Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mekanikal
Uploaded by
CikLavenderCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mekanikal
Uploaded by
CikLavenderCopyright:
Available Formats
Theories related to heat transfer The natural laws of physics always allow the driving energy in a system to flow
until equilibrium is reached. Heat leaves the warmer body or the hottest fluid, as long as there is a temperature difference, and will be transferred to the cold medium. A heat exchanger follows this principle in its endeavor to reach equalization. With a plate type heat exchanger, the heat penetrates the surface, which separates the hot medium from the cold one very easily. It is therefore possible to heat or cool fluids or gases which have minimal energy levels. The theory of heat transfer from one media to another, or from one fluid to another, is determined by several basic rules. Heat will always be transferred from a hot medium to a cold medium. There must always be a temperature difference between the media. The heat lost by the hot medium is equal to the amount of heat gained by the cold medium, except for losses to the surroundings
Heat exchangers A heat exchanger is a piece of equipment that continually transfers heat from one medium to another in order to carry process energy. There are two main types of heat exchangers. Direct heat exchanger, where both media between which heat is exchanged are in direct contact with each other. It is taken for granted that the media are not mixed together. An example of this type of heat exchanger is a cooling tower, where water is cooled through direct contact with air. Indirect heat exchanger, where both media are separated by a wall through which heat is transferred .
Concepts of heat transfer from one body to another body
Under the kinetic theory, the internal energy of a substance is generated from the motion of individual atoms or molecules. Heat energy is the form of energy which transfers this energy from one body or system to another. This heat transfer can take place in a number of ways:
Conduction is when heat flows through a heated solid. Convection is when heated particles transfer heat to another substance, such as cooking something in boiling water.
Radiation is when heat is transferred through electromagnetic waves, such as from the sun. Radiation can transfer heat through empty space, while the other two methods require some form of matter-on-matter contact for the transfer.
In order for two substances to affect each other they must be in thermal contact with each other. If you leave your oven open while turned on and stand several feet in front of it, you are in thermal contact with the oven and can feel the heat it transfers to you (by convection through the air). Normally, of course, you do not feel the heat from the oven when you're several feet away and that is because the oven has thermal insulation to keep the heat inside of it, thus preventing thermal contact with the outside of the oven. This is of course not perfect, so if you stand nearby you do feel some heat from the oven. Thermal equilibrium is when two items that are in thermal contact no longer transfer heat between them. Effects of Heat Transfer The basic effect of heat transfer is that the particles of one substance collide with the particles of another substance. The more energetic substance will typically lose internal energy (cool down) while the less energetic substance will gain internal energy (heat up). The most blatant effect of this in our day-to-day life is a phase transition, where a substance changes from one state of matter to another, such as ice melting from a solid to a liquid as it
absorbs heat. The water contains more internal energy (the water molecules are moving around faster) than in the ice. In addition, many substances go through either thermal expansion or thermal contraction as they gain and lose internal energy. Water (and other liquids) often expands as it freezes, which anyone who has put a drink with a cap in the freezer for too long has discovered.
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5782)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Kitamura Mycenter HX 630i Stock No 2560Document3 pagesKitamura Mycenter HX 630i Stock No 2560Yang MuzeNo ratings yet
- Metrode Duplex Welding EWDDocument7 pagesMetrode Duplex Welding EWDClaudia MmsNo ratings yet
- OMEGAS 2.16.4 manualDocument5 pagesOMEGAS 2.16.4 manualFrank FrankNo ratings yet
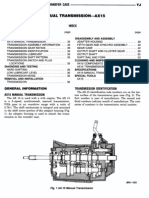
- Ax 15Document37 pagesAx 15cwarren1067% (3)
- IPhO2012 Theoretical ProblemDocument5 pagesIPhO2012 Theoretical ProblemJohnJachersonNo ratings yet
- Significance of aircraft characteristics for airport designDocument17 pagesSignificance of aircraft characteristics for airport designCharan Deep100% (1)
- Rockerbogie Mechanism Blackbook DataDocument42 pagesRockerbogie Mechanism Blackbook Dataharshal kaduNo ratings yet
- 001joint ChecksheetDocument5 pages001joint ChecksheetMahibul HasanNo ratings yet
- Snap Fits Are Commonly Used As An Assembly Method For Injection Molded PartsDocument6 pagesSnap Fits Are Commonly Used As An Assembly Method For Injection Molded PartsDillip SahooNo ratings yet
- Oil Tender Part 3Document40 pagesOil Tender Part 3Dhrubajyoti SonowalNo ratings yet
- MGF and Softner ControlDocument1 pageMGF and Softner ControlSameer WareNo ratings yet
- P13303EN Opticruise tcm40-358169 PDFDocument6 pagesP13303EN Opticruise tcm40-358169 PDFWin Min TunNo ratings yet
- Use New Machine SafelyDocument42 pagesUse New Machine SafelyOggy ToffyNo ratings yet
- Numerical Simulation Nugget Formation 14Document15 pagesNumerical Simulation Nugget Formation 14tobiasNo ratings yet
- Audi - Efficient and Clean - Exhaust Aftertreatment For Gasoline and Diesel Engines - Automotive WorldDocument7 pagesAudi - Efficient and Clean - Exhaust Aftertreatment For Gasoline and Diesel Engines - Automotive WorldPrasadNo ratings yet
- Avances en Maquinas y MecanismosDocument693 pagesAvances en Maquinas y MecanismosMauricio Veloza100% (1)
- Drying in Mass TransferDocument57 pagesDrying in Mass TransferMohammad JunaidNo ratings yet
- Eni E&P Casing Design PresentationDocument87 pagesEni E&P Casing Design PresentationLeon ZidaneNo ratings yet
- Impact Testing ExplainedDocument8 pagesImpact Testing Explainedعباس احمد المبدعNo ratings yet
- B.Tech - Mechanical Engg. 538 572Document35 pagesB.Tech - Mechanical Engg. 538 572Sachin BarthwalNo ratings yet
- HydraulicsDocument3 pagesHydraulicsItzikRazonNo ratings yet
- Omega / Omega V: General Arrangement DrawingsDocument84 pagesOmega / Omega V: General Arrangement DrawingsOkta D. SusantoNo ratings yet
- Equipment Upload FormatDocument80 pagesEquipment Upload FormatPankaj PandeyNo ratings yet
- CQUL - 2 Design For Strength Due To Static LoadingDocument26 pagesCQUL - 2 Design For Strength Due To Static LoadingPierce HardinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5: Heat Transfer in Food ProcessingDocument34 pagesLecture 5: Heat Transfer in Food ProcessingTaytoNo ratings yet
- C70SS-C90SDR PLC Complete Manual PDFDocument290 pagesC70SS-C90SDR PLC Complete Manual PDFthuanNo ratings yet
- Davit Anchor CalculationDocument6 pagesDavit Anchor CalculationRiyas RafiNo ratings yet
- Epicyclic Gear TrainDocument6 pagesEpicyclic Gear TrainLow Kian JinNo ratings yet
- 26-Spirax Sarco Tech 1.PppDocument1 page26-Spirax Sarco Tech 1.PppFarah OmarNo ratings yet
- Eweco Mud PumpsDocument28 pagesEweco Mud Pumpsnjava19780% (1)