Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Location & Economies of Scale
Uploaded by
ammadey21@gmail.comOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Location & Economies of Scale
Uploaded by
ammadey21@gmail.comCopyright:
Available Formats
9/3/2012
1
Location
Business Location
In general a business will look to locate its
activities where the costs of production are
minimised
The nature of the business will heavily
influence location decisions:
Type and nature of market
Type of business production of goods or
services, retail, wholesale?
Sector primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary?
Factors determining location
The market
Land
Raw materials
Government support
Labor
Communication
Power supplies
Ancillary industries
Transportation
Planning permission
Environment factors
Safety requirements
Managements
preference
Amenities
The market
How close is your market?
Depends on the type of business.
A business which produce items which are
fragile and bulk in quantity and difficult to
transport without damage would likely to
locate near its market. (furniture)
Most businesses want to locate near its
customers especially retail outlets and super
markets.
9/3/2012
2
Land
The availability and the cost of land.
Expansions.
Firms which need large areas of land might
consider cost of land before locating.
Automobile manufacturing plants need large
chunks of land.
Raw materials
Locating where there is easy access to raw
materials required for the business
Coal mines near coal, brick manufacturers
near clay, mineral water companies near
spring etc.
The extraction industries such as coal mines
have limited location options
Also depends on the transportation and
bulkiness of the raw materials.
Government Support
Government regulations
Regional policy
Government helps in terms of providing grants
and loans for the businesses
Tax reliefs, EU
Labor
Easy access to skilled labors
The cost of labors
Taking work to workers or taking workers to
work
Many multi nationals often target the
countries where there is cheap labor
9/3/2012
3
Communication
Easier and faster access to all kinds of
communication is essential
This especially important for firms such as
multinational companies and the businesses
which have so many branches across the
country
Ancillary industries
Ancillary industries are those which
manufacture parts and components to be
used by larger industries. E.g.- Companies like
GE (ancillary) produce engines for the aircraft
industry.
These are small firms providing support
services to the businesses.
Transportation
Depends on the nature of the business
For instance, a large assembly plant must have
good road, rail and sea links for easy access for
its access for its suppliers as well as for
distribution of finished cars, especially if they
are exporting across the nations.
Supermarkets, the location of workers etc.
Environmental/Climate factors
The environmental climate is very important
depending on the nature of the business
Agriculture businesses, earth quakes etc
9/3/2012
4
Amenities
Availability of water, electricity and gas is vital
for location of the businesses
Other services such as banking and insurance
are also very important when choosing a
locations
Managements preference
Many of the location decisions are often
influenced by the management's view about
the locations.
They would consider factors such as the
current workers, current market especially
when relocating.
International Location
Ease of access to international markets
Possible language and cultural issues
Political stability of the location
Economic stability of the location
Perception about the amount of red tape
associated with the location
Existence of trade barriers
Economies of scale
and
Diseconomies of scale
9/3/2012
5
Economies of scale
The advantages of large scale production that
result in lower unit (average) costs (cost per
unit)
'the reduction in average costs of production,
that occur as a firm increases its scale of
production'
Economies of scale spreads total costs over a
greater range of output
Internal Economies of scale
Internal Reductions in average or unit cost
because of increasing internal efficiencies of the
firm.
Technical
Marketing
Financial
Managerial
Risk Bearing
Purchasing
Technical
As businesses grow they are able to use the latest equipment
and incorporate new methods of production.
Specialisation large organisations
can employ specialised labour.
Indivisibility of plant machinery is available only
in minimum sizes. Small firms often are not able to
utilize fully even smallest size available.
Principle of multiples If output is expanded by a
certain proportional use of all machines, they could be
fully utilized and the average cost may be lower. Firms
using more than one machine of different capacities
Increased dimensions bigger containers can
reduce average cost. Cost wont increase
proportionality with size.
Marketing
Can spread its advertising and
marketing budget over a much
greater output and it can also
purchase its factor inputs in bulk
at discounted prices
Large firms may have advantages
in keeping prices higher because
of their market power
9/3/2012
6
Financial
Large firms able to negotiate
cheaper finance deals
Large firms able to be more
flexible about finance share
options, rights issues, etc.
Financial institutions often regard
large firms as less risky so they
will attract finance easier than
small firms.
Managerial
Use of specialists accountants,
marketing, lawyers, production,
human resources, etc.
Division of labour among
management staffs.
Purchasing
Bulk buying
Bulk discounts
Favourable credit terms
Special prices and offers
Risk Bearing
Diversification
Markets across regions/countries
Product ranges
R&D
Splitting risk by having more
suppliers
9/3/2012
7
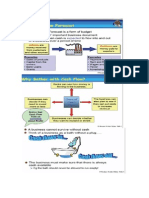
External Economies of Scale
External economies of scale exist when the long-term
expansion of an industry leads to the development of ancillary
services which benefit all or the majority of suppliers in the
industry
A labour force skilled in the specific crafts of the industry
Components suppliers equipped to supply the right parts re-locate close to
production centres reducing transportation costs
Trade magazines in which all firms can advertise cheaply and disseminate
information
Local colleges will set up training schemes suited to the largest employers
needs, giving an available pool of skilled labor, this reduces recruitment
and training costs
External economies partially explain the tendency for firms to
cluster geographically
Good examples to quote
Car industry in the West Midlands
Silicon Valley & its pool of computer experts
Financial services industry in London and New York
Is Bigger Really Better?
As with all things, as industries get bigger
so does the infrastructure and the
problems associated with economies of
scale.
There is a fine line between making
money and losing money.
This can result in:
Internal Diseconomies of Scale
External Diseconomies of Scale
Internal Diseconomies of Scale
These occur when the firm has become too large and
inefficient. As the firm increases production, eventually
average costs begin to rise because:
The disadvantages of the division of labour take effect- too
many people doing different jobs add to costs. (poor morale)
Management becomes out of touch with the shop floor and
some machinery becomes over-manned- costs increase.
Decisions are not taken quickly and there is too much form
filling. (delay in responding to market changes)
Lack of communication in a large firm means that management
tasks sometimes get done twice. (longer chain of command)
Poor labour relations may develop in large companies.
Bureaucracy, which will result in excessive administration costs.
Information overload for managers results in poor decisions.
External Diseconomies of Scale
These occur when too many firms have located in one
area
Local labour becomes scarce and firms now have to bid
wages higher to attract and retain new workers
Land and factories become scarce and rents begin to
rise
The local traffic infrastructure become congested and
so transport costs begin to rise
Breakdown of relationships with suppliers and buyers.
9/3/2012
8
Survival of small firms
Some industries do not require use of heavy
equipments. So there is a lack of technical
economies of scale. E.g. hair dressing, window
cleaning
The size of the market is small
Personal service
Frequent changes in the market
Filling the niche
Individual skills craft work
To be your own boss
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Leadership Matrix Self Assessment QuestionnaireDocument4 pagesLeadership Matrix Self Assessment QuestionnaireKanupriyamNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Paper T6 (Int) Drafting Financial Statements: Sample Multiple Choice Questions - June 2009Document155 pagesPaper T6 (Int) Drafting Financial Statements: Sample Multiple Choice Questions - June 2009haroldpsb50% (4)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Husky InjectionDocument4 pagesHusky InjectionGravhund63% (8)
- Emperor BTC-Volume Profile Seasson VolumeDocument10 pagesEmperor BTC-Volume Profile Seasson VolumeJasiresya GroupNo ratings yet
- Oracle Applications Cloud: Functional Setup Manager For ImplementersDocument38 pagesOracle Applications Cloud: Functional Setup Manager For ImplementersFerasHamdanNo ratings yet
- Management AgreementDocument6 pagesManagement AgreementButch KhanNo ratings yet
- Amazon Supply Chain AnalysisDocument16 pagesAmazon Supply Chain AnalysisFredrick LiyengaNo ratings yet
- BSBSTR601 Student Assessment TasksDocument19 pagesBSBSTR601 Student Assessment TasksRohan Shrestha0% (2)
- D-Mart Ready Business ModelDocument3 pagesD-Mart Ready Business ModelRahul Verma100% (2)
- Chapter 10 Crafting The Brand PositioningDocument20 pagesChapter 10 Crafting The Brand Positioningjana mohammad15100% (2)
- Lecture 1Document16 pagesLecture 1ammadey21@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Excercise - TBDocument2 pagesExcercise - TBammadey21@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Books of Prime Entry TransactionsDocument1 pageBooks of Prime Entry Transactionsammadey21@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- 1) Dec 2002 - QDocument5 pages1) Dec 2002 - QNgo Sy VinhNo ratings yet
- F5 Past Paper AnalysisDocument5 pagesF5 Past Paper AnalysisIzhar MumtazNo ratings yet
- Blake and MoutonDocument3 pagesBlake and Moutonammadey21@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Accounting and FinanceDocument7 pagesAccounting and Financeammadey21@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- F5 Past Paper AnalysisDocument5 pagesF5 Past Paper AnalysisIzhar MumtazNo ratings yet
- Business OrganizationDocument6 pagesBusiness Organizationammadey21@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Medical SciencesDocument10 pagesMedical Sciencesammadey21@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Accounting and FinanceDocument13 pagesAccounting and Financeammadey21@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- HRMDocument17 pagesHRMammadey21@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- John KotterDocument2 pagesJohn Kotterammadey21@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Approach Most Appropriate Example Advantage Education and CommunicationDocument2 pagesApproach Most Appropriate Example Advantage Education and Communicationammadey21@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- The Budgeting ProcessDocument3 pagesThe Budgeting Processammadey21@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Corporate Aims, Corporate Objectives and Corporate StrategyDocument2 pagesCorporate Aims, Corporate Objectives and Corporate Strategyammadey21@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Effective Communication in The Workplace.: 2008 Spec. Issue 2 Sept. 2009Document5 pagesEffective Communication in The Workplace.: 2008 Spec. Issue 2 Sept. 2009ammadey21@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Sectors of EconomyDocument2 pagesSectors of Economyammadey21@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- MarketingDocument8 pagesMarketingammadey21@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Cash FlowDocument2 pagesCash Flowammadey21@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Tuition Centre Business PlanDocument17 pagesTuition Centre Business PlanisqmaNo ratings yet
- GM - M (Oh$ (DKMZ$: (Zym© (Av G - ' Kêq O A (Yh$V - A H$Document34 pagesGM - M (Oh$ (DKMZ$: (Zym© (Av G - ' Kêq O A (Yh$V - A H$neetus creationNo ratings yet
- Org Chart Updated 2021Document1 pageOrg Chart Updated 2021Shan Dela VegaNo ratings yet
- Ultra HNI SegmentDocument7 pagesUltra HNI SegmentShantanu SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Determinants in Uencing Consumers Purchasing Intention For Sustainable Fashion: Evidence From Ho Chi Minh CityDocument11 pagesDeterminants in Uencing Consumers Purchasing Intention For Sustainable Fashion: Evidence From Ho Chi Minh CityCherieNo ratings yet
- Fuel Truck Driver SOPDocument2 pagesFuel Truck Driver SOPSugan Byang PradhanNo ratings yet
- Penerapan Sistem Pelayanan Perizinan Berusaha Terintegrasi Secara Elektronik Pada Dinas Penanaman Modal Dan Pelayanan Terpadu Satu Pintu Kabupaten BalanganDocument10 pagesPenerapan Sistem Pelayanan Perizinan Berusaha Terintegrasi Secara Elektronik Pada Dinas Penanaman Modal Dan Pelayanan Terpadu Satu Pintu Kabupaten BalanganJoerdan OkthianzaNo ratings yet
- Pinnacle FileDocument35 pagesPinnacle Filethe kingfishNo ratings yet
- Krystelle Jane DeticDocument2 pagesKrystelle Jane DeticelledeticNo ratings yet
- The Exxon-Mobil Merger: An Archetype: J. Fred WestonDocument20 pagesThe Exxon-Mobil Merger: An Archetype: J. Fred WestonTRANNo ratings yet
- Partnership Definition and CharacteristicsDocument45 pagesPartnership Definition and CharacteristicsKaloy HoodNo ratings yet
- RAgmngDocument32 pagesRAgmngRami AloanNo ratings yet
- FEXAM - Attempt ReviewDocument6 pagesFEXAM - Attempt ReviewGian PeñaflorNo ratings yet
- Why Diverse Teams Are SmarterDocument5 pagesWhy Diverse Teams Are SmarterVishwa RvceNo ratings yet
- Indus Group Profile Updated Final1Document19 pagesIndus Group Profile Updated Final1aqsa imranNo ratings yet
- Synopsis: A Study On Inventory Management AT Super Spinning Mills LTD., HindupurDocument6 pagesSynopsis: A Study On Inventory Management AT Super Spinning Mills LTD., HindupurAnu GraphicsNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 (Income From House Property)Document13 pagesUnit 2 (Income From House Property)Vijay GiriNo ratings yet
- Lyceum-Northwestern University: L-NU AA-23-02-01-18Document8 pagesLyceum-Northwestern University: L-NU AA-23-02-01-18Amie Jane MirandaNo ratings yet
- Sistem Informasi Operasional Apotek Berbasis Customer: Relationship Management (CRM)Document12 pagesSistem Informasi Operasional Apotek Berbasis Customer: Relationship Management (CRM)Riza Septian Agus ArisandyNo ratings yet
- Chapin Inc divisions coffee donut profits transfer pricingDocument4 pagesChapin Inc divisions coffee donut profits transfer pricingMeriskaNo ratings yet
- Recruit For Designers Using Dribbble & BehanceDocument5 pagesRecruit For Designers Using Dribbble & Behancehemanth vNo ratings yet
- 8 Problems With FNBDocument5 pages8 Problems With FNBGwendolyn EmnacenNo ratings yet