Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy of Airways
Uploaded by
gdubs215Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anatomy of Airways
Uploaded by
gdubs215Copyright:
Available Formats
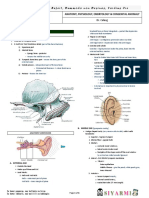
The Mouth
Oral Vestibule: Area between the teeth and lips, or the teeth and cheeks Most anterior portion of the oral cavity Oral Cavity Proper: The space occupied by the tongue Oral Cavity Proper Boundaries Anterior: lips Posterior: oropharyngeal isthmus of fauces Roof: Hard palate, soft palate more posterior Floor: Tongue and mucosa under the tongue Note: The teeth are inserted into the alveolar process of mandible and maxilla bones
Cheek Lateral walls of oral cavity Four major layers: 1. Skin - Non-keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium 2. Buccopharyngeal fascia - Covers buccinator muscle 3. Buccinator muscle - From outer surface of alveolar processes of mandible and maxilla 4. Mucous membrane Floor of Mouth The anterior 2/3 of the tongue constitutes its body, and makes up most of the floor of the mouth The floor also consists of the mucous membrane region from the base of the tongue to the gingiva of the mandible. This includes the lingual frenulum, a fold of mucous membrane which connects the tongue to the floor. The submandibular duct is located at the base of the frenulum, with papillae on either side. Posteriorly and laterally from the papilla is the location of the sublingual folds which contain the sublingual salivary glands. The anterior 2/3 of the tongue is innervated by all branches of the trigeminal nerve, particularly the lingual branch. These branches transmit sensory information.
Teeth Usually there are 32 permanent teeth 16 on the upper jaw, and 16 on the lower jaw Each side of the jaw contains the same 4 tooth types, constituting 8 teeth on each side 1. Incisor (x2) 2. Canine 3. Premolar (x2) 4. Upper molar (x3) Palate: Hard and Soft Forms roof of mouth and floor of nasal cavity Hard Anterior Formed by 2 bones 1. Palatal process of maxilla 2. Horizontal plate of palatine bone Covered by periosteum and oral mucosa (mucoperiosteum) Sharpeys fibers - Thin fibers of bone which connect the mucoperiosteum to the underlying bone - Absent at the horizontal plate Soft No bones Posterior to hard palate Attaches to hard palate by the tensor veli palatini aponeurosis Muscular posteriorly 1. Levator veli palatini: raises the soft palate during swallowing 2. Palatoglossus: elevated posterior 1/3 of tongue 3. Palatopharyngeus: pulls pharynx up and forward during swallowing 4. Tensor veli palatini: swallowing Muscles attach to hyoid bone
Palate continued Blood Supply Arterial: Greater palatine artery on each side Emerges through greater palatine foramen, lateral to the greater palatine nerve Venous: pterygoid plexus and pharyngeal plexus Lymph Retropharyngeal cervical nodes Deep cervical nodes Nerve Trigeminal nerve (maxillary branch) supplies the palate Branches into greater palatine nerve
Tongue Body: anterior 2/3 Root: posterior 1/3 Movement Intrinsic and extrinsic muscles Intrinsic: alter the shape of the tongue Extrinsic: alter position of the tongue 1. Genioglossus - Bulk of the tongue - Protrusion/forward movement - Side to side 2. Styloglossus - Retracts tongue - Curls sides 3. Hyoglosus - Draws sides of the tongue down - Aids retraction - Depresses tongue 4. Palatoglossus 5. Mylohyoid - Muscular floor of oral cavity - Runs from mandible to hyoid bone - Swallowing and speaking
Pharynx Muscular tube that is deficient anteriorly due to openings of nasal and oral cavities Extends from posterior nasal cavity to oesophagus (continuous with oesophagus and larynx) Anterior to pre-vertebral fascia Three Parts 1. Nasopharynx 2. Oropharynx 3. Laryngopharynx
Layers of Pharyngeal Wall External: buccopharyngeal fascia Muscle - Outer circular constrictor muscles (x3) ! Superior, middle, and inferior ! Forms a muscular sleeve - Inner longitudinal muscles: stylopharyngeus, palatopharyngeus, salpingopharyngeus Submucosa Mucous membrane
Four Constrictor Gaps: openings for structures to and from the pharynx 1. Above superior constrictor - Auditory tube 2. Between superior and middle constrictor - Stylopharangeus muscle - Glossopharyngeal nerve 3. Between middle and inferior constrictor - Internal laryngeal nerve - Superior laryngeal artery (from superior thyroid artery) 4. Below inferior constrictor - Recurrent laryngeal nerve - Inferior laryngeal artery
Carotid Triangle Boundaries Superior: stylohyoid Posterior: sternocleidomastoid Inferior: superior omohyoid Floor: pharynx
You might also like
- Pediatric Anesthesia For StudentsDocument4 pagesPediatric Anesthesia For StudentsMarco TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology MnemonicsDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Physiology MnemonicsLalajimNo ratings yet
- Brachial Plexus Most ImportantDocument2 pagesBrachial Plexus Most ImportantFlowerNo ratings yet
- Step-Wise Approaches in Clinical Examination - SampleDocument8 pagesStep-Wise Approaches in Clinical Examination - Samplecsbully913No ratings yet
- Mechanism of Drug Action PDFDocument1 pageMechanism of Drug Action PDFraviomjNo ratings yet
- Meninges, Ventricles - CSF - Study GuideDocument3 pagesMeninges, Ventricles - CSF - Study Guideshivani patelNo ratings yet
- ChemotherapyDocument11 pagesChemotherapyNedaAbdullahNo ratings yet
- Algorithms of Care (Myocardial Infarction)Document3 pagesAlgorithms of Care (Myocardial Infarction)Julius Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Block 2Document53 pagesRespiratory Block 2Maya LaPradeNo ratings yet
- Ascending Tracts Spinal CordDocument1 pageAscending Tracts Spinal CordChristopher Samuel0% (1)
- EAR Anatomy, Physiology, Embryology & Congenital AnomalyDocument6 pagesEAR Anatomy, Physiology, Embryology & Congenital AnomalyThakoon TtsNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Notes (Chris Andersen, ICUPrimaryPrep - Com)Document14 pagesRespiratory Notes (Chris Andersen, ICUPrimaryPrep - Com)PkernNo ratings yet
- Nose & Paranasal Sinuses 2018Document63 pagesNose & Paranasal Sinuses 2018yasrul izadNo ratings yet
- Examination of The Central Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesExamination of The Central Nervous Systemkenners100% (13)
- I 2x Get Laid On FridaysDocument3 pagesI 2x Get Laid On FridaysRoma Fe MabanagNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Neuromuscular Blocking Drugs: Succinylcholine, Atracurium, Cis-Atracurium, Rocuronium, VDocument1 pageComparison of Neuromuscular Blocking Drugs: Succinylcholine, Atracurium, Cis-Atracurium, Rocuronium, VMarshallMcGoughNo ratings yet
- Special Senses Physiology of Hearing and Balance: Dr. CalaquianDocument6 pagesSpecial Senses Physiology of Hearing and Balance: Dr. CalaquianHanako Sasaki AranillaNo ratings yet
- General-Anesthesia Part 3Document5 pagesGeneral-Anesthesia Part 3Dianne GalangNo ratings yet
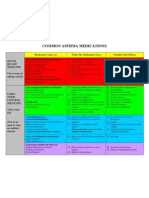
- Common Asthma MedicationsDocument1 pageCommon Asthma MedicationsHeart of the Valley, Pediatric CardiologyNo ratings yet
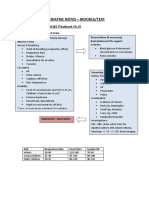
- Paediatric Emergencies NotesDocument6 pagesPaediatric Emergencies NotesJana AldourNo ratings yet
- Manual Muscle Testing: RD TH TH TH TH TH TH TH THDocument6 pagesManual Muscle Testing: RD TH TH TH TH TH TH TH THAljon S. TemploNo ratings yet
- Handouts Integumentary Sys Sp11 B201Document7 pagesHandouts Integumentary Sys Sp11 B201Kelly TrainorNo ratings yet
- AortaDocument1 pageAortadankirsh100% (1)
- Cranial+Nerves 1styearDocument2 pagesCranial+Nerves 1styearashleyyanez3100% (1)
- Examination of The HipDocument33 pagesExamination of The HipTumbal BroNo ratings yet
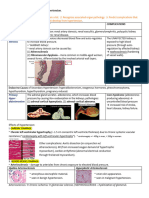
- Week 10 - Hypertension, Atherosclerosis, ArrhythmiaDocument14 pagesWeek 10 - Hypertension, Atherosclerosis, Arrhythmiashivani patel100% (1)
- Thyroid Gland: Sheena Mae SangutanDocument27 pagesThyroid Gland: Sheena Mae SangutanMarrah Avila Acuin100% (1)
- Arrhythmia & Anti-Arrhythmic DrugsDocument49 pagesArrhythmia & Anti-Arrhythmic DrugsNitesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas Workshop Dr. Lanzona 12.06.07: Lala 3C-Med-09 1Document4 pagesArterial Blood Gas Workshop Dr. Lanzona 12.06.07: Lala 3C-Med-09 1pramastutiNo ratings yet
- Inguinal CanalDocument4 pagesInguinal CanalspiraldaoNo ratings yet
- Accordion Sign-Appearance (C. Difficile)Document41 pagesAccordion Sign-Appearance (C. Difficile)Andra HijratulNo ratings yet
- Table of 12 Cranials and TractusDocument5 pagesTable of 12 Cranials and TractusjuwitavalenNo ratings yet
- Vertebral Arteries, and Their Divisions. Arteries Fuse To Form The Basilar ArteryDocument6 pagesVertebral Arteries, and Their Divisions. Arteries Fuse To Form The Basilar Arterymurali_bharadwazNo ratings yet
- Regional Anesthesia Part 2Document9 pagesRegional Anesthesia Part 2Dianne GalangNo ratings yet
- Abg InterpretationDocument1 pageAbg InterpretationPrincess EspadaNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves OverviewDocument17 pagesCranial Nerves OverviewRiki AntoNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument7 pagesEpithelial TissueJoan PaulineNo ratings yet
- STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE HEARTDocument16 pagesSTRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE HEARTPkernNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument2 pagesCranial NervesakexisNo ratings yet
- PharynxDocument2 pagesPharynxameerabest0% (1)
- Embryological DerivativesDocument1 pageEmbryological DerivativesDr Ishtiaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Post-Strep Infxn Ddressler's Sydrome: Endocarditis Valvular Dse Pericarditis Cardiac TamponadeDocument5 pagesPost-Strep Infxn Ddressler's Sydrome: Endocarditis Valvular Dse Pericarditis Cardiac TamponadeEben Ezar Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Concise SEO-Optimized Title for Clotting DocumentDocument3 pagesConcise SEO-Optimized Title for Clotting DocumentRyan TurnerNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience Pathways Fall 2012Document46 pagesNeuroscience Pathways Fall 2012Yezin ShamoonNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Blood FlowDocument39 pagesCerebral Blood FlowRajat ThakurNo ratings yet
- Anatomy (2023 Reviewer) Musculoskeletal Brachial Plexus Injuries - 3 Cords Terminal Branches MotorDocument11 pagesAnatomy (2023 Reviewer) Musculoskeletal Brachial Plexus Injuries - 3 Cords Terminal Branches MotorStephen MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves and BranchesDocument5 pagesCranial Nerves and Branchesballer0417No ratings yet
- GI + Renal OSCE: AMSA Edinburgh X IMU Y4Document41 pagesGI + Renal OSCE: AMSA Edinburgh X IMU Y4Abby LiewNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology A - NSAIDSDocument14 pagesPharmacology A - NSAIDSselflessdoctorNo ratings yet
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus 6. Aortic Stenosis: Signs and Symptoms: Signs and SymptomsDocument3 pagesPatent Ductus Arteriosus 6. Aortic Stenosis: Signs and Symptoms: Signs and SymptomsKIANA LOUISE ROMANONo ratings yet
- Anastomosis Left Anterior Cerebral Artery BlockageDocument5 pagesAnastomosis Left Anterior Cerebral Artery BlockagemcwnotesNo ratings yet
- General-Anesthesia Part 1Document5 pagesGeneral-Anesthesia Part 1Dianne GalangNo ratings yet
- CerebellumDocument14 pagesCerebellumapi-508474347No ratings yet
- Disease Signs & SymptomsDocument3 pagesDisease Signs & SymptomsJose Dangali AlinaoNo ratings yet
- 'Aliah's Cardiovascular SystemDocument45 pages'Aliah's Cardiovascular SystemLuqman Al-Bashir FauziNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Circulatory Shock, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Circulatory Shock, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Anesthesiology Review: Clinical Cases for Self-AssessmentFrom EverandPediatric Anesthesiology Review: Clinical Cases for Self-AssessmentNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Exam 1 Review - Muscles of the Back, Shoulder, Arm, Forearm & HandDocument27 pagesAnatomy Exam 1 Review - Muscles of the Back, Shoulder, Arm, Forearm & Handgdubs215No ratings yet
- About BlankDocument2 pagesAbout Blankgdubs215No ratings yet
- Vegetable Freezing ChartDocument2 pagesVegetable Freezing Chartgdubs215100% (1)
- Staph. AureusDocument1 pageStaph. Aureusgdubs215No ratings yet
- Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone SystemDocument1 pageRenin Angiotensin Aldosterone Systemgdubs215No ratings yet
- Important Vertebral Landmarks Level StructureDocument5 pagesImportant Vertebral Landmarks Level Structuregdubs215No ratings yet
- Anatomy of AirwaysDocument5 pagesAnatomy of Airwaysgdubs215No ratings yet
- M&E SPC 4 PS-RDocument12 pagesM&E SPC 4 PS-Ramirul8686No ratings yet
- World-Wide Technical Reference Guide: Grand RegulationDocument16 pagesWorld-Wide Technical Reference Guide: Grand Regulationcjarcher1677No ratings yet
- Bts World Cards StatusDocument7 pagesBts World Cards StatusJohzzyluck R. Maghuyop0% (1)
- 01 6partial FractionsDocument4 pages01 6partial FractionseamcetmaterialsNo ratings yet
- Intermediate First Half Lesson GuideDocument14 pagesIntermediate First Half Lesson GuideLuwani LinoNo ratings yet
- 2013 Wright Specifications CatalogDocument189 pages2013 Wright Specifications CatalogcenicercNo ratings yet
- UB - Alpha - .PDF - Google DriveDocument1 pageUB - Alpha - .PDF - Google DriveYury MeloNo ratings yet
- t2 M 2278 Uks2 Negative Numbers Challenge Cards - Ver - 1Document3 pagest2 M 2278 Uks2 Negative Numbers Challenge Cards - Ver - 1Chitra ThadaniNo ratings yet
- Comprehension Questions Diary of A Wimpy KidDocument9 pagesComprehension Questions Diary of A Wimpy KidNoemi Martinez Turull67% (3)
- Lesson Plan GonzaloDocument2 pagesLesson Plan Gonzaloapi-252176454No ratings yet
- Assessment: Challenge YourselfDocument1 pageAssessment: Challenge YourselfLester KalacasNo ratings yet
- SHInee - Ring Ding DongDocument1 pageSHInee - Ring Ding DongAmirulFaizNo ratings yet
- VIO55-5B Parts Catalog (Engine) PDFDocument27 pagesVIO55-5B Parts Catalog (Engine) PDFsuriantoNo ratings yet
- 2020 CastleX Snowmobile CatalogDocument198 pages2020 CastleX Snowmobile CatalogCastle X Snow Gear, Castle Motorcycle Gear, and HelmetsNo ratings yet
- WiitdbDocument161 pagesWiitdbteknoallahNo ratings yet
- Eevee: @shea - CrochetDocument13 pagesEevee: @shea - CrochetKarina Magaña100% (4)
- Compact Refrigerator: FFPE2411QBDocument2 pagesCompact Refrigerator: FFPE2411QBmember1000No ratings yet
- Queen Elizabeth The Second: Answer The Following Questions About The Queen in Full SentencesDocument2 pagesQueen Elizabeth The Second: Answer The Following Questions About The Queen in Full SentencesAna Claudia da SilveiraNo ratings yet
- Conservation of EnergyDocument2 pagesConservation of EnergyShaine InoveroNo ratings yet
- An Annotated Bibliography - Sky WritingsDocument42 pagesAn Annotated Bibliography - Sky WritingsYulande LindsayNo ratings yet
- HFF Carquest Friction 2010Document29 pagesHFF Carquest Friction 2010gearhead1No ratings yet
- My Computer DetailsDocument2 pagesMy Computer DetailsSoinik PanditNo ratings yet
- 2012 June Paper 2Document12 pages2012 June Paper 2Ricky MartinNo ratings yet
- Engine and Gearbox Oil List From CINAAUTOPARTSDocument7 pagesEngine and Gearbox Oil List From CINAAUTOPARTSCINA auto partsNo ratings yet
- Free Time ActivitiesDocument5 pagesFree Time ActivitiesElena CovalciucNo ratings yet
- FFRTC LogDocument1,177 pagesFFRTC LogLinda BlancoNo ratings yet
- Lukas KatalogDocument31 pagesLukas KatalogJosko SpehNo ratings yet
- Danh Sach KH MB Da NangDocument4,235 pagesDanh Sach KH MB Da NangTùng Thiện NguyễnNo ratings yet
- E CatalogDocument29 pagesE CatalogdajglimosneroNo ratings yet