Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Written Response Test: 8 International Geography Olympiad
Uploaded by
SonyYonAryanto0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views10 pagesigeo
Original Title
IGEO
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentigeo
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views10 pagesWritten Response Test: 8 International Geography Olympiad
Uploaded by
SonyYonAryantoigeo
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
1
Wri tten Response Test
Marki ng scheme
8
th
Internati onal Geography Ol ympi ad
Tai pei , Tai wan
Jul y 29 - August 4 2010
Marki ng scheme - overvi ew
2
1 MDGs
2 Fl ood
3 Popul at i on
geography
4 Landf orms
5 Agri cul ture
6 Natural
hazards
1 - 3m 1 - 3m 1 - 3m 1 - 1m 1 - 3m 1 - 3m
2 - 2m 2 - 4m 2 - 2m 2 - 1m 2 - 3m 2 - 3m
3 - 2m 3 - 2m 3 - 3m 3 - 1m 3 - 1m 3 - 3m
4 - 2m 4a - 1m 4a - 2m 4 - 1m 4 - 1m 4 - 6m
5 - 3m 4b - 3m 4b - 2m 5a - 1m 5 - 2m
5 - 2m 5b - 2m 6 - 3m
6 - 1m
7 - 2m
8 - 3m
12 marks 13 marks 14 marks 13 marks 13 marks 15 marks
Q Answers Marks
Marki ng
3
Sect i on I - Mi l l enni um Devel opment Goal s (MDGs)
1 3 marks (any 3 of four)
- Achieve universal primary education
- Eradicate extreme poverty and hunger
- Promote gender equality and empower women
- Global partnership for development
2 2 marks (2 full reasons)
Status of women in the community improves.
The target is to eliminate gender disparities in education.
Children learn from their mothers so learning about finance is given to the next
generation.
It gives them hope and they start to save money.
3 2 marks (4x)
Micro-loans are used for any f our of the following answers:
- food production
- small manufacturing
- to buy cattle or sheep
- to repair a house
- to buy small tools
or any other valid answer. It does not specifically say in Burkina Faso
4 2 marks (-1 for each country not mentioned)
- Bangladesh
- Nicaragua
- Sudan
5 3 marks (3 x 1)
- Canada is a prosperous country in need of low skilled workers
- Germany is a country with an ageing population in need of all kind of
workers
- Workers in either of these countries do not want to do manual work
- Kuwait is a very small, rich and sparsely populated country in need of
workers for the oil industry and for domestic work
Any other valid reason
1
1
1
1
Q Answers Marks
4
Sect i on II - Fl ood
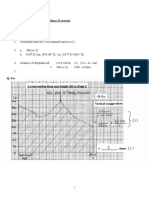
1 3 marks
see Source 1 (1925 = 1.19, 1938 = 3.10, 1944 = 15.50)
2 4 marks ( 3 marks for accuracy of points + 1 for best fit line)
3 2 marks
(marking will take into account students best-fit curve and answers)
- 250,000 cfs
- 2.9 years
1
1
4a 1 mark
Any interpretation of
- Observation: 7 of the top 10 discharges occur during the last decade.
- The majority of the higher discharges occur in the most recent years.
1
4b 3 marks
Possible causes are: (3 x1)
- deforestation in the river basin
- draining of marshes along the river
- removing obstacles (dredging) in the stream
- urbanisation of the river banks (impermeable surfaces)
- increased rainfall
any other valid answer
Q Answers Marks
5
Sect i on III - Popul at i on Geography
1 3 marks (3 x 1)
This should be descriptions of the pyramids, eg.
- changes from large population under 30 years of age in 1960 to projected
majority of over 40 in 2050
- life expectancy increased from 52.4 to 78.3
- fertility rate decreased from 6.2 to 1.08
- population has increased from 25m to 47m etc.
any other valid answer
2 2 marks
South Koreas transition from an aging to a super-aged society has been rapid,
with either the time taken or the years it happens/happened quoted.
It is not enough to just say rapid, as students have been told to support their
answer with data.
E.g.: transition is only expected to take 26 years - or broken down into its
2 steps - 18 +8 years. Or: transition is rapid, becoming an aging society in 2000
and a super-aged society by 2026.
3 3 marks
- Speed: The transition was much more rapid than for Western countries,
e.g. South Korea 26 years, France 154 years, USA 94 years. Or, South
Koreas transition is taking a generation, Western countries took decades
- Date of onset: The transition started much later than that for Western
countries, e.g. South Korea became an aging society in 2000, France in
1864, Germany in 1932
- J apan and Korea (Asia) similar as compared to Europe/USA (Western)
1
1
1
4a 2 marks
- Civilisation illnesses, e.g. obesity, high blood pressure, diabetes, heart
attack (2x)
- Main causes, e.g. lack of physical activity, wrong eating patterns, air
pollution, stress (2x)
4b 2 marks
- Parasite and infectious diseases, e.g. malaria, cholera, yellow fever,
tuberculosis etc. (2x)
- Main causes, e.g. lack of fresh and clean water, poor health service, low
hygiene standards, insects transmitting diseases, low awareness of
threats and ways of preventing infection (2x)
5 2 marks (2x1)
Two of the following answers:
- High mobility of people being a result of increased tourism and business
travels, popularity of air transportation
- Growing number of people
- Mutations and resilience of viruses due to common antibiotics use
Q Answers Marks
6
Sect i on IV - Land f orms
1 1 mark (2 x 1/2 from these three)
- A
- E
- F
2 1 mark (2 x 1/2)
- B
- C
- D
3 1 mark
- b (sill)
4 1 mark
- b (wadi)
5 3 marks
a: barchans
b: description of process below :
- The wind blows consistently from one direction
- sand collects around a small obstruction
- sand piles up with the arms of the barchan parallel to the wind direction
1
2
6 1 mark (2x)
Are students going to recognise this as a loess area?
China, Midwestern United States (with very thick loess deposits)
Suggest take other answers such as South West USA and Central Asi a
7 2 marks
- b with basalt columns in the picture
- c igneous rock
1
1
8 3 marks
- geyser
- forms in a volcanic area
- ground water comes into contact with magma below the earths surface
which is at a high temperature
- The water boils and turns to steam
- Pressure increases and the water column on top of the steam is forced
out of the cavity at regular intervals as a spout or fountain of hot water.
1
1
1
Q Answers Marks
7
Sect i on V - Agri cul t ure and envi ronment
1 3 marks (3 x 1)
- most of farm holdings less than 1 ha in size
- decreasing average size of holdings.
- only 1% of holdings are greater than 10ha in size
- primitive subsistence farming any other valid observation
2 3 marks
An example of elements of a right vicious circle is:
Poverty - No money to buy fertilizers/pesticides et cetera - Low yields -
Low income - Bad health - Low output/workforce - Poverty
Every component mi ssi ng under 5 i s 1 mark l ess.
3 1 mark
- retaining walls have to be built to enclose the water
- transporting water to the fields from wells, or reservoirs can be expensive
- Water must be shared out between all the farmers so all get a fair share.
1
1
1
4 1 mark
massive deforestation
5 2 marks (2 x 1)
- lack of energy resources (therefore, wood is used as charcoal)
- population growth (overpopulation / pressure on natural resources,
including forests; need for jobs etc)
- population poverty (wood as the only source of income for many people)
6 3 marks (3 x 1)
- land and soil degradation
- deterioration of hydrological balance (fresh water shortages in many
places, including the capital, Port au Prince; underground resources will
no longer be properly supplied by rainwater, as massive runoff will erode
the slopes)
- increase of natural hazards effects
any other valid answer
Q Answers Marks
8
Sect i on VI - Nat ural hazards
Disasters of the 21
st
century
1 3 marks (6x)
Photo Count ry and cause
A Chile - earthquake, tsunami
B Haiti - earthquake
C Iceland - volcano eruption
D Indonesia - earthquake, tsunami
E USA - hurricane (Katrina) floods
F USA - (Gulf of Mexico), oil platform explosion and spill
2 3 marks (6x)
Locations of these disasters (A F) on map.
A
B
C
D
E F
Q Answers Marks
9
3 3 marks (1 + 4x)
Earthquakes
Four of the following:
- cause tsunamis and landslides,
- can have many aftershocks,
- happen unexpectedly,
- affect large areas,
- demolish buildings and infrastructures,
- failure of infrastructures interferes with rescue operations.
1
2
4 6 marks (2 x 0.5 marks)
Note
Di sasters must be of di fferent ori gi n
Onl y t wo di sast ers shoul d be chosen and t hen 2 ef f ect s i n each box.
Di saster Ef f ect s on l ocal ...
... popul at i on ... envi ronment ... economy
A Death, injuries,
homelessness,
diseases, lack of fresh
water, food and
medications,
psychological trauma,
prison escapes, riots
Decrease in number
of plants and
animals, destruction
of habitats, floods,
contamination,
pollution from
broken
infrastructures
Loosing income,
repairing buildings,
factories and
infrastructures
B Death, injuries,
homelessness,
diseases, violence,
lack of fresh water,
food and medications,
psychological trauma
Decrease in number
of plants and
animals, destruction
of habitats, floods,
contamination,
pollution from
broken
infrastructures
Loosing income,
repairing buildings
and infrastructures
C Evacuation because
of ash, smothering,
loosing homes and
property, fires
Changes on
temperature (clouds,
less sunshine),
alkaline rains, ash
rains, changes in
soil, smothering
plants, fires
Reparations of
infrastructure,
flights cancelled, all
other sorts of
transportation
used, people did
not make it to their
jobs
Q Answers Marks
10
D Death, injuries,
homelessness,
diseases, lack of fresh
water, food and
medications,
psychological trauma,
panic
Contamination of
fields with salt
water, changes in
the sea-bottom,
washed away sands,
impact on
mangroves, coral
reefs, forests,
wetlands and dunes,
groundwater
Loss of fisheries,
unemployment,
decrease in tourism
E Evacuation, death,
injuries, looting,
homelessness,
psychological trauma,
largest diaspora in the
USA
Forest lands
destroyed, beach
erosion, loss of
habitats, breeding
areas, loss of
marshes, oil spills,
contaminated water
pumped to a lake
Expensive
reconstruction
works in Gulf of
Mexico
transportation and
oil platforms,
missing crops,
unemployment, no
taxes, increased
insurances
F Affects people who
are living on the
beach, cannot swim
Impact on marine
and coastal habitats,
long-term food chain
changes, eggs do
not develop
Closing down
fisheries, decrease
in tourism,
collecting oil, taking
precautionary
measures
* The response is not all inclusive.
You might also like
- Comprehensive Test N 1 Bac ArtsDocument5 pagesComprehensive Test N 1 Bac ArtsHafnawi SwilhiNo ratings yet
- Our Country, The Planet: Forging A Partnership For SurvivalFrom EverandOur Country, The Planet: Forging A Partnership For SurvivalNo ratings yet
- Guide To Junior Cert Geography Higher LevelDocument10 pagesGuide To Junior Cert Geography Higher LevelBrian CroninNo ratings yet
- Wildlife-Habitat Relationships: Concepts and ApplicationsFrom EverandWildlife-Habitat Relationships: Concepts and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- NỘI DUNG ÔN TẬP KHỐI 10 - HK2 - 22-23Document17 pagesNỘI DUNG ÔN TẬP KHỐI 10 - HK2 - 22-23Ngân LêNo ratings yet
- MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2006 Question Paper: University of Cambridge International Examinations GCE O LevelDocument9 pagesMARK SCHEME For The May/June 2006 Question Paper: University of Cambridge International Examinations GCE O Levelmstudy123456No ratings yet
- Concours ITA Session 2014: Read The Text and Fulfil The Tasks BelowDocument2 pagesConcours ITA Session 2014: Read The Text and Fulfil The Tasks Belowkunto massouoNo ratings yet
- Grade 10-Lesson Plan-Agriculture October 2018Document10 pagesGrade 10-Lesson Plan-Agriculture October 2018Amaziah GedaliahNo ratings yet
- Thesis On Land DegradationDocument8 pagesThesis On Land Degradationdebbirchrochester100% (2)
- Pakistan Studies-P2-10-MSDocument13 pagesPakistan Studies-P2-10-MSzeesha tahirNo ratings yet
- World Regions in Global Context People Places and Environments 6Th Edition Marston Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument51 pagesWorld Regions in Global Context People Places and Environments 6Th Edition Marston Test Bank Full Chapter PDFRuthWilsoncoejg100% (9)
- World Regions in Global Context People Places and Environments 6th Edition Marston Test BankDocument30 pagesWorld Regions in Global Context People Places and Environments 6th Edition Marston Test Bankthuygladys5x0100% (22)
- 8291 w13 Ms 22Document8 pages8291 w13 Ms 22Caterina De LucaNo ratings yet
- MARK SCHEME For The June 2005 Question PaperDocument8 pagesMARK SCHEME For The June 2005 Question PaperFarrukh Zaheer MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Enviromental Degradation - Ana AraceliDocument18 pagesEnviromental Degradation - Ana AraceliLourdes BlancoNo ratings yet
- Problem Causes by EnvironmentDocument29 pagesProblem Causes by EnvironmentRafiaNabilaNo ratings yet
- Topic ResearchDocument8 pagesTopic Researchphuongnga8b0No ratings yet
- Unit 5Document10 pagesUnit 5giang lehoangNo ratings yet
- 13-14 F3 Geog 1st Term Exam (Answers)Document4 pages13-14 F3 Geog 1st Term Exam (Answers)jonas hoNo ratings yet
- EnvironmentDocument7 pagesEnvironmentNhu NguyenNo ratings yet
- Capitalizing On Assets: Vulnerability and Adaptation To Climate Change in NepalDocument23 pagesCapitalizing On Assets: Vulnerability and Adaptation To Climate Change in Nepaljiayichen889No ratings yet
- Major Causes of Environmental DegradationDocument12 pagesMajor Causes of Environmental DegradationMDevS NPTNo ratings yet
- READINGDocument223 pagesREADINGTran NgocHan TranNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2Document2 pagesQuiz 2JenemarNo ratings yet
- Envi. Sci. - Second Quarter Examination 2024 FDocument11 pagesEnvi. Sci. - Second Quarter Examination 2024 Feddielyolvido1002No ratings yet
- 2019 S1 Y9 Geog Exam Checklist and Summary NotesDocument8 pages2019 S1 Y9 Geog Exam Checklist and Summary NotesYeetusNo ratings yet
- Dowload Solution Manual For Environmental Issues Looking Towards A Sustainable Future 4th Edition by Daniel C. Abel PDFDocument5 pagesDowload Solution Manual For Environmental Issues Looking Towards A Sustainable Future 4th Edition by Daniel C. Abel PDFjen778No ratings yet
- CivilsTap - CSAT - English 9Document21 pagesCivilsTap - CSAT - English 9PPPNo ratings yet
- 10th Geography 21-22 - RemovedDocument24 pages10th Geography 21-22 - Removedrathermusaib800No ratings yet
- CN 3f. GeoambientalDocument71 pagesCN 3f. GeoambientalEduardoRiveraCruzNo ratings yet
- English 2sci21 2trim1Document2 pagesEnglish 2sci21 2trim1brook candyNo ratings yet
- 15 BÀI TẬP ĐỌC HIỂU TADocument40 pages15 BÀI TẬP ĐỌC HIỂU TA05 Nguyễn Văn DũngNo ratings yet
- Key Test 18 ListeningDocument5 pagesKey Test 18 ListeningNguyễn Hằng50% (2)
- Summative Test Eapp Week1&2Document3 pagesSummative Test Eapp Week1&2AbbegailPearl AguirreNo ratings yet
- Environmente 9 GradeDocument4 pagesEnvironmente 9 GradeCarla NascimentoNo ratings yet
- Geography SBA - Rachelle Mahabir PDFDocument38 pagesGeography SBA - Rachelle Mahabir PDFKrystin ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Environmental Systems and Societies Paper 2 SL MarkschemeDocument11 pagesEnvironmental Systems and Societies Paper 2 SL MarkschemeAfra LamisaNo ratings yet
- Exam Date - PeriodDocument10 pagesExam Date - Periodapi-270387817No ratings yet
- World Geography 2: Hydrosphere: FocusDocument7 pagesWorld Geography 2: Hydrosphere: FocusHamari PotliNo ratings yet
- Answer Key For EvsDocument4 pagesAnswer Key For EvsAbhishek FfNo ratings yet
- Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and WildlifeDocument14 pagesLand, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and WildlifeYamini SharmaNo ratings yet
- MLP Land Soilwater and Natural Vegetation 1Document7 pagesMLP Land Soilwater and Natural Vegetation 1PianoPianistNo ratings yet
- Suggested Answer For Form 3 Final Examination 2012Document3 pagesSuggested Answer For Form 3 Final Examination 2012jonas hoNo ratings yet
- Academic Question Paper Test 4Document24 pagesAcademic Question Paper Test 4Mai Anh Nguyen0% (1)
- Climate Change Is Altering Patterns of Weather Around The World, Causing Droughts in Many Regions. AroundDocument5 pagesClimate Change Is Altering Patterns of Weather Around The World, Causing Droughts in Many Regions. Aroundleila salehNo ratings yet
- C. B. S. E. Sample Question Paper (2020-21) GEOGRAPHY (029) Class 12Document18 pagesC. B. S. E. Sample Question Paper (2020-21) GEOGRAPHY (029) Class 12Abdella nemoNo ratings yet
- Geography SBA1Document19 pagesGeography SBA1Kaniel BenjamiteNo ratings yet
- 16-Core Subject-Science 11-Earth - Lide Science-Q1-Module 16Document23 pages16-Core Subject-Science 11-Earth - Lide Science-Q1-Module 16BruceNo ratings yet
- Gatundu 2015 Geo Pp1 Marking SchemeDocument9 pagesGatundu 2015 Geo Pp1 Marking Schemeedward mokayaNo ratings yet
- Test EnvironmentDocument6 pagesTest EnvironmentboteamanuelacorinaNo ratings yet
- Environment: Name and Surname: - Points AchievedDocument16 pagesEnvironment: Name and Surname: - Points AchievedNastja VogrincNo ratings yet
- Answer Keys. Retake Exam of GeographyDocument9 pagesAnswer Keys. Retake Exam of GeographyBawan AhmedNo ratings yet
- SBI PO 2019 Prelims: Memory Based Question PaperDocument75 pagesSBI PO 2019 Prelims: Memory Based Question PaperJoseph V. RalteNo ratings yet
- Soil and ChangeDocument16 pagesSoil and Changeapi-241480872No ratings yet
- Land Degradation AmericaDocument26 pagesLand Degradation Americaapi-253104811No ratings yet
- GRADE 9 Edexcel EnglishDocument10 pagesGRADE 9 Edexcel EnglishLithumya BasnayakeNo ratings yet
- Environmental Globalization (Rev) - Group4Document34 pagesEnvironmental Globalization (Rev) - Group4JOSHUA GUIMBANGUNANNo ratings yet
- 2010 Lessons CombinedDocument10 pages2010 Lessons CombinedKevin CammNo ratings yet
- C CCCC C C !"#$%&#&' # '& +,+Document8 pagesC CCCC C C !"#$%&#&' # '& +,+Versha RustagiNo ratings yet
- Text Structure 3Document4 pagesText Structure 3api-328694348No ratings yet
- Keyza Persuasiveessay 2Document4 pagesKeyza Persuasiveessay 2api-302228724No ratings yet
- MSDS Hydrated LimeDocument4 pagesMSDS Hydrated Limemechanical_qutu3636No ratings yet
- Environmental: Systems SocietiesDocument19 pagesEnvironmental: Systems SocietiesVIVIANA LISETTE MEDINA NARANJONo ratings yet
- Arc 504 Final Review in The Age of Covid-19: Alejandro Zaera-Polo With Joon MaDocument3 pagesArc 504 Final Review in The Age of Covid-19: Alejandro Zaera-Polo With Joon MadodmaddodNo ratings yet
- Gateway B2+ Test Unit 2 ADocument6 pagesGateway B2+ Test Unit 2 Aana maria csalinas67% (3)
- Prevention of Energy CrisisDocument3 pagesPrevention of Energy CrisisNaveen IdxNo ratings yet
- 02 Flood Control Purpose and Flood Control Master PlanningDocument45 pages02 Flood Control Purpose and Flood Control Master PlanningJapoyNo ratings yet
- Pelamis Wave Energy Converter (Le202)Document26 pagesPelamis Wave Energy Converter (Le202)Dasari Ramamohana0% (1)
- Brown Laws Reaction PaperDocument3 pagesBrown Laws Reaction PaperSai RosalesNo ratings yet
- Đề thi học kì 2 lớp 9 môn Tiếng AnhDocument4 pagesĐề thi học kì 2 lớp 9 môn Tiếng AnhMin MinNo ratings yet
- Devcom Paper - RachoDocument9 pagesDevcom Paper - RachoJhelen RachoNo ratings yet
- On Thi Vao Lop 10 Chuyen de Doc Hieu Tieng AnhDocument17 pagesOn Thi Vao Lop 10 Chuyen de Doc Hieu Tieng AnhMỹ HàNo ratings yet
- Bhendi Bazaar - Calculation AnalysisDocument45 pagesBhendi Bazaar - Calculation AnalysisAmit K. YadavNo ratings yet
- English Speech Save Our Earth Save Our RainforestDocument3 pagesEnglish Speech Save Our Earth Save Our RainforestYeremia Billy100% (1)
- Environmental Change and Security Program Report 3Document240 pagesEnvironmental Change and Security Program Report 3The Wilson CenterNo ratings yet
- Isopropyl Alcohol MsdsDocument5 pagesIsopropyl Alcohol MsdsMátyás KabaiNo ratings yet
- Case Study: ProblemDocument2 pagesCase Study: ProblemArashdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science and Engineering R2017 SyllabusDocument2 pagesEnvironmental Science and Engineering R2017 SyllabusPrasannakumar S Asst.profNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - Booming Population Leader: Tan, Maria Fatima O Secretary: Villamor, Mariella LoisDocument2 pagesGroup 1 - Booming Population Leader: Tan, Maria Fatima O Secretary: Villamor, Mariella LoisPhilip CastroNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Exercises Geography An I PDFDocument16 pagesVocabulary Exercises Geography An I PDFDenisaElenaNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Affects Land-Disposed WasteDocument2 pagesClimate Change Affects Land-Disposed WasteXI CHENNo ratings yet
- FA2020 - ENE505 - L5.5 - Nuclear Power AccidentsDocument22 pagesFA2020 - ENE505 - L5.5 - Nuclear Power AccidentsTommy TrojanNo ratings yet
- Background: A Case Study: Earthquake in Izmit, Turkey 1999Document8 pagesBackground: A Case Study: Earthquake in Izmit, Turkey 1999OZDEN ERYASAR YILDIRMAZNo ratings yet
- Thirsty ConcreteDocument21 pagesThirsty ConcreteARVIND SINGH RAWAT100% (1)
- CASA Technology's Heat Wave Mind MapDocument1 pageCASA Technology's Heat Wave Mind MapseanvaislerNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Risk Factors Underlying DisastersDocument28 pagesLesson 2 Risk Factors Underlying DisastersStefen SantosNo ratings yet
- Environmental Sociology An IntroductionDocument12 pagesEnvironmental Sociology An IntroductionEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Environmental Management and Disasters: Contributions of The Discipline To The Profession and Practice of Emergency ManagementDocument30 pagesEnvironmental Management and Disasters: Contributions of The Discipline To The Profession and Practice of Emergency Managementichchhit srivastavaNo ratings yet
- FlavomycinDocument1 pageFlavomycinAftar RaffNo ratings yet
- When Helping Hurts: How to Alleviate Poverty Without Hurting the Poor . . . and YourselfFrom EverandWhen Helping Hurts: How to Alleviate Poverty Without Hurting the Poor . . . and YourselfRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (36)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessFrom EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessNo ratings yet
- The Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorFrom EverandThe Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (137)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldFrom EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (597)
- The Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterFrom EverandThe Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterNo ratings yet
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (812)
- Water to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesFrom EverandWater to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (21)
- Smokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersFrom EverandSmokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersNo ratings yet
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- Fire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutFrom EverandFire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (142)
- The Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsFrom EverandThe Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (65)
- When You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsFrom EverandWhen You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (13)
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsFrom EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (223)
- High-Risers: Cabrini-Green and the Fate of American Public HousingFrom EverandHigh-Risers: Cabrini-Green and the Fate of American Public HousingNo ratings yet
- Come Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogFrom EverandCome Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (10)
- The Meth Lunches: Food and Longing in an American CityFrom EverandThe Meth Lunches: Food and Longing in an American CityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)