Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thermo Equations CH1-CH6
Uploaded by
Karuppiah ArunachalamCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Thermo Equations CH1-CH6
Uploaded by
Karuppiah ArunachalamCopyright:
Available Formats
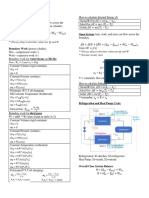
Basic Thermodynamic Formulas (Exam Equation Sheet)
Control Mass (no mass flow across system boundaries)
Conservation of mass: =
Conservation of energy (1st Law):
=
=
+ +
+
Entropy Balance (2nd Law): = +
22 12
2
+ (2 1 )
Control Volume (mass flow across system boundaries)
Conservation of mass:
Conservation of energy (1st Law):
Entropy Balance (2nd Law):
Heat Transfer and Work Relationships
= + +
2
2
+ +
+ +
Conduction: =
Convection: = ( )
4
)
Radiation: = (4
Heat transfer for an internally reversible process: . =
Boundary work: =
=
2
Polytropic process: = 1, = 1 1
1, =
2
1
Polytropic process for Ideal Gas:
1
2 2 1 1
(1)/
= 2
2
1
= 1
2
Reversible steady flow work: = +
12 22
2
+ (1 2 )
Ideal gas, no change in kinetic and potential energy
Isentropic: =
(1 2 )
1
Isothermal: = 1
Polytropic: =
(1 2 )
1
2
2
Thermal Efficiency of Cycles
Heat engine: =
Heat pump: = =
Isentropic (Adiabatic) Efficiencies:
Nozzle: =
Compressor: =
=1
Refrigeration: = =
Turbine: =
Specific Heat Relationships =
= =
2 /2
2 /2
,
, =
Incompressible Substance (solids and liquids)
Use saturation tables: @ ; @ ; @ + ( ) ; @
OR
= ()
Variable specific heat: = () +
Constant specific heat: = +
= 2
Ideal Gases = , = + , =
Use ideal gas tables =
OR
; = Molar mass (Table A-1)
= ()
= ()
Variable specific heats:
= 2 1 2
2
Isentropic process:
2
1
Constant specific heats:
Isentropic process:
1 2
=
2
1
2
1
= ,
= ,
= 1 1
2 1
2 = 1
2
1
1
2 1
(1)
1
2
2
1
=
2
1
2
Other (saturated liquid/vapor mixtures, superheated vapors, e.g. water and refrigerants) Use Tables A2 - A18
Useful Relations: = + ; = + ; = + ; = + ; = + ; =
You might also like
- Balloon and Travoltage AnswersDocument4 pagesBalloon and Travoltage Answersosama47% (17)
- Ansys Fluent 12.0 Theory Guide - 7.1Document3 pagesAnsys Fluent 12.0 Theory Guide - 7.1Tg DgNo ratings yet
- Physics Internal AssessmentDocument14 pagesPhysics Internal AssessmentRachitNo ratings yet
- Static Studies of Magneto-Electro-Elastic 3-D Beam Using ANSYS - FINALDocument8 pagesStatic Studies of Magneto-Electro-Elastic 3-D Beam Using ANSYS - FINALjssrikantamurthyNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document28 pagesWeek 4Mohamed nasserNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document17 pagesWeek 2Mohamed nasserNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics ExplainedDocument10 pagesChemical Engineering Thermodynamics ExplainedP P DNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Second Law of Thermo - Entropy Gibbs Free EnergyDocument24 pagesChapter 1. Second Law of Thermo - Entropy Gibbs Free Energyyuan comandanteNo ratings yet
- First LawDocument10 pagesFirst LawAhmed Al-ayatNo ratings yet
- FM IntroductionDocument14 pagesFM IntroductionJayden PangilinanNo ratings yet
- LectureNotes - Thermal - Ch2,3,4Document33 pagesLectureNotes - Thermal - Ch2,3,4Huy NguyenNo ratings yet
- CET I 3.PVT Relationship 2021 Part 2Document47 pagesCET I 3.PVT Relationship 2021 Part 2Dhruv AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 2021-물리화학-Chapter 2_1st law of thermodynamicsDocument30 pages2021-물리화학-Chapter 2_1st law of thermodynamics박희원No ratings yet
- Module 2.4 Enthalpy and 2ND Corollary of 1ST LawDocument6 pagesModule 2.4 Enthalpy and 2ND Corollary of 1ST LawsubyNo ratings yet
- APSC 252 Final Exam Formula SheetDocument3 pagesAPSC 252 Final Exam Formula SheetYosloNo ratings yet
- Tugas Termo DameDocument13 pagesTugas Termo DamedesisitompulNo ratings yet
- Full Notes For Air Conditioning and Ventilation PDFDocument97 pagesFull Notes For Air Conditioning and Ventilation PDFBLa ProductionNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document14 pagesLec 2أمجد هاتف منفي جفالNo ratings yet
- 1st Puc Physics Chapter12-Thermodynamics Notes by U N SwamyDocument10 pages1st Puc Physics Chapter12-Thermodynamics Notes by U N Swamyashwinikumari bNo ratings yet
- The Entropy Change of Pure SubstancesDocument5 pagesThe Entropy Change of Pure SubstancesAbd El-Razek AhmedNo ratings yet
- The Entropy Change of Pure SubstancesDocument5 pagesThe Entropy Change of Pure SubstancesAbd El-Razek AhmedNo ratings yet
- Group 7 FixDocument30 pagesGroup 7 Fixyuni fitriaNo ratings yet
- Cheat - Sheet - Exam 1Document2 pagesCheat - Sheet - Exam 1LoganNo ratings yet
- Chemical ThermodynamicsDocument33 pagesChemical ThermodynamicsPsyrah GuintoNo ratings yet
- TFS I CH5 Lecture NotesDocument16 pagesTFS I CH5 Lecture Notes高誠蔚No ratings yet
- Problem 2: First and Second Law of Thermodynamics Thermodynamics Coursechemical Engineering DepartmentDocument17 pagesProblem 2: First and Second Law of Thermodynamics Thermodynamics Coursechemical Engineering DepartmentTita Ari UtamiNo ratings yet
- Closed System: Heat and Work Can Flow Across The: Always Plug in Absolute Values For Q and WDocument2 pagesClosed System: Heat and Work Can Flow Across The: Always Plug in Absolute Values For Q and WShyam PolacondaNo ratings yet
- 1ST Law of ThermodynamicsDocument19 pages1ST Law of ThermodynamicsZamanoden D. UndaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Project ReportDocument17 pagesThermodynamics Project ReportAbubakar abdullahiNo ratings yet
- Ornek SorularDocument27 pagesOrnek SorularFatih ErogluNo ratings yet
- Q4 WEEK 1 Gen Chem 2 Worksheet 10 THERMODYNAMICSDocument11 pagesQ4 WEEK 1 Gen Chem 2 Worksheet 10 THERMODYNAMICSMarielle TibayNo ratings yet
- jee-mains-chemistry-formulas-list-pdf-1008973aDocument4 pagesjee-mains-chemistry-formulas-list-pdf-1008973aaugustNo ratings yet
- Thermoquations SummarryDocument2 pagesThermoquations Summarryhthaier4062No ratings yet
- Damping: Single Degree of FreedomDocument28 pagesDamping: Single Degree of FreedomAbdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- (T, V Variables) (P, V Variables)Document3 pages(T, V Variables) (P, V Variables)123 456No ratings yet
- TDY1 - Les 3 EngDocument28 pagesTDY1 - Les 3 EngBrandon GesterkampNo ratings yet
- Lec3 - Final - Revised Stat MechDocument16 pagesLec3 - Final - Revised Stat MechnokosamNo ratings yet
- Complete Class Note CH14 Ec9e0688f1aa58804c66cac62c214e47Document37 pagesComplete Class Note CH14 Ec9e0688f1aa58804c66cac62c214e47ChrisNo ratings yet
- Chaters of ThermodynamicsDocument106 pagesChaters of ThermodynamicsAzooNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometric Numbers Continue...Document11 pagesStoichiometric Numbers Continue...Hambeleleleni NgotipeniNo ratings yet
- Physics 2Document16 pagesPhysics 2Dane Mica Rint QuinonesNo ratings yet
- Advanced Molecular DynamicsDocument11 pagesAdvanced Molecular Dynamicsquarksteam2023No ratings yet
- Reversible and Irreversible ProcesesDocument12 pagesReversible and Irreversible ProcesesFarouk BassaNo ratings yet
- Notes03 Forreview PDFDocument46 pagesNotes03 Forreview PDFLeslie LeeNo ratings yet
- MP 2 Finite Element MethodDocument12 pagesMP 2 Finite Element MethodDon Nelson CaserNo ratings yet
- Lecture 29: 1st Law of Thermodynamics: Thermodynamic WorkDocument15 pagesLecture 29: 1st Law of Thermodynamics: Thermodynamic WorkJUVY ANN PATOSANo ratings yet
- Chemistry Equation SheetDocument2 pagesChemistry Equation SheetpetergotgotaoNo ratings yet
- Equations & ConstantsDocument5 pagesEquations & ConstantsJoserineNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Process BalancesDocument17 pagesAir Conditioning Process Balancesİkigül Aşçıevladı KirlitaşNo ratings yet
- 05+LMTD+&+effectivness+method SDocument67 pages05+LMTD+&+effectivness+method SAdolfNo ratings yet
- 2 Physico-Chemical Principles of Steelmaking Processes: Heterogeneous Vs Homogeneous SystemsDocument11 pages2 Physico-Chemical Principles of Steelmaking Processes: Heterogeneous Vs Homogeneous SystemsMir RafsanNo ratings yet
- CBE3508 Sp21 FinalDocument6 pagesCBE3508 Sp21 Finalsasuke uchihaNo ratings yet
- 4 Thermodyn WorkDocument6 pages4 Thermodyn Workosolobrandon2No ratings yet
- Module4 - (2) Conservation of Energy (Work, Work Flow & Heat)Document13 pagesModule4 - (2) Conservation of Energy (Work, Work Flow & Heat)John Dalton ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02Document21 pagesLecture 02ᄏᄏᄏNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer BookletDocument10 pagesHeat Transfer Bookletdhilee100% (1)
- F 11 Place 2Document8 pagesF 11 Place 2paimoNo ratings yet
- “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence: Cipher 4”: “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence, #4From Everand“Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence: Cipher 4”: “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence, #4No ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Models for Chemical Engineering: Design, Develop, Analyse and OptimizeFrom EverandThermodynamic Models for Chemical Engineering: Design, Develop, Analyse and OptimizeNo ratings yet
- TurboDocument1 pageTurboKaruppiah ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ToolsDocument1 pageIntroduction To ToolsKaruppiah ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Self RelianceDocument3 pagesSelf RelianceKaruppiah ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Turbo JetDocument1 pageTurbo JetKaruppiah ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To GearsDocument1 pageIntroduction To GearsKaruppiah ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- CNC RouterDocument1 pageCNC RouterKaruppiah ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- PumpDocument1 pagePumpKaruppiah ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Turbo FanDocument1 pageTurbo FanKaruppiah ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- TurbineDocument1 pageTurbineKaruppiah ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Numeric ControlDocument1 pageNumeric ControlKaruppiah ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Electric MotorDocument1 pageElectric MotorKaruppiah ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing TopicsDocument10 pagesManufacturing TopicsKaruppiah ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Electric GeneratorDocument1 pageElectric GeneratorKaruppiah ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Rotational Energy Moment of Inertia Rotational Speed TorqueDocument1 pageRotational Energy Moment of Inertia Rotational Speed TorqueNisha SharmaNo ratings yet
- JigsDocument1 pageJigsKaruppiah ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- FixturesDocument1 pageFixturesKaruppiah ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- List of Countries in The WorldDocument5 pagesList of Countries in The WorldDan MihaitaNo ratings yet
- What is a Machine? Tools, Energy, and Moving PartsDocument1 pageWhat is a Machine? Tools, Energy, and Moving PartsKaruppiah ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Group 2 A Syllabus: PhysicsDocument7 pagesGroup 2 A Syllabus: PhysicsKaruppiah ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Basic Sentence Patterns Writing CenterDocument1 pageBasic Sentence Patterns Writing CenterFazril AminNo ratings yet
- C++ Programming Style GuidelinesDocument28 pagesC++ Programming Style GuidelinesFenil DesaiNo ratings yet
- Top 100 Engineering Colleges in India 2014Document3 pagesTop 100 Engineering Colleges in India 2014Karuppiah ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Latest Developments on Indian State Reorganisation and Autonomous CouncilsDocument28 pagesLatest Developments on Indian State Reorganisation and Autonomous Councilsmadhub_17No ratings yet
- Transfer MoldingDocument1 pageTransfer MoldingKaruppiah ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Me TrologyDocument1 pageMe TrologyKaruppiah ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Thermo FormingDocument1 pageThermo FormingKaruppiah ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Material Requirements PlanningDocument1 pageMaterial Requirements PlanningKaruppiah ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing: Manufacturing Is The Production of Goods For Use or Sale Using LaborDocument1 pageManufacturing: Manufacturing Is The Production of Goods For Use or Sale Using LaborKaruppiah ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Just in TimeDocument1 pageJust in TimeKaruppiah ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument1 pageStrength of MaterialsKaruppiah ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- G.D.GOENKA PUBLIC SCHOOL CLASS 10 CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 2 ACIDS BASES SALTS ASSIGNMENTDocument3 pagesG.D.GOENKA PUBLIC SCHOOL CLASS 10 CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 2 ACIDS BASES SALTS ASSIGNMENTvikas aggarwal100% (1)
- Tos Mathematics 8 q2Document1 pageTos Mathematics 8 q2Kenny Ann Grace BatiancilaNo ratings yet
- Direct Shear Test ResultsDocument19 pagesDirect Shear Test ResultsAh Gus100% (9)
- Refraction Through Spherical Surfaces and LensesDocument2 pagesRefraction Through Spherical Surfaces and LensesOrbit MBBS PreparationNo ratings yet
- HW1Document2 pagesHW1Jimmy LauNo ratings yet
- Love My LifeDocument5 pagesLove My LifeLinda Veronica0% (1)
- Tuning Equation of State ModelsDocument34 pagesTuning Equation of State Modelswelltest vspNo ratings yet
- Experiment #2: Continuous-Time Signal Representation I. ObjectivesDocument14 pagesExperiment #2: Continuous-Time Signal Representation I. ObjectivesMarvin AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Lucia 1995 Rock-FabricPetrophysical Classification of Carbonate Pore SpaceDocument26 pagesLucia 1995 Rock-FabricPetrophysical Classification of Carbonate Pore SpaceMarcos Antonio Romero Arteaga100% (1)
- Plate Bending Element Formulation and Stiffness Matrix DevelopmentDocument6 pagesPlate Bending Element Formulation and Stiffness Matrix DevelopmentSeyhan ÖzenNo ratings yet
- Thermo Scientific Pierce Protein Assay Technical HandbookDocument44 pagesThermo Scientific Pierce Protein Assay Technical HandbookAnwar_Madkhali_9172No ratings yet
- 50 Years of The Turbidite Paradigm (Shanmugam, 2000)Document58 pages50 Years of The Turbidite Paradigm (Shanmugam, 2000)hilman_satriaNo ratings yet
- The M A R S H Cone As A Viscometer: Theoretical Analysis and Practical LimitsDocument6 pagesThe M A R S H Cone As A Viscometer: Theoretical Analysis and Practical LimitsAye LwinNo ratings yet
- Latent Heat of Fusion VaporizationDocument18 pagesLatent Heat of Fusion Vaporizationapi-449002661No ratings yet
- Carrfoster 2Document5 pagesCarrfoster 2SauravNo ratings yet
- ACET208 Theodolite PresentationDocument6 pagesACET208 Theodolite Presentationsilverm_4No ratings yet
- Expt 01Document10 pagesExpt 01Kathleen De Vera BarrilNo ratings yet
- Especificacion SHY73MC4 UDocument3 pagesEspecificacion SHY73MC4 UYgor Salgado100% (3)
- Cement Chapter 4Document11 pagesCement Chapter 4shani5573100% (2)
- Molecular Partition Function ExplainedDocument18 pagesMolecular Partition Function ExplainedAnimasahun Olamide HammedNo ratings yet
- How retinal adaptation maintains visual perception despite illumination changesDocument1 pageHow retinal adaptation maintains visual perception despite illumination changesAkicaNo ratings yet
- Math II Tutorial 1Document2 pagesMath II Tutorial 1devang_siNo ratings yet
- Fortran (For NACA)Document7 pagesFortran (For NACA)hdslmnNo ratings yet
- Clarke and Park TransfomationDocument9 pagesClarke and Park TransfomationGREATJUSTGREATNo ratings yet
- P Ractical Approaches To Fast Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Muy BuenoDocument28 pagesP Ractical Approaches To Fast Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Muy BuenoJavier Joao Lloyd IglesiasNo ratings yet