Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Synthesis and Recrystallization of Aspirin
Uploaded by
Lisa LittleOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Synthesis and Recrystallization of Aspirin
Uploaded by
Lisa LittleCopyright:
Available Formats
1. Write the reaction involved in the synthesis of Aspirin.
Acetylation, a type of nucleophilic acyl substitution is a reaction employed in the synthesis of aspirin. It involves acid- catalyzed reaction of an acetyl group (-COCH3) with a hydroxyl group (-OH) of an alcohol and phenol producing a functional group, ester. In the experiment, acetic anhydride is the source of the acetyl group which is a carboxylic acid derivative. Salicylic acid on the other hand, is the source of the hydroxyl group which is an aromatic compound. Carboxylic acid is the acid catalyst used in the process.
The synthesis of aspirin involves acetylation, the acid catalyzed reaction of acetyl ( COCH3) group with a hydroxyl (OH) group of an alcohol and phenol, yielding an ester. Acetylation is a type of nucleophilic acyl substituion, and it is also closely related to esterification (the difference being that esterification involves a carboxyl group, not acetyl). In this experiment, the source of the acetyl group is acetic anhydride, a carboxylic acid derivative; the source of the hydroxyl group is salicyclic acid, an aromatic compound; and the acid catalyst is carboxylic acid.
3. Explain why in the recrystallization of Aspirin the water should not be heated above 80C.
The water should not be heated at a temperature above 80C in the recrystallizaion of aspirin in order to avoid the hydrolysis of ester which will reverse the reaction, producing carboxylic acid as a reactant instead of ester as a product.
The recrystallization of aspirin in water must not exceed a temperature of 80C in order to prevent hydrolysis of the ester, which will reverse the reaction, yielding reactant (carboxylic acid) instead of product (ester).
4. Explain the results obtained when Aspirin and salicyclic acid were treated with FeCl3.
A purple or violet coloration was observed when FeCl3 reacted to phenol which indicates a positive result. If the synthesized product gives a purple or violet color with FeCl3 solution, this means that not all of the salicylic acid has been used up.
Ferric chloride reacts with phenol to give a purple solution. Since salicylic acid has a phenol group, it is expected to give a positive result, that is, become purple. If the synthesized product gives a purple color with ferric chloride solution, it means that not all of the salicylic acid has been consumed.
APPLICATIONS: Phenol must first be reacted with NaOH, yielding salt and water. The salt is reacted with salicylic acid to produce phenyl salicylate, or salol, and NaOH. Aspirin is more acidic than salol because of the stability of its conjugate base and its COOH functional group. Aspirin will be hydrolyzed easily because it is acidic. Aspirin (acety salicylic acid) is a stronger acid than salol, because aspirin contains the carboxylic acid functional group (pKa ~3) and salol contains a phenol (pKa ~10) Aspirin is hydrolysed easier since the leaving group (LG) is acetate (pKa of conjugate acid is ~5). The LG for salol would be phenol (pKa ~10). The more stable the LG the better it is at leaving and the easier the ester is to hydrolyse. Incidentally the same reasoning can be used to explain acid strength above, resonance stability of carboxylate
ASPIRIN Aspirin is in a group of drugs called salicylates. It works by reducing substances in the body that cause pain, fever, and inflammation. It is used to treat mild to moderate pain, and also to reduce fever or inflammation. It is sometimes used to treat or prevent heart attacks, strokes, and angina. Aspirin should be used for cardiovascular conditions only under the supervision of a doctor. SYNTHESIS OF ASPIRIN Can be prepared by the esterification of the phenolic hydroxyl group of salicylic acid with the acetyl group from acetic anhydride or acetyl chloride. It involves primarily of 3 parts HOW TO MAKE ASPIRIN S Synthesize I Isolate P Purify SYNTHESIS The synthesis involves the reaction of salicylic acid and acetic anhydride in the presence of a catalyst, phosphoric acid, H3PO4. The synthesis of aspirin is classified as an esterification reaction. Salicylic acid is treated with acetic anhydride, an acid derivative, causing a chemical reaction that turns salicylic acid's hydroxyl group into an ester group. This process yields aspirin and acetic acid, which is considered a byproduct of this reaction. Small amounts of sulfuric acid (and occasionally phosphoric acid) are almost always used as a catalyst. WHY THE NEED FOR ACIDIC CATALYST? The minute amount of acid is needed to produce hydronium ions in the solution(both by dissociation and by water dissociation and this is why it is considered a catalyst because it is not consumed) The hydronium ions acts as the electrophile which attacks the acid anhydride which in turns attacks the salycilic acid. ISOLATION Once the aspirin is prepared it must be isolated from the reaction solution and purified. The aspirin is insoluble in cold water, and can be isolated by filtering the chilled reaction solution.
The aspirin is insoluble in cold water, and can be isolated by filtering the chilled reaction solution. Purification is necessary to remove any unreacted salicylic acid and acetic anhydride, as well as the acetic acid product and phosphoric acid. Acetic anhydride is caused to decompose by the addition of water once the formation of aspirin is complete:
ESTIMATION OF PURITY The melting point of a compound can be used to identify it and also to estimate its purity. Generally an impure compound will exhibit a melting point which is lower than that of the pure compound. Recrystallization Salicylic acid is only slightly soluble in water and is not completely removed in the washing step. The impure aspirin is dissolved in warm ethanol. The solution is then cooled slowly, and the aspirin crystallizes out of solution leaving the salicylic acid and other impurities behind. Explain why in the crystallization of aspirin, the water should not be heated above 80C Excess acetic anhydride present along with the aspirin decomposes upon heating. The reaction is exothermic and hot vapor and spattering of the solution may occur. Aspirin may degrade to form back into acetic anhydride and salicylic acid Explain the results obtained when aspirin and salicylic acid were treated with FeCl3 solution. The addition of ferric chloride to salicylic acid produces a specific color caused by the reaction of salicylic acid with aqueous ferric (Fe(H2O)6+3) ion. The oxygen atoms of the acid group COOH, and of the -OH group on the salicylic acid together can form a complex with Fe(H2O)6+3. That complex has an intense violet color. In aspirin, the OH group of salicylic acid has been replaced by a O-COCH group which prevents the second bond from being formed. The resulting complex with aspirin shows only a slight yellow color, not very different from that of Fe(H2O)6+3 itself. Another pharmaceutical product derived from salicylic acid is salol (phenyl salicylate), the phenyl ester of salicylic acid. Since phenol cannot be esterified by direct interaction with salicylic acid, some indirect method must be used. Write equations for a sequence that might be used to prepare salol from phenol and salicylic acid. Aspirin and salol are both acidic substances. Which is the stronger acid? Which would be more easily hydrolyzed in an alkaline medium? Why?
You might also like
- A Further Investigation of the Symmetrical Chloride of Paranitroorthosulphobenzoic AcidFrom EverandA Further Investigation of the Symmetrical Chloride of Paranitroorthosulphobenzoic AcidNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Experiment 9 FinalDocument7 pagesExperiment 9 FinalGneiss Louie Gem AlmazanNo ratings yet
- Full Report: Synthesis of AspirinDocument3 pagesFull Report: Synthesis of AspirinNor Ashikin IsmailNo ratings yet
- Aspirin SythesisDocument4 pagesAspirin Sythesiskramnuj92% (12)
- ASPIRINDocument3 pagesASPIRINVALDEZ, Teresita B.No ratings yet
- Laporan AspirinDocument16 pagesLaporan AspirinMUHAMMAD DIAN WARDANA PUTRANo ratings yet
- Exercise 11 Synthesis of Aspirin (Aceylsalicylic Acid From Salicylic Acid)Document8 pagesExercise 11 Synthesis of Aspirin (Aceylsalicylic Acid From Salicylic Acid)MNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab Report 1Document10 pagesChemistry Lab Report 1karyensamNo ratings yet
- Orgchem Formal ReportDocument6 pagesOrgchem Formal ReportKATHLEEN CALALANGNo ratings yet
- Aspirin SynthesisDocument10 pagesAspirin SynthesisCalleosisNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Synthesis of AspirinDocument5 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Synthesis of AspirinClarissa Macanas100% (1)
- Preparation of AspirinDocument12 pagesPreparation of AspirinYugaraj BalarNo ratings yet
- Aspirin 2007Document10 pagesAspirin 2007Dini KartikaNo ratings yet
- Synthesis and Analysis of AspirinDocument4 pagesSynthesis and Analysis of AspirinMich TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of AspirinDocument6 pagesSynthesis of AspirinVanessaOlgaJ.Dagondon100% (1)
- 03results and Discussion For AspirinDocument2 pages03results and Discussion For AspirinReg LagartejaNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Aspirin Results and DiscussionDocument9 pagesSynthesis of Aspirin Results and DiscussionGellie Dela Rosa Valencia33% (3)
- Preparation of Aspirin From Salicylic AcidDocument10 pagesPreparation of Aspirin From Salicylic AcidMoona SonikaNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Aspirin and Oil of WintergreenDocument5 pagesSynthesis of Aspirin and Oil of WintergreenJason Raquin Roque100% (3)
- Experiment 1 AspirinDocument4 pagesExperiment 1 AspirinMiin Devine100% (1)
- CHEM 251 Author's Name Institute's Name Due DateDocument8 pagesCHEM 251 Author's Name Institute's Name Due DateSepehrNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of AspirinDocument3 pagesSynthesis of AspirinShoomyla RashidNo ratings yet
- Exp4 chm456Document8 pagesExp4 chm456Mawar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Report Synthesis Aspirin Greef Rose Aulia 22923010Document12 pagesReport Synthesis Aspirin Greef Rose Aulia 22923010Greef Rose AuliaNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Acetyl Salicylic AcidDocument5 pagesSynthesis of Acetyl Salicylic AcidSilvia AryaniNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of AspirinDocument4 pagesSynthesis of Aspirinホアキン 印33% (3)
- The Synthesis of A Medicinal Agent-AspirinDocument5 pagesThe Synthesis of A Medicinal Agent-AspirinD ROYNo ratings yet
- Functional Groups: Naming of EstersDocument6 pagesFunctional Groups: Naming of EsterspappadakunduNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Aspirin and Oil of WintergreenDocument3 pagesSynthesis of Aspirin and Oil of WintergreenAnonymous orNHXM0f0No ratings yet
- 4.preparation of Acetylsalicylic AcidDocument10 pages4.preparation of Acetylsalicylic AcidYoussef KamounNo ratings yet
- Synthesizing Aspirin: A Medicinal AgentDocument5 pagesSynthesizing Aspirin: A Medicinal Agentoussama dieselNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Benzyl Acetate Through Fischer Esterification ReactionDocument10 pagesSynthesis of Benzyl Acetate Through Fischer Esterification ReactionAnonymous GO6JVW9Wud100% (4)
- Synthesis of Acetylsalicylic AcidDocument7 pagesSynthesis of Acetylsalicylic Acidjeniccax17No ratings yet
- Aspirin 1Document16 pagesAspirin 1Dini KartikaNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Theory: Experiment 2Document7 pages2.3 Theory: Experiment 2Abinet DinkinehNo ratings yet
- Aspirin Synthesis Catalyst ComparisonDocument12 pagesAspirin Synthesis Catalyst ComparisonArchit GargNo ratings yet
- D 03 ManDocument13 pagesD 03 ManNor Ashikin IsmailNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentKumar AryanNo ratings yet
- Formal Report - AspirinDocument4 pagesFormal Report - AspirinMeah PachecoNo ratings yet
- Chem Lab 2 EXP 21Document6 pagesChem Lab 2 EXP 21Kirthinee JegatheesanNo ratings yet
- Chem Lab 2 Exp 3Document8 pagesChem Lab 2 Exp 3Charishaa LaturiuwNo ratings yet
- Recrystallization and Aspirin (Full)Document30 pagesRecrystallization and Aspirin (Full)Irvandar Nurviandy0% (1)
- A. Experiment Title: The Making of N-Butyl Acetate B. Experiment Started Date: Wednesday, March 4Document21 pagesA. Experiment Title: The Making of N-Butyl Acetate B. Experiment Started Date: Wednesday, March 4Era MelaniaNo ratings yet
- Synthesize Aspirin from Salicylic AcidDocument23 pagesSynthesize Aspirin from Salicylic AcidCyrene MBolañosNo ratings yet
- EsterDocument16 pagesEsterBk CmNo ratings yet
- Formal Report - Group 2Document6 pagesFormal Report - Group 2Ayshee CapuchinoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 9Document6 pagesExperiment 9clairedemotica100% (1)
- Laporan AspirinDocument14 pagesLaporan AspirinErna KristinaNo ratings yet
- Laporan AspirinDocument15 pagesLaporan AspirinAnonymous ldgGa5LYNo ratings yet
- Aspirin 2Document8 pagesAspirin 2saniyabora87No ratings yet
- Isolation of Acetylsalicylic Acid from Aspirin TabletsDocument4 pagesIsolation of Acetylsalicylic Acid from Aspirin TabletsPrince Pulvera100% (1)
- EsterificareaDocument43 pagesEsterificareaMahagney SalehNo ratings yet
- Chem 101.1 Back Titration Formal ReportDocument5 pagesChem 101.1 Back Titration Formal ReporttoopiarNo ratings yet
- ESTERS: Derivatives of Carboxylic AcidsDocument13 pagesESTERS: Derivatives of Carboxylic AcidsMohd NazriNo ratings yet
- Result and Discussion of Fecl3 and Starch Test Wi AspirinDocument3 pagesResult and Discussion of Fecl3 and Starch Test Wi AspirinKc CalderonNo ratings yet
- How To Make AspirinDocument5 pagesHow To Make Aspirinthomas9631No ratings yet
- Aspirin SynthesisDocument13 pagesAspirin SynthesisJM DreuNo ratings yet
- Reactions and Uses of EstersDocument14 pagesReactions and Uses of Estersdela2No ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterNo ratings yet
- The Empyrean TubeDocument8 pagesThe Empyrean TubeLucas RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Proposed waiting shed in Lumbia, Cagayan de Oro CityDocument7 pagesProposed waiting shed in Lumbia, Cagayan de Oro CityMac KYNo ratings yet
- Chem 340 Hw6 Key 2011 Physical Chemistry For Biochemists 1Document18 pagesChem 340 Hw6 Key 2011 Physical Chemistry For Biochemists 1andrevini89No ratings yet
- Readymix ProfileDocument33 pagesReadymix ProfileAyman HammodehNo ratings yet
- Waterproofing: Part - 8 Waterproofing and Low Energy Consumption Roofing SystemsDocument20 pagesWaterproofing: Part - 8 Waterproofing and Low Energy Consumption Roofing SystemsVaishamNo ratings yet
- Resistivity Log: Well Logging (Pe413)Document9 pagesResistivity Log: Well Logging (Pe413)Ramy MaamounNo ratings yet
- Wilma Ty Nueva SpecificationsDocument10 pagesWilma Ty Nueva SpecificationsJubs DejitoNo ratings yet
- Product Data Sheet: Product Description Product Description Product Description Product DescriptionDocument3 pagesProduct Data Sheet: Product Description Product Description Product Description Product DescriptionVaittianathan MahavapillaiNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Physics and Chemistry Notes: Temperature & HeatDocument1 pageClass 7 Physics and Chemistry Notes: Temperature & Heatishwari vermaNo ratings yet
- The First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument10 pagesThe First Law of ThermodynamicsArpit PatelNo ratings yet
- Dow Science Paper-A Commercially Viable Solution Process To Control Long-Chain Branching in PolyethyleneDocument1 pageDow Science Paper-A Commercially Viable Solution Process To Control Long-Chain Branching in Polyethylenefengshaohua_gmailNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Welding Procedure Specification Pwps PDF FreeDocument1 pagePreliminary Welding Procedure Specification Pwps PDF FreeFirozNo ratings yet
- Groove Boards by Jaali in PDFDocument44 pagesGroove Boards by Jaali in PDFGunjan ShahNo ratings yet
- Cofran Marathon Premium 15w40 enDocument1 pageCofran Marathon Premium 15w40 enAhmed KabbajNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Municipal Solid Waste in Yenagoa Metropolis and Its Associated Management Problems, NigeriaDocument9 pagesCharacterization of Municipal Solid Waste in Yenagoa Metropolis and Its Associated Management Problems, NigeriaIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- MSDS Intersorb Nonindicating Diving GradeDocument5 pagesMSDS Intersorb Nonindicating Diving GradeEdward BennettNo ratings yet
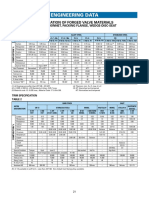
- Forged Engineering DataDocument4 pagesForged Engineering DataretrogradesNo ratings yet
- 1sdg3y7p9 - AdGE Module 12-Rev Covalent CompoundsDocument15 pages1sdg3y7p9 - AdGE Module 12-Rev Covalent CompoundsJohn RomasantaNo ratings yet
- KHKKKDocument39 pagesKHKKKdaney67299No ratings yet
- The Ncuk International Foundation Year IFYCH002 Chemistry End of Semester 1 Test 2018-19Document12 pagesThe Ncuk International Foundation Year IFYCH002 Chemistry End of Semester 1 Test 2018-19Mfanafuthi100% (1)
- Platinum Silicone Paint Base: Product OverviewDocument2 pagesPlatinum Silicone Paint Base: Product OverviewGrace LNo ratings yet
- Reseach Paper On BAMBOO Its Use and ConstructionDocument10 pagesReseach Paper On BAMBOO Its Use and Constructionsimran deoNo ratings yet
- Discussion Exp 2 PicklingDocument2 pagesDiscussion Exp 2 PicklingFarah Izzati100% (6)
- ASTM E 165 - 2012 (Standard Practice For Liquid Penetrant Examination For General Industry) - 2012Document18 pagesASTM E 165 - 2012 (Standard Practice For Liquid Penetrant Examination For General Industry) - 2012omar quiñonesNo ratings yet
- Thin Layer Chromatography NSDocument32 pagesThin Layer Chromatography NSAnand NanavatyNo ratings yet
- Plasma SterilizationDocument28 pagesPlasma SterilizationSutan Muhamad SadamNo ratings yet
- Moles and Equations WorksheetDocument3 pagesMoles and Equations WorksheetArshad KhanNo ratings yet
- 5 SLS RequiermentsDocument13 pages5 SLS RequiermentssuniljayaNo ratings yet
- Basic Type Heat ExchangerDocument25 pagesBasic Type Heat ExchangerTaifurNo ratings yet
- Is 10500 SpecificationDocument10 pagesIs 10500 SpecificationbrahmishtanNo ratings yet