Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vending Machine Refrigeration
Uploaded by
xenohjbCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Vending Machine Refrigeration
Uploaded by
xenohjbCopyright:
Available Formats
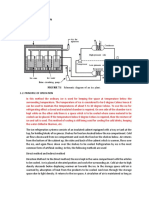
Vending Machine Refrigeration- some of the products dispensed by a vending machine require
refrigeration. These may be beverages, sandwiches or frozen products such as ice cream. The
refrigeration portion of the vending machine is only a small part of the mechanical and electrical
operation of the machine. This refrigeration system is similar to domestic refrigeration.
Water Coolers- are used in many public buildings to cool drinking water to a temperature similar to ice
water. The water is dispensed either through a fixture called a bubbler or through a snout used to fill a
cup.
Refrigerated Air Driers- are basically refrigeration systems located in the air supply, after the storage
tank. The air may be cooled in a heat exchanger, then moved to the storage tank where much of the
water will separate from the air.
Commercial Ice Machines- are refrigeration systems which make ice from the evaporator temperatures
between medium and low temperature ranges of about 10F with the ice at 32F. It is accomplished by
accumulating the ice on some type of evaporator surface and then catching and saving it after a defrost
cycle, commonly called the harvest cycle
Railway refrigeration- Product shipped and refrigerated by rail are mechanically refrigerated either by a
self-contained unit located at one end of the refrigerated car or by and axle-driven unit. The axle unit is
an older type and not being used to any extent now. The railcar would only have refrigeration while the
train is in motion using axle-driven units.
Cooling Towers- is a heat rejection device which extracts waste heat to the atmosphere through the
cooling of a water stream to a lower temperature. Cooling towers may either use the evaporation of water
to remove process heat and cool the working fluid to near the wet-bulb air temperature or, in the case
of closed circuit dry cooling towers, rely solely on air to cool the working fluid to near the dry-bulb air
temperature.
Refrigerator- A refrigerator (colloquially fridge) is a common household appliance that consists of a
thermally insulated compartment and a heat pump (mechanical, electronic, or chemical) that transfers
heat from the inside of the fridge to its external environment so that the inside of the fridge is cooled to a
temperature below the ambient temperature of the room. Refrigeration is an essential food storage
technique in developed countries. Lower temperatures in a confined volume lowers the reproduction rate
of bacteria, so the refrigerator reduces the rate of spoilage.
Quick Freezers- flash freezing is used in the food industry to quickly freeze perishable food items
(see frozen food). In this case, food items are subjected to temperatures well below
water's melting/freezing point (32F or 0C), which is contained as intracellular and extracellular water.
The freezing process results in the formation of ice crystals and their subsequent increase in size. The
freezing speed has direct influence on the nucleation process and the ice crystal size. Insufficient
propagation of the initially formed ice crystals is a result of a high heat removal rate and causes an
increased rate of nucleation. An increase in ice nuclei result in a decrease of ice crystals formed and
hence causing minimal damage to the cell membranes.
You might also like
- Cold Stores: Mansoura University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Power DepartmentDocument12 pagesCold Stores: Mansoura University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Power DepartmentKhaled HakimNo ratings yet
- What Is RefrigerationDocument10 pagesWhat Is RefrigerationxyonieNo ratings yet
- Mini Ice Plant ReportDocument40 pagesMini Ice Plant ReportLeyzer MalumayNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Small Scale Ice PlantsDocument54 pagesAnalysis of Small Scale Ice PlantsThaungShanHtet PalatarNo ratings yet
- MINI ICE PLANT EFFICIENCYDocument40 pagesMINI ICE PLANT EFFICIENCYCherry Obias100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Refrigeration MethodsDocument84 pagesFundamentals of Refrigeration MethodsibrahimNo ratings yet
- Mahika Saxena Refrigeartion.Document9 pagesMahika Saxena Refrigeartion.Warrior InsideNo ratings yet
- Myat Noe KhinDocument42 pagesMyat Noe KhinThaungShanHtet PalatarNo ratings yet
- Basic Refrigeration System PDFDocument15 pagesBasic Refrigeration System PDFJC BenitezNo ratings yet
- How Refrigeration WorksDocument29 pagesHow Refrigeration Worksaaisha pariNo ratings yet
- RefrigerationDocument3 pagesRefrigerationscampydudeNo ratings yet
- R&ac Unit-1Document27 pagesR&ac Unit-1Dinesh ManikantaNo ratings yet
- Use in Air Conditioning: Air Conditioning Air Handling Units Sensible Heat Latent HeatDocument7 pagesUse in Air Conditioning: Air Conditioning Air Handling Units Sensible Heat Latent Heatprasha_patNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration - Air Conditioner - Air-Cooled ChillerDocument3 pagesRefrigeration - Air Conditioner - Air-Cooled ChillerFujailNo ratings yet
- Rac Module 4Document128 pagesRac Module 4James MathewNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration SystemDocument37 pagesRefrigeration SystemSatish KumarNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Systems: Chapter # 02Document3 pagesRefrigeration Systems: Chapter # 02Umar RiazNo ratings yet
- ICE PRODUCTION PROCESSDocument7 pagesICE PRODUCTION PROCESSRonaldNo ratings yet
- Pre-Cooling and RefrigerationDocument9 pagesPre-Cooling and RefrigerationOliver TalipNo ratings yet
- 2019 DLSUD Refrigeration Engr Methods of Refrigeration SDocument8 pages2019 DLSUD Refrigeration Engr Methods of Refrigeration SJake Polo SantiagoNo ratings yet
- 1 Ref Intro 3rd Term June 2016Document15 pages1 Ref Intro 3rd Term June 2016Nicolai CeloNo ratings yet
- Introduction - : Refrigeration Is The Process ofDocument11 pagesIntroduction - : Refrigeration Is The Process ofNikita ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- lecture 1Document6 pageslecture 1Preethi RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Freezers: Cooled Air, Liquid and Surface TypesDocument5 pagesMechanical Freezers: Cooled Air, Liquid and Surface TypesbestxeroxshopNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Cryogenics Liquefied Natural Gas LNG Gas Treatment UnitDocument20 pagesRefrigeration Cryogenics Liquefied Natural Gas LNG Gas Treatment Unitwei wangNo ratings yet
- RefrigerationDocument14 pagesRefrigerationJhon Walter Ortega CondeNo ratings yet
- ChillerDocument72 pagesChillerMYLENE BUENONo ratings yet
- Optimize HVAC System EfficiencyDocument12 pagesOptimize HVAC System EfficiencyOmarAbdAzizNo ratings yet
- Study of Airflow Patterns in Spiral Blast Freezers On Energy Utilization Efficiency and Freezing Quality.Document13 pagesStudy of Airflow Patterns in Spiral Blast Freezers On Energy Utilization Efficiency and Freezing Quality.Kalejaiye AdedayoNo ratings yet
- Choosg The ChillerDocument8 pagesChoosg The ChillerskluxNo ratings yet
- Me22 E01 SW3Document2 pagesMe22 E01 SW3Faye AnneNo ratings yet
- Q.21 RefrigerationDocument6 pagesQ.21 RefrigerationBilal AhmadNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning by Waqas Ali Tunio (21-10-10)Document15 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning by Waqas Ali Tunio (21-10-10)waqasalitunioNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration: SystemsDocument38 pagesRefrigeration: SystemsRickson Viahul Rayan CNo ratings yet
- ManojDocument13 pagesManojpranavNo ratings yet
- Mini Ice Plant Working PrincipleDocument8 pagesMini Ice Plant Working PrincipleKent NabzNo ratings yet
- Freeze Drying - An Introduction to the ProcessDocument39 pagesFreeze Drying - An Introduction to the ProcessrajagopalNo ratings yet
- LypholizationDocument19 pagesLypholizationNaeem Khan MalizaiNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument52 pagesRefrigeration and Air ConditioningRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Basic Refrigeration Cycle and Concepts, Standard Rating of Refrigerating MachinesDocument3 pagesLesson 1 Basic Refrigeration Cycle and Concepts, Standard Rating of Refrigerating MachinesEdrielleNo ratings yet
- Mini Ice PlantDocument28 pagesMini Ice PlantCharlie RamirezNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration SystemDocument38 pagesRefrigeration SystemAdrian Derek IvashkoveNo ratings yet
- IJCTER Scientific Journal Impact Fabrication of Hot and Cold Water DispenserDocument6 pagesIJCTER Scientific Journal Impact Fabrication of Hot and Cold Water Dispensersentot ali basahNo ratings yet
- Yu Ki Myat NoeDocument26 pagesYu Ki Myat NoeThaungShanHtet PalatarNo ratings yet
- Vapour Compression RefrigerationDocument30 pagesVapour Compression RefrigerationLohith Narasimha swamyNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration CycleDocument23 pagesRefrigeration CycleTajTajNo ratings yet
- Defrost MethodsDocument18 pagesDefrost Methodse4erkNo ratings yet
- Terms LangDocument7 pagesTerms LangJanelle D. Puti-anNo ratings yet
- Acitivity 1 (Daga, Kristan O'Neal C.)Document9 pagesAcitivity 1 (Daga, Kristan O'Neal C.)Kristan Oneal DagaNo ratings yet
- Filar, Refrigeration 1Document9 pagesFilar, Refrigeration 1Rahwan Qadir SlemanNo ratings yet
- Refrigerator Revelations: A User's Guide to Operation and MaintenanceFrom EverandRefrigerator Revelations: A User's Guide to Operation and MaintenanceNo ratings yet
- How to Use and Enjoy Your New Frigidaire RefrigeratorFrom EverandHow to Use and Enjoy Your New Frigidaire RefrigeratorNo ratings yet
- Freeze Drying Cookbook : Preserving Freshness, Unlocking Flavours: Your Comprehensive Guide to Freeze Drying Techniques and RecipesFrom EverandFreeze Drying Cookbook : Preserving Freshness, Unlocking Flavours: Your Comprehensive Guide to Freeze Drying Techniques and RecipesNo ratings yet
- Aquaponics in Winter: How to Heat Your Aquaponic Garden in Cold ClimateFrom EverandAquaponics in Winter: How to Heat Your Aquaponic Garden in Cold ClimateNo ratings yet
- 1,001 Kitchen Tips & Tricks: Helpful Hints for Cooking, Baking, and CleaningFrom Everand1,001 Kitchen Tips & Tricks: Helpful Hints for Cooking, Baking, and CleaningNo ratings yet
- Infinite Harvest : Maximizing Yield in Your Greenhouse GardenFrom EverandInfinite Harvest : Maximizing Yield in Your Greenhouse GardenNo ratings yet
- Oral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseFrom EverandOral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseNo ratings yet
- 1ST YEAR Tabulated DataDocument20 pages1ST YEAR Tabulated DataxenohjbNo ratings yet
- Effect of Secondary Current Ideal TransformerDocument13 pagesEffect of Secondary Current Ideal TransformerxenohjbNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction To Magnetic CircuitsDocument26 pages1 - Introduction To Magnetic Circuitsxenohjb100% (1)
- Vending and Commercial Refrigeration SystemsDocument1 pageVending and Commercial Refrigeration SystemsxenohjbNo ratings yet
- Vending and Commercial Refrigeration SystemsDocument1 pageVending and Commercial Refrigeration SystemsxenohjbNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction To Magnetic CircuitsDocument26 pages1 - Introduction To Magnetic Circuitsxenohjb100% (1)
- Ee41nl Engl23 Es25 Me410 Me411l Me412 Me413 Me417 Me417l Meelec Ee41nl Me411mDocument2 pagesEe41nl Engl23 Es25 Me410 Me411l Me412 Me413 Me417 Me417l Meelec Ee41nl Me411mxenohjbNo ratings yet
- ZXCZXCZXCZXCZXZXCZXCZXCZXCZXCDocument4 pagesZXCZXCZXCZXCZXZXCZXCZXCZXCZXCxenohjbNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws ApplicationDocument15 pagesNewton's Laws ApplicationxenohjbNo ratings yet
- Balata YoDocument1 pageBalata YoxenohjbNo ratings yet
- Ya NoDocument1 pageYa NoxenohjbNo ratings yet