Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Managing For Results Day 2
Uploaded by
manik_elaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Managing For Results Day 2
Uploaded by
manik_elaCopyright:
Available Formats
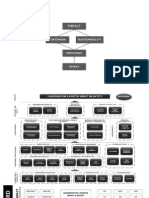
MANAGING FOR RESULTS
Results
Productivity
PERSONAL PRODUCTIVITY FROM MANAGEMENT THEORIES
Maslows Hierarchy Of Needs
McGregors Theory X vs. Theory Y
You are all lazy!
My employees enjoy their work
Ouchis Theory Z
Group Work
Looking at the three (3) Management Theories,
how can you use the concepts to increase personal productivity?
PERSONAL PRODUCTIVITY USING TIME MANAGEMENT
TIME MANAGEMENT PROFILE
FIRST THINGS FIRST
What one thing could you do (you arent doing
now) that if you did on a regular basis, would make a tremendous difference in your personal life?
What one thing in your professional life would
yield the similar results?
Generations of Time Management
NOTES and CHECKLISTS CALENDARS and APPOINTMENT BOOKS PRIORITIZATION
TIME MANAGEMENT MATRIX
URGENT NOT URGENT
I
Crises Pressing problems Deadline-driven projects Preparation Planning/goal-setting Relationship-building
II
IMPORTANT NOT IMPORTANT
III
Interruptions Some phone calls Some meetings Escape Activities Diversions Time wasters
IV
PARETO PRINCIPLE
Number of Tasks versus Importance of Tasks Focus on Activities, Not Accomplishments Motivate Yourself
THE ART OF SCHEDULING
SCHEDULE BACKWARDS
THE ART OF SCHEDULING
BE HONEST ABOUT DEADLINES
THE ART OF SCHEDULING
THINK PROCESS IMPROVEMENT
PRODUCTIVITY THROUGH PLANNING
The Management Functions
Benefits of planning
Improves focus and flexibility. Improves action orientation. Improves coordination. Improves control. Improves time management.
Steps in the planning process
Define your objectives. Determine where you stand vis--vis objectives. Develop premises regarding future conditions. Analyze and choose among action alternatives. Implement the plan and evaluate results.
A sample means-ends chain for total quality management.
Types of plans
Short-range and long-range plans
Short-range plans = 1 year or less Intermediate-range plans = 1 to 2 years Long-range plans = 3 or more years
Types of plans
Strategic and operational plans
Strategic plans set broad, comprehensive, and longer-term action directions for the entire organization.
Operational plans define what needs to be done in specific
areas to implement strategic plans.
Production plans Financial plans Facilities plans Marketing plans Human resource plans
Types of plans
Budgets and project schedules
Single-use plans
Only used once to meet the needs and objectives of a well-defined situation in a timely manner.
Budgets
Single-use plans that commit resources to activities, projects, or programs. Fixed, flexible, and zero-based budgets.
Projects
One-time activities that have clear beginning and end points. Project management and project schedules.
Planning tools and techniques
Forecasting
Making assumptions about what will happen in the future.
Qualitative forecasting uses expert opinions. Quantitative forecasting uses mathematical and statistical analysis.
Planning tools and techniques
Contingency planning
Identifying alternative courses of action that can be implemented to meet the needs of changing circumstances.
Contingency plans anticipate changing conditions. Contingency plans contain trigger points.
Planning tools and techniques
Scenario planning
A long-term version of contingency planning. Identifying alternative future scenarios. Plans made for each future scenario. Increases organizations flexibility and preparation for future shocks.
Useful planning tools and techniques
Benchmarking
Use of external comparisons to better evaluate current performance and identify possible actions for the future.
Adopting best practices of other organizations that achieve superior performance.
Useful planning tools and techniques
Use of staff planners
Coordinating the planning function for the total organization or one of its major components.
Possible communication gaps between staff planners and line management.
Useful planning tools and techniques
Participation and involvement
Participatory planning requires that the planning process include people who will be affected by the plans and/or
will help implement them.
Benefits of participation and involvement:
Promotes creativity in planning. Increases available information. Fosters understanding, acceptance, and commitment to the final plan.
How participation and involvement help build commitments to plans.
Management by Objectives (MBO)
A structured process of regular communication. Supervisor/team leader and workers jointly set
performance objectives.
Supervisor/team leader and workers jointly review
results.
Management by objectives as an integrated planning and control framework.
MBO involves a formal agreement specifying
Workers performance objectives for a specific
time period.
Plans through which performance objectives will
be accomplished.
Standards for measuring accomplishment of
performance objectives .
Procedures for reviewing performance results.
The MBO process
Supervisor and workers jointly set objectives,
establish standards, and choose actions.
Workers act individually to perform tasks;
supervisors act individually to provide necessary support.
Supervisor and workers jointly review results,
discuss implications, and renew the MBO cycle.
Types of MBO performance objectives
Improvement Personal development Maintenance
Criteria for effective performance objectives
SMART not GLOBE
Advantages of MBO
Focuses workers on most important tasks and
objectives.
Focuses supervisors efforts on important areas of
support.
Contributes to relationship building. Gives workers a structured opportunity to
participate in decision making.
GROUP WORK
QUESTIONS
How do planning and controlling seem to be linked
at Wal-Mart?
As planning consultants, what alternative future
scenarios would you identify for Wal-Marts executives to consider as they plan for the future in todays dynamic times?
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Subject Predicate CrosswordDocument1 pageSubject Predicate Crosswordmanik_elaNo ratings yet
- 6 Steps To Creating A Talent Pool Based Successsion Planning Process PDFDocument1 page6 Steps To Creating A Talent Pool Based Successsion Planning Process PDFmanik_elaNo ratings yet
- Com Skil Pearl 2012Document87 pagesCom Skil Pearl 2012manik_elaNo ratings yet
- Situational Leadership Self AssessmentDocument4 pagesSituational Leadership Self AssessmentAftab Majeed83% (12)
- TP Leadership QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesTP Leadership Questionnairemanik_elaNo ratings yet
- Ongoing Feedback ToolkitDocument4 pagesOngoing Feedback Toolkitmanik_elaNo ratings yet
- Leader Vs Manager CompetencyDocument1 pageLeader Vs Manager Competencymanik_elaNo ratings yet
- MBT DescriptionsDocument16 pagesMBT Descriptionsmanik_elaNo ratings yet
- Presentation Tips by Presentation ZenDocument6 pagesPresentation Tips by Presentation ZenmuhjaerNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Timing of Merger ActivityDocument28 pagesThe Timing of Merger ActivityZackyNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial Marketing Performance of Cottage Industries in Kendal RegencyDocument4 pagesEntrepreneurial Marketing Performance of Cottage Industries in Kendal RegencyOzal KhanNo ratings yet
- Dissertation On Hindustan Unilever LTDDocument56 pagesDissertation On Hindustan Unilever LTDNishant PrabhakarNo ratings yet
- PNJ Vad 2024Document34 pagesPNJ Vad 2024EricNo ratings yet
- Listing PresentationDocument50 pagesListing PresentationMelissaWegenerNo ratings yet
- Small Business: Distribution and LocationDocument40 pagesSmall Business: Distribution and LocationMahmoud AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Taj Hotels Case Activity (Yash Thakkar 167263)Document2 pagesTaj Hotels Case Activity (Yash Thakkar 167263)Yash ThakkarNo ratings yet
- 360 AgreementDocument22 pages360 AgreementJef Powell100% (6)
- Key Performance Indicators (KPI) For Parts Managers: de Mystifying The Financial Statement!Document20 pagesKey Performance Indicators (KPI) For Parts Managers: de Mystifying The Financial Statement!MF JilaniNo ratings yet
- How PepsiCo's Kurkure grabbed and retained market dominanceDocument5 pagesHow PepsiCo's Kurkure grabbed and retained market dominancePrakash BaskaranNo ratings yet
- TPM2 Funds ManagementDocument112 pagesTPM2 Funds ManagementChakka Ramesh Gupta100% (1)
- Caitlin Coughlin ResumeDocument1 pageCaitlin Coughlin Resumeapi-400343336No ratings yet
- Chapter Twelve: Marketing Channels: Delivering Customer ValueDocument37 pagesChapter Twelve: Marketing Channels: Delivering Customer ValueAgustinNo ratings yet
- Consumer Culture Brand Positioning Strategies: An Experimental InvestigationDocument10 pagesConsumer Culture Brand Positioning Strategies: An Experimental InvestigationKrishna MohanNo ratings yet
- Brand Personality and IdentityDocument49 pagesBrand Personality and Identityambarishramanuj91% (11)
- Unit 1003 Payment Log DetailsDocument1,621 pagesUnit 1003 Payment Log Detailsjejo1453No ratings yet
- 14) Dec 2004 - ADocument16 pages14) Dec 2004 - ANgo Sy VinhNo ratings yet
- Concept PaperDocument8 pagesConcept PaperClarence James GagnaoNo ratings yet
- Sach Speaking Full 3 Parts Ngoc Bach - Version 1Document381 pagesSach Speaking Full 3 Parts Ngoc Bach - Version 1- K40 Tài Chính 789No ratings yet
- VNW Terms and Conditions enDocument8 pagesVNW Terms and Conditions enThang NguyenNo ratings yet
- 8bs0 01 Que 20190518Document24 pages8bs0 01 Que 20190518zainab khushiNo ratings yet
- AIESEC Balanced ScorecardDocument29 pagesAIESEC Balanced ScorecardCarl ChiangNo ratings yet
- Essay About PatriotismDocument4 pagesEssay About Patriotismafhbebhff100% (2)
- PriceDocument28 pagesPricesimply_cooolNo ratings yet
- VGSM Manufacturing Strategy - Jan 2011Document405 pagesVGSM Manufacturing Strategy - Jan 2011Ignacio Gutierrez NarvaezNo ratings yet
- Enhancing Export Performance of Zimbabwean SMEs in ManufacturingDocument19 pagesEnhancing Export Performance of Zimbabwean SMEs in ManufacturinghonzNo ratings yet
- Project TopicDocument7 pagesProject TopicmehmudNo ratings yet
- Principles of Mktng-Q3-Module-8Document22 pagesPrinciples of Mktng-Q3-Module-8Maristela RamosNo ratings yet
- Fashion Knits Ali VisionDocument4 pagesFashion Knits Ali Visionsalman712100% (1)
- Offer LetterDocument4 pagesOffer LetterCadcam CentreNo ratings yet