Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Systematic Outline of Basic Human Needs
Uploaded by
api-252173623Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A Systematic Outline of Basic Human Needs
Uploaded by
api-252173623Copyright:
Available Formats
A Systematic Outline of Basic Human Needs
PHYSIOLOGICAL NEEDS
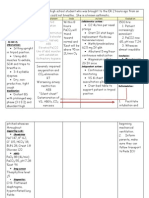
I. Physiological Homeostasis A. Oxygenation (The Big O) 1. Patent airway (trachea, bronchus, smaller branches) 2. Ability to move the air in and out of the airway a. Neurological 1) Respiratory Control Centers 2) Connections from brain to muscles b. Chest wall and pleural space intact c. Diaphragm can move 3. Sufficient amounts of oxygen can move across the alveolar membrane a. There is enough alveolar membrane available for diffusion b. All the alveolae that have oxygen in them are adequately perfused 4. There is enough hemoglobin to transport oxygen to the tissues 5. The heart works well enough to move the oxygen to the tissues 6. There is no blockage between the heart and the tissues that need oxygen B. Fluid and Electrolytes, Acid-Base Balance 1. Enough fluid in the body to provide necessary volume in vasculature a. Intake is unimpeded b. Kidneys are able to get rid of excess 2. Fluid has the right balance of cations and anions 3. No excess production of acids (volatile or fixed) a. CO2 is lost via respiration at the same rate it is being producedb. b. Kidneys are able to excrete fixed acids at the rate they are produced C. Nutrition 1. Appropriate intake of calories (in correct balance of carbohydrate, protein, fats) 2. Appropriate intake of vitamins and trace elements 3. Normal digestive processing and absorption of nutrients 4. Maintenance of adequate blood glucose
5. Normal transport of nutrients into cells. (Insulin) D. Elimination 1. Waste products of metabolism eliminated appropriately by liver and kidney 2. Bulk waste product of food intake eliminated normally by bowel E. Rest and Recovery 1. Normal sleep 2. Ability to rest comfortably in balance with normal activity F. Mobility 1. Ability to move all body parts in coordinated fashion 2. Normal weight-bearing capacity 3. Normal balance G. Physiological Safety Systems 1. Functioning cortex (ability to respond appropriately to environment) 2. Special senses (sight, hearing, smell, taste) 3. Appropriate autonomic function 4. Intact skin, mucous membranes and other defensive barriers 5. Functioning immune system 6. Balanced coagulation 7. Intact hypothalamic action a. Endocrine function (thyroid, cortisol etc.) b. Osmo-regulation c. Maintenance of normal body temperature II. Safety and Security (Situational Safety as opposed to physiological safety mentioned above.) A. Prevention of disease and normal health maintenance autonomy B. Regular supply of food and water C. Shelter sufficient to meet basic human needs dependably D. Control over events, predictability of (known) future E. Public Health systems F. Safety from physical violence and abuse G. Civil society, a legal system providing justice III. Love and Belongingness A. Normal affection and intimacy B. Membership in group with shared history and ideology (Roots) C. Placement in family and community IV. Self Esteem A. Competence and mastery B. Earned respect C. Dignity and positive reputation D. Independence E. Respect for others V. Self-Actualization A. Life mission and purpose B. Fulfillment of life goal C. A domain of ones own
You might also like
- Dka CRTDocument4 pagesDka CRTapi-252173623No ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes Mrs RDocument3 pagesFluid and Electrolytes Mrs Rapi-252173623No ratings yet
- Copd Exascerbation CRTDocument5 pagesCopd Exascerbation CRTapi-252173623No ratings yet
- A Systematic Outline of Basic Human Needs - OxygenDocument1 pageA Systematic Outline of Basic Human Needs - Oxygenapi-252173623No ratings yet
- Anemia CRTDocument4 pagesAnemia CRTapi-252173623No ratings yet
- Maslovian Approach To Clinical Reasoning - Higher Order NeedsDocument2 pagesMaslovian Approach To Clinical Reasoning - Higher Order Needsapi-252173623No ratings yet
- Asthma Patient CRTDocument2 pagesAsthma Patient CRTapi-252173623No ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes Mrs RDocument3 pagesFluid and Electrolytes Mrs Rapi-252173623No ratings yet
- Maslovian Approach To The Clinical Reasoning - Physiological Needs Big FontDocument13 pagesMaslovian Approach To The Clinical Reasoning - Physiological Needs Big Fontapi-252173623No ratings yet
- Blank CRTDocument2 pagesBlank CRTapi-252173623No ratings yet
- A Patient With Epilepsy Alcoholism and Pneumonia CRTDocument1 pageA Patient With Epilepsy Alcoholism and Pneumonia CRTapi-252173623No ratings yet
- Asthma Patient CRT With Evaluation and ReformulationDocument3 pagesAsthma Patient CRT With Evaluation and Reformulationapi-252173623No ratings yet
- Clinical Reasoning For MR F - Heme IssuesDocument1 pageClinical Reasoning For MR F - Heme Issuesapi-252173623No ratings yet
- Asthma Patient CRTDocument2 pagesAsthma Patient CRTapi-252173623No ratings yet
- Asthma Patient CRTDocument2 pagesAsthma Patient CRTapi-252173623No ratings yet
- Clinical Reasoning For MR F - NextDocument1 pageClinical Reasoning For MR F - Nextapi-252173623No ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Work Procedure For CCB Installation of Raised Floor 2Document13 pagesWork Procedure For CCB Installation of Raised Floor 2ResearcherNo ratings yet
- Battery: Ultrasonic Welding TechnologyDocument12 pagesBattery: Ultrasonic Welding TechnologyNam Cao HuỳnhNo ratings yet
- JSS20-48 Single Time Control Digital Display Time Relay: Page 1 / 2Document2 pagesJSS20-48 Single Time Control Digital Display Time Relay: Page 1 / 2FranciscoNo ratings yet
- SKC EPAM-5000 Instruction Manual PDFDocument90 pagesSKC EPAM-5000 Instruction Manual PDFmegacobNo ratings yet
- Higuey, Dom Rep Mdpc/Puj: .Eff.23.MayDocument5 pagesHiguey, Dom Rep Mdpc/Puj: .Eff.23.MayVanessa Yumayusa0% (1)
- Mms For Household Uses-S.pardee-1Document7 pagesMms For Household Uses-S.pardee-1Manny JorgeNo ratings yet
- JD - Hygiene Promotion OfficerDocument2 pagesJD - Hygiene Promotion OfficerBeauty ChigwazaNo ratings yet
- YUMMY TUMMY - Beef Biryani Recipe - Beef Dum Biryani RecipeDocument48 pagesYUMMY TUMMY - Beef Biryani Recipe - Beef Dum Biryani RecipeWilliam Cj LyngdohNo ratings yet
- Electrical ManualDocument145 pagesElectrical ManualAbhishek KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Rules of SungazingDocument2 pagesRules of SungazingaustralexdiNo ratings yet
- Red Velvet Cake RecipeDocument6 pagesRed Velvet Cake RecipeRuminto SubektiNo ratings yet
- PreparationDocument2 pagesPreparationmghaffarzadehNo ratings yet
- Ate-U2 - Steam Boilers - PPT - Session 3Document13 pagesAte-U2 - Steam Boilers - PPT - Session 3MANJU R BNo ratings yet
- Pronunciation Pairs Unit 2-6 Answer KeyDocument5 pagesPronunciation Pairs Unit 2-6 Answer KeyChloe Liu50% (2)
- Desensitization ProtocolsDocument28 pagesDesensitization ProtocolsAnonymous 9dVZCnTXSNo ratings yet
- List of Job Specific Safety PPE Used On Site.Document2 pagesList of Job Specific Safety PPE Used On Site.Aejaz MujawarNo ratings yet
- Evonik Copi BrochureDocument5 pagesEvonik Copi BrochureRovshan HasanzadeNo ratings yet
- List of Employees with Start and End DatesDocument394 pagesList of Employees with Start and End DatesMuhammad Faishal TazakkaNo ratings yet
- Establishment of Retirement PlanDocument3 pagesEstablishment of Retirement PlanVioleta StancuNo ratings yet
- RRL CapstoneDocument3 pagesRRL CapstoneMatthew Dane SitoNo ratings yet
- ClindamycinDocument1 pageClindamycinTanalie Dulawan100% (3)
- 02-Plant Morphology (Exercise)Document5 pages02-Plant Morphology (Exercise)varshavishuNo ratings yet
- Schematic 1280 - So Do Nokia 1 PDFDocument18 pagesSchematic 1280 - So Do Nokia 1 PDFanh3saigon0% (1)
- Crypto Hash Algorithm-Based Blockchain Technology For Managing Decentralized Ledger Database in Oil and Gas IndustryDocument26 pagesCrypto Hash Algorithm-Based Blockchain Technology For Managing Decentralized Ledger Database in Oil and Gas IndustrySIMON HINCAPIE ORTIZNo ratings yet
- AquaNereda Brochure 1017 WebDocument4 pagesAquaNereda Brochure 1017 WebdmnNo ratings yet
- DSI-DYWIDAG Geotechnics Rock Bolts enDocument6 pagesDSI-DYWIDAG Geotechnics Rock Bolts enTomás Nunes da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Corrosion and Its Objective QuestionsDocument2 pagesCorrosion and Its Objective QuestionsSrinivasan Alagappan100% (4)
- New Haven Harbor Connecticut Navigation Improvement Project Integrated Feasibility Report and Environmental Impact StatementDocument23 pagesNew Haven Harbor Connecticut Navigation Improvement Project Integrated Feasibility Report and Environmental Impact StatementHelen BennettNo ratings yet
- Litreature On Automatic Dipper Circuit For Vehicle-2Document10 pagesLitreature On Automatic Dipper Circuit For Vehicle-2Rushikesh TajneNo ratings yet
- Ransburg 76652 01 - 04Document24 pagesRansburg 76652 01 - 04enticoNo ratings yet