Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Allama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad (Department of Computer Science) Warning
Uploaded by
ziabuttOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Allama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad (Department of Computer Science) Warning
Uploaded by
ziabuttCopyright:
Available Formats
ALLAMA IQBAL OPEN UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD (Department of Computer Science) WARNING
1. 2. PLAGIARISM OR HIRING OF GHOST WRITER(S) FOR SOLVING THE ASSIGNMENT(S) WILL DEBAR THE STUDENT FROM AWARD OF DEGREE/CERTIFICATE, IF FOUND AT ANY STAGE. SUBMITTING ASSIGNMENTS BORROWED OR STOLEN FROM OTHER(S) AS ONES OWN WILL BE PENALIZED AS DEFINED IN AIOU PLAGIARISM POLICY.
Course: Network Design (3418)
Level: Bachelor Total Marks: 100 Semester: Spring, 2013
ASSIGNMENT No. 1
Note: All questions carry equal marks. Q.1 Describe the design goals of various network topologies. Q.2 What are the advantages of queuing techniques? Elaborate. Q.3 Differentiate between CSMA/CD and CSMA/CA. Q.4 Define OSI model. How the different layer of OSI model work? Q.5 How TCP/IP protocol organizes various communication tasks?
ASSIGNMENT No. 2
Total Marks: 100
Note: All questions carry equal marks. Q.1 Write a detail explanation of satellite network. Q.2 What are the attribute of a LAN. Also describe the characteristics of ISDN network? Q.3 Discuss the various techniques of flow control in communication network. Q.4 What are the advantages of digital system and carrier system? Q.5 What are the techniques for analog to digital transmission?
1
3418 Networking Design
Credit Hours: 3(3 + 0)
Recommended Book: Computer Networks Protocols, Standard, and Interfaces By UYLESS BLACK 2nd Edition Course Outlines: Unit No.1 Introduction to Computer Network
The Use of Networks, Advantages of Networks, Communications Networks, Point to Point and Multidrop Circuits, Networks Topologies and Design Goals, Connecting the Analog and Digital Worlds, The Modem Synchronizing Networks Components, Synchronization Codes, Asynchronous and Synchronous Transmission, The Communication Port, Additional Networks Components
Unit No.2 Communication between Computers and Terminals
Traffic Control and Accountability, Checking For Error, WANs, and LANs, Classification of Communication Protocols, Polling/Selection Systems, Selective and Group Polling, Stop and Wait, Sliding Windows, Nonpolluting Systems, Request to Send/Clear, Xon/Xoff, TDMA, TDM, Registrar Insertion. Carrier Sense, Token Passing, Priority Slot, Carrier Sense Collision-Free System, Token Passing Priority System.
Unit No.3 Layered Protocols, Networks And OSI Model
Rational for Layered Protocols, Goals of Layered Protocols, New Design Problems, Communication between Layers, A Pragmatic Illustration, Standards Organization, ISI Standard, Layers of OSI
Unit No.4 TCP/IP
Introduction to Internet, Protocols
Unit No.5 Satellite Networks
Pros and Cons of Satellite Networks, Conventional Multiplexing, Polling/Selection, Non Polling Peer/Peer System, Non Polling Primary/Secondary System, Sdus, The Teleport
Unit No.6 Networks
Primary Attributes of a LAN, Broadband and Base band LANs, LAN Standards, Connection Options with LAN, LAN Topologies and Protocols, Token Ring, Token Bus, Isdn
Unit No.7 Switching and Routing In Networks & X.25 Network
Telephone Switching Systems, Electromechanical Systems, Stored Program Control System, Message Switching, Packet Routing, Packet Switching Support, Layers Of X.25, Features of X.25, Channel Options, Flow Control, Internetworking
Unit No.8 Digital Networks & Personal Computer Networks
Advantages of Digital Systems, Signal Conversion, Digital Carrier Systems, Analog to Digital Techniques, Waveform Analysis, Communication Characteristics, Error Handling, Pc as a Server, Pc and Mainframe Computer, Pc and An, Pc Networks and OSI Model Unit No.9 Internet Services
2
You might also like
- Serial Port Complete: COM Ports, USB Virtual COM Ports, and Ports for Embedded SystemsFrom EverandSerial Port Complete: COM Ports, USB Virtual COM Ports, and Ports for Embedded SystemsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (9)
- 3429-Data Communication and NetworkDocument5 pages3429-Data Communication and NetworkKashif Zafar SaleemiNo ratings yet
- 3438Document4 pages3438AhsanShahidNo ratings yet
- 7 17ec64 Syllabus PDFDocument2 pages7 17ec64 Syllabus PDFAmbica AnnavarapuNo ratings yet
- MCA19Document201 pagesMCA19Bhushan AkolkarNo ratings yet
- Computer Communication NetworksDocument2 pagesComputer Communication NetworksMahalaxmi GinnamNo ratings yet
- Government College Women University Sialkot: Course Outline: CMP-301Document7 pagesGovernment College Women University Sialkot: Course Outline: CMP-301Muzalfa KhanNo ratings yet
- TmaDocument48 pagesTmaekpereka50% (2)
- ECE 422 Feknous - LTDocument3 pagesECE 422 Feknous - LTtanis581No ratings yet
- Btech 5 SyllabusDocument14 pagesBtech 5 SyllabusSandeep Kumar PatelNo ratings yet
- CCN Syllabus BAMU ETCDocument2 pagesCCN Syllabus BAMU ETCanilbNo ratings yet
- TN 202 Course ContentDocument3 pagesTN 202 Course ContentJohnBenardNo ratings yet
- Course Structure & Syllabus of Bachelor of Technology (B.Tech)Document5 pagesCourse Structure & Syllabus of Bachelor of Technology (B.Tech)anupNo ratings yet
- Lecture Plan (CSC305 - CN Theory)Document2 pagesLecture Plan (CSC305 - CN Theory)cokope9857No ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Computer Networks LabDocument11 pagesAssignment 1: Computer Networks LabNickNo ratings yet
- Gtu PaperDocument4 pagesGtu Paperkaushal.21beect008No ratings yet
- CS471/EE471/CS573: Computer NetworksDocument3 pagesCS471/EE471/CS573: Computer Networksahmedsanaullah_1No ratings yet
- Sample Exam Paper-2019-SEM-1Document9 pagesSample Exam Paper-2019-SEM-1Aspen BelleNo ratings yet
- Advanced Data CommunicationsDocument2 pagesAdvanced Data CommunicationsAlluri SreenivasNo ratings yet
- Identifies Pieces of Data As Part of The Same CommunicationDocument4 pagesIdentifies Pieces of Data As Part of The Same CommunicationEsteban ValerioNo ratings yet
- Syllabus in Comp. Science 4 (Network Technology) : Philippine Science High SchoolDocument7 pagesSyllabus in Comp. Science 4 (Network Technology) : Philippine Science High SchoolAlexander Bermejo AvilaNo ratings yet
- Data Communications and Networks: Course DescriptionDocument4 pagesData Communications and Networks: Course DescriptionHasnain AhmadNo ratings yet
- DC and CN Group-AssignmentDocument2 pagesDC and CN Group-AssignmentmekuriaNo ratings yet
- Course Plan (1) SGDocument14 pagesCourse Plan (1) SGAnonymous BOreSFNo ratings yet
- CE505-N Computer NetworksDocument4 pagesCE505-N Computer NetworksSasta LalaNo ratings yet
- CE505-N Computer NetworksDocument4 pagesCE505-N Computer NetworksabcNo ratings yet
- Revised Syllabus Old Syllabus: Fundamentals of Networking (MBIT-207) Unit 1Document1 pageRevised Syllabus Old Syllabus: Fundamentals of Networking (MBIT-207) Unit 1Athar KhanNo ratings yet
- Osi Model NotesDocument7 pagesOsi Model NotesSuman KumarNo ratings yet
- acknowledgments, Sequencing, and Flow Control Are Characteristics of Which OSI Layer?Document9 pagesacknowledgments, Sequencing, and Flow Control Are Characteristics of Which OSI Layer?Desmond KcNo ratings yet
- Introducing To NetworkingDocument5 pagesIntroducing To Networkinggheorghe_tiberiu96No ratings yet
- ECE635 Computer Communication & Networks SyllabusDocument5 pagesECE635 Computer Communication & Networks Syllabuspaku deyNo ratings yet
- The OSI Reference ModelDocument21 pagesThe OSI Reference ModelNaureen HossainNo ratings yet
- Networking With TCP-IP NotesDocument25 pagesNetworking With TCP-IP Notes0901CS211114 SOURAV DINKARNo ratings yet
- CN Unit 2Document13 pagesCN Unit 2SS The BrandNo ratings yet
- CCNA Notes Compiled by Mr. MalooDocument216 pagesCCNA Notes Compiled by Mr. MalooDarren Owen100% (1)
- Network Interface LayerDocument3 pagesNetwork Interface LayerdhasalswapnilNo ratings yet
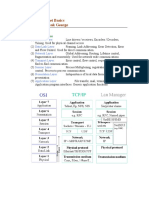
- LAN and Ethernet Basics - Deepak George: OSI Network LayersDocument12 pagesLAN and Ethernet Basics - Deepak George: OSI Network LayersUseful Videos DevotionalNo ratings yet
- CCN 059Document3 pagesCCN 059Zayn RajpootNo ratings yet
- 5 Days IP ModuleDocument4 pages5 Days IP ModuleAshish ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking Refers To Connected Computing Devices 222Document13 pagesComputer Networking Refers To Connected Computing Devices 222RAY COOLNo ratings yet
- Computer Network No.1 (Introduction) From APCOMSDocument36 pagesComputer Network No.1 (Introduction) From APCOMSNaveed100% (2)
- 7th & 8th Sem SyllabusDocument33 pages7th & 8th Sem SyllabusAkshay BharadwajNo ratings yet
- SVKM'S NMIMS University: Mukesh Patel School of Technology Management & EngineeringDocument3 pagesSVKM'S NMIMS University: Mukesh Patel School of Technology Management & Engineeringnitin_798443935No ratings yet
- Sardar Raja College of Engineering, Raja Nagar, Alangulam: Department of Computer Applications Micro Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesSardar Raja College of Engineering, Raja Nagar, Alangulam: Department of Computer Applications Micro Lesson PlanAnonymous uHT7dDNo ratings yet
- Lab Document Cse 312Document74 pagesLab Document Cse 312RAKIB UDDIN CHOWDHURY 1804107No ratings yet
- AI2003 Computer NetworkDocument4 pagesAI2003 Computer NetworkVaradNo ratings yet
- CSC3002 Computer-Networks ETH 1 AC37Document3 pagesCSC3002 Computer-Networks ETH 1 AC37;(No ratings yet
- Ccna 1Document3 pagesCcna 1Enrique BecerraNo ratings yet
- Steps To Clean A ComputerDocument9 pagesSteps To Clean A Computerchawla_tarunNo ratings yet
- Rajalakshmi Engineering CollegeDocument17 pagesRajalakshmi Engineering Collegechituuu100% (2)
- OSI Model - Internet and Networking, Computer Awareness - General Awareness and Knowledge - Bank Exams PDF DownloadDocument4 pagesOSI Model - Internet and Networking, Computer Awareness - General Awareness and Knowledge - Bank Exams PDF DownloadDavuluri Sunil KumarNo ratings yet
- Interview QuestionsDocument9 pagesInterview Questionshatfied862No ratings yet
- Bitszc 481Document3 pagesBitszc 481Ravichandran NagarajNo ratings yet
- Bitszc 481Document3 pagesBitszc 481rvtymcaNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Lab Manual-17ECL68Document87 pagesComputer Networks Lab Manual-17ECL68LikithaReddy Yenumula80% (5)
- Syllabus & Scheme For M.Tech. (ECE)Document27 pagesSyllabus & Scheme For M.Tech. (ECE)Siddharth SidNo ratings yet
- Investigacion Modelo OSI, IP HeaderDocument5 pagesInvestigacion Modelo OSI, IP HeaderKnowhereDLNo ratings yet
- Ict1532 - 6Document3 pagesIct1532 - 6Mbali NdabaNo ratings yet
- 651-1st Autumn 2017Document8 pages651-1st Autumn 2017ziabuttNo ratings yet
- PAFA-409 Life Certificate, Letter of Authority Pensioners Not Able To Appear in Person To Receive PaymentDocument2 pagesPAFA-409 Life Certificate, Letter of Authority Pensioners Not Able To Appear in Person To Receive Paymentziabutt71% (17)
- De Notation Connotation ClustersDocument2 pagesDe Notation Connotation ClustersShanique GrantNo ratings yet
- Wise Result BoysDocument5 pagesWise Result BoysziabuttNo ratings yet
- (AIOU) Steps of Proposal WritingDocument8 pages(AIOU) Steps of Proposal WritingziabuttNo ratings yet
- 6400-1st Autumn 2018 FinalDocument14 pages6400-1st Autumn 2018 FinalziabuttNo ratings yet
- BEd Aut 2017Document22 pagesBEd Aut 2017ziabutt100% (1)
- Managing Local Brands in Facing Challenges of GlobDocument16 pagesManaging Local Brands in Facing Challenges of GlobziabuttNo ratings yet
- 8704Document5 pages8704ziabuttNo ratings yet
- Paper Englis A 7th (Subjective+ Objective)Document3 pagesPaper Englis A 7th (Subjective+ Objective)ziabuttNo ratings yet
- Final: 10-5-2017Document5 pagesFinal: 10-5-2017ziabuttNo ratings yet
- KIPS Physics Chapter 1 CompleteDocument5 pagesKIPS Physics Chapter 1 CompleteziabuttNo ratings yet
- Application FormDocument2 pagesApplication FormIrfan Ullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Welfare Policy: Governance History and Political Philosophy: Bernard Cadogan, D.Phil (Oxon)Document147 pagesWelfare Policy: Governance History and Political Philosophy: Bernard Cadogan, D.Phil (Oxon)ziabuttNo ratings yet
- Methodofcontentselection 150411091347 Conversion Gate01Document11 pagesMethodofcontentselection 150411091347 Conversion Gate01ziabuttNo ratings yet
- 0651Document2 pages0651ziabuttNo ratings yet
- Phonetic Keyboard Layout PDFDocument1 pagePhonetic Keyboard Layout PDFziabutt100% (1)
- KIPS Physics Chapter 1 CompleteDocument5 pagesKIPS Physics Chapter 1 CompleteziabuttNo ratings yet
- BIO-1st Chapter CompleteDocument7 pagesBIO-1st Chapter CompleteziabuttNo ratings yet
- Instructions For Meter Readers For Proper Meter Reading Through Mobile SetDocument2 pagesInstructions For Meter Readers For Proper Meter Reading Through Mobile SetziabuttNo ratings yet
- CURRICULUM DESIGN AND ORGANIZATION PrepaDocument16 pagesCURRICULUM DESIGN AND ORGANIZATION Prepaziabutt100% (1)
- What Were The Discoveries Made by DRDocument5 pagesWhat Were The Discoveries Made by DRziabuttNo ratings yet
- 10-Pakistan Men Zarai Islahaat EditedDocument16 pages10-Pakistan Men Zarai Islahaat EditedziabuttNo ratings yet
- 0444Document5 pages0444ziabuttNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument2 pagesMultiple Choice QuestionsziabuttNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 Adding Value To Core Products With Supplementary ServicesDocument7 pagesLecture 11 Adding Value To Core Products With Supplementary ServicesAditya VikramNo ratings yet
- QDocument2 pagesQziabuttNo ratings yet
- Admission Form (Private) SSC 9th 2015Document5 pagesAdmission Form (Private) SSC 9th 2015ziabuttNo ratings yet
- Verification of CertificateDocument1 pageVerification of CertificateziabuttNo ratings yet
- Soundrop Style GuideDocument13 pagesSoundrop Style GuideAlcaNo ratings yet
- Patientory WhitepaperDocument19 pagesPatientory WhitepaperakshatNo ratings yet
- Website Design CSCDocument1 pageWebsite Design CSCBobbyNo ratings yet
- The History of Computers - Grade 8Document25 pagesThe History of Computers - Grade 8ukrkis201450% (2)
- MSRP A1Document110 pagesMSRP A1JayeshNo ratings yet
- Astrolabe 1Document8 pagesAstrolabe 1Stevanus Kristianto NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Script VirusDocument35 pagesScript VirusRayson SaputraNo ratings yet
- 3 GPPDocument96 pages3 GPPDeepinder SinghNo ratings yet
- SEMAC-S1WEB Configuration ManualDocument42 pagesSEMAC-S1WEB Configuration ManualjaalayonNo ratings yet
- Dissenting Voices 2010: Targeting The Intellectuals, Writers and Cultural FiguresDocument141 pagesDissenting Voices 2010: Targeting The Intellectuals, Writers and Cultural FiguresTibetan Centre for Human Rights and DemocracyNo ratings yet
- EmtechDocument13 pagesEmtechrichNo ratings yet
- Ieee 802.11E Qos For Wireless LanDocument26 pagesIeee 802.11E Qos For Wireless Lanseriesv2No ratings yet
- Wireline Niche Guide V 1.2Document9 pagesWireline Niche Guide V 1.2Mark MarquezNo ratings yet
- PlannerDocument36 pagesPlannerFaull JackmanNo ratings yet
- SOC Manager SlidesDocument7 pagesSOC Manager SlidesriadelidrissiNo ratings yet
- IoT Based Real Time Water Monitoring System For Smart CityDocument6 pagesIoT Based Real Time Water Monitoring System For Smart CityInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Zabbix ApplianceDocument5 pagesZabbix ApplianceAndres SBNo ratings yet
- GSM - Quick GuideDocument16 pagesGSM - Quick GuideRoyalRächerNo ratings yet
- Copyright Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesCopyright Cheat SheetTony CombsNo ratings yet
- JMC250Document2 pagesJMC250abhijit99541623974426No ratings yet
- Informaton Technology and File HandlingDocument9 pagesInformaton Technology and File HandlingTamerlan MirzayevNo ratings yet
- Xs Analyse Service ManualDocument170 pagesXs Analyse Service ManualPablo A. Flores78% (9)
- Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm: Fifteenth EditionDocument19 pagesManagement Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm: Fifteenth EditionShaunak RawkeNo ratings yet
- Life Death - Volume 1 - Poems On Life, DeathDocument143 pagesLife Death - Volume 1 - Poems On Life, DeathNikhil ParekhNo ratings yet
- Comunicacion Serial en ATMega328PDocument7 pagesComunicacion Serial en ATMega328PFrancisco ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Mergers Acquisitions Sam ChapDocument24 pagesMergers Acquisitions Sam ChapNaveen RaajNo ratings yet
- Building Mod Auth Radius 2.0Document2 pagesBuilding Mod Auth Radius 2.0Zeljko PetakNo ratings yet
- Serving Raspberry Pi With FlaskDocument15 pagesServing Raspberry Pi With FlaskBobbyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Pre-Quize 354Document13 pagesChapter 3 Pre-Quize 354smaude01100% (1)
- Participatory GIS and MappingDocument56 pagesParticipatory GIS and MappingThierry Joliveau100% (1)