Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Definisi
Uploaded by
Siew FangOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Definisi
Uploaded by
Siew FangCopyright:
Available Formats
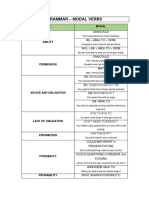
Momentum Definisi Momentum adalah kuantiti fizikal yang menggabungkan jisim dan halaju. Ia juga adalah kuantiti vektor.
P = m.v
P = momentum (kg.m/s) M=jisim (kg) V=halaju (m/s)
SI unit bagi momentum ialah kg m s-1 or N s. the Newton's Law of Motion: All moving bodies will continue to be in the state of rest or motion unless interfered by some external force. The same law applies to momentum as well. That is, if the mass and velocity of an object remain the same then the momentum of the object remains constant, i.e., mv = Constant.
For Example: It is evident from the fact that it is difficult to stop a truck than a bicycle because of the momentum difference. It can also be visualized from the fact that a truck involved in an accident will do more harm than any bicycle.
Parabola Definisi Parabola adalah himpunan titik-titik yang jaraknya terhadap suatu titik F dan suatu garis lurus (sejajar sumbu-x atau sumbu-y) adalah sama. Garis L disebut directrix dan titik F disebut fokus. Tiap titik pada parabola berjarak sama terhadap F dan directrix.
Contohnya,Jika kamu menendang bola ke atas ia akan membentuk lengkung apabila berada di langir lalu jatuh ke lantai.
Projectile Definisi A projectile has a single force that acts upon it - the force of gravity. If there were any other force acting upon an object, then that object would not be a projectile. Thus, the free-body diagram of a projectile would show a single force acting downwards and labeled force of gravity . Regardless of whether a projectile is moving downwards, upwards, upwards and rightwards, or downwards and leftwards, the free-body diagram of the projectile is still as in the diagram at the right. For example: A ball dropped from rest is a projectile (provided that the influence of air resistance is negligible). A ball that is thrown vertically upward is also a projectile (provided that the influence of air resistance is negligible). A ball which is thrown upward at an angle to the horizontal is also a projectile (provided that the influence of air resistance is negligible). A ball that once projected or dropped continues in motion by its own inertia and is influenced only by the downward force of gravity.
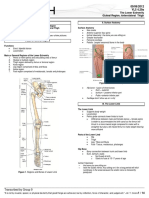
Range of motion Definisi Latihan range of motion (ROM) adalah latihan yang dilakukan untuk mempertahankan atau memperbaiki tingkat kesempurnaan kemampuan menggerakan persendian secara normal dan lengkap untuk meningkatkan massa otot dan tonus otot dan sebagai dasar untuk menetapkan adanya kelainan ataupun untuk menyatakan batas gerakan sendi yang abnormal Jenis ROM 1. ROM Pasif Latihan ROM pasif adalah latihan ROM yang dilakukan oleh pesakit dengan bantuan perawat bagi setiap gerakan.Indikasi latihan pasif adalah pesakit semikoma dan tidak sedar, pesakit dengan keterbatasan mobilisasi tidak mampu melakukan beberapa atau semua latihan dengan sendiri.Ia berguna untuk menjaga kelenturan otot-otot dan persendian dengan menggerakkan otot orang lain secara pasif misalnya perawat mengangkat dan menggerakkan kaki pesakit.
ROM Aktif Latihan Perawat memberikan motivasi, dan membimbing klien dalam melaksanakan pergerakan sendi secara sendiri sesuai dengan rentang gerak sendi normal. Hal ini untuk melatih kelenturan dan kekuatan otot serta sendi dengan cara menggunakan otot-ototnya secara aktif Contohya 1. Leher, spina, serfikal Fleksi : Menggerakan dagu menempel ke dada, rentang 45
Ekstensi : Mengembalikan kepala ke posisi tegak, rentang 45 Hiperektensi : Menekuk kepala ke belakang sejauh mungkin, rentang 40-45 Fleksi lateral : Memiringkan kepala sejauh mungkin sejauh mungkin kearah setiap bahu, rentang 40-45 Rotasi : Memutar kepala sejauh mungkin dalam gerakan sirkuler, rentang 180 Ulangi gerakan berturut-turut sebanyak 4 kali.
2. Jari-Jari Kaki
Fleksi : Menekukkan jari-jari kaki ke bawah, rentang 30-60 Ekstensi : Meluruskan jari-jari kaki, rentang 30-60 Abduksi : Menggerakan jari-jari kaki satu dengan yang lain, rentang 15 Adduksi: Merapatkan kembali bersama-sama, rentang 15 Ulang gerakan berturut-turut sebanyak 4 kali Tujuan ROM 1. Mempertahankan atau memelihara kekuatan otot 3.Merangsang sirkulasi darah 4. Mencegah kelainan bentuk
Summation of force Definisi The combination of forces produced by different parts of the human body. When a person is moving or attempting to move an object, several different parts of the body act together to maximize the force. In theory, force summation occurs when all body parts act simultaneously In practice, the strongest and lowest body parts around the centre of gravity (e.g. trunk and thighs) move first, followed by the weaker, lighter.This is known as sequential acceleration and results in successive force summation. To obtain a maximum force, summation also needs sequential stabilization of body parts, with some body parts having to be fixed at stable points while other parts produce the effective forces. Example :A volleyball player needs a good stable base from which to start the movement. The volleyball serve begins with flexion of the knee joint caused by the hamstrings, then extention of knees as well as hip flexion to start the movement; both of these movements are initiated by the quadriceps. The Erector Spinae muscle causes trunk extension to allow the abdominals to fully flex the trunk and generate the force that is then transferred to the upper body. The deltoids and pectorals major are used to flex the shoulder. These muscles are used to accelerate the whole arm while also stablising the shoulder. Once the arm has begun to accerate towards the ball, the triceps is then used to extend the elbow , thus accelerating the forearm and wrist. Just before contact with the ball, the wrist flexors contract, which allows the combined forces of all muscles to be applied to the ball by way of the hand. The timing of movements at each joint determines the control of the hand and the size and direction of the force applied to the ball. The end result is a more powerful force that can be transferred to the ball so that it travels as hard as it can, over the net to the opposite side.
Range of motion is the distance (linear or angular) that a movable object may normally travel while properly attached to another.
Definition: Range of motion (ROM) is a term commonly used to refer to the movement of a joint from full flexion to full extension.
Exercise physiologist and physical therapists measure range of motion in a joint with an instrument called a goniometer that measures joint range of motion in degrees from the starting position.
Extension is a physical position that decreases the angle between the bones of the limb at a joint. It occurs when muscles contract and bones move the joint into a bent position. The opposite movement, flexion, bends the joint so that the joint angle shortens.
Each joint has a normal range of motion. However, the amount of movement in a joint varies greatly between individuals. Joints maintain a balanced range of motion by regular use and stretching of the surrounding soft tissues (muscles, tendons and ligaments).
Injuries to the soft tissues surrounding a joint often reduce range of motion due to swelling and tissue damage. Regaining range of motion in a joint is one of the first phases of injury rehabilitation, and physical therapists often prescribe specific ROM exercises for each joint.
factors can affect normal range of motion at a joint. Swelling and inflammation caused by an injury, arthritis, tendinitis, bursitis or a joint infection commonly diminish range of motion. Sprains, strains, bone fractures, muscle weakness and nerve abnormalities can also affect range of motion. With conditions that cause joint pain or muscle weakness, active range of motion is typically more limited than passive range of motion.
Health-care professionals employ physical therapy to reestablish and maintain normal range of motion when joint movement is limited due to injury or disease. This typically involves gentle stretching of the joint, which is done with the help of a therapist. Prescribed range of motion exercises that you perform on your own improve joint flexibility and muscle strength. Medications to reduce pain, inflammation and swelling are commonly used in conjunction with physical therapy. Heat treatments using ultrasound, warm wax or a whirlpool can also help reduce joint pain and improve range of motion. For example: As used in the weightlifting communities, range of motion refers to the distance and direction a joint can move between the flexed position and the extended position.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- PE Essay Answers 2Document2 pagesPE Essay Answers 2Mary Grace ElizaldeNo ratings yet
- Jordan Fitness BrochureDocument150 pagesJordan Fitness BrochureAndrew Richard ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Submodule 2.5 - 2.6Document14 pagesSubmodule 2.5 - 2.6Zeejiah NelleNo ratings yet
- Gymnastics Basics Positions GuideDocument5 pagesGymnastics Basics Positions GuideCamille Joyce RoxasNo ratings yet
- G5 English Work SheetDocument4 pagesG5 English Work SheetMetsihafe MekbibNo ratings yet
- Read The Story. Write Some Words To Complete The Sentences About The Story. You Can Use 1, 2, 3 or 4 WordsDocument1 pageRead The Story. Write Some Words To Complete The Sentences About The Story. You Can Use 1, 2, 3 or 4 WordsEnrique RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Betting On YourselfDocument185 pagesBetting On YourselfBrent Caldwell100% (7)
- Discussion Details: Module 3 TopicDocument13 pagesDiscussion Details: Module 3 TopicMatttNo ratings yet
- Second Term Study PackDocument43 pagesSecond Term Study PackMartin KhumaloNo ratings yet
- 7 Monday Morning Habits of Highly Successful PeopleDocument4 pages7 Monday Morning Habits of Highly Successful PeopleXenia SabinaNo ratings yet
- PE 1 Midterm ModuleDocument14 pagesPE 1 Midterm ModulecherryNo ratings yet
- Grammar Unit 8Document2 pagesGrammar Unit 8Laura CarniceroNo ratings yet
- 50 EMOM Workouts From Amateur To Amimal (Fortner, Tyler)Document20 pages50 EMOM Workouts From Amateur To Amimal (Fortner, Tyler)BartNo ratings yet
- Visual PoiseDocument64 pagesVisual PoisePrincess Jenita CanlapanNo ratings yet
- 4.29a - The Lower Extremities - Gluteal Region, Anterolateral ThighDocument14 pages4.29a - The Lower Extremities - Gluteal Region, Anterolateral ThighShariq ArshadNo ratings yet
- Gymstick Fitness Collection 2013Document78 pagesGymstick Fitness Collection 2013GymstickSverigeNo ratings yet
- ACSM's Guidelines Exercise-Testing Prescrip 11e 2021 (190-212)Document23 pagesACSM's Guidelines Exercise-Testing Prescrip 11e 2021 (190-212)Leticia RiveraNo ratings yet
- Grammar U5 L2Document3 pagesGrammar U5 L2uzielNo ratings yet
- Link L7 U9 Extra Vocabulary WsDocument1 pageLink L7 U9 Extra Vocabulary WsMal SwierNo ratings yet
- Past ContinuousDocument2 pagesPast ContinuousFlorencia RoldánNo ratings yet
- PE11 Q4 Module4a Weeks1and2Document20 pagesPE11 Q4 Module4a Weeks1and2Kristelle BigawNo ratings yet
- KH!Winter!Challenge!-!Weeks!1&5: Workout 1-Legs, Calves, CardioDocument4 pagesKH!Winter!Challenge!-!Weeks!1&5: Workout 1-Legs, Calves, CardioJessika CastilloNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 MAPEH - ReviewerDocument3 pagesGrade 10 MAPEH - ReviewerBabe SugarolNo ratings yet
- Innovation Project Basketball CourtDocument3 pagesInnovation Project Basketball CourtPaulo MoralesNo ratings yet
- History of Physical EducationDocument34 pagesHistory of Physical EducationAiro emmanuelNo ratings yet
- Shakespeare's Characters Still Fascinate TodayDocument5 pagesShakespeare's Characters Still Fascinate TodayScarlette GarciaNo ratings yet
- Rock Lee Workout PDFDocument11 pagesRock Lee Workout PDFShadia CarolineNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitledИнатулло АсламовNo ratings yet
- Eren Yeager Calisthenics Workout PDFDocument12 pagesEren Yeager Calisthenics Workout PDFMusadiq AhmedNo ratings yet
- 4000 PT ManualDocument71 pages4000 PT ManualManunoghiNo ratings yet