Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How Rare Is Heterochromia Iridis?
Uploaded by
Bentoys StreetOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
How Rare Is Heterochromia Iridis?
Uploaded by
Bentoys StreetCopyright:
Available Formats
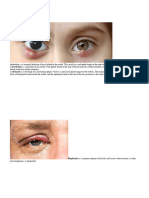
HETEROCHROMIA IRIDIS
How rare is heterochromia iridis?
Heterochromia can be present at birth (congenital) or acquired. The incidence of congenital heterochromia iridis is approximately six out of a 1,000, although in most of these cases, it is hardly noticeable and unassociated with any other abnormality.
What causes heterochromia iridis
Heterochromia is classified primarily by its time of onset as either genetic (congenital, present at or shortly after birth) or acquired. Most cases of heterochromia are hereditary, and these may be associated with a congenital syndrome. Other cases are acquired and caused by a disease or due to an injury. Sometimes one eye may change color following certain diseases or injuries. Heterochromia present at or shortly after birth is usually hereditary or due to intrauterine disease or injury. Congenital heterochromia may be familial and is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait. Inherited eye color is determined by multiple genes. Environmental or acquired factors can alter these inherited traits. An infant with heterochromia should be examined by both a pediatrician and an ophthalmologist for other possible problems. If another disorder is suspected, diagnostic tests, such as blood tests or chromosome studies, may be done to confirm the diagnosis. Most cases of heterochromia at birth are genetic and unassociated with any other ocular or systemic abnormality. This is simply called congenital heterochromia iridis. The lighter eye usually shows some loss of iris and therefore is regarded as the affected eye. The lighter iris may be differently colored throughout or only in part.
Congenital syndromes which may be characterized by heterochromia iridis include: Waardenburg syndrome, a genetic condition that can cause hearing loss and changes in coloring of the hair, skin, and eyes.
"Piebaldism" is similar to Waardenburg syndrome but is unassociated with deafness. People with this condition have patches of depigmented skin on their head and trunk, as well as on their eyebrows, eyelids, eyelashes, and hair. Affected people sometimes have heterochromia iridis. Congenital "Horner's syndrome" is not a genetic syndrome, but a group of findings due to birth injury or intrauterine brain injury involving the sympathetic nervous system innervation to one eye. On the affected side, the pupil is small, the lid is drooping, and the iris is lighter. It is not associated with hearing loss or additional pigmentation anomalies. Sturge-Weber syndrome, a syndrome characterized by a port-wine stain in the distribution of the trigeminal nerve on the face and tumors known as angiomas of the brain and choroid. Neurofibromatosis type 1, also known as von Recklinghausen disease, is a disorder in which there are tumors of nerve cells together with disorders of melanin, causing abnormalities of skin (and eye) pigmentation. Lisch nodules are usually present in the iris. These are clear yellow to brown dome-shaped elevations on the iris and, although they are usually present in both eyes, may be more apparent in one eye. Tuberous sclerosis, also known as Bourneville disease, causes nonmalignant tumors in various organs including the eyes. Hirschsprung disease, a bowel disorder, may be associated with iris heterochromia due to reduction is iris pigmentation. Incontinentia pigmenti, also known as BlochSulzberger syndrome, affects the skin, hair, teeth, nails, and central nervous system. In this condition, the iris may be darker in the affected eye.
Parry-Romberg syndrome, or progressive hemifacial atrophy, is a condition that causes the breakdown of the skin and soft tissues of half of the face.
Acquired conditions or diseases that may present with heterochromia iridis include: The inflammation of iritis or anterior uveitis of any cause, includingtuberculosis, sarcoidosis, and herpes simplex, may cause loss of iris pigment in the affected eye.
Fuchs' heterochromic cyclitis is a condition characterized by a low-grade, asymptomatic uveitis in which the iris in the affected eye becomes hypochromic and has a washed-out, somewhat moth-eaten appearance. Posner-Schlossman Syndrome, or glaucomatocyclitic crisis, may cause a lighter iris with repeated attacks. Pigment dispersion syndrome is a condition characterized by loss of pigmentation from the posterior iris surface. This pigment is dispersed throughout the interior of the eye and deposited on various intraocular structures, including the anterior surface of the iris, causing it to darken. This condition also causes pigmentary glaucoma. Trauma, either blunt or penetrating, may cause unilateral lightening of the iris through atrophy of the iris. Prostaglandin analogue eyedrops (Xalatan, Lumigan, Travatan, and others), frequently used for the treatment of glaucoma, may cause darkening of the iris, especially in people with light-colored irises. This occurs from the stimulation of melanin production. This type of medication is also sometimes used for cosmetic purposes (Latisse) to darken and thicken the eyelashes. Retained iron-containing intraocular foreign body may cause siderosis (iron deposition within the eye) resulting in a darker iris. Blood in the anterior chamber (hyphema) of long duration from trauma can lead to iron deposition in the iris from the breakdown of blood products.
Ocular melanosis, or nevus of Ota, is a condition characterized by increased pigmentation of the eye and surrounding tissue. Iris ectropion syndrome is a condition in which the back of the iris, which is always dark and full of melanin pigment, turns onto the front of the iris through the pupillary space. Benign tumors of the iris, iris cysts, and iris abscesses can cause darkening or lightening of the iris. Malignant melanoma of the iris or metastatic tumors of the iris. Neovascular changes of the iris (rubeosis iridis) resulting from diabetes mellitus or following central retinal vein occlusion. Acquired Horner syndrome from neuroblastoma or injury/disease affecting the sympathetic nervous system in the neck. Chediak-Higashi syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that may manifest in childhood with recurrent infections, peripheral neuropathy, and color changes in the skin and eye. Clouding of the cornea or color changes in the cornea from a multitude of conditions may cause the iris to falsely appear to be different in color. Conditions such as corneal scars, the very common condition of arcus senilis, or the rare condition of Wilson disease can give the appearance of iris color differences.
Reviewed by Melissa Conrad Stppler, MD on 5/21/2013 http://www.medicinenet.com/heterochromia_iridis/page2.htm
Heterochromia iridis: Rare Disease
Heterochromia iridis is listed as a "rare disease" by the Office of Rare Diseases (ORD) of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). This means that Heterochromia iridis, or a subtype of Heterochromia iridis, affects less than 200,000 people in the US population.
About prevalence and incidence statistics:
The term 'prevalence' of Heterochromia iridis usually refers to the estimated population of people who are managing Heterochromia iridis at any given time. The term 'incidence' of Heterochromia iridis refers to the annual diagnosis rate, or the number of new cases of Heterochromia iridis diagnosed each year. Hence, these two statistics types can differ: a short-lived disease like flu can have high annual incidence but low prevalence, but a lifelong disease like diabetes has a low annual incidence but high prevalence. For more information see about prevalence and incidence statistics.
http://www.rightdiagnosis.com/h/heterochromia_iridis/prevalence.htm
18 Celebrities with Heterochromia Iridis
Celebrities with heterochromia have a fascinating condition: Their eyes are actually two different colors. In some cases, this anomaly is extremely noticeable, in other cases it is a bit more subtle. Either way, everyone listed here has the relatively rare and really cool condition called "heterochromia iridis," meaning the irises of their eyes are different colors. Prepare to be amazed, because some of these famous people with different colored eyes are without question among the most beautiful women in Hollywood and some of the greatest film actors and actresses of all time, too. Is having heterochromia a blessing, or a curse? Looking at the celebrities with different-colored eyes here, it's easy to believe it's a blessing.
1. Kate Bosworth
2. Jane Seymour
3. Kiefer Sutherland
4. Mila Kunis
5. Alice Eve
6. Max Scherzer
7. Dan Aykroyd
8. Christopher Walken
9. Josh Henderson
10. Michael Flatley
11. Elizabeth Berkley
12. Simon Pegg
13. Demi Moore
14. Henry Cavill
15. Jonathan Rhys Meyers
16. Tim McIlrath
17. Jessica Cauffiel
18. Michael Schwimer
19. Not David Bowie
https://www.google.com.ph/#q=heterochromia+iridum+celebrities
You might also like
- Heterochrmia PresDocument7 pagesHeterochrmia Presapi-38660940350% (2)
- Heterochromia: I. Rationale or IntroductionDocument5 pagesHeterochromia: I. Rationale or IntroductionNoreenNo ratings yet
- Bio Investigatory ProjectDocument18 pagesBio Investigatory ProjectBushraNo ratings yet
- Diseases and DisordersDocument10 pagesDiseases and DisordersGrace Ocampo Villamayor TitularNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Developmental Disorders of The Oral CavityDocument6 pagesChapter 1 Developmental Disorders of The Oral CavityArafat Masud NiloyNo ratings yet
- ENT ExaminationDocument36 pagesENT ExaminationLiji GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Paediatric NeurophthalmologyDocument49 pagesPaediatric NeurophthalmologyNavami KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Intro To SpedDocument13 pagesIntro To SpedRodel FaulveNo ratings yet
- OphthoDocument2 pagesOphthoGayathriNo ratings yet
- Where Can Hypoplasia Occur?: An Abnormally Small Cerebellum Abnormally Small Thumbs Insufficient EnamelDocument2 pagesWhere Can Hypoplasia Occur?: An Abnormally Small Cerebellum Abnormally Small Thumbs Insufficient EnamelShannen Joyce FloresNo ratings yet
- Albanism Concep MapDocument5 pagesAlbanism Concep MapGio GallegoNo ratings yet
- BlepharitisDocument2 pagesBlepharitisPranay SriNo ratings yet
- Genodermatosis: The IchthyosisDocument4 pagesGenodermatosis: The IchthyosisOman ArifNo ratings yet
- 1 ST Lesson MTDocument7 pages1 ST Lesson MTUSMLE InDocNo ratings yet
- Kimberly Cruz - OphthalmologyDocument5 pagesKimberly Cruz - OphthalmologyKimberly CruzNo ratings yet
- KELAINAN REFRAKSI NadiaDocument6 pagesKELAINAN REFRAKSI NadiaNadia A. DestiantiNo ratings yet
- OPTIC NEURITIS CAUSES SUDDEN VISION LOSSDocument28 pagesOPTIC NEURITIS CAUSES SUDDEN VISION LOSSJamal Kadir100% (2)
- FACIAL EXPRESSIONS BROUGHT ABOUT BY EFFECTS OF DISEASEs (Legal Med)Document4 pagesFACIAL EXPRESSIONS BROUGHT ABOUT BY EFFECTS OF DISEASEs (Legal Med)KarlvindeCardoNo ratings yet
- Eye Osce 3Document39 pagesEye Osce 3epic sound everNo ratings yet
- Macular DegenerationDocument5 pagesMacular DegenerationPauleen Jambora RodilNo ratings yet
- 12 Kasper Notes 2020 OphthalmologyDocument33 pages12 Kasper Notes 2020 OphthalmologyMohamed Rikarz Ahamed RikarzNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The EyeDocument14 pagesDiseases of The EyeGunel AliyevaNo ratings yet
- Neuritis OpticDocument13 pagesNeuritis OpticBimo Nugroho saktiNo ratings yet
- HyperDocument12 pagesHyperp4b5No ratings yet
- Congenital HeterochromiaDocument8 pagesCongenital Heterochromiaapi-307736616No ratings yet
- Eye Manifestations in Systemic Diseases - AudioDocument22 pagesEye Manifestations in Systemic Diseases - AudioPerfect GirlNo ratings yet
- Congenital AniridiaDocument16 pagesCongenital AniridiaManish MahabirNo ratings yet
- Blepharitis Disease and Its ManagementDocument7 pagesBlepharitis Disease and Its Managementνικος νικουNo ratings yet
- Goldenhar SyndromeDocument16 pagesGoldenhar Syndromesaeid seyedraoufiNo ratings yet
- Approach To The Adult With Acute Persistent Visual LossDocument17 pagesApproach To The Adult With Acute Persistent Visual LossMauricio SvNo ratings yet
- How Eye Disease Can Indicate Systemic IllnessDocument62 pagesHow Eye Disease Can Indicate Systemic IllnesslonguseridNo ratings yet
- Dry Eye Syndrome - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf PDFDocument7 pagesDry Eye Syndrome - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf PDFnum padNo ratings yet
- Eye InfectionsDocument9 pagesEye InfectionsRatnaPrasadNalamNo ratings yet
- Disorder of The Eye LashesDocument9 pagesDisorder of The Eye Lasheshonovezaann.a.campita.ctucvmNo ratings yet
- Ectodermal Dysplasia - DermNetDocument3 pagesEctodermal Dysplasia - DermNetAtul MhetreNo ratings yet
- ANIRIDIA Hingorani-Hanson Ejhg2012100aDocument8 pagesANIRIDIA Hingorani-Hanson Ejhg2012100aESMERNo ratings yet
- Congenital Corneal DisordersDocument101 pagesCongenital Corneal Disorderseyemd_in_training100% (1)
- Dry Eyes, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandDry Eyes, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- classification of hyperopiaDocument3 pagesclassification of hyperopiap4b5No ratings yet
- VISION DISORDERSDocument4 pagesVISION DISORDERSAkhwand SaulatNo ratings yet
- Degenerative MyopiaDocument49 pagesDegenerative MyopiaSekar CiptaningrumNo ratings yet
- Ectodermal Dysplasia-EGUILLIONDocument21 pagesEctodermal Dysplasia-EGUILLIONMonica EguillionNo ratings yet
- Visual ImpairmentDocument57 pagesVisual ImpairmentNavami KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Corneal DystrophyDocument5 pagesCorneal DystrophyDejan JanevNo ratings yet
- 2013 PROF 220 AniridiaDocument5 pages2013 PROF 220 Aniridiaavram_elenaNo ratings yet
- Visual Field ScienceDocument8 pagesVisual Field ScienceMuhammad Zarak NiaziNo ratings yet
- Optic NeuritisDocument31 pagesOptic NeuritisUsman ImtiazNo ratings yet
- RetinoschisisDocument11 pagesRetinoschisisapi-248099296No ratings yet
- Diseases and DisordersDocument4 pagesDiseases and DisordersGrace Ocampo Villamayor TitularNo ratings yet
- Ectodermal Dysplasia - WikipediaDocument8 pagesEctodermal Dysplasia - WikipediaAtul MhetreNo ratings yet
- Diseases and DisordersDocument4 pagesDiseases and DisordersGrace Ocampo Villamayor TitularNo ratings yet
- Distrofias RetinialesDocument7 pagesDistrofias Retinialesmartin.ruda93No ratings yet
- Eye and Vision Problems GuideDocument11 pagesEye and Vision Problems GuideDarius CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology For 5th Year Exams: Visual AcuityDocument7 pagesOphthalmology For 5th Year Exams: Visual AcuitySaloni PatelNo ratings yet
- Blindness: Introduction:-Low Vision Is A General Term Describing Visual Impairment That Requires Patients To UseDocument12 pagesBlindness: Introduction:-Low Vision Is A General Term Describing Visual Impairment That Requires Patients To UseaparnaNo ratings yet
- Baldivino, John Patrick B. 9:00 AM-11:00 AM: Eye DiseasesDocument5 pagesBaldivino, John Patrick B. 9:00 AM-11:00 AM: Eye DiseasesPat BaldivinoNo ratings yet
- Ocular Pathology of Hyperopic Patients Presenting To The Tertiary Health Care CentreDocument7 pagesOcular Pathology of Hyperopic Patients Presenting To The Tertiary Health Care CentreIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Name: Shumaila Azam Reg No: 70098213 Section: B Topic: Causes of Blindness Mam: Tahira Kalsoom Subject: Optometric ProceduresDocument8 pagesName: Shumaila Azam Reg No: 70098213 Section: B Topic: Causes of Blindness Mam: Tahira Kalsoom Subject: Optometric Proceduresshumaila khanNo ratings yet
- Speak TestDocument81 pagesSpeak TestBentoys StreetNo ratings yet
- Speak TestDocument81 pagesSpeak TestBentoys StreetNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25Document46 pagesChapter 25Angela Nina EstradaNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure Guide: Causes, Symptoms, TreatmentsDocument64 pagesCongestive Heart Failure Guide: Causes, Symptoms, TreatmentsBentoys StreetNo ratings yet
- The Top 250 Most Difficult WordsDocument25 pagesThe Top 250 Most Difficult WordsBentoys Street50% (2)
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument55 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseBentoys Street100% (1)
- QuotesDocument33 pagesQuotesBentoys StreetNo ratings yet
- What Is Angina?Document30 pagesWhat Is Angina?Bentoys Street100% (1)
- Theories of AgingDocument7 pagesTheories of AgingBentoys Street100% (1)
- Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDocument9 pagesRheumatic Heart DiseaseBentoys StreetNo ratings yet
- Craniocerebral TraumaDocument64 pagesCraniocerebral TraumaBentoys StreetNo ratings yet
- MT Medical Transcription Process Converts Speech to TextDocument17 pagesMT Medical Transcription Process Converts Speech to TextBentoys StreetNo ratings yet
- LaborDocument22 pagesLaborBentoys StreetNo ratings yet
- ChokingDocument22 pagesChokingBentoys StreetNo ratings yet
- HmoleDocument29 pagesHmoleBentoys StreetNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument11 pagesBreast CancerBentoys StreetNo ratings yet
- Dissociative DisordersDocument15 pagesDissociative DisordersBentoys StreetNo ratings yet
- AmlodipineDocument4 pagesAmlodipineBentoys StreetNo ratings yet
- DicDocument2 pagesDicBentoys StreetNo ratings yet
- CefuroximeDocument14 pagesCefuroximeBentoys StreetNo ratings yet
- Cervical SpondylosisDocument1 pageCervical SpondylosisBentoys StreetNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular DiseaseDocument26 pagesCerebrovascular DiseaseBentoys StreetNo ratings yet
- CandidiasisDocument13 pagesCandidiasisBentoys StreetNo ratings yet
- BooksDocument31 pagesBooksBentoys StreetNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Training at Bentoy's Place RestaurantDocument1 pageCertificate of Training at Bentoy's Place RestaurantBentoys StreetNo ratings yet
- Certificate of TrainingDocument1 pageCertificate of TrainingBentoys StreetNo ratings yet
- Brief History of MiagaoDocument11 pagesBrief History of MiagaoBentoys StreetNo ratings yet
- AkinetonDocument6 pagesAkinetonBentoys StreetNo ratings yet
- Certificate of TrainingDocument1 pageCertificate of TrainingBentoys StreetNo ratings yet
- Pathology Chapterwise Year Questions. 2nd Yr BdsDocument10 pagesPathology Chapterwise Year Questions. 2nd Yr Bds76 S.SHRAVAN KUMARNo ratings yet
- Essential Nutrition Actions PDFDocument144 pagesEssential Nutrition Actions PDFAmany MokhtarNo ratings yet
- Insulin Adjustment Workbook CompleteDocument53 pagesInsulin Adjustment Workbook CompletetskumarphdNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching PlanDocument3 pagesHealth Teaching PlanditamandaNo ratings yet
- Idea DisabilitiesDocument6 pagesIdea Disabilitiesapi-425284294No ratings yet
- CPG Management of Dengue Infection in Adults (Revised 2nd Edition)Document68 pagesCPG Management of Dengue Infection in Adults (Revised 2nd Edition)umiraihana1No ratings yet
- World Hunger Web QuestDocument5 pagesWorld Hunger Web Questapi-313403351No ratings yet
- Raji Tribe11Document12 pagesRaji Tribe11Keya PandeyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 MHPPDocument11 pagesAssignment 4 MHPPBabar AliNo ratings yet
- Human Behavior & Victimology FactorsDocument25 pagesHuman Behavior & Victimology FactorsAyessa Maycie Manuel OlgueraNo ratings yet
- CHN-Week 1Document4 pagesCHN-Week 1rich_dela_china100% (3)
- Bipolar SOAP NoteDocument8 pagesBipolar SOAP NoteRich AmbroseNo ratings yet
- Emergency Room Care Plan for HyperthermiaDocument7 pagesEmergency Room Care Plan for HyperthermiaNatasha Alaine E. CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Medication BasicsDocument16 pagesPsychiatric Medication BasicsCarmen HollidayNo ratings yet
- 2Document43 pages2myNo ratings yet
- Antifungal Drugs: Dr:Samah AlshygiDocument19 pagesAntifungal Drugs: Dr:Samah AlshygiKhan Khan100% (1)
- Investigation On Gastrointestinal Tract A ReviewDocument6 pagesInvestigation On Gastrointestinal Tract A ReviewHafidz Ma'rufNo ratings yet
- Students With Mental RetardationDocument3 pagesStudents With Mental RetardationNorain KasanNo ratings yet
- EnvMonitoringHygieneGuideforEHOs PDFDocument16 pagesEnvMonitoringHygieneGuideforEHOs PDFPramod SivanandanNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Emergencies and Their ManagementDocument65 pagesMetabolic Emergencies and Their ManagementSea WolfNo ratings yet
- Obesity: Sharmila A/P Rajendran E20141008930 Diploma Sains Dan MatematikDocument18 pagesObesity: Sharmila A/P Rajendran E20141008930 Diploma Sains Dan MatematikSharmila RajNo ratings yet
- Community Assessment of Irvington FINAL1Document50 pagesCommunity Assessment of Irvington FINAL1Marissa RodgersNo ratings yet
- Nursing Health History: Princess Jamela Camu Celline Isabelle ReyesDocument11 pagesNursing Health History: Princess Jamela Camu Celline Isabelle ReyesCelline Isabelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ramachandran Medical Application FormDocument3 pagesRamachandran Medical Application FormRuban JebaduraiNo ratings yet
- Birth Salt Bio ChemicDocument14 pagesBirth Salt Bio ChemicHomoeopath Aamir Saleem0% (1)
- Lista de Enfermedades Raras OrphanetDocument176 pagesLista de Enfermedades Raras OrphanetbrianNo ratings yet
- Paliative CareDocument402 pagesPaliative CarewardahNo ratings yet
- Risk Factors and Teaching for Laryngeal Cancer PatientDocument2 pagesRisk Factors and Teaching for Laryngeal Cancer Patientatarisgurl08100% (1)
- Journal of Anatomy - 2017 - Kirkpatrick - The Plantar Calcaneal Spur A Review of Anatomy Histology Etiology and KeyDocument9 pagesJournal of Anatomy - 2017 - Kirkpatrick - The Plantar Calcaneal Spur A Review of Anatomy Histology Etiology and KeyUlla NasNo ratings yet
- KWC Antimicrobial Therapy HandbookDocument149 pagesKWC Antimicrobial Therapy HandbookJoyceNo ratings yet