Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Glossary
Uploaded by
Felipe FCOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Glossary
Uploaded by
Felipe FCCopyright:
Available Formats
Glossary
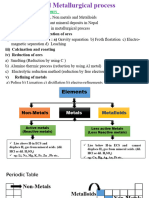
Blster copper: An impure intermediate product in the refining of copper, produced by blowing copper matte in a converter. Crush: Breakage of supports of underground workings under roof pressure. Froth flotation 1. A flotation process in which the minerals floated gather in and on the surface of bubbles of air or gas driven into or generated in the liquid in some convenient manner. 2. The separating of finely crushed minerals from one another by causing some to float in a froth and others to remain in suspension in the pulp. Oils and various chemicals are used to activate, make floatable, or depress the minerals. 3. A process for cleaning fine coal, copper, lead, zinc, phosphate, kaolin, etc. with the aid of a reagent; the coal or minerals become attached to air bubbles in a liquid medium and float as a froth. Gangue: 1. (Metallurgy) valueless and undesirable material, such as quartz in small quantities, in an ore 2. (Mining & Quarrying) valueless and undesirable material, such as quartz in small quantities, in an ore. Grinding: 1. Size reduction into fine particles; comminution. See also: dry grinding; wet grinding 2. The process of erosion by which rock fragments are worn down, crushed, sharpened, or polished through the frictional effect of continued contact and pressure by larger fragments. Quarry: An open or surface mineral working, usually for the extraction of building stone, as slate, limestone, etc. It is distinguished from a mine because a quarry usually is open at the top and front, and, in ordinary use of the term, by the character of the material extracted. Layer: A bed or stratum of rock. Molten: (Especially of materials with a high melting point, such as metal and glass) liquefied by heat. Ore: 1.- a metal-bearing mineral or rock, or a native metal, that can be mined at a profit. 2.- a mineral or natural product serving as a source of some nonmetallic substance, as sulfur. Scrap: Discarded metallic material, from whatever source, which may be reclaimed through melting and refining.
Sedimentary: adj. Pertaining to or containing sediment; e.g., sedimentary deposit or a sedimentary complex. Shaft: excavation in the earth from which ores and minerals are extracted. Roasting: 1. Heating an ore to effect some chemical change that will facilitate smelting. 2. The operation of heating sulfide ores in air to convert to oxide or sulfate. 3. Calcination, usually with oxidation. Good, dead, or sweet roasting is complete roasting; i.e., it is carried on until sulfurous and arsenious fumes cease to be given off. Kernel roasting is a process of treating poor sulfide copper ores, by roasting in lumps, whereby copper and nickel are concentrated in the interior of the lumps. 4. The heating of solids, frequently to promote a reaction with a gaseous constituent in the furnace atmosphere. See also: magnetizing roast
You might also like
- Job DefinitionsDocument1 pageJob DefinitionsFelipe FCNo ratings yet
- Practice 3: Simple CoordinationDocument3 pagesPractice 3: Simple CoordinationFelipe FCNo ratings yet
- Types of Coordination 1Document12 pagesTypes of Coordination 1Felipe FCNo ratings yet
- Writing Academic English (Fourth Edition)Document181 pagesWriting Academic English (Fourth Edition)Felipe FC94% (33)
- Signal Phrases to Introduce Source MaterialDocument1 pageSignal Phrases to Introduce Source MaterialFelipe FCNo ratings yet
- Answer PDFDocument64 pagesAnswer PDFFelipe FCNo ratings yet
- Linking Verbs ExplainedDocument1 pageLinking Verbs ExplainedFelipe FCNo ratings yet
- VegetablesDocument1 pageVegetablesFelipe FCNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Metal and ExtractionDocument57 pagesMetal and ExtractionMirawati EfendiNo ratings yet
- Metals and Metallurgy Note XiDocument50 pagesMetals and Metallurgy Note Xidjalokfree11No ratings yet
- Calcination and RoastingDocument4 pagesCalcination and Roastingmohamed ElsayedNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy in 1 ShotDocument62 pagesMetallurgy in 1 ShotArsalan UddinNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy (Mega)Document20 pagesMetallurgy (Mega)Anant JainNo ratings yet
- Lec-01 PyrometallurgyDocument48 pagesLec-01 PyrometallurgyTanvir HossainNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0304386X02001391 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S0304386X02001391 MainPetras PetricaNo ratings yet
- Aluminium Dross Waste - Topics by Science - GovDocument198 pagesAluminium Dross Waste - Topics by Science - GovPramod Reddy TilletiNo ratings yet
- Extraction of Manganese From Ferro-Manganese Slag: 'Karnataka Regional F, Rrgineerirtg College, Suratlrkal, IndiaDocument7 pagesExtraction of Manganese From Ferro-Manganese Slag: 'Karnataka Regional F, Rrgineerirtg College, Suratlrkal, IndiaravibelavadiNo ratings yet
- Study Material Class 10 Chapter 3 2017 PDFDocument10 pagesStudy Material Class 10 Chapter 3 2017 PDFKaran Pratap67% (3)
- 12th Chemistry V1 EM LowResDocument296 pages12th Chemistry V1 EM LowResSri VatsanNo ratings yet
- Pyrometalllurgy ModuleDocument66 pagesPyrometalllurgy ModuleFelix TinasheNo ratings yet
- Ores and MetallurgyDocument37 pagesOres and MetallurgyGurshaan Singh BajajNo ratings yet
- Hydrometallurgy Part 1Document88 pagesHydrometallurgy Part 1Ayman AydanNo ratings yet
- Oxidation of Iron?Ore PelletsDocument4 pagesOxidation of Iron?Ore PelletsKrol PrietoNo ratings yet
- Std12 Chemistry EM 1 WWW - Tntextbooks.inDocument296 pagesStd12 Chemistry EM 1 WWW - Tntextbooks.inSeetha Lakshmi PalaniswamyNo ratings yet
- 10.0 Introduction To Pyrometallurgy 13.05.2020Document10 pages10.0 Introduction To Pyrometallurgy 13.05.2020Joshua LunguNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Unit 1 Study Material em 215343Document28 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Unit 1 Study Material em 215343HarishNo ratings yet
- Environmentally Friendly Extraction of Gold From Refractory Concentrate Using A Copper - Ethylenediamine - Thiosulfate SolutionDocument13 pagesEnvironmentally Friendly Extraction of Gold From Refractory Concentrate Using A Copper - Ethylenediamine - Thiosulfate SolutionAldoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16Document4 pagesLecture 16Ahmad Wildan ZakawaliNo ratings yet
- Fathi Habashi PYRITE THE STRATEGIC MINERAL THAT BECAME AN INDUSTRIAL NUISANCE PDFDocument16 pagesFathi Habashi PYRITE THE STRATEGIC MINERAL THAT BECAME AN INDUSTRIAL NUISANCE PDFboanerges wino pattyNo ratings yet
- Chem MCQ MetalsDocument8 pagesChem MCQ MetalsArundathyNo ratings yet
- 12C 29 Extractive Metallurgy PDFDocument63 pages12C 29 Extractive Metallurgy PDFgovind_galamNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3: Metals and Non MetalsDocument23 pagesChapter - 3: Metals and Non Metalsuma mishraNo ratings yet
- 2 How Ore Minerals Are Mined and UsedDocument45 pages2 How Ore Minerals Are Mined and UsedEsther Ruth santillanNo ratings yet
- 01-Metals & Non MetalsDocument23 pages01-Metals & Non Metalssandeep kumar yadavNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Chloride Leaching of Base Metal SulphidesDocument15 pagesAtmospheric Chloride Leaching of Base Metal SulphidesDennis Daniel Condori EspilcoNo ratings yet
- The Manufacturing Process of LeadDocument10 pagesThe Manufacturing Process of LeadJACKULIN DAFNEENo ratings yet
- Jitendra Hirwani: Inorganic ChemistryDocument7 pagesJitendra Hirwani: Inorganic ChemistryabhishekNo ratings yet
- MetallurgyDocument40 pagesMetallurgyMothi KarunaNo ratings yet