Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Position and Displacement Chapter
Uploaded by
prasaad08Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Position and Displacement Chapter
Uploaded by
prasaad08Copyright:
Available Formats
7
Chapter 2
Position and Displacement
2.1 Describe and sketch the locus of a point A which moves according to the equations
x = atcos 2t , R y = atsin 2 t , R z = 0 . RA ( ) A ( ) A
2.2
Find the position difference from point P to point Q on the curve y = x 2 + x 16 , where
x = 2 and R x = 4 . RP Q
2 y RP = ( 2 ) + 2 16 = 10 ; R P = 2 i 10 j 2 y RQ = ( 4 ) + 4 16 = 4 ; R Q = 4 i + 4 j R = R R = 2 i + 14 j = 14.14281.9
QP Q P
Ans.
2.3
The path of a moving point is defined by the equation y = 2 x 2 28 . Find the position
x = 4 and difference from point P to point Q if RP x = 3 . RQ
y RP = 2 ( 4 ) 28 = 4 ;
R P = 4 i + 4 j
2 y RQ = 2 ( 3) 28 = 10 ; R Q = 3 i 10 j R = R R = 7 i 14 j = 15.652243.4
QP Q P
Ans.
2.4
The path of a moving point P is defined by the equation y = 60 x3 / 3 . What is the
x = 0 and ends when R x = 3 ? displacement of the point if its motion begins when RP P
3 y RP j ( 0 ) = 60 ( 0 ) / 3 = 60 ; R P ( 0 ) = 60
3 y RP i + 51 j ( 3) = 60 ( 3) / 3 = 51 ; R P ( 3) = 3 R = R ( 3) R ( 0 ) = 3 i 9 j = 9.487 71.6
P P P
Ans.
2.5
If point A moves on the locus of Problem 2.1, find its displacement from t = 2 to t =2.5.
R A ( 2.0 ) = 2.0a cos 4 i + 2.0a sin 4 j = 2.0a i R ( 2.5 ) = 2.5a cos 5 i + 2.5a sin 5 j = 2.5a i
A
R A = R A ( 2.5 ) R A ( 2.0 ) = 4.5a i 2.6
Ans.
The position of a point is given by the equation R = 100e j 2t . What is the path of the point? Determine the displacement of the point from t = 0.10 to t = 0.40. The point moves in a circle of radius 100 with its center at the origin. Ans.
R ( 0.10 ) = 100e j 0.628 = 80.902 i + 58.779 j R ( 0.40 ) = 100e j 2.513 = 80.902 i + 58.779 j R = R ( 0.40 ) R ( 0.10 ) = 161.803 i = 161.803180 2.7
Ans.
The equation R = t 2 + 4 e j t /10 defines the position of a point. In which direction is the position vector rotating? Where is the point located when t = 0? What is the next value t can have if the direction of the position vector is to be the same as it is when t = 0? What is the displacement from the first position of the point to the second? Since the polar angle for the position vector is = j t /10 , then d / dt is negative and therefore Ans. the position vector is rotating clockwise. 2 j 0 R ( 0) = 0 + 4 e = 40 Ans.
The position vector will next have the same direction when t /10 = 2 , that is, when t=20. Ans. 2 j 2 R ( 20 ) = ( 20 + 4 ) e = 4040
R = R ( 20 ) R ( 0 ) = 4000
Ans.
2.8
2 The location of a point is defined by the equation R = ( 4t + 2 ) e j t / 30 , where t is time in
seconds. Motion of the point is initiated when t = 0. What is the displacement during the first 3 s? Find the change in angular orientation of the position vector during the same time interval. R ( 0 ) = ( 0 + 2 ) e j 0 = 20 = 2 i R ( 3) = (12 + 2 ) e j 9 / 30 = 1454 = 8.229 i + 11.326 j
R = R ( 3) R ( 0 ) = 6.229 i + 11.326 j = 12.92661.2
Ans. Ans.
= 54 0 = 54 ccw
10
2.9
Link 2 in the figure rotates according to the equation = t / 4 . Block 3 slides outward on link 2 according to the equation r = t 2 + 2 . What is the absolute displacement R P from t = 1 to t = 2? What is the apparent displacement R P ?
3 3/ 2
R P3 = re j = ( t 2 + 2 ) e j t / 4 R P3 (1) = 345 = 2.121 i + 2.121 j R ( 2 ) = 690 = 6 j
P3
R P3 = R P3 ( 2 ) R P3 (1) = 2.121 i + 3.879 j = 4.421118.7
Ans.
R P3 / 2 = re j 0 = ( t 2 + 2 ) i2 R P3 / 2 (1) = 3 i2 R ( 2 ) = 6 i
P3 / 2
R P3 / 2 = R P3 / 2 ( 2 ) R P3 / 2 (1) = 3 i2 2.10
Ans.
A wheel with center at O rolls without slipping so that its center is displaced 10 in to the right. What is the displacement of point P on the periphery during this interval? Since the wheel rolls without slipping, RO = RPO . = RO / RPO = 10 in / 6 in = 1.667 rad = 95.5 For R PO , = + = 270 95.5 = 174.5 R = 6174.5 = 5.972 i + 0.574 j in
PO
R P = R O + R PO R PO
R P = 4.028 i + 6.574 j = 7.71058.5 in
i 5.972 i + 0.574 = 10 j + 6 j
Ans.
2.11
A point Q moves from A to B along link 3 while link 2 rotates from 2 = 30 to = 120 . Find the absolute displacement of Q. 2 R = 7530 = 64.95 i + 37.5 j
Q3
R Q3 = 75120 = 37.5 i + 64.95 j
R Q3 = R Q3 R Q3 = 102.45 i + 27.45 j
R Q5 / 3 = R BA = 150 i
R Q5 = R Q3 + R Q5 / 3 R Q5 = 47.5 i + 27.5 j = 5530 mm
11
2.12
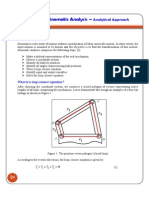
The linkage shown is driven by moving the sliding block 2. Write the loop-closure equation. Solve analytically for the position of sliding block 4. Check the result graphically for the position where = 45 . The loop-closure equation is R A = R B + R AB .
RAe j /12 = RB + RAB e j ( + ) = RB RAB e j
Taking the imaginary components of this, we get RA sin15 = RAB sin sin sin 45 RA = RAB = 200 = 546 mm sin15 sin15 2.13
Ans.
The offset slider-crank mechanism is driven by rotating crank 2. Write the loop-closure equation. Solve for the position of the slider 4 as a function of 2 .
R C = R A + R BA + R CB
RC = RAe j / 2 + RBAe j 2 + RCB e j3
Taking real and imaginary parts, RC = RBA cos 2 + RCB cos 3 and 0 = RA + RBA sin 2 + RCB sin 3 and, solving simultaneously, we get R RBA sin 2 3 = sin 1 A with 90 < 3 < 90 RCB
2 RC = RBA cos 2 + RCB ( RA + RBA sin 2 ) = 63cos 2 + 1043.75 125sin 2 + 156.25cos 2 2 2
Ans.
2.14
Write a calculator program to find the sum of any number of two-dimensional vectors expressed in mixed rectangular or polar forms. The result should be obtainable in either form with the magnitude and angle of the polar form having only positive values. Because the variety of makes and models of calculators is vast and no standards exist for programming them, no standard solution is shown here.
12
2.15
Write a computer program to plot the coupler curve of any crank-rocker or double-crank form of the four-bar linkage. The program should accept four link lengths and either rectangular or polar coordinates of the coupler point relative to the coupler. Again the variety of programming languages makes it difficult to provide a standard solution. However, one version, written in FORTRAN IV, is supplied here as an example. There are no accepted standards for programming graphics. Therefore the Tektronix PLOT-10 subroutine library, for display on Tektronix 4010 series displays, is chosen as an older but somewhat recognized alternative. The symbols in the program correspond to the notation shown in Figure 2.19 of the text. The required input data are: X5, Y5, -1 R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, 5, 1 The program can be verified using the data of Example 2.7 and checking the results against those of Table 2.3.
PROGRAM CCURVE C C C C C C C C C C C C C A FORTRAN IV PROGRAM TO PLOT THE COUPLER CURVE OF ANY CRANK-ROCKER OR DOUBLE-CRANK FOUR-BAR LINKAGE, GIVEN ITS DIMESNIONS. WRITTEN FOR A DEC 11/70 COMPUTER SYSTEM, USING SUBROUTINES FROM TEKTRONIX PLOT-10 FOR DISPLAY ON 4010 SERIES DISPLAYS. REF:J.J.UICKER,JR, G.R.PENNOCK, & J.E.SHIGLEY, THEORY OF MACHINES AND MECHANISMS, THIRD EDITION, OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS, 2003. EXAMPLE 2.6 WRITTEN BY: JOHN J. UICKER, JR. ON: 01 JANUARY 1980
READ IN THE DIMENSIONS OF THE LINKAGE. READ(5,1000)R1,R2,R3,R4,X5,Y5,IFORM 1000 FORMAT(6F10.0,I2) C C FIND R5 AND ALPHA. IF(IFORM.LE.0)THEN R5=SQRT(X5*X5+Y5*Y5) ALPHA=ATAN2(Y5,X5) ELSE R5=X5 ALPHA=Y5/57.29578 END IF Y5=AMAX1(0.0,R5*SIN(ALPHA)) C C INITIALIZE FOR PLOTTING AT 120 CHARACTERS PER SECOND. CALL INITT(1200) C C SET THE WINDOW FOR THE PLOTTING AREA. CALL DWINDO(-R2,R1+R2+R4,-R4,R4+R4+Y5) C C CYCLE THROUGH ONE CRANK ROTATION IN FIVE DEGREE INCREMENTS. TH2=0.0 DTH2=5.0/57.29578 IPEN=-1 DO 2 I=1,73 CTH2=COS(TH2) STH2=SIN(TH2) C
13 C CALCULATE THE TRANSMISSION ANGLE. CGAM=(R3*R3+R4*R4-R1*R1-R2*R2+2.0*R1*R2*CTH2)/(2.0*R3*R4) IF(ABS(CGAM).GT.0.99)THEN CALL MOVABS(100,100) CALL ANMODE WRITE(7,1001) 1001 FORMAT(// *** THE TRANSMISSION ANGLE IS TOO SMALL. ***) GO TO 1 END IF SGAM=SQRT(1.0-CGAM*CGAM) GAM=ATAN2(SGAM,CGAM) C C CALCULATE THETA 3. STH3=-R2*STH2+R4*SIN(GAM) CTH3=R3+R1-R2*CTH2-R4*COS(GAM) TH3=2.0*ATAN2(STH3,CTH3) C C CALCULATE THE COUPLER POINT POSITION. TH6=TH3+ALPHA XP=R2*CTH2+R5*COS(TH6) YP=R2*STH2+R5*SIN(TH6) C C PLOT THIS SEGMENT OF THE COUPLER CURVE. IF(IPEN.LT.0)THEN IPEN=1 CALL MOVEA(XP,YP) ELSE IPEN=-1 CALL DRAWA(XP,YP) END IF TH2=TH2+DTH2 2 CONTINUE C C DRAW THE LINKAGE. CALL MOVEA(0.0,0.0) CALL DRAWA(R2,0.0) XC=R2+R3*COS(TH3) YC=R3*SIN(TH3) CALL DRAWA(XC,YC) CALL DRAWA(XP,YP) CALL DRAWA(R2,0.0) CALL MOVEA(XC,YC) CALL DRAWA(R1,0.0) 1 CALL FINITT(0,0) CALL EXIT STOP END
14
2.16
For each linkage shown in the figure, find the path of point P: (a) inverted slider-crank mechanism; (b) second inversion of the slider-crank mechanism; (c) straight-line mechanism; (d) drag-link mechanism.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
15
2.17
Using the offset slider-crank mechanism of Fig. 2.15, find the crank angles corresponding to the extreme values of the transmission angle. As shown, = 90 3 . Also from the figure e + r2 sin 2 = r3 cos . Differentiating with respect to 2 , d r2 cos 2 = r3 sin ; d 2 r cos 2 d = 2 . d 2 r3 sin
Therefore, we conclude that 2 = ( 2k + 1) / 2 = 90, 270, Ans. Now, setting d / d 2 = 0 , we get cos 2 = 0 .
2.18
In Section 1.10 it is pointed out that the transmission angle reaches an extreme value for the four-bar linkage when the crank lies on the line between the fixed pivots. Referring to Fig. 2.19, this means that reaches a maximum or minimum when crank 2 is coincident with the line O2 O4 . Show, analytically, that this statement is true. From O4O2 A :
s 2 = r12 + r22 2r1r2 cos 2 . Also, from ABO4 : s 2 = r32 + r42 2r3 r4 cos . Equating these we differentiate with respect to 2 to obtain d 2r1r2 sin 2 = 2r3 r4 sin or d 2 r r sin 2 d = 12 . d 2 r3 r4 sin
Now, for
d = 0 , we have sin 2 = 0 . Thus, 2 = 0, 180, 360, d 2
Q.E.D.
16
2.19
The figure illustrates a crank-and-rocker linkage in the first of its two limit positions. In a limit position, points O2 , A, and B lie on a straight line; that is, links 2 and 3 form a straight line. The two limit positions of a crank-rocker describe the extreme positions of the rocking angle. Suppose that such a linkage has r 1 = 400 mm , r2 = 200 mm ,
r3 = 500 mm , and r4 = 400 mm .
(a) (b) (c)
Find 2 and 4 corresponding to each limit position. What is the total rocking angle of link 4? What are the transmission angles at the extremes? (a) From isosceles triangle O4O2 B we can calculate or measure 2 = 29 , 4 = 58 = 248 , 4 = 136 . and 2 4 = 78 . Then 4 = 4 Ans. (b) Finally, from isosceles triangle (c) O4O2 B , = 29 and = 68 . Ans.
2.20
A double-rocker mechanism has a dead-center position and may also have a limit position (see Prob. 2.19). These positions occur when links 3 and 4 in the figure lie along a straight line. In the dead-center position the transmission angle is 180 and the mechanism is locked. The designer must either avoid such positions or provide the external force, such as a spring, to unlock the linkage. Suppose, for the linkage shown in the figure, that r1 = 14 in , r2 = 5.5 in , r3 = 5 in , and r4 = 12 in . Find 2 and 4 corresponding to the dead-center position. Is there a limit position? For the given dimensions, there are two dead-center positions, and they correspond to the two extreme travel positions of crank O2 A . From O4 AO2 using the law of cosines, we can find 2 = 114.0 , 4 = 162.8 and, symmetrically, = 114.0 , 4 = 162.8 . There 2 are also two limit positions, these = 56.5 , 4 = 133.1 occur at 2 = 56.5 , and, symmetrically, at 2 = 133.1 . 4 Ans.
17
2.21
The figure shows a slider-crank mechanism that has an offset e and that is placed in one of its limiting positions. By changing the offset e, it is possible to cause the angle that crank 2 makes in traversing between the two limiting positions to vary in such a manner that the driving or forward stroke of the slider takes place over a larger angle than the angle used for the return stroke. Such a linkage is then called a quick-return mechanism. The problem here is to develop a formula for the crank angle traversed during the forward stroke and also develop a similar formula for the angle traversed during the return stroke. The ratio of these two angles would then constitute an time ratio of the drive to return strokes. Also determine which direction the crank should rotate.
180 ) or From the figure we can see that e = ( r3 + r2 ) sin 2 = ( r3 r2 ) sin ( 2
2 = sin 1
e e = 180 + sin 1 , 2 r3 + r2 r3 r2
e e 1 2 = 180 + sin 1 drive = 2 sin r3 r2 r3 + r2 e e 1 = 180 + sin 1 return = 2 + 360 2 sin r3 + r2 r3 r2 Assuming driving when sliding to the right, the crank should rotate clockwise.
Ans. Ans. Ans.
You might also like
- 218 39 Solutions Instructor Manual Chapter 9 Spatial MechanismsDocument21 pages218 39 Solutions Instructor Manual Chapter 9 Spatial Mechanismskentetsu123456789No ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 07 Autocad 3d Basics-Arce, KDocument13 pagesLaboratory Activity 07 Autocad 3d Basics-Arce, KKalvinNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 System Techniques in Water Resuorce PPT YadesaDocument32 pagesCHAPTER 6 System Techniques in Water Resuorce PPT YadesaGod is good tubeNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 05 Compressible Fluid FlowDocument70 pagesCHAPTER 05 Compressible Fluid FlowNik Hafiy HafiziNo ratings yet
- Krar Unit 71Document31 pagesKrar Unit 71Ranjan SahooNo ratings yet
- Metrology Lab Viva Voce QuestionsDocument6 pagesMetrology Lab Viva Voce Questionsmrbalaji88No ratings yet
- MECH1230 Dynamics Unit 2 - Rigid Body KinematicsDocument48 pagesMECH1230 Dynamics Unit 2 - Rigid Body KinematicsJamie ThomsonNo ratings yet
- Transport Phenomena: CHE411 ADocument5 pagesTransport Phenomena: CHE411 Aonyx100% (1)
- EeeDocument88 pagesEeeShalom HaileNo ratings yet
- MillingDocument54 pagesMillingVickyVenkataramanNo ratings yet
- Fosma Maritime Institute & Research Organisation: Awarded Grade A1 (Outstanding) With A Score of 93.04% by DNV-GLDocument1 pageFosma Maritime Institute & Research Organisation: Awarded Grade A1 (Outstanding) With A Score of 93.04% by DNV-GLNIDHI SINGHNo ratings yet
- CH 1 2 3 and 7Document47 pagesCH 1 2 3 and 7NigaraNo ratings yet
- 15ME202 Manufacturing Technology: Unit - 5 Machine ToolsDocument68 pages15ME202 Manufacturing Technology: Unit - 5 Machine ToolsMouriya0% (1)
- Chapter 5Document25 pagesChapter 5dickinaround87100% (1)
- Unit-4 - Development of SurfacesDocument91 pagesUnit-4 - Development of SurfacesSamyuktha KatkamNo ratings yet
- Autocad Lab ManualDocument84 pagesAutocad Lab ManualRaghu RamNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Classification, Applications and Operations of MachinesDocument19 pagesModule 4 - Classification, Applications and Operations of MachinesIsmaeli KielNo ratings yet
- Auto CadDocument67 pagesAuto CadMani velNo ratings yet
- ProposalDocument16 pagesProposalmakawiss1No ratings yet
- CH 21Document45 pagesCH 21Anonymous p0mg44xNo ratings yet
- Assignment6 SolutionsDocument5 pagesAssignment6 SolutionsVishal NadiyaNo ratings yet
- Calculator Flowchart 8051Document1 pageCalculator Flowchart 8051Dwiky ErlanggaNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document21 pagesModule 1AzizNo ratings yet
- Determining Thermal Properties of Foods Using Computational MethodsDocument10 pagesDetermining Thermal Properties of Foods Using Computational MethodsHeliNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Course OutlineDocument3 pagesFluid Mechanics Course Outlinemeku44No ratings yet
- Sectional OrthographicDocument80 pagesSectional OrthographicKrish Hams100% (1)
- Module IV-Milling MachineDocument26 pagesModule IV-Milling MachineNalluriRavindra100% (2)
- Engineering Shop: Multiple ChoiceDocument7 pagesEngineering Shop: Multiple ChoiceAlfredo CondeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Size ReductionDocument50 pagesChapter 11 Size ReductionCharmaine A. OlivasNo ratings yet
- Grinding Process OverviewDocument8 pagesGrinding Process OverviewhainerajaramanNo ratings yet
- Abstract Title and AuthorDocument25 pagesAbstract Title and AuthorSana AbdiNo ratings yet
- Overview of OtDocument40 pagesOverview of OtNaman Ku SangerNo ratings yet
- Revision Questions: Introduction + Irrigation SystemsDocument11 pagesRevision Questions: Introduction + Irrigation SystemsKiprop VentureNo ratings yet
- Keys and Couplings Types DesignDocument85 pagesKeys and Couplings Types DesignMannam Sarath Sarath100% (1)
- Project ResearchDocument92 pagesProject Researchmbatechcs100% (1)
- Unit IV - Abrasive Process and Broaching PDFDocument80 pagesUnit IV - Abrasive Process and Broaching PDFKanda SamyNo ratings yet
- Assignment ON Operation ResearchDocument15 pagesAssignment ON Operation ResearchHimansu Sekhar BarikNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - CHAPTER - 1Document27 pagesMicrosoft Word - CHAPTER - 1Khairul FahzanNo ratings yet
- Modern Bamboo SplitterDocument14 pagesModern Bamboo SplitterSenthil Kumar100% (1)
- THERMODYNAMICSDocument12 pagesTHERMODYNAMICSVaibhav Vithoba NaikNo ratings yet
- Drainage of Irrigation Lands: Rajat Mishra Asst. Professor Civil Engineering DepartmentDocument52 pagesDrainage of Irrigation Lands: Rajat Mishra Asst. Professor Civil Engineering DepartmentDileesha WeliwaththaNo ratings yet
- Drilling, Planing and Shaping Machine ProcessesDocument70 pagesDrilling, Planing and Shaping Machine ProcessesIrfan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Unit I Operation Research Introduction: Characteristics of Operations ResearchDocument90 pagesUnit I Operation Research Introduction: Characteristics of Operations ResearchhariroopganeshNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment Sem 2 20162017Document3 pagesIndividual Assignment Sem 2 20162017Anis NabilaNo ratings yet
- FLUID MECHANICS Lab ManualDocument65 pagesFLUID MECHANICS Lab ManualPaulNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document2 pagesTutorial 4Beesam Ramesh KumarNo ratings yet
- ME 425 (PPD) Syllabus-First Sem 2021-2022-FinalDocument13 pagesME 425 (PPD) Syllabus-First Sem 2021-2022-FinalArhon Barcelon100% (1)
- 5 Mechanism of Chip FormationDocument17 pages5 Mechanism of Chip FormationPRASAD326100% (9)
- GEDocument25 pagesGEFaith WangNo ratings yet
- Desing of An Automated Vegetabe Cutter and Slicer 1 AugDocument35 pagesDesing of An Automated Vegetabe Cutter and Slicer 1 AugAshiasmanNo ratings yet
- TVET Strategy in AfricaDocument54 pagesTVET Strategy in AfricaAasia Farooqi100% (3)
- Cad Lab ManualDocument79 pagesCad Lab Manualblazer100% (1)
- Local Media6686144101601395137Document2 pagesLocal Media6686144101601395137Christian Laurenz AndradeNo ratings yet
- SizeReduction Ques&AnsDocument20 pagesSizeReduction Ques&AnsRick KingNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machines and Mechanisms 3rd Ed. Solutions CH 1-4Document62 pagesTheory of Machines and Mechanisms 3rd Ed. Solutions CH 1-4orcunozb66% (29)
- Mathematical Tools-NeetDocument45 pagesMathematical Tools-NeetResonance Dlpd78% (32)
- PHY103 MidSem SolutionsDocument9 pagesPHY103 MidSem SolutionsShreyaNo ratings yet
- Mechines of Mechinism Chapter 2Document13 pagesMechines of Mechinism Chapter 2abdulmajeedNo ratings yet
- S - Feb Geom Indiv SolutionsDocument3 pagesS - Feb Geom Indiv SolutionsJake ZengNo ratings yet
- Route SurveyingDocument69 pagesRoute Surveyingronald_feliciano_175% (4)
- HMT Mod 5 NotesDocument66 pagesHMT Mod 5 Notesprasaad08No ratings yet
- Connecting RodDocument29 pagesConnecting Rodprasaad08No ratings yet
- Question Bank III B.Tech-II Sem Design of Machine Members-Ii Unit - I A Design of Curved Beams Short Answer QuestionsDocument11 pagesQuestion Bank III B.Tech-II Sem Design of Machine Members-Ii Unit - I A Design of Curved Beams Short Answer Questionsprasaad08No ratings yet
- Experimental Studies On The Combustion and Emission Characteristics of A Diesel EngineFuelled With Used Cooking Oil Methyl Esterand Its Diesel BlendsDocument7 pagesExperimental Studies On The Combustion and Emission Characteristics of A Diesel EngineFuelled With Used Cooking Oil Methyl Esterand Its Diesel Blendsprasaad08No ratings yet
- FIE FormDocument10 pagesFIE Formprasaad08No ratings yet
- GearsDocument44 pagesGearsprasaad08No ratings yet
- 10th Maths em 24-Jul-2016 21-44-08 - WatermarkedDocument1 page10th Maths em 24-Jul-2016 21-44-08 - Watermarkedprasaad08No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of SurveyingDocument611 pagesFundamentals of Surveyingrvkumar361969091% (58)
- NotesDocument20 pagesNotesprasaad08No ratings yet
- ES 2 MarksDocument17 pagesES 2 Marksprasaad08No ratings yet
- Iron-Carbon DiagramDocument11 pagesIron-Carbon DiagramrampradNo ratings yet
- Energies: Emission Characteristics of A CI Engine Running With A Range of Biodiesel FeedstocksDocument17 pagesEnergies: Emission Characteristics of A CI Engine Running With A Range of Biodiesel FeedstocksArul JONo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology: Course: B.E & B.Tech Subject: APPLIED CHEMISTRY Unit: VDocument10 pagesNanotechnology: Course: B.E & B.Tech Subject: APPLIED CHEMISTRY Unit: Vprasaad08No ratings yet
- 9A01303 SurveyingDocument4 pages9A01303 Surveyingprasaad08No ratings yet
- IJEE 11 v4n5Document12 pagesIJEE 11 v4n5prasaad08No ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document6 pagesLecture 1prasaad08No ratings yet
- 9A01304 Fluid MechanicsDocument1 page9A01304 Fluid MechanicssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- After Gate Guide 2015Document100 pagesAfter Gate Guide 2015JaydeepRanipaNo ratings yet
- Production Engineering Syllabus (1) - 2Document34 pagesProduction Engineering Syllabus (1) - 2prasaad08No ratings yet
- Aluminium: A Large Aluminium Billet From Which Wrought Products Will Be ProducedDocument38 pagesAluminium: A Large Aluminium Billet From Which Wrought Products Will Be Producedprasaad08No ratings yet
- Cad Cam Viva QueDocument5 pagesCad Cam Viva QueJeeva KarunyaNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Members-IIDocument8 pagesDesign of Machine Members-IIprasaad08No ratings yet
- M.Tech - F Semester Regulor Exqminotions April 20t5: TimetobleDocument1 pageM.Tech - F Semester Regulor Exqminotions April 20t5: Timetobleprasaad08No ratings yet
- DV03PUB1 Study GuideDocument5 pagesDV03PUB1 Study Guideprasaad08No ratings yet
- NMDC Et AdvertisementDocument8 pagesNMDC Et AdvertisementbecbellaryNo ratings yet
- Production Engineering Syllabus (1) - 2Document34 pagesProduction Engineering Syllabus (1) - 2prasaad08No ratings yet
- Cad Cam Viva QueDocument5 pagesCad Cam Viva QueJeeva KarunyaNo ratings yet
- R09 B.Tech III Year I Semester Machine Elements ExamDocument1 pageR09 B.Tech III Year I Semester Machine Elements Examprasaad08No ratings yet
- YVC RaoDocument98 pagesYVC Raoprasaad08No ratings yet
- Jntua B.tech Eee r13 SyllabusDocument116 pagesJntua B.tech Eee r13 Syllabusprasaad08No ratings yet
- Representing Temperature Data on a Number LineDocument17 pagesRepresenting Temperature Data on a Number Linesoundu ranganathNo ratings yet
- Hard Margin SVM Dual Problem DerivationDocument2 pagesHard Margin SVM Dual Problem DerivationSat AdhaNo ratings yet
- Exponent Lifting Sol 2Document2 pagesExponent Lifting Sol 2johnsonNo ratings yet
- 192 - Elements of Functional Analysis PDFDocument412 pages192 - Elements of Functional Analysis PDFVishakh Kumar100% (1)
- Analytical Geometry For BeginnersDocument234 pagesAnalytical Geometry For Beginnersscubadru100% (3)
- 4 Grade 8 LPDocument389 pages4 Grade 8 LPJobert Cagas100% (1)
- Linear Programming PDFDocument22 pagesLinear Programming PDFChristine Joy OriginalNo ratings yet
- AE06Document3 pagesAE06Sanjeev PanwarNo ratings yet
- NAT Grade 10 Reviewer (MathematicsDocument13 pagesNAT Grade 10 Reviewer (MathematicsAnthony CaputolNo ratings yet
- Elementary Algebra Hall KnightDocument540 pagesElementary Algebra Hall Knightmadangk83% (18)
- 465 - C Applied MathematicsDocument23 pages465 - C Applied MathematicsAlwin KoshyNo ratings yet
- Surfaces in Classical Geometries: Gary R. Jensen Emilio Musso Lorenzo NicolodiDocument576 pagesSurfaces in Classical Geometries: Gary R. Jensen Emilio Musso Lorenzo Nicolodivguardiano100% (1)
- Chapter 01Document28 pagesChapter 01society RejectedNo ratings yet
- In-Cylinder CFD Simulation Using A C++ Object Oriented Toolkit SAE2004Document11 pagesIn-Cylinder CFD Simulation Using A C++ Object Oriented Toolkit SAE2004AghajaniNo ratings yet
- 2.4c Substitution Suggested by EqDocument3 pages2.4c Substitution Suggested by EqMycon EchanoNo ratings yet
- 2014 TF JamesKraft Intro To NumberTheory PDFDocument2 pages2014 TF JamesKraft Intro To NumberTheory PDFDannyNo ratings yet
- 1966 EngulfingDocument3 pages1966 Engulfingnishio fdNo ratings yet
- Cape Pure Mathematics: Syllabus Specimen Paper Mark Scheme Subject ReportsDocument450 pagesCape Pure Mathematics: Syllabus Specimen Paper Mark Scheme Subject Reportsamrit100% (1)
- TI4101 Facility Layout ModelsDocument60 pagesTI4101 Facility Layout ModelsJonathan HaryantoNo ratings yet
- 04-05 Water Flowing Into Triangular Trough - Differential Calculus ReviewDocument3 pages04-05 Water Flowing Into Triangular Trough - Differential Calculus ReviewRommelBaldagoNo ratings yet
- Bangayan, Melody D. Discussion 4Document1 pageBangayan, Melody D. Discussion 4Melody Domingo BangayanNo ratings yet
- FactorisingExercises132 PDFDocument4 pagesFactorisingExercises132 PDFБ. ЖавхланNo ratings yet
- Laplace & Z Transforms Lab: Filter DesignDocument5 pagesLaplace & Z Transforms Lab: Filter DesignMy citaraNo ratings yet
- How I Applied Engineering Knowledge and SkillsDocument6 pagesHow I Applied Engineering Knowledge and SkillsireshnNo ratings yet
- Amm 2010 N5Document97 pagesAmm 2010 N51110004No ratings yet
- PHD - Laurent - Keersmaekers - Decoupling of Mechanical Systems Based On In-Situ Frequency Response Functions The LPD MethodDocument283 pagesPHD - Laurent - Keersmaekers - Decoupling of Mechanical Systems Based On In-Situ Frequency Response Functions The LPD MethodLaurent KeersmaekersNo ratings yet
- Section 1.7 Combinations of Functions: Composite FunctionsDocument28 pagesSection 1.7 Combinations of Functions: Composite FunctionsdavogezuNo ratings yet
- Linear Contextual Transformations: Rachel Wells Hall June 11, 2009Document22 pagesLinear Contextual Transformations: Rachel Wells Hall June 11, 2009josemariaxx100% (1)
- Factoring Polynomials CalculatorDocument4 pagesFactoring Polynomials Calculatorcircleteam123No ratings yet
- Geometric Wave EquationDocument279 pagesGeometric Wave EquationUirá MatosNo ratings yet