Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Action: Indications:: Drug: Oxygen Class of Medication: Oxidizing Agent (Gas)
Uploaded by
AndreasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Action: Indications:: Drug: Oxygen Class of Medication: Oxidizing Agent (Gas)
Uploaded by
AndreasCopyright:
Available Formats
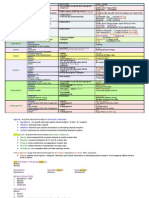
Drug: OXYGEN
Generic
Class of medication: Oxidizing agent (gas)
ACTION: Reverses Hypoxia, Increases arterial oxygen, Increases hemoglobin saturation, Increases tissue oxygenation
Indications: Hypoxia or anticipated hypoxia, or in any medical
or trauma patient to improve respiratory efficiency.
Contraindications: There are no contraindications to oxygen
therapy.
Dose: Route: Oral
DOSAGE: Adult: 1-6 LPM via NC; 10-15 LPM via NRB; 15 LPM via
BVM
Pediatric: 1-6 LPM via NC; 10-15 LPM via NRB; 15 LPM via BVM
Common side effects:
Dry or bloody nose, skin irritation from the nasal cannula or face mask
Precautions/major interactions:
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and very
prolonged administration of high concentrations in the
newborn.
Drug: Oral Glucose
Generic Glutose, Insta-Glucose
Class of medication: Monosaccharide
Carbohydrate
ACTION: After absorption from GI tract, glucose is distributed in the tissues and provides a prompt increase in circulating
blood sugar
Onset: 10 min
Indications: Patients with altered mental status and known
history of diabetes mellitus
Contraindications:
Unconsciousness; known diabetic who has not taken insulin for
days; patient who is unable to swallow
Dose: Route: Oral
DOSAGE/ROUTE:Adult: One tube or packet; repeat based on BGL
Pediatric: One tube or packet; repeat based on BGL minimum age
3 yrs
Common side effects:
Nausea, may be aspirated by the patient without a gag reflex
Precautions/major interactions
Assure patient has control of swallowing and airway.
Drug: Glucagon
Generic: GlucaGen
Class of medication: Hormone, antihypoglycemic
ACTION: Glucagon is a protein secreted by pancreatic cells that causes a breakdown of stored glycogen into glucose and inhibits
the synthesis of glycogen from glucose.
Indications:
Hypoglycemia without IV access.
Contraindications:
Hypersensitivity to glucagon or protein compounds.
Dose: Route: Intramuscular
Adult:1-2mg IM, repeat in 15 minutes if BGL <60.
Ped:0.1 mg/kg IM, repeat in 15 minutes if BGL <60;age > 3 years
Common side effects:
Nausea, vomiting
Precautions/major interactions
Cardiovascular or renal impairment. Effective only if
there are sufficient stores of glycogen in the liver.
Drug: 50% Dextrose in water (D50)
Generic
Class of medication: Monosaccharide, Carbohydrate
ACTION: Dextrose is a simple sugar that the body can rapidly metabolize to create energy.
Indications: Hypoglycemia confirmed by glucometer.
(Coma or seizure of unknown etiology)
Contraindications:
None in hypoglycemia.
Dose: Route: IV
Adult:1 amp or 25g D50WIV bolus, repeat based on BGL.
Common side effects:
Tissue necrosis and phlebitis at injection site.
Precautions/major interactions: Increased ICP. Determine
blood glucose level before administration. Ensure good venous access.
Drug: Lactated Ringer's
Generic LR
Class of medication: Isotonic crystalloid solution
ACTION:
Assist in fluid replacement for dehydration or blood loss
Indications:
Manage hypovolemia (uses lactate as a buffer and contains
electrolytes)
Contraindications:
CHF or renal failure
Dose: Route: IV
Adult Dose: 200-500cc
Pediatric Dose:20cc/kg for fluid replacement
Max:60cc/kg or 2-3 liters of fluid
Common side effects:
Rare
Precautions/major interactions
CVA, Diabetics, Mixing with blood sets.
Drug: 0.9% NaCl
Generic Normal Saline
Class of medication: Isotonic crystalloid solution
ACTION:
- Electrolyte solution which equivalent osmotically to blood.
- Increases the circulating volume in the vascular system. (2/3 of infused volume leaves vascular space within 1 hour.)
Indications:
Replaces water and electrolytes; useful in heat exhaustion, freshwater
dorwning, hypovolemia, DKA
Contraindications: CHF and circulatory overload, Rales for
fluid bolus
Dose: Route: IV
Hypolemia
1. 1 L blood lost = 3 L of NS to infuse
2. Attempt to achieve SBP of 100 mmHg
Common side effects:
Rare
Precautions/major interactions
Be conservative in use of fluids with a suspected head injury patient to minimize
the risk of developing cerebral edema. Judicious fluid use may be needed for
hypotension associated with head injury to maintain cerebral perfusion.
Check BP and lung sounds to determine if fluid overload may be developing.
Drug: albuterol sulfate (nebulized)
Generic: Proventil, Ventolin
Class of medication: Sympathomimetic Bronchodilator
(sympathomimetic = mimics effects of sympathetic nervous system)
ACTION: Albuterol is a synthetic sympathomimetic that causes bronchodilatation with less cardiac effect than epinephrine and
reduces mucus secretion, pulmonary capillary leaking, and edema in the lungs during allergic reactions.
Indications: Bronchospasm and asthma in COPD.
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to the drug, history of cardiac
disease, heart rate >150 in adults, heart rate >200 in pediatrics
Dose: Adult: 2.5-5.0 mg (3cc)via nebulizer continuously, x3
doses,if no history of cardiac disease and heart rate 150.
Ped:2.5mg (3cc) via nebulizer continuously, x3 doses, if no
history of cardiac disease and heart rate 200
Common side effects: Increased pulse rate (tachycardia)
,anxiety, nausea, cough, wheezing, tremors, and/or dizziness
Precautions/major interactions
The patient may experience tachycardia, anxiety, nausea, cough,
wheezing, and/or dizziness. Vital signs and breath sounds must be
monitored; use caution with elderly, cardiac, or hypertensive patients.
Drug: ipatromium bromide
Trade: Atrovent, Apovent, Ipraxa, Aerovent and Rinatec
Class of medication: Anticholinergic
ACTION: Ipratropium bromide is an anticholinergic agent. It blocks muscarinic cholinergic receptors, without specificity for subtypes, resulting
in a decrease in the formation of cyclic guanosine monophosphate
Indications: Bronchospasm associated with COPD
Can be used alone or combined with albuterol
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to ipratropium or
atropine. Use caution in patients with narrow angle glaucoma
Dose:
500 mcg in 2.5 mL unit dose via SVN or in-line with ventilator device.
Repeat per Medical Direction. May mix one unit of ipratropium with one
unit of albuterol
Common side effects Resp: coughing, sputum increased
CNS: dizziness, insomnia, tremor, nervousness
GI: nausea GU: Urinary retention.
Precautions/major interactions
Ipratropium bromide inhalation solution is not a fast-acting medication
and cannot replace fast-acting rescue inhalers. Treatment of acute
episodes of bronchospasm where rescue therapy is required for rapid
response
Drug: Nitroglycerine
Trade: (Nitrostat)
Class of medication: Nitrate
ACTION: Relaxes blood vessels, decreases workload of heart
Indications: Chest pain associated with angina and acute
myocardial infarction.
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity, tolerance to nitrates, severe
anemia, head trauma, hypotension, increased ICP, patients taking
sildenafil (Viagra), glaucoma, and shock.
Dose: Route: Oral
Adult: 1 tablet or spray (0.4 mg) SL every 5 minutes
until pain- free or 3 doses. If SBP <100, contact medical control.
Ped:Not indicated.
Common side effects: Hypotension (lowers blood pressure),
headache, pulse rate changes.
Precautions/major interactions May induce headache
that is sometimes severe. Nitroglycerin is light sensitive and will
lose potency when exposed to the air
Drug: epinephrine (for anaphylaxis only)
Generic: Adrenalin
Class of medication: Sympathomimetic
ACTION: Epinephrine is a naturally occurring catecholamine that increases heart rate, cardiac contractile force myocardial electrical activity,
systemic vascular resistance, and systolic blood pressure and decreases overall airway resistance and automaticity. It also, through bronchial artery
constriction, may reduce pulmonary congestion and increase tidal volume and vital capacity
Indications: severe allergic reactions.
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to sympathomimetic amines,
narrow angle glaucoma, hemorrhagic, organic brain or or during labor
Dose: Allergic reactions
Adult:0.3 mg of 1:1000 IM (if age <50)
0.15 mg of 1:1000 IM (if age >50)
Ped:0.01 mg/kg of 1:1000 IM (use Broselow);
max dose 0.3 mg
Common side effects: Increased heart rate, pallor, dizziness,
chest pain, headache,nausea, vomiting, excitability, anxiety.
Precautions/major interactions Elderly, debilitated
patients, hypertension, diabetes,hyperthyroidism, Parkinsons
disease, tuberculosis, asthma,emphysema, and in children < 6 year
Drug: nitrous oxide (50/50 mix)
Generic: Nitronox
Class of medication: Gaseous Analgesic/Anasthetic
ACTION: CNS depressant
Indications: Patients that are alert and complaining of pain caused
by the following: Musculoskeletal injuries/fractures, kidney stones,
suspected AMI (if NTG or morphine are ineffective or contraindicated),
active labor during an uncomplicated delivery, thermal burns
Contraindications:Any altered level of consciousness or head
injury.
Chronic Obstructive pulmonary disease.
Chest trauma or actual/suspected pneumothorax.
Abdominal distention
major facial trauma
acutely psychotic patients
Decompression sickness
Patients who cannot self-administer
Dose: Route: Self-administered via mask
Self-administer and self-regulated by the patient, who must hold the
mask to face to create an airtight seal until the pain is significantly
relieved or the patient drops the mask.
Common side effects Hypotension/Dizziness
Precautions/major interactions
Must be self-administered
Check machine gauges daily for proper concentrations.
Monitor blood pressure and pulse oximetry values
Drug: naloxone
Generic: NARCAN
Class of medication: Narcotic antagonist
ACTION: Naloxone is a pure narcotic antagonist that blocks the effects of both natural and synthetic narcotics and may reverse
respiratory depression.
Indications: Narcotic and synthetic narcotic overdose, coma
of unknown origin
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to the drug, non-narcotic
induced respiratory depression.
Dose: Adult: 0.5-2 mg IV bolus titrated to patients respiratory
response; may be given IM if unable to establish IV.
Ped:0.1 mg/kg IV (max 2 mg), repeated in 5 minutes if no effect.
Common side effects: Abrupt reversal of narcotic depression
may result in nausea, vomiting, sweating, tachycardia, increased
blood pressure, tremulousness, seizures and cardiacarrest
Precautions/major interactions Possible dependency.
Short also half-life than that of mostnarcotics; hence the patient
may return to the overdose state.
Drug: activated charcoal
Generic:
Class of medication: Adsorbent (binding agent)
ACTION: Activated charcoal is a specially prepared charcoal that will adsorb and bind toxins from the gastrointestinal tract;
combined with Sorbitol to promote GI motility
Indications: Acute ingested poisoning
Contraindications: An airway that cannot be controlled;
ingestion of cyanide, mineral acids, caustic alkalis, organic solvents,
iron, ethanol, methanol.
Dose: Adult: 50 gms PO Route: Oral
Ped:1g/kg PO, max 25 gms
Common side effects Constipation, diarrhea, temporary
darkening of the stool, vomiting.
Precautions/major interactions
Administer only after emesis or in those cases where
emesis is contraindicate
Drug: acetaminophen
Trade: Tylenol, Anacin-3
Class of medication: Non-narcotic Analgesic, Antipyretic
ACTION: Antipyretic Activity, Analgesic Activity - Inhibition of central & peripheral prostaglandin synthesis
Indications: For pain and fever control
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity, children under 3 years
Dose:
Adult: 1000mg PO
Pediatric: 10mg/kg PO
Common side effects: When used appropriately, side effects
with acetaminophen are rare. The most serious side effect is liver
damage due to large doses
Precautions/major interactions
Extreme caution must be used when considering the use on a suspected
liver dysfunction.
Drug: ibuprofen
Trade: Advil, Motrin
Class of medication: Analgesic, Antipyretic, Anti-inflammatory,
NSAID
ACTION: Reduces the inflammatory response through the chemotaxis. Reduces the fever by blocking the prostaglandin synthesis
Indications: Fever, Pain, Inflammation Reducer
Contraindication:
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity
Dose: Adult Dose: 200-800mg p.o. every 6-8 hours
Pediatric Dose:10mg/kg p.o. max of 40mg/kg per day (liquid
form)
Common side effects: G.I. intolerance, many others possible
Precautions/major interactions
You may want to alternate with Acetaminophen
Drug: Aspirin (Acetylsalicylic Acid)
Trade: Alka-Seltzer, Bayer, Emperin, St Joseph Childrens
Class of medication: Platelet inhibitor/Anti-inflammatory
ACTION: Blocks platelet aggregation
Indications: Chest pain suggestive of an MI Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to salicylates, active ulcer
disease, asthma
Dose: Adult: chewable baby aspirin (81mg each) PO
Pediatric: Not indicated
Common side effects: Nausea, vomiting, heartburn, bleeding.
Wheezing is possible with an allergic reaction.
Precautions/major interactions: GI bleeding and upset
Drug: Atropine (Auto Injector)
Generic:
Class of medication: Parasympatholytic
(increases heart rate)
ACTION: Atropine blocks the parasympathetic nervous system, specifically the vagal effects on the heart rate. It does
not increase contractility but may increase myocardial oxygen demand. Atropine decreases airway secretions
Dose: Adult: 2 mg IM via autoinjector Pediatric: Per medical control
only
Contraindications: None in an emergency setting
Common side effects:: Dry mouth, blurred vision, urinary
retention, tachycardia, constipation, decreased sweating
Precautions/major interactions: AMI, glaucoma.
Drug: Pralidoxime (2-PAM)
Generic:
Class of medication: Cholinesterase reactivator
ACTION: Pralidoxime reactivates cholinesterase and
reinstitutes the degrading of acetylcholine and restores normal
neuromuscular transmission. It is used to reverse severe
organophosphate poisoning.
Indications: Organophosphate poisoning
Contraindications: Carbamate insecticides (Sevin), inorganic
phosphates, and organophosphates having no anticholinesterase activity,
asthma, peptic ulcer disease, severe cardiac disease, or
patients receiving aminophylline, theophylline, morphine,
succinylcholine, reserpine, or phenothiazines
Dose:
Adult: 600 mg IM via (Auto Injector)
Ped: Per medical control only
Common side effects: blurred or double vision, difficulty in
focusing eyes, difficulty in speaking, difficult or rapid breathing,
dizziness, fast heartbeat, muscle stiffness or weakness, pain at the place
of injection.
Precautions/major interactions
Rapid administration may result in tachycardia, laryngospasm, and
muscle rigidity. Excited or manic behavior may be noted after regaining
consciousness
You might also like
- Drug CardsDocument10 pagesDrug CardsMaria Robustelli100% (3)
- AEMT Medications: Drug Card InformationDocument2 pagesAEMT Medications: Drug Card InformationAlex Lupi50% (2)
- Drug CardsDocument38 pagesDrug CardsJason D Wilkins92% (25)
- Acetazolamide drug profileDocument33 pagesAcetazolamide drug profileAshley Topp100% (1)
- Emt PosterDocument1 pageEmt PosterDrThant Zin Tun50% (2)
- ParamedicDocument33 pagesParamedicKayMelton88% (8)
- Study Guide NREMTDocument4 pagesStudy Guide NREMTdebbiemedic355725% (4)
- Paramedic Drugs in EMSDocument12 pagesParamedic Drugs in EMSJim Hoffman100% (4)
- Math Practice For Paramedic StudentsDocument8 pagesMath Practice For Paramedic StudentsGreg Zeitlin50% (2)
- AEMT Medication AdministrationDocument24 pagesAEMT Medication AdministrationEmily KeenNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Emergency and Trauma NursingDocument11 pagesStudy Guide Emergency and Trauma NursingMarie Angelique Cruz Crestani100% (5)
- Drug Cards CNSDocument23 pagesDrug Cards CNSChristine Schroeder100% (2)
- Paramedic Drugs: Drug Class Indications Dosage NameDocument14 pagesParamedic Drugs: Drug Class Indications Dosage NameIbrahem Al100% (6)
- Paramedic MegacodesDocument7 pagesParamedic MegacodesAnonymous wu6RXuNo ratings yet
- ACLS PharmacologyDocument5 pagesACLS PharmacologyKuruva MallikarjunaNo ratings yet
- EMS Respiratory Emergency Management DeMYSTiFieDFrom EverandEMS Respiratory Emergency Management DeMYSTiFieDRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Acid Base BalanceDocument5 pagesAcid Base BalanceTinaHo100% (4)
- Drug Card TemplateDocument1 pageDrug Card TemplateE100% (4)
- Paramedic PowerpointDocument43 pagesParamedic PowerpointKayMelton100% (1)
- National Registry Paramedic Prep: Practice + Proven StrategiesFrom EverandNational Registry Paramedic Prep: Practice + Proven StrategiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- EMT Drug ManualDocument236 pagesEMT Drug ManualMicherre MacMillan100% (2)
- Drug Cards PDFDocument136 pagesDrug Cards PDFTasha100% (3)
- Drug CardsDocument16 pagesDrug Cardsp_dawg100% (7)
- Type Drug ChartDocument3 pagesType Drug ChartKarina Rodriguez100% (3)
- EMT Pharmacology HandoutDocument11 pagesEMT Pharmacology HandoutDavid100% (1)
- Drug Cards (PDF Library)Document5 pagesDrug Cards (PDF Library)Jim Stewart0% (2)
- 1000 Drug CardsDocument33 pages1000 Drug Cardstfish106588% (90)
- Advanced Level Examination Coordinator ManualDocument117 pagesAdvanced Level Examination Coordinator ManualTmason47No ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument24 pagesEmergency Drugsourladymediatrixhospital hemodialysisunitNo ratings yet
- Flash Cards Nclex Part 2Document24 pagesFlash Cards Nclex Part 2Amanda Simpson100% (3)
- Acls DrugsDocument5 pagesAcls DrugsDebby Christiana SNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary TraumatologyDocument15 pagesPulmonary Traumatologynoor88No ratings yet
- 5 PT Med Surg Brain SheetDocument2 pages5 PT Med Surg Brain SheetJan Marcus100% (2)
- CCRNDocument17 pagesCCRNNílo Stárn100% (1)
- EMT (Emergency Medical Technician) Crash Course with Online Practice Test, 2nd Edition: Get a Passing Score in Less TimeFrom EverandEMT (Emergency Medical Technician) Crash Course with Online Practice Test, 2nd Edition: Get a Passing Score in Less TimeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Toxicology: by Group 4 2018/2019 Tan Geok Eng Reena DewiDocument59 pagesToxicology: by Group 4 2018/2019 Tan Geok Eng Reena DewiTan Geok EngNo ratings yet
- Drug Card TemplateDocument1 pageDrug Card TemplateE80% (20)
- ORLANDO MEDICAL INSTITUTE PARAMEDIC FLIPPED CLASS PROGRAMDocument21 pagesORLANDO MEDICAL INSTITUTE PARAMEDIC FLIPPED CLASS PROGRAMRob Veitch100% (1)
- Cheetsheet 6Document1 pageCheetsheet 6Rick Frea92% (12)
- Mosby's EMT-Basic Textbook - Revised Reprint, 2nd Edition1.1Document22 pagesMosby's EMT-Basic Textbook - Revised Reprint, 2nd Edition1.1whadyaknow1233% (6)
- Paramedic Pediatric Scenario 2017Document3 pagesParamedic Pediatric Scenario 2017Chad StreetNo ratings yet
- Cheatsheet 5Document1 pageCheatsheet 5Rick Frea80% (5)
- AMLS Mobile Reference GuideDocument6 pagesAMLS Mobile Reference GuideLim Jun BinNo ratings yet
- FLASH CardsDocument3 pagesFLASH Cardsclarheena100% (2)
- LSCPR Pals Study Guide 2020Document57 pagesLSCPR Pals Study Guide 2020Juan Ma100% (1)
- ACLS Official GuideDocument11 pagesACLS Official GuideICU RSPGNo ratings yet
- Adult III Cardiac Study GuideDocument15 pagesAdult III Cardiac Study GuideNursingSchoolNotes100% (6)
- Drug CardsDocument19 pagesDrug Cardslani83% (6)
- FP-C GuideDocument107 pagesFP-C GuideJames100% (3)
- TNCC Study GuideDocument4 pagesTNCC Study Guidescroasdell83% (6)
- Nurse Brain Sheet Telemetry Unit SBARDocument1 pageNurse Brain Sheet Telemetry Unit SBARashdmb217No ratings yet
- 7mosby's EMT-Basic Textbook - Revised Reprint, 2nd EditionDocument22 pages7mosby's EMT-Basic Textbook - Revised Reprint, 2nd EditionKathrina AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Hesi FundamentalsDocument14 pagesHesi Fundamentalscharitoave90% (20)
- CEN+Online+Review Module+12 Final GENITODocument26 pagesCEN+Online+Review Module+12 Final GENITOTamara Cooper67% (3)
- Dimensional Analysis For Nursing StudentsFrom EverandDimensional Analysis For Nursing StudentsNo ratings yet
- Back to Basics: Critical Care Transport Certification ReviewFrom EverandBack to Basics: Critical Care Transport Certification ReviewNo ratings yet
- EMERGENCY MEDICAL TECHNICIANS-PARAMEDIC EXAMINATION (EMT): Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandEMERGENCY MEDICAL TECHNICIANS-PARAMEDIC EXAMINATION (EMT): Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Measles, Chickenpox, TB Airborne Precautions GuideDocument4 pagesMeasles, Chickenpox, TB Airborne Precautions GuideAndreasNo ratings yet
- Omaha System AlzhimersDocument1 pageOmaha System AlzhimersAndreasNo ratings yet
- Military Nurses' Care of Iraqi PatientsDocument19 pagesMilitary Nurses' Care of Iraqi PatientsAndreasNo ratings yet
- Lewis and Clark ReloadedDocument5 pagesLewis and Clark ReloadedAndreas100% (1)
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument7 pagesChemical Coordination and IntegrationAnonymous -No ratings yet
- Endometab Exam 2018Document8 pagesEndometab Exam 2018teabagmanNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Glipizide in Commercial Drugs by RP - HPLCDocument6 pagesEstimation of Glipizide in Commercial Drugs by RP - HPLCjamonline100% (1)
- User Guide: Blood Glucose Monitoring SystemDocument30 pagesUser Guide: Blood Glucose Monitoring SystemVince CentenoNo ratings yet
- Managing Medical EmergenciesDocument42 pagesManaging Medical EmergenciesRichard Starr100% (2)
- Carbohydrates Clinical SignificanceDocument10 pagesCarbohydrates Clinical SignificanceMay Ann EnoserioNo ratings yet
- Epigenetics As Fuel For Brain HealthDocument4 pagesEpigenetics As Fuel For Brain HealthDavidPerlmutterMD100% (1)
- Glibenclamide For Diabetic Tipe IIDocument5 pagesGlibenclamide For Diabetic Tipe IIAnonymous A1qFGIXACNo ratings yet
- Pharmacognostic and Phytochemical Properties of Aloe Vera LinnDocument5 pagesPharmacognostic and Phytochemical Properties of Aloe Vera LinnazaliaswNo ratings yet
- Urgencias MetabolicasDocument11 pagesUrgencias MetabolicasviaereaNo ratings yet
- Hypoglycemia in Exclusively Breastfed High-Risk Neonates - A Hospital-Based StudyDocument7 pagesHypoglycemia in Exclusively Breastfed High-Risk Neonates - A Hospital-Based StudyNeta Aza MaineztNo ratings yet
- Diabetes NCPDocument6 pagesDiabetes NCPMonique Sacherow BacherNo ratings yet
- Blood Chemistry and CBC Analysis - Clinical Laboratory Testing From A Functional Perspective - Quick Reference GuideDocument29 pagesBlood Chemistry and CBC Analysis - Clinical Laboratory Testing From A Functional Perspective - Quick Reference Guidejamesilluminare73% (15)
- Procedures and Notes for Medical SpecialtiesDocument9 pagesProcedures and Notes for Medical SpecialtiesKeith CoralNo ratings yet
- Endo Test Bank 1Document6 pagesEndo Test Bank 1mildred alidon100% (1)
- 1 DMDocument49 pages1 DMDrMohammad KhadrawyNo ratings yet
- Near Misses in Pediatric AnesthesiaDocument253 pagesNear Misses in Pediatric Anesthesiashak31kem7420No ratings yet
- Markers for complications among diabetic patientsDocument162 pagesMarkers for complications among diabetic patientsayudilaNo ratings yet
- Blood Sugar Book 4.18Document13 pagesBlood Sugar Book 4.18Razkhal KunmoNo ratings yet
- Nclex AobyDocument7 pagesNclex Aobyvienny kayeNo ratings yet
- Horm S 23 00313 1Document32 pagesHorm S 23 00313 1andreopNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Facts and Guidelines: en Te RDocument53 pagesDiabetes Facts and Guidelines: en Te Rroche_reyesNo ratings yet
- Fasting Yom Kippur HalachaDocument7 pagesFasting Yom Kippur HalachaBenjamin Kelsen100% (1)
- Chapter I RepairedDocument23 pagesChapter I RepairedJunicorn BessonNo ratings yet
- Approach To Diabetic ComaDocument15 pagesApproach To Diabetic ComaRukman Mecca100% (1)
- Simulation ActivityDocument6 pagesSimulation Activityjustgraduate1408100% (1)
- Carbohydrates PDFDocument8 pagesCarbohydrates PDFWrigley PatioNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Drug CardsDocument33 pagesPharmacology Drug CardsAidenhunter05100% (1)
- Module 5 CarbohydratesDocument21 pagesModule 5 CarbohydratesSpongebob SquarepantsNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Guideline Set Final CHeRP 2007Document35 pagesNeonatal Guideline Set Final CHeRP 2007Aji WibowoNo ratings yet