Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Inflation
Uploaded by
Salam ZeeshanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Inflation
Uploaded by
Salam ZeeshanCopyright:
Available Formats
INFLATION
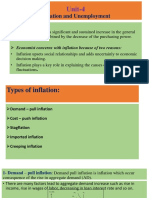
Inflation means a rise in prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of time. Inflation is caused by some demand side factors (Demand Pull Inflation) and supply side factors (Cost Push Inflation). TYPES OF INFLATION Demand Pull Inflation Cost Push Inflation Pricing Power Inflation Sectoral Inflation Fiscal Inflation Hyperinflation MEASURES OF INFLATION CPI WPI GDP Deflator TREND OF INFLATION
Year 1960's 1970's 1980's 1990-91 1991-92 1992-93 1993-94 1994-95 1995-96 1996-97 1997-98 1998-99 1999-2000 2000-01 2001-02 2002-03 CPI 3.3 11.9 7.5 12.66 10.58 9.83 11.27 13.02 10.79 11.8 7.81 5.74 3.58 4.41 3.54 3.1 WPI 2.6 13.5 7.1 11.73 9.84 7.36 16.4 16 11.1 13.01 6.58 6.35 1.77 6.21 2.13 5.6 SPI 12.59 10.54 10.71 11.13 15.69 10.71 12.45 7.35 6.44 1.83 4.84 3.37 3.8
2003-04 2004-05 2005-06 2006-07 2007-08 2008-09 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12
4.6 9.3 7.9 7.8 12 20.8 11.7 14.1 10.8
7.9 6.8 10.1 6.9 16.4 18.2 12.6 23.3
6 11.1 7.8 9.2 14.2 22.7 13.2 18.2
REASON S The main reason of inflation is the increase in the prices of regular items, such as wheat, sugar, ghee and other items. The government has totally failed to control the prices of these items. Petrol and gas price hikes is the second main cause. When oil and gas prices are increased it affects prices of its complementary goods too. Such as transportation fares, etc. Thirdly, most of the industries are closed due to government policies creating unemployment. Increase in excise duties and the increase in the utility tariffs Rising international commodity prices are also playing a role in intensifying domestic inflationary pressures. . Large government borrowing from central bank to finance budget deficit. Currency depreciation Production losses due to power and infrastructure problem During current period food has remained the major driver of the inflation on the back of major supply disruptions owing to devastating floods at the beginning of FY11 damaged the crops and disrupted the production and supply chain, worsening inflationary pressures Food inflation is persistently rising and recorded at 18.4 percent as against 12.0 percent in the comparable period of last year.
Non-food component witnessed an increase of 10.4 percent in this period which shows some adjustment against 11 percent in the comparable period of last year. EFFECTS OF INFLATION Inflation affects the diverse sectors of the economy Effects on production Monetary Policy Social Sector Political environment
And effect different classes of people (Debtors & Creditors, Salaried Class, Wages earners, Fixed income group, Investors and shareholders, Businessmen, Agriculturists as well). REMEDIES Inflation is one of the barriers on the way of progress. In Pakistan, it has grasped the major part of the population. It needs to be controlled by strategic planning. 1. Domestic production should be encouraged instead of imports; 2. Investment should be given preference in consumer goods instead of luxuries, 3. Agriculture sector should be given subsidies, 4. Control budget deficit 5. Reduction in public borrowings 6. Adoption of strict price control 7. A strong monitoring system should be established on different levels in order to have a sound assessment of the process at every stage. 8. The major increase in the prices is because of the increasing prices of oil (as increased prices of oil increase the cost of production), steps should be taken to control the oil prices. 9. Effective economic planning to enhance efficiency, productivity in the real sector (commodity sector) require for the sustainable growth in the supply of goods and services in the economy.
You might also like
- Analysis of Inflation: Presented By: Pooja Singh. 44 Apeksha Thakare. 43 Manoj Bhosale. 31 Veena Mhatre. 49 Sushma Pol. 4Document39 pagesAnalysis of Inflation: Presented By: Pooja Singh. 44 Apeksha Thakare. 43 Manoj Bhosale. 31 Veena Mhatre. 49 Sushma Pol. 4anubajajNo ratings yet
- Inflation-Pattern Over 1991-2011 Reasons and Impact (India)Document38 pagesInflation-Pattern Over 1991-2011 Reasons and Impact (India)Vinayak PadwalNo ratings yet
- Inflation in India: When Everything Gets More Valuable "Except Money"Document24 pagesInflation in India: When Everything Gets More Valuable "Except Money"chayanika9636837No ratings yet
- Inflation UmerDocument16 pagesInflation Umerkhan 0No ratings yet
- Effect of Oil On The Nigerian EconomyDocument56 pagesEffect of Oil On The Nigerian EconomyOmotosho AdamNo ratings yet
- Current Challenges With Inflation in NigeriaDocument23 pagesCurrent Challenges With Inflation in Nigeriajamessabraham2No ratings yet
- Economic StabilizationDocument11 pagesEconomic Stabilizationopenid_aku6f5n8No ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Business EnvironmentDocument53 pagesUnit 4 - Business Environmentdrishtimanchanda23No ratings yet
- Inflation in Pakistan Economics ReportDocument15 pagesInflation in Pakistan Economics ReportQanitaZakir75% (16)
- Inflation Money Supply and Economic GrowthDocument13 pagesInflation Money Supply and Economic GrowthHassan Md RabiulNo ratings yet
- Inflation: Alok Singh Ambesh Kumar SrivastavaDocument24 pagesInflation: Alok Singh Ambesh Kumar Srivastavaambesh Srivastava100% (15)
- Grain and FeedDocument14 pagesGrain and FeedsaadNo ratings yet
- Inflation, Types and Pakistan's Inflation: Mam Fadia NazDocument16 pagesInflation, Types and Pakistan's Inflation: Mam Fadia NazGhulamMuhammad ChNo ratings yet
- 1606122274.575.1.1.macroeconomics 2 1606122274 Kaunda RobertDocument19 pages1606122274.575.1.1.macroeconomics 2 1606122274 Kaunda RobertMaxwell chandaNo ratings yet
- Inflation in India 2010Document30 pagesInflation in India 2010Varun VinayakNo ratings yet
- Inflation Impact On EconmyDocument4 pagesInflation Impact On EconmyRashid HussainNo ratings yet
- Inflation Impact On Indian Economy AgricultureDocument4 pagesInflation Impact On Indian Economy AgricultureAvirup ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Inflation: Presented byDocument18 pagesInflation: Presented byKhan ProductionsNo ratings yet
- Economic Slowdown and Macro Economic PoliciesDocument38 pagesEconomic Slowdown and Macro Economic PoliciesRachitaRattanNo ratings yet
- Final Prenstation of Economics by DynoDocument30 pagesFinal Prenstation of Economics by DynolibradynoNo ratings yet
- InflationDocument42 pagesInflationAman SharmaNo ratings yet
- InflationDocument4 pagesInflationAsif MalikNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document15 pagesPresentation 1jawadmalik6467No ratings yet
- Inflation in NepalDocument25 pagesInflation in NepalAvay ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics BCOM 21113: InflationDocument38 pagesMacroeconomics BCOM 21113: InflationTishani HerathNo ratings yet
- Impact of Inflation On A Developing EconomyDocument35 pagesImpact of Inflation On A Developing Economynuttynehal17No ratings yet
- Macro Economics: Inflation and UnemploymentDocument11 pagesMacro Economics: Inflation and UnemploymentHashim RiazNo ratings yet
- Inflation in India (Auto-Saved)Document63 pagesInflation in India (Auto-Saved)Lakshay GoelNo ratings yet
- Chapter02 The Problem of Inflation and Its Solution Paths PDFDocument12 pagesChapter02 The Problem of Inflation and Its Solution Paths PDFAsma HashmiNo ratings yet
- 6504 16164 1 PB PDFDocument6 pages6504 16164 1 PB PDFYew Wen KhangNo ratings yet
- Inflation in IndiaDocument18 pagesInflation in Indiagouravsaikia24No ratings yet
- Unit-4 With NumericalsDocument22 pagesUnit-4 With NumericalsRajabNo ratings yet
- Inflation & UnemploymentDocument13 pagesInflation & UnemploymentNathaniel MadugaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1maria aghaNo ratings yet
- InflationDocument6 pagesInflationabdulhadiqureshi100% (8)
- Inflation 161202135538Document18 pagesInflation 161202135538Sidhartha MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Inflation FinalDocument9 pagesInflation FinalFaizi NikNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 InflationDocument26 pagesUnit 6 InflationdawsonNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Inflation India: ObjectivesDocument12 pagesUnit 4 Inflation India: ObjectivesRohit Kumar 4170No ratings yet
- INFLATIONDocument4 pagesINFLATIONMohd Ayaz RazaNo ratings yet
- Inflation-Conscious Investments: Avoid the most common investment pitfallsFrom EverandInflation-Conscious Investments: Avoid the most common investment pitfallsNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Business Economics Study Resource: CIMA Study ResourcesFrom EverandFundamentals of Business Economics Study Resource: CIMA Study ResourcesNo ratings yet
- In de StagflationDocument24 pagesIn de StagflationSHEKHAWAT FAMILYNo ratings yet
- Analyze The Cause of Inflation in VietnamDocument16 pagesAnalyze The Cause of Inflation in VietnamTrang HaNo ratings yet
- The Challenges of Food InflationDocument21 pagesThe Challenges of Food InflationShiva JainNo ratings yet
- InflationDocument20 pagesInflationjamwalakash777No ratings yet
- Causes of InflationDocument4 pagesCauses of InflationAlina SlavuNo ratings yet
- Inflation and DeflationDocument10 pagesInflation and Deflationredsalute100% (1)
- Inflation-and-Deflation-Presentation 20240223 221928 0000Document17 pagesInflation-and-Deflation-Presentation 20240223 221928 0000shenamaecordez.sccNo ratings yet
- The Ogre of Inflation Causes, Solutions and Side Effects: Submitted To, Siji CyriacDocument15 pagesThe Ogre of Inflation Causes, Solutions and Side Effects: Submitted To, Siji CyriacVikas KhNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics 2Document6 pagesMacroeconomics 2Bhavya MehtaNo ratings yet
- Caie As Economics 9708 Model Answers v1Document11 pagesCaie As Economics 9708 Model Answers v1Uzair siddiqui100% (1)
- Chapitre 5 - MacroeconomicsDocument6 pagesChapitre 5 - MacroeconomicsAxelNo ratings yet
- Angol Kozepfoku Gazdasagi Nyelvvizsga Tetelek 2001 2001 81 OldalDocument54 pagesAngol Kozepfoku Gazdasagi Nyelvvizsga Tetelek 2001 2001 81 OldalNagy RolandNo ratings yet
- Measurement of InflationDocument20 pagesMeasurement of InflationNELSONNo ratings yet
- InflationDocument8 pagesInflationFergus DeanNo ratings yet
- Money & BankingDocument31 pagesMoney & BankingMohsin BhattiNo ratings yet
- Me Review Assignent - Arunima Viswanath - m200046msDocument4 pagesMe Review Assignent - Arunima Viswanath - m200046msARUNIMA VISWANATHNo ratings yet
- Business Economics: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageFrom EverandBusiness Economics: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageNo ratings yet
- Kant's Categorical ImperativeDocument3 pagesKant's Categorical ImperativeSalam ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Buiness LawDocument115 pagesBuiness LawSalam ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Definition of Financial MisconductDocument1 pageDefinition of Financial MisconductSalam ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Discuss in Detail The Position of A Quasi-Contract When The Obligations of Contract Are Imposed by The Law or What Are The Types of Quasi Contract?Document19 pagesDiscuss in Detail The Position of A Quasi-Contract When The Obligations of Contract Are Imposed by The Law or What Are The Types of Quasi Contract?Salam ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Marketing Plan On PepsicoDocument24 pagesMarketing Plan On PepsicoWaqar AfzaalNo ratings yet
- Pepsi PortfolioDocument3 pagesPepsi PortfolioSalam ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Caleb Bradham of New BernDocument3 pagesCaleb Bradham of New BernSalam ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- HP 12c Loan AmortizationDocument6 pagesHP 12c Loan AmortizationRyan SiuNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTIONDocument13 pagesINTRODUCTIONSalam ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Caleb Bradham of New BernDocument3 pagesCaleb Bradham of New BernSalam ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Coca ColaDocument30 pagesCoca ColaSalam ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Polycythemia VeraDocument8 pagesPolycythemia VeraSalam ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument14 pagesGenetic EngineeringSalam ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Agricultural and Industrial Sector Betterment Is A Key For The Development OfpakistanDocument5 pagesAgricultural and Industrial Sector Betterment Is A Key For The Development OfpakistanSalam ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- F 4562Document2 pagesF 4562Salam ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Agriculture Problems in Pakistan and Their SolutionsDocument6 pagesAgriculture Problems in Pakistan and Their SolutionsSalam Zeeshan67% (3)
- Trade DeficitDocument8 pagesTrade DeficitSalam ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTIONDocument13 pagesINTRODUCTIONSalam ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Job AnalysisDocument9 pagesJob AnalysisSalam ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Abraham Lincoln: Childhood & Early LifeDocument4 pagesAbraham Lincoln: Childhood & Early LifeSalam ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Jobs Holding A WhiteDocument3 pagesJobs Holding A WhiteSalam ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- What Are Mutual Funds?Document8 pagesWhat Are Mutual Funds?Salam ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Global Halal Market OpportunityDocument18 pagesGlobal Halal Market OpportunityDiana BlueseaNo ratings yet
- Shipping & Billing Address: Neha Singh: Date: 23/02/2024Document2 pagesShipping & Billing Address: Neha Singh: Date: 23/02/2024tyrainternationalNo ratings yet
- Application of Demand and SupplyDocument60 pagesApplication of Demand and SupplyJody Singco CangrejoNo ratings yet
- Barops Labor LawDocument390 pagesBarops Labor LawJordan TumayanNo ratings yet
- Albright Stonebridge Group Newsletter ArticlesDocument4 pagesAlbright Stonebridge Group Newsletter Articlesanurag_sikder2703No ratings yet
- Tcs BpsoverviewDocument25 pagesTcs BpsoverviewArockia RajNo ratings yet
- SM 2 - Konsep Dasar Dan Model Sistem ManufakturDocument34 pagesSM 2 - Konsep Dasar Dan Model Sistem ManufakturMuhammad Iman SyahNo ratings yet
- Symbion, Inc. Sued For Anti-Kickback Whistleblower Retaliation!Document58 pagesSymbion, Inc. Sued For Anti-Kickback Whistleblower Retaliation!Mark Anchor AlbertNo ratings yet
- Hiller's Layoff NoticesDocument6 pagesHiller's Layoff NoticesClickon DetroitNo ratings yet
- Buying and SellingDocument67 pagesBuying and Sellinganne89% (19)
- PhilAm LIFE vs. Secretary of Finance Case DigestDocument2 pagesPhilAm LIFE vs. Secretary of Finance Case DigestDenn Reed Tuvera Jr.No ratings yet
- E51 Curswap Eur UsdDocument2 pagesE51 Curswap Eur UsdkoushikNo ratings yet
- PEG SchemeDocument13 pagesPEG Schemed-fbuser-120619586No ratings yet
- Summative Test in Business FinanceDocument1 pageSummative Test in Business FinanceRhea Jane V. CagasNo ratings yet
- MaricoDocument23 pagesMaricopompresntNo ratings yet
- About Tata AigDocument3 pagesAbout Tata Aigsatishyadav1234No ratings yet
- Business StandardDocument11 pagesBusiness StandardAbhinav GuptaNo ratings yet
- JIT Mod 5Document11 pagesJIT Mod 5hetsagarNo ratings yet
- The Integrated Report FrameworkDocument5 pagesThe Integrated Report FrameworkteslimsNo ratings yet
- ch17 New PptsDocument22 pagesch17 New Pptsapi-216265989No ratings yet
- Sadikpur Dudh U.S.M.L - 312: Payment RegisterDocument5 pagesSadikpur Dudh U.S.M.L - 312: Payment RegistertaheraliNo ratings yet
- Miss Samantha D Erlston Doreen 56 B High RD Edenvale 1609: Transactions in RAND (ZAR) Accrued Bank ChargesDocument2 pagesMiss Samantha D Erlston Doreen 56 B High RD Edenvale 1609: Transactions in RAND (ZAR) Accrued Bank ChargesSamantha Erlston100% (1)
- Accenture Trends in Shared ServicesDocument20 pagesAccenture Trends in Shared ServicesMartin BelfioriNo ratings yet
- Finance SyllabusDocument11 pagesFinance SyllabusEarl Russell S PaulicanNo ratings yet
- CVE156 SampleDocument14 pagesCVE156 SampleLightning SparkNo ratings yet
- Hibernate Reference EnversDocument42 pagesHibernate Reference EnverslifedjNo ratings yet
- Bsp-Credit Risk ManagementDocument69 pagesBsp-Credit Risk Managementjhomar jadulanNo ratings yet
- IPL BouncerDocument31 pagesIPL BouncerNCS FreeNo ratings yet
- USAA Code of ConductDocument18 pagesUSAA Code of Conductbdittrich100% (1)