Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Customs and Excise by M.H Ali
Uploaded by
Syed Fawad Ali Shah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesAccounting Glossary of Terms
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAccounting Glossary of Terms
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesCustoms and Excise by M.H Ali
Uploaded by
Syed Fawad Ali ShahAccounting Glossary of Terms
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
4/9/2014
Business organization by M.H Ali
Syed Fawad Ali Shah
CHAPTER FROM BUSINESS ORGANIZATION BY M.H ALI PAGE 332-335
(In the Book Of Business Organization by M.H Ali on page332-335)
1
Custom and excise
April 9, 2014
Duty is nothing but the taxes levied on the gods by the government. The principal aim of duty is to increase the revenue of the
government. Another object of duty is to restrain the people from the use of some particular commodity. Duty may be of two types:
A Custom duty is levied upon the goods which pass out of or enter into a country. Thus it is a duty which is levied upon the imports
and exports. The duty imposed on the imported goods is termed as import Duty and the duty levied on exported goods is known as Export
Duty.
There are two main objectives of Customs Duty. Firstly, it gives revenue to the government and secondly, it protects home industry.
If an import duty is imposed without corresponding excise duty on the domestic products, the prices of the imported goods rise up. This gives
an opportunity to the home industry to compete with the foreign goods. In this way, the import duty gives protection to the home industry. To
make an import duty fully protective, it should be adequate for prohibiting imports. A fully protective import duty should yield no revenue.
In export duty is mainly imposed for increasing revenue of the government. It is usually levied on a commodity which is in the nature
of monopoly. Sometimes it is also levied for restricting of prohibiting exports for strategic or other considerations.
From different points of view, custom duty may be classified into various classes. Broadly speaking, it may be either import Duty or
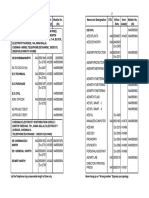
Export Duty as described previously. The import and Export Duties may again be sub-divided into some classes. A chart showing the different
types of Import and export Duties is given below:
When the duty is levied on the imported goods for the purpose of collecting some revenue and swelling the figures of the
exchequer, it is known as Revenue Custom Duty. When the duty is imposed in the imported goods with a view to protecting or safeguarding
national industries, it is called Protective Import Duty.
Similarly, when the duty is imposed on the exported goods for the purpose of collecting revenue for the government it is called
Revenue Export Duty. When the duty is levied on the exported goods in order to protecting and safeguarding national industries it is termed as
Protective Export Duty.
The Revenue and Protective duties may again be divided into two classes Ad valorem Duty and Specific Duty. When the duty is
levied on the value of the goods or the quality of the goods, irrespective of their quantity, it is called on Ad valorem Duty. On the other hand,
when the duty is levied on the quantity of the goods, irrespective of their value, it is said to be a Specific Duty.
An Excise Duty is a sort of tax, levied upon the commodities produced and consumed within a country. In Pakistan, there is excise
duty on pans, drugs, opium etc. Excise Duty may also be levied upon other than goods, e.g. entertainment taxes, duties on patents, etc.
The main object of an Excise Duty is to raise the revenue for the government. As revenue is the main objective of our excise duty, it
is imposed upon a commodity of general consumption. Sometimes, the excise duty is imposed upon a commodity with a view to discouraging
or stopping its consumption.
Customs Duty
Import duty
Revenue
Custom Duty
Ad valorem
Duty
Specific Duty
Protective
Custom Duty
Ad valorem
Duty
Specific Duty
Export Duty
Revenue
Export Duty
Ad valorem
Duty
Specific Duty
Protectie
Export Duty
Ad valorem
Duty
Specific Duty
(In the Book Of Business Organization by M.H Ali on page332-335)
2
Custom and excise
April 9, 2014
An excise duty cannot protect or safeguard a national industry. If excise duties are levied upon a commodity which competes with
an imported article, the protective effect of an excise duty is removed by levying an equivalent import duty on the competitive foreign
countries,
The following are the points of distinction between the Customs Duty and the Excise Duty:
(a) The Place of production and consumption of the goods of Customs Duty is not the same. These goods are produced in one country
and consumed in another country. But the place of production and consumption of the goods of Excise Duty is the same. These
goods are produced in one country and consumed in the same country.
(b) The objects of the Customs Duty are to protect, safeguard and develop the national industries, to control exports and imports and
also to raise revenue for the government; while the aims of the Excise Duty are to raise revenue for the government and to control
the use of those articles which are harmful to health.
(i) Drawback: When an Excise Duty or Import Duty is imposed upon a commodity which is meant for domestic consumption, a
refund of the duty paid may be claimed, if the commodity is exported. Such a refund is termed as Drawback and this refund is
made by a document called Debenture. This debenture is transferable by endorsement and signature. Drawback is also paid for
a commodity, which has already paid Excise Duty, is exported, as the same commodity cannot be taxed twice.
(ii) Bounty: Bounty is a bonus or financial aid given by a government to encourage its development and to increase the
exportation of its products. It is given in proportion to output.
(iii) Subsidy: Subsidy denotes a lump sum of money which is given by a government to an industry with a view to competing with
the established foreign industry. Sometimes subsidy is granted to an industry by the government on the Coalition that it will
render some services to the state:
Though both bounty and subsidy are actual payments made by a government with a view to encouraging production and
exportations. Yet there is a difference between them.
(a) Bounty is a payment of a definite sum per unit commodity produced or exported, while subsidy is a payment of
lump-sum.
(b) Bounty confers benefits on a particular industry, a subsidy is given with the primary idea of benefiting a nation.
QUESTIONS
1. What is the difference between Customs Duties and Excise Duties? Give a broad classification of Customs Duties.
2. What do you mean by duty on goods and why is it levied? Distinguish clearly between Customs Duty and Excise Duty.
3. Explain the meaning of the terms:
(a) Drawback,
(b) Bounties,
(c) Subsidies.
4. Write short notes on (a) Customs Duty and (b) Excise Duty. (D.U. 1965)
5. What is the difference between the Revenue Duty and Protective Duty?
Explain clearly why the government of a country imposes Protective Duty upon foreign import of goods which are also manufactured
within the country.
6. Write notes on: Customs and Excise. (D.U. 1968)
You might also like
- My Tests KPPSCDocument1 pageMy Tests KPPSCSyed Fawad Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Software ArchitectureDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Software ArchitectureSyed Fawad Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Fgo FormDocument3 pagesFgo FormAbdul BasitNo ratings yet
- FPSC Adv 22018Document8 pagesFPSC Adv 22018kawashNo ratings yet
- First 10 General Elections of PakistanDocument84 pagesFirst 10 General Elections of PakistanSyed Fawad Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Islamiat Solved MCQS 2005 To 2011Document8 pagesIslamiat Solved MCQS 2005 To 2011alibutt000192% (12)
- Comparative Study of ReligionsDocument4 pagesComparative Study of ReligionsAmir SultanNo ratings yet
- 4K UltraHD TorrentsDocument4 pages4K UltraHD TorrentsSyed Fawad Ali Shah0% (2)
- Working For The Few: Political Capture and Economic InequalityDocument32 pagesWorking For The Few: Political Capture and Economic InequalityOxfamNo ratings yet
- Physical Geography SyllabusDocument2 pagesPhysical Geography SyllabusSyed Fawad Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Ijtihad PDFDocument5 pagesIjtihad PDFZeeshan Ali100% (1)
- PMS Syllabus PDFDocument25 pagesPMS Syllabus PDFSyed Fawad Ali Shah0% (1)
- Economic System in Islam PDFDocument6 pagesEconomic System in Islam PDFZeeshan AliNo ratings yet
- Blasphemy (Response of Islam & Other Religion - Class WorkDocument14 pagesBlasphemy (Response of Islam & Other Religion - Class WorkSyed Fawad Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Unesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Population GeographyDocument9 pagesUnesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Population GeographySyed Fawad Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Sentence Correction Solved Class WorkDocument14 pagesSentence Correction Solved Class WorkRai AhsanNo ratings yet
- RandDocument1 pageRandSyed Fawad Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Direct & Indirect Speech PDFDocument29 pagesDirect & Indirect Speech PDFZeeshan Ali100% (3)
- Divine Authority, by Orson Pratt 1Document22 pagesDivine Authority, by Orson Pratt 1Syed Fawad Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- How To Write Great EssaysDocument127 pagesHow To Write Great Essaysa100% (25)
- CLLDocument1 pageCLLaymenNo ratings yet
- Concept of God in Major World Religions - Dr. Zakir NaikDocument29 pagesConcept of God in Major World Religions - Dr. Zakir NaikArshad Farooqui100% (5)
- English Grammar - ExercisesDocument224 pagesEnglish Grammar - ExercisesSyed Fawad Ali Shah100% (7)
- Peer e KamilDocument382 pagesPeer e KamilSyed Fawad Ali Shah92% (24)
- Peer e KamilDocument382 pagesPeer e KamilSyed Fawad Ali Shah92% (24)
- Peer e KamilDocument382 pagesPeer e KamilSyed Fawad Ali Shah92% (24)
- PTCL Student Package Subcription PDFDocument1 pagePTCL Student Package Subcription PDFSyed Fawad Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Build Your Career PDFDocument31 pagesBuild Your Career PDFSyed Fawad Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Time Management PDFDocument12 pagesTime Management PDFBesart KryeziuNo ratings yet
- Importance of Studying Economics ExplainedDocument2 pagesImportance of Studying Economics ExplainedSyed Fawad Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Lumad Struggle for Land and Culture in the PhilippinesDocument10 pagesLumad Struggle for Land and Culture in the PhilippinesAlyssa Molina100% (1)
- DBBL (Rasel Vai)Document1 pageDBBL (Rasel Vai)anik1116jNo ratings yet
- COA - M2017-014 Cost of Audit Services Rendered To Water DistrictsDocument5 pagesCOA - M2017-014 Cost of Audit Services Rendered To Water DistrictsJuan Luis Lusong67% (3)
- Edwin Vieira, Jr. - What Is A Dollar - An Historical Analysis of The Fundamental Question in Monetary Policy PDFDocument33 pagesEdwin Vieira, Jr. - What Is A Dollar - An Historical Analysis of The Fundamental Question in Monetary Policy PDFgkeraunenNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument1 pageAssignmentdibakar dasNo ratings yet
- Eco - Grade 9 Question Bank 15-16Document13 pagesEco - Grade 9 Question Bank 15-16Vedic MantriNo ratings yet
- Assumptions in EconomicsDocument9 pagesAssumptions in EconomicsAnthony JacobeNo ratings yet
- Extra Oligopolio PDFDocument17 pagesExtra Oligopolio PDFkako_1984No ratings yet
- 01 Fairness Cream ResearchDocument13 pages01 Fairness Cream ResearchgirijNo ratings yet
- International Finance - TCS Case StudyDocument22 pagesInternational Finance - TCS Case StudyPrateek SinglaNo ratings yet
- Receipt Voucher: Tvs Electronics LimitedDocument1 pageReceipt Voucher: Tvs Electronics LimitedKrishna SrivathsaNo ratings yet
- SHFL Posting With AddressDocument8 pagesSHFL Posting With AddressPrachi diwateNo ratings yet
- 25818Document273 pages25818Amir KhanNo ratings yet
- Customer Master Data Views in CMDDocument22 pagesCustomer Master Data Views in CMDVasand SundarrajanNo ratings yet
- Impacts of Globalization on Indian AgricultureDocument2 pagesImpacts of Globalization on Indian AgricultureSandeep T M SandyNo ratings yet
- Tao Wang - World Bank Experience On Carbon Finance Operations in BiogasDocument20 pagesTao Wang - World Bank Experience On Carbon Finance Operations in BiogasEnergy for AllNo ratings yet
- 2nd Annual Latin America Rail Expansion SummitDocument16 pages2nd Annual Latin America Rail Expansion SummitenelSubteNo ratings yet
- 03 - Review of Literature PDFDocument8 pages03 - Review of Literature PDFDevang VaruNo ratings yet
- Instructor'S Manual Instructor'S Manual: An Introduction To Business Management 8Document18 pagesInstructor'S Manual Instructor'S Manual: An Introduction To Business Management 8arulsureshNo ratings yet
- YMCA 2010 Annual Report - RevisedDocument8 pagesYMCA 2010 Annual Report - Revisedkoga1No ratings yet
- IIP - Vs - PMI, DifferencesDocument5 pagesIIP - Vs - PMI, DifferencesChetan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Daily LogDocument14 pagesDaily Logdempe24No ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Planning The Firm's Financing Mix2Document88 pagesChapter 16 Planning The Firm's Financing Mix2api-19482678No ratings yet
- Current Org StructureDocument2 pagesCurrent Org StructureJuandelaCruzVIIINo ratings yet
- Balakrishnan MGRL Solutions Ch06Document64 pagesBalakrishnan MGRL Solutions Ch06deeNo ratings yet
- Upstox ApplicationDocument40 pagesUpstox ApplicationMilan K VachhaniNo ratings yet
- Dissertation NikhilDocument43 pagesDissertation NikhilSourabh BansalNo ratings yet
- Act 51 Public Acts 1951Document61 pagesAct 51 Public Acts 1951Clickon DetroitNo ratings yet
- BIM Report 2019Document31 pagesBIM Report 2019ziddar100% (1)
- CH North&south PDFDocument24 pagesCH North&south PDFNelson Vinod KumarNo ratings yet