Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ingles
Uploaded by
CientificamenteSaraOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ingles
Uploaded by
CientificamenteSaraCopyright:
Available Formats
ENGLISH TEXT
READ THE TEXT ENTITLED TEMPERATURE AND ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS. 1. state Functions: a) Are of little importance in thermodynamics. b) Play a necessary role in thermodynamics. c) Are not emphasized in thermodynamics. 2. Due to the fact that the results of many experiments depend on what we qualitatively experience as hotness. a) No quantitative temperature was introduced. b) The idea of a qualitative temperature was introduced. c) A quantitative temperature was introduced. 3. In sentence (6) which refers to: a) Temperature. b) Density of liquid mercury. c) Distance. 4. When we place 99 aqually spaced marks between the two calibration points we define: a) The density of liquid mercury. b) The temperature scale. c) Intermediate temperature. 5. The temperature indicated by placing 99 equally spaced marks between two calibration points depends on: a) The properties of the materials used in the construction of the thermometer. b) The length of the mercury column when the thermometer is immersed in an ice-water bath. c) The length of the columns when the thermometer is immersed in an ice-water bath. 6. In sentence (9) its refers to: a) temperature. b) Construction. c) Thermometer.
7. If we use water as the working liquid in a thermometer: a) The resulting temperature scale is the same as that for mercury. b) A resulting temperature scale cannot be obtained. c) The resulting temperature scale is different than the mercury scale. 8. When we put a mercury and water thermometer in a bath at 0 and slowly raise the temperature: a) The mercury thermometer reads higher than the water thermometer. b) The mercury thermometer reads lower than de water thermometer. c) Both thermometers read the same. 9. When the mercury thermometer reads 4, the water thermometer reads 0.36: a) Because as the temperature is raised on the mercury scale, water expands. b) Because as the temperature is lowered on the mercury scale, water contracts. c) Because as the temperature is raised on the mercury scale, there is water contraction. 10. When hotness increases, temperature sometimes goes up and sometimes goes down describes: a) A mercury thermometer. b) A water thermometer. c) Either a mercury or a water thermometer.
TEMPERATURE. We have emphasized that state functions are of foremost importance in thermodynamics l. Some of these state functions, like pressure, volume, and chemical composition are familiar quantities and need no elaborate explanation 2. On the other hand, temperature, although a common, quantity, has rather subtle conceptual origins 3. The idea of a quantitative temperature was introduced because it became obvious that the results of many experiments depended on what we qualitatively experience as "hotness" 4. The first step in creating a temperature scale is to find some convenient property of matter which depends in a simple way on hotness 5. Temperature can be indicated, for example, by the density of liquid mercury, which is commonly measured by the distance mercury expands from a bulb into a glass capillary tube 6. The centigrade temperature scale is defined by assigning a value of zero temperature units, or degrees, to the length of the mercury column when the thermometer is immersed in an ice-water bath and 100 degrees to the length of the column when the thermometer is in
contact with water at its normal boiling point 7. Intermediate temperatures are defined by placing 99 equally spaced marks between the two calibration points 8. lt is clear that the temperature indicated by this thermometer depends on the properties of the materials used in its construction 9. Furthermore, by dividing the length between 0 and 100 into 100 equal units, we are really saying that temperature is something which depends linearly on the volume of mercury 10. lf some other liquid is used in the thermometer, the resulting temperature is different 11. For example, suppose we use water as the working liquid 12. We mark the thermometer in the same way, noting the length of the water column at the ice point and boiling point and divide the interval into 100 equal units.13. Now we put our mercury thermometer and water thermometer in a bath at 0 and slowly 14 raise the temperature . When the mercury thermometer reads 4, the 15 water thermometer reads -0.36 . This happens because as the temperature is raised from 0 to 4 on the mercury scale, water 16 contracts instead of expanding . lf we use the properties of water to define temperature, we would have to say that when hotness in17 creases, temperature sometimes goes up and sometimes goes down .
You might also like
- Tr6 Electronic Distributorless Ignition Kit Part1Document9 pagesTr6 Electronic Distributorless Ignition Kit Part1Kunta Si Kun KunNo ratings yet
- Calibrating Thermometers Lab ReportDocument15 pagesCalibrating Thermometers Lab ReportJeshua LloreraNo ratings yet
- Heat Olevel NotesDocument42 pagesHeat Olevel NoteskimbugweNo ratings yet
- Iso 2553Document54 pagesIso 2553lokesh38100% (2)
- Experiment 1 - Bomb CalorimetryDocument12 pagesExperiment 1 - Bomb CalorimetryBryle Camarote100% (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- ISO 3046 1989 PT 3 Part 3 Test MeasurementsDocument12 pagesISO 3046 1989 PT 3 Part 3 Test MeasurementsbunnykfaNo ratings yet
- A GENERAL PHYSICS I 12 Q2M2 Teacher PDFDocument17 pagesA GENERAL PHYSICS I 12 Q2M2 Teacher PDFRETCHIE JOY PISANANo ratings yet
- Title: Practical 1 (Charles' Law) : V Is The Volume of The GasDocument6 pagesTitle: Practical 1 (Charles' Law) : V Is The Volume of The Gashusnaazman100% (1)
- Experiment No1 (Calibration of Thermometers)Document17 pagesExperiment No1 (Calibration of Thermometers)justinndonn80% (5)
- Celsius ThermometerDocument5 pagesCelsius Thermometerapi-384212889No ratings yet
- Ordinary Level Heat NotesDocument44 pagesOrdinary Level Heat Notespatrick omonyNo ratings yet
- Thermal expansion and temperature scalesDocument19 pagesThermal expansion and temperature scalesDedy Setiawan ستياوانNo ratings yet
- Understanding Thermal PrincipleDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Thermal PrincipleAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Temperature Lab Objective: TemperatureDocument8 pagesTemperature Lab Objective: TemperatureEmily RubensteinNo ratings yet
- 8-5 Zkcelsius ThermometerDocument6 pages8-5 Zkcelsius Thermometerapi-384186386No ratings yet
- Lesson 4.1 (Smtai 09) .Document5 pagesLesson 4.1 (Smtai 09) .Ilman MohamadNo ratings yet
- Celsius ThermometerDocument6 pagesCelsius Thermometerapi-384212832No ratings yet
- Please Remember To Photocopy 4 Pages Onto One Sheet by Going A3 A4 and Using Back To Back On The PhotocopierDocument10 pagesPlease Remember To Photocopy 4 Pages Onto One Sheet by Going A3 A4 and Using Back To Back On The PhotocopierChrise RajNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Thermal ExitDocument25 pagesFluid and Thermal Exitdavididosa40No ratings yet
- Exp. 2 (Calorimeter)Document14 pagesExp. 2 (Calorimeter)Hotaru Rei نور اكماليناNo ratings yet
- To The Best Known Fixed Points On The Temperature Scale, The Melting and Boiling Point of Pure WaterDocument5 pagesTo The Best Known Fixed Points On The Temperature Scale, The Melting and Boiling Point of Pure Waterapi-384205644No ratings yet
- TemperatureDocument14 pagesTemperatureFajar SanjayaNo ratings yet
- Non-Contact ThermometerDocument8 pagesNon-Contact ThermometerSino Ba ToNo ratings yet
- Measuring Temperature Using a ThermometerDocument5 pagesMeasuring Temperature Using a ThermometerAkmad ManabilangNo ratings yet
- Thermometry Physics A LevelDocument16 pagesThermometry Physics A LevelNayana GaleaNo ratings yet
- Celsius ThermometerDocument6 pagesCelsius Thermometerapi-384189404No ratings yet
- TemperatureDocument10 pagesTemperatureAli BastiNo ratings yet
- Celsius ThermometerDocument6 pagesCelsius Thermometerapi-384188509No ratings yet
- Measuring Heat with ThermometersDocument3 pagesMeasuring Heat with ThermometersNagendra RamNo ratings yet
- Celcius ThermometerDocument5 pagesCelcius Thermometerapi-384205707No ratings yet
- Calorimetria FULLDocument6 pagesCalorimetria FULLferney.velasquezNo ratings yet
- Thermo CalibrationDocument10 pagesThermo CalibrationAngelo De AsisNo ratings yet
- Physics 41 Calorimetry: Determination of Specific Heat Capacity of CopperDocument2 pagesPhysics 41 Calorimetry: Determination of Specific Heat Capacity of CopperAmeva Ameve Sinangote CañosoNo ratings yet
- HEAT CHECKDocument10 pagesHEAT CHECKRahul RajNo ratings yet
- The Latent Heat of Fusion of Ice PDFDocument4 pagesThe Latent Heat of Fusion of Ice PDFNaeem GulNo ratings yet
- Temperature Measurement Methods & StandardsDocument78 pagesTemperature Measurement Methods & StandardsKing BommNo ratings yet
- SCHOOL OF BIO AND CHEMICAL DEPARTMENT INSTRUMENTATIONDocument129 pagesSCHOOL OF BIO AND CHEMICAL DEPARTMENT INSTRUMENTATIONKeerthana UrukutiNo ratings yet
- Unique Topic 14 NotesDocument15 pagesUnique Topic 14 Notesnadiamuhorakeye29No ratings yet
- P103 Chapter10 TAT wk3wk4Document62 pagesP103 Chapter10 TAT wk3wk4Muhammad SaeedNo ratings yet
- BME-Temperature Measurement - NOTESDocument5 pagesBME-Temperature Measurement - NOTESAisha JainNo ratings yet
- Weather Station Siting: Effects On Phenological ModelsDocument17 pagesWeather Station Siting: Effects On Phenological ModelsAhmedAhmedNo ratings yet
- Thermal Conductivity of MetalsDocument6 pagesThermal Conductivity of Metalsiabub3330% (1)
- Lab 14Document3 pagesLab 14Sulaiman Musa MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Lab Demonstrates Conduction, Convection & RadiationDocument5 pagesHeat Transfer Lab Demonstrates Conduction, Convection & RadiationAnisNo ratings yet
- Thermal Conductivity Using Searle's ApparatusDocument10 pagesThermal Conductivity Using Searle's ApparatusShlôkä Jõshï86% (7)
- Celsius ThermometerDocument6 pagesCelsius Thermometerapi-384072296No ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument4 pagesPhysicsDexter the DoubledmintNo ratings yet
- Measurment of Thermal Conductivity K of Copper by Searls Method.Document5 pagesMeasurment of Thermal Conductivity K of Copper by Searls Method.Møďđý SåñâýāNo ratings yet
- Specific HeatDocument2 pagesSpecific HeatJorge Rodríguez SedanoNo ratings yet
- F 4 C 4Document3 pagesF 4 C 4jalrizal7No ratings yet
- Thermometry and Thermal Expansion: Physics Class-IX Question Bank 1Document21 pagesThermometry and Thermal Expansion: Physics Class-IX Question Bank 1TajiriMollelNo ratings yet
- Measurement of temperatureDocument7 pagesMeasurement of temperaturetalithaonkabetse723No ratings yet
- Clausius Clap LabDocument4 pagesClausius Clap LabBunty MandaliaNo ratings yet
- Heat and Temperature: Understanding Key ConceptsDocument57 pagesHeat and Temperature: Understanding Key ConceptsJeanette Valera JimenezNo ratings yet
- Thermometry: There Are Triple Points For Many Other Substances Besides WaterDocument7 pagesThermometry: There Are Triple Points For Many Other Substances Besides WaterIMJ JNo ratings yet
- PassportDocument146 pagesPassportDenisNo ratings yet
- Thermal Physics FundamentalsDocument1,133 pagesThermal Physics FundamentalsFatin IshraqueNo ratings yet
- Iclass ThermometersDocument14 pagesIclass Thermometersajiloremiracle1No ratings yet
- Ch.11 Heat and ThermoDocument10 pagesCh.11 Heat and ThermoJoanne Aga EslavaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1Document6 pagesExperiment No. 1Yhuloopz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- CHE486 - Marcet BoilerDocument6 pagesCHE486 - Marcet BoilerHaikal SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Lab Report - CHM02 - CO3 - Virtual Lab - Determining Heat Capacity of A Calorimeter - Grp2Document7 pagesLab Report - CHM02 - CO3 - Virtual Lab - Determining Heat Capacity of A Calorimeter - Grp2Antonio AbanoNo ratings yet
- Weather Studies: The Commonwealth and International Library: Rural and Environmental Studies DivisionFrom EverandWeather Studies: The Commonwealth and International Library: Rural and Environmental Studies DivisionNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 11 - MS3220 Rekayasa Termal (Mark Scheme)Document6 pagesTutorial 11 - MS3220 Rekayasa Termal (Mark Scheme)i need documentsNo ratings yet
- Project References TableDocument4 pagesProject References TableDiane Joy Fojas PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Entropy: Reference: J.M. Smith, H.C. Van Ness, M.M. Abbott. Introduction To Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics7 EditionDocument34 pagesEntropy: Reference: J.M. Smith, H.C. Van Ness, M.M. Abbott. Introduction To Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics7 EditionNelsonNo ratings yet
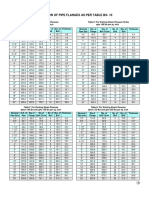
- PIPE FLANGE DIMENSIONSDocument5 pagesPIPE FLANGE DIMENSIONSViral ParmarNo ratings yet
- Pelton TurbineDocument4 pagesPelton TurbineHenDricky Magosi100% (1)
- Cruise Control System (CCS) ,: 1.6 ltr./74 KW Simos, Engine Code AEH, 1.6 ltr./74 KW Simos, Engine Code AKLDocument4 pagesCruise Control System (CCS) ,: 1.6 ltr./74 KW Simos, Engine Code AEH, 1.6 ltr./74 KW Simos, Engine Code AKLBrett MercadoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Fizz MartinNo ratings yet
- Rheolube 363F: Rust Inhibited, PTFE FortifiedDocument1 pageRheolube 363F: Rust Inhibited, PTFE FortifiedMed Elhedi NasfiNo ratings yet
- Department of Fluid Mechanics: Delhi Technological UniversityDocument10 pagesDepartment of Fluid Mechanics: Delhi Technological University2K20-ME-161 Mridul AnandNo ratings yet
- Tension Structures: A. Buchholdt BSC PHDDocument10 pagesTension Structures: A. Buchholdt BSC PHDRoach Gabriele SandersonNo ratings yet
- Amie Q Bank Thermal ScienceDocument98 pagesAmie Q Bank Thermal ScienceAurvin SinghNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER2 -منهج جديد pdf2- m PDFDocument39 pagesCHAPTER2 -منهج جديد pdf2- m PDFmohammed elobideNo ratings yet
- 4500 Manifold Manual Rev FDocument34 pages4500 Manifold Manual Rev FDora Mejia Ramirez100% (1)
- Sanwa Export 02 Gate ValveDocument1 pageSanwa Export 02 Gate ValveTou SvnkNo ratings yet
- Eclaté Technique Fusion APDocument1 pageEclaté Technique Fusion APaadNo ratings yet
- Amos Module 4 Part2Document11 pagesAmos Module 4 Part2bokax95577No ratings yet
- Boston Export (Profile-Brochure) PDFDocument10 pagesBoston Export (Profile-Brochure) PDFGIRISH RAJ PUROHITNo ratings yet
- List of IllustrationsDocument12 pagesList of IllustrationsJorge LopesNo ratings yet
- AckermanDocument11 pagesAckermanVansh JainNo ratings yet
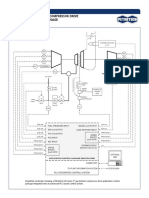
- Ge Frame 3 Gas Turbine Compressor Drive Application Control PackageDocument3 pagesGe Frame 3 Gas Turbine Compressor Drive Application Control PackagehasnaNo ratings yet
- Slab On Grade Reinforcing DesignDocument11 pagesSlab On Grade Reinforcing DesignAti KhongNo ratings yet
- Cosfb - Composite Slim-Floor Beam: Experimental Test Campaign and EvaluationDocument15 pagesCosfb - Composite Slim-Floor Beam: Experimental Test Campaign and EvaluationDima OvsiiNo ratings yet
- Simulate Piccolo Tube Anti-Icing System with CFDDocument7 pagesSimulate Piccolo Tube Anti-Icing System with CFDsanjoshi21No ratings yet
- Vibratoin Severity - ISO 2372Document1 pageVibratoin Severity - ISO 2372HARSHANo ratings yet
- 4he75m Part ListDocument6 pages4he75m Part ListJvlValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- الفصل الرابعDocument11 pagesالفصل الرابعdark darkNo ratings yet