Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Air
Uploaded by
Santhosh KumarCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Air
Uploaded by
Santhosh KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
AIR COMPRESSORS
SINGLE ACTING COMPRESSOR
In single acting reciprocating compressor, the suction, compression and delivery of the air take place on one side of the piston only. Such type of compressors has one delivery stroke per revolution of the crank shaft
DOUBLE ACTING COMPRESSOR
In double acting reciprocating compressor, the suction, compression and delivery of the air take place on both sides of the piston only. Such type of compressors has two delivery stroke per revolution of the crank shaft
FREE AIR DELIVERED
The free air delivered is the actual volume delivered at stated pressure, reduced to standard pressure and temperature expressed in cubic meter per minute. This term is used to specify the capacity of the compressor for standardization.
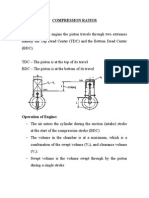
COMPRESSION OR PRESSURE RATIO
The ratio of absolute discharge pressure to the absolute inlet pressure.
COMPRESSION WITHOUT CLEARANCE
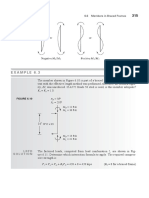
Fig 1. Theoretical pv diagram for single acting compressor without clearance
COMPRESSION WITH CLEARANCE
Vc = Clearance volume Vs = stroke volume Va = actual air intake
CLEARANCE VOLUME
1. Clearance volume is always given in the compressor to provide space for valves, so that the piston does not strike the cylinder at the end of the delivery stroke. 2. It is expressed as a percentage of stroke volume CLEARANCE RATIO = 3. The clearance volume reduces the free air delivered(Va) because the high pressure air left in the clearance volume expands and suction for the next cycle starts only when the air pressure falls below atmospheric pressure. 4. Clearance volume has no effect on the work of compression per kg of air, but decreases the free air delivered.
VOLUMETRIC EFFICIENCY =
The actual power input to the compressor is greater than the indicated power due to work necessary to overcome losses due to friction. SHAFT POWER = INDICATED POWER + FRICTION POWER MECHANICAL EFFICIENCY =
COMPARING VARIOUS COMPRESSION PROCESS
The work done is minimum in isothermal compression process, because no energy is wasted in heating the air (increasing the internal energy of air)
ISOTHERMAL EFFICIENCY
ISENTROPIC EFFICIENCY =
METHODS ADOPTED FOR IMPROVING THE ISOTHERMAL EFFICIENCY OF COMPRESSOR 1. SPRAY INJECTION 5. Water is injected into the compressor cylinder towards the end of compression stroke to cool the air. 2. WATER JACKETING Water circulated around the cylinder through the water jacket cools the air. 3. INTER-COOLING
Used for multistage compression. Air compressed in the first stage is cooled in a heat exchanger to its original temperature before it is taken to the second stage. 4. EXTERNAL FINS Fins are provided on the external surface of the compressor, used for small capacity compressors.
MULTISTAGE COMPRESSION
The maximum pressure attainable by the compressor in single stage is limited by the clearance volume; hence for very high pressures multistage compression is required. Inter-cooling is done to reduce the temperature of the air(approximate the isothermal process); the specific volume of air reduces thus decreasing the steady flow work. And the compression work is reduced.
You might also like
- Unit 6 Air CompressorDocument8 pagesUnit 6 Air Compressorsample useNo ratings yet
- CompressorsDocument45 pagesCompressorssubscruNo ratings yet
- Advanced Thermodynamics Air CompressorsDocument6 pagesAdvanced Thermodynamics Air CompressorsNikhil PatidarNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics Unit Iv Compressors, Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument28 pagesApplied Thermodynamics Unit Iv Compressors, Refrigeration and Air ConditioningMuthuvel MNo ratings yet
- EC-II 22-23 (Prac1)Document53 pagesEC-II 22-23 (Prac1)Archana MaskeNo ratings yet
- AT PPT Air Compressors 04Document47 pagesAT PPT Air Compressors 04Antony YtNo ratings yet
- Air CompressorDocument23 pagesAir CompressorsaadNo ratings yet
- TE-2 Unit - 4 &5 NotesDocument110 pagesTE-2 Unit - 4 &5 NotesKrishna VamsiNo ratings yet
- Exp 4 Centrifugal CompressorDocument11 pagesExp 4 Centrifugal CompressorFaris HamirNo ratings yet
- Applied ThermodynamicsDocument30 pagesApplied ThermodynamicsRutvik100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - FullDocument60 pagesChapter 1 - FullMohamad Zulamirulfaha100% (1)
- Mam II, Answers To Question Bank, 20-4-11Document57 pagesMam II, Answers To Question Bank, 20-4-11Giri VenkatesanNo ratings yet
- Thermo Unit IVDocument9 pagesThermo Unit IVNatesan MahendranNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor SeminarDocument15 pagesAir Compressor SeminarAshish Deotale75% (4)
- Compressor Fundamentals ExplainedDocument4 pagesCompressor Fundamentals Explainedvikash kumarNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating Air Compressor GuideDocument15 pagesReciprocating Air Compressor Guide2AG19ME411 JagadeeshNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor - Notes and QuestionnarieDocument89 pagesAir Compressor - Notes and QuestionnariedevNo ratings yet
- Isothermal Work and Polytropic WorkdoneDocument53 pagesIsothermal Work and Polytropic WorkdoneGeorgeNo ratings yet
- Study of Reciprocating Air CompressorDocument4 pagesStudy of Reciprocating Air Compressor01parth100% (5)
- Air CompDocument15 pagesAir ComppaviliondmNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcomes:: Some Other Ways of Classifying CompressorsDocument18 pagesLearning Outcomes:: Some Other Ways of Classifying CompressorsRyan CalicaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2:components of Pneumatic Component Unit 1:the Air Service Unit ComponentDocument5 pagesChapter 2:components of Pneumatic Component Unit 1:the Air Service Unit ComponentEdrian Rey Tablante BrizoNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document9 pagesLab 2Uet brilliant SttudentNo ratings yet
- CompressorDocument35 pagesCompressordadrahim0% (1)
- Learn Key Concepts of Air Compressors Including Types, Parts, and PV DiagramsDocument13 pagesLearn Key Concepts of Air Compressors Including Types, Parts, and PV Diagramsjerick garlejoNo ratings yet
- COMPRESSION RATIO GUIDEDocument14 pagesCOMPRESSION RATIO GUIDEDirkMyburghNo ratings yet
- Air and Gas Compressors 2 PDH PDFDocument15 pagesAir and Gas Compressors 2 PDH PDFJohn barry CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Test of An Air Compressor ME LAB 2Document27 pagesTest of An Air Compressor ME LAB 2nibin venugopal0% (1)
- Exp 4 Centrifugal CompressorDocument11 pagesExp 4 Centrifugal CompressorMohamedZakariaAbdullahNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor PresentationDocument34 pagesAir Compressor PresentationBhupender Ramchandani100% (1)
- Assignment 4 Reciprocating Air CompressorsDocument8 pagesAssignment 4 Reciprocating Air CompressorsAkshay A KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document5 pagesChapter 7esraaoraby24No ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Centrifugal CompressorsDocument87 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Centrifugal Compressorswarakorn6jame100% (1)
- Everything you need to know about air compressorsDocument31 pagesEverything you need to know about air compressorsNikhil SaraswathNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Centrifugal Compressors and FansDocument54 pagesChapter 3 Centrifugal Compressors and FansMichael Mesfin100% (1)
- Air Compressor TermsDocument9 pagesAir Compressor TermsUniversal CollabNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument33 pagesUntitledBuriro HayatNo ratings yet
- Air CompressorDocument31 pagesAir CompressorEr Bali Pandhare33% (3)
- PressorsDocument23 pagesPressorsAINAMANI AMOSNo ratings yet
- Materials Used For Construction: 1. Reciprocating CompressorDocument6 pagesMaterials Used For Construction: 1. Reciprocating CompressorEdemNo ratings yet
- Unit IV - Air Compressors: Classification and Working of Reciprocating CompressorsDocument10 pagesUnit IV - Air Compressors: Classification and Working of Reciprocating CompressorsKONDERU RAJKUMARNo ratings yet
- Boiler 2Document16 pagesBoiler 2Aatharva ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine System Theory PDFDocument30 pagesGas Turbine System Theory PDFAbdul GafurNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal CompressorDocument18 pagesCentrifugal CompressornisasoberiNo ratings yet
- Air Compresser: Motion of Piston or Rotary Motion of BladesDocument28 pagesAir Compresser: Motion of Piston or Rotary Motion of BladesYogesh ShindeNo ratings yet
- Single Cylinder Air Compressor WorkingDocument2 pagesSingle Cylinder Air Compressor WorkingBarbie JooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document17 pagesChapter 2تاج نيسهاNo ratings yet
- Gte Components LastDocument41 pagesGte Components LastTw Carlo BeltranNo ratings yet
- Pawer Enggineering and Reff. Air CompressorDocument13 pagesPawer Enggineering and Reff. Air Compressorsaurabh LagheNo ratings yet
- Development of High-Efficiency Centrifugal Compressor For Turbo ChillerDocument8 pagesDevelopment of High-Efficiency Centrifugal Compressor For Turbo ChillerarbnormorinaNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor & Refrigeration EfficienciesDocument31 pagesAir Compressor & Refrigeration EfficienciesAbubakkar SiddiqNo ratings yet
- Chapter No 3 Air CompressorsDocument59 pagesChapter No 3 Air Compressorsahsan8arshad-4No ratings yet
- Pneumatic CompressionDocument23 pagesPneumatic Compressionketanbsurwase2002No ratings yet
- Gas CompressorDocument10 pagesGas Compressoramir100% (2)
- Unit-5) Air CompressorsDocument40 pagesUnit-5) Air CompressorsChinmay LearningNo ratings yet
- 0.5 KG 1.0 KG 1.3 KG 2.2 KG 3.2 KG.: Compressors Questions and AnswersDocument32 pages0.5 KG 1.0 KG 1.3 KG 2.2 KG 3.2 KG.: Compressors Questions and AnswersMoloyBanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Air Compressors: Elements of Mechincal Engineering ElectricalDocument24 pagesAir Compressors: Elements of Mechincal Engineering ElectricalHarsun ParanthamanNo ratings yet
- Grills and RegistersDocument11 pagesGrills and RegistersSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- ChatGPT Prompts Article PDFDocument17 pagesChatGPT Prompts Article PDFSanthosh Kumar100% (2)
- LLP Form Addendum To FillipDocument4 pagesLLP Form Addendum To FillipSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- IIM Mumbai Campus Work Volume IDocument77 pagesIIM Mumbai Campus Work Volume ISanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- A8ZUYZ9tReL58evU5E2S EXCEL Stock Analysis Spreadsheet 10YR 2021 Vers 3.1Document13 pagesA8ZUYZ9tReL58evU5E2S EXCEL Stock Analysis Spreadsheet 10YR 2021 Vers 3.1Santhosh KumarNo ratings yet
- CBD Business Banking GeneraltermsDocument43 pagesCBD Business Banking GeneraltermsSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Date Description Air & Trans. Lodging Fuel / Mlg. Phone Meals & Tips Other Total Entertainmen TDocument2 pagesDate Description Air & Trans. Lodging Fuel / Mlg. Phone Meals & Tips Other Total Entertainmen TRobinNo ratings yet
- Form-5 Certificate by Architect / Licensed Surveyor (Certificate For The Purpose of Completion of Layout/ Sub-Division Project)Document1 pageForm-5 Certificate by Architect / Licensed Surveyor (Certificate For The Purpose of Completion of Layout/ Sub-Division Project)Santhosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Someka Templates Info PDFDocument1 pageSomeka Templates Info PDFnkemoviaNo ratings yet
- Layer Chicken Business Planning Calculator - Final VersionDocument51 pagesLayer Chicken Business Planning Calculator - Final VersionSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- CBD Business Banking GeneraltermsDocument43 pagesCBD Business Banking GeneraltermsSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- VillagesDocument325 pagesVillagessuriwaits50% (2)
- Someka Templates Info PDFDocument1 pageSomeka Templates Info PDFnkemoviaNo ratings yet
- Creating A Database: Base HandbookDocument28 pagesCreating A Database: Base HandbookSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Liye - Info Fundamental Accounting Principles 20th Edition PDF Book PRDocument2 pagesLiye - Info Fundamental Accounting Principles 20th Edition PDF Book PRSanthosh Kumar50% (2)
- Fundamental Accounting Principles Vol 1 Chapters 1 12 With Working Papers 20th Edition by John Wild Ken Shaw Barbara ChiappettaDocument8 pagesFundamental Accounting Principles Vol 1 Chapters 1 12 With Working Papers 20th Edition by John Wild Ken Shaw Barbara ChiappettaSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Algebra PDFDocument189 pagesAlgebra PDFAlmir AdrovicNo ratings yet
- Business Financial Plan SummaryDocument7 pagesBusiness Financial Plan SummarySanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Database Maintenance: Base HandbookDocument8 pagesDatabase Maintenance: Base HandbookSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Preface: Base HandbookDocument8 pagesPreface: Base HandbookSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- BH5001 IntroductionToBaseDocument40 pagesBH5001 IntroductionToBaseSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Checklist Finding Employment PCC PDFDocument1 pageChecklist Finding Employment PCC PDFSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Town & Country Planning Act 1971Document87 pagesTown & Country Planning Act 1971kmbkrisNo ratings yet
- BG4201 IntroducingBaseDocument45 pagesBG4201 IntroducingBaseSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Linking To Databases: Base HandbookDocument31 pagesLinking To Databases: Base HandbookSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- BH5003 TablesDocument45 pagesBH5003 TablesSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- BH5004 FormsDocument78 pagesBH5004 FormsSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Conda Cheat Sheet: Bit - Ly/trycondaDocument2 pagesConda Cheat Sheet: Bit - Ly/trycondamaxellligue5487No ratings yet
- Open Space Reservation Madras Musings - We Care For Madras That Is ChennaiDocument6 pagesOpen Space Reservation Madras Musings - We Care For Madras That Is ChennaiSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Tamil Nadu Panchayats Building RulesDocument17 pagesTamil Nadu Panchayats Building RulesYuva RajNo ratings yet
- M41-F.o Supply UnitDocument351 pagesM41-F.o Supply UnitPavel PaskarNo ratings yet
- 8 - PressurevalvesDocument68 pages8 - PressurevalvesMohamed ZahranNo ratings yet
- CST Studio Suite - Thermal and Mechanical SimulationDocument69 pagesCST Studio Suite - Thermal and Mechanical SimulationZainNo ratings yet
- Esfueros Insitu Colombia SPE 81074 FDocument13 pagesEsfueros Insitu Colombia SPE 81074 Fsantiago ruedaNo ratings yet
- UPVC Technical Data SheetDocument1 pageUPVC Technical Data SheetRND KencanaNo ratings yet
- Retaining Wall Design For Us Wing WallDocument13 pagesRetaining Wall Design For Us Wing WallBalaji Rao Ch100% (1)
- Quiz 3Document2 pagesQuiz 3Vishruta KathuriaNo ratings yet
- MT Ii - HW 1Document1 pageMT Ii - HW 1Omkar RoyNo ratings yet
- PIC 1 /SIC-1 N/A N/A N/A N2 Secondary Barrier: Exhaust Filter Safety Valve Exhaust Filter Safety Valve ClassificationDocument2 pagesPIC 1 /SIC-1 N/A N/A N/A N2 Secondary Barrier: Exhaust Filter Safety Valve Exhaust Filter Safety Valve ClassificationRanchojiNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics and Hydraulic Machinery by DR Nekkanti KumaraswamyDocument39 pagesHydraulics and Hydraulic Machinery by DR Nekkanti KumaraswamyAnonymous zwnFXURJNo ratings yet
- Modelling of Laser Welding of Aluminium Using COMSOL MultiphysicsDocument73 pagesModelling of Laser Welding of Aluminium Using COMSOL MultiphysicsAli NasserNo ratings yet
- STEADY AND UNSTEADY HEAT CONDUCTION PROBLEMSDocument4 pagesSTEADY AND UNSTEADY HEAT CONDUCTION PROBLEMSErwin CabangalNo ratings yet
- IRC 37-2012 - BTechDocument19 pagesIRC 37-2012 - BTechVibhanshu MishraNo ratings yet
- AST 441-Chapter 4-Rev 1Document80 pagesAST 441-Chapter 4-Rev 1samilkolsuz63No ratings yet
- Pharma Engineering: (How To) Calculate NPSH - Net Positive Suction HeadDocument8 pagesPharma Engineering: (How To) Calculate NPSH - Net Positive Suction HeadpratikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Microscopic Displacement Eficiency - Part IIDocument40 pagesChapter 3 - Microscopic Displacement Eficiency - Part IIMohamed ModerNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 1: Precious Arlene Villaroza-MelendrezDocument35 pagesThermodynamics 1: Precious Arlene Villaroza-MelendrezJhonny English100% (1)
- John Harding 1983Document17 pagesJohn Harding 1983Huifang LiuNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Steam TrapsDocument88 pagesPresentation On Steam TrapsSalman ShafiqueNo ratings yet
- WRC107 297Document4 pagesWRC107 297MasoodMiyanNo ratings yet
- Disain Kolom-Segui PDFDocument4 pagesDisain Kolom-Segui PDFulalaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic CalculationDocument8 pagesHydraulic CalculationMichael NewellNo ratings yet
- A Drop S Journey AnswersDocument2 pagesA Drop S Journey AnswersMuhammad Muzammil58% (48)
- SP 721 V 201Document36 pagesSP 721 V 201Mandar KardekarNo ratings yet
- Virgin Ptfe DatasheetDocument1 pageVirgin Ptfe DatasheetFelipe Zúñiga ParedesNo ratings yet
- EN1993 BenchmarksDocument212 pagesEN1993 BenchmarksDomostatikosNo ratings yet
- Peek Short-Term Mechanical PropertiesDocument15 pagesPeek Short-Term Mechanical PropertiesSh.nasirpurNo ratings yet
- 1996 Bookmatter ReinforcedConcreteDesignToEuro PDFDocument20 pages1996 Bookmatter ReinforcedConcreteDesignToEuro PDFJy YeshiberNo ratings yet
- Punching Shear and One Way Shear Check.Document2 pagesPunching Shear and One Way Shear Check.ElancheliyanNo ratings yet
- Mid Question FluidDocument1 pageMid Question FluidSubrata DebnathNo ratings yet