesMpu 2312Sherly TanNo ratings yet



















![UNIT_IV[1]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/721699312/149x198/4b23d9c709/1712730179?v=1)