Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Questio 1
Uploaded by
Ankit GuptaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Questio 1
Uploaded by
Ankit GuptaCopyright:
Available Formats
Question .1. State Snells law of refraction.
Snells law of refraction - The ratio of the sine of angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is always constant.
Question .2. The refractive index of air with respect to glass is defined as
g
a
= sin i / sin r
(i) Write down a similar expression for a g in terms of angle i and angle r.
(ii) In (i) above, if angle r = 90 what is the corresponding angle i called ?
(iii) What is the physical significance of i in part (ii) above ?
(i) The corresponding expression for
a
g
is
a
g
= sin r / sin i
(ii) The i for which r = 90 is called the critical angle of incidence. It is the angle of incidence for which the angle of refraction in
the rarer medium is 90. When the angle of incidence exceeds this angle, the incident ray is reflected back in the same medium
and does not get refracted into the second medium. This situation is referred to as the phenomenon of total internal reflection.
Question .3. What is meant by
(i) Critical angle
(ii) Total internal reflection.
(i) Critical angle The incident angle in the denser medium for which the angle of refraction in the rarer medium is 90 is called
the critical angle.
(ii) Total internal reflection When light travels from a denser to a rarer medium it bounces back into the denser medium under
suitable condition, this phenomena is called total internal reflection.
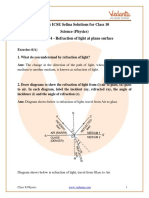
Question .4. Draw a ray diagram to illustrate how a ray of light incident obliquely on one face of a rectangular glass slab of
uniform thickness emerges parallel to its original direction. Mention which pairs of angles are equal.
For drawing consult a T. B.
(i) Angle of incidence is equal to the angle of emergent in the air.
(ii) Angle of refraction is equal to the angle of incidence in the glass.
Question .5. Water in a pond appears to be only three quarter of its actual depth.
(i) What property of light is responsible for this observation ?
(ii) Illustrate your answer with the help of a ray diagram.
(i) Refraction of light is responsible for this property. When light coming from denser medium inters rarer medium , it is bent
away from the normal.
(ii) For ray diagram consult a T. B.
Question .6. (i) With the help of a well labelled diagram show that the apparent depth of an object, such as a coin, in water
is less than its real depth.
(ii) How is the refractive index of water related to the real depth and the apparent depth of a column of water ?
i) For diagram consult a T. B.
(ii) The refractive index is related to the real depth and the apparent depth as,
= Real depth / Apparent depth.
Question .8. What is an optical fibre ? Give one practical use of an optical fibre.
An optical fibre is a fibre of diameter of the order of 2 m, made of glass plastic. It ia made of a high refractive index core
surrounded by a low refractive coating called cladding. It is widely used for communication purposes.
Question .9. Explain briefly what causes the twinkling of stars at night.
Light coming from the stars passes through the different layers of the atmosphere. There are random variation in the refractive
index of the different layers of the atmosphere. Due to this there is random variation in the path of the refracted light coming from
the stars. The light of a particular star , therefore, seems to change direction often thereby showing the twinkling of that star.
Question .10. What is meant by the statement, the critical angle for diamond is 24 ? How is the critical angle of the
material related to its refractive index ?
When the light ray passing from diamond to air , incident at the boundary at an angle of incidence equal to 24, it is refracted
along the boundary surface i.e. the angle of refraction becomes 90. As, the sine of the critical angle is equal to the reciprocal of
the refractive index of that material i.e. sinic = 1/.
Question .11. A glass slab is placed over a page on which the word VIBGYOR is printed with each letter in its
corresponding colour.
(i) Will the image of all the letters be in the same place ?
(ii) If not, state which letter will be raised to the maximum. Give a reason for your answer.
i) No, the images of letters of different colours will be raised by slightly different heights.
(ii) The letter, V, corresponding to the violet colour will be raised to the maximum. As, = real depth / apparent depth . Now is
maximum for the violet colour and apparent depth would , therefore, be the least. Hence the violet colour (V) would be raised to
the maximum.
Question .12. What is meant by refraction ?
The phenomenon in which the path of a ray of light changes when it moves from one medium to another is called refraction.
Question .13. Express the refractive index of a medium
(i) in terms of the velocity of light;
(ii) in terms of the angle of incidence i in air and the angle of refraction r in a denser medium.
(i) = velocity of light in vacuum / velocity of light in medium.
(ii) = sin i / sin r.
Question .14. If a ray of light passes from medium I to medium II without any change of direction, what can be said about
the refractive indices of these media (angle i is not 0) ?
These two media have the same refractive index.
Question .15. Mention two properties of a wave: one property which varies and the other which remains constant when the
wave passes from one medium to another.
(i) Wavelength and
(ii) Frequency.
Question .16. A prism deviates a monochromatic ray of light through an angle when the angle of incidence on the
surface of the prism is i:
(i) Draw a diagram showing the variation of with i. On your graph show the angle of minimum deviation.
(ii) What is the relation between the angle of incidence and the angle of emergence when the ray suffers minimum
deviation ?
(i) For diagram contact a T. B.
(ii) In the position of minimum deviation, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of emergence
Question .17.Mention one difference between reflection of light from a plane mirror and total internal reflection of light
from a prism.
Refection of light from a plane mirror Total internal reflection of light from a prism
1. The reflection of light incident on the mirror
takes place for all angles of incidence.
1. The incident ray is first refracted and then
suffers total reflection from the other face only, if
light is incident at an angle greater than the critical
angle.
2. A lot of light energy is absorbed in ordinary
reflection.
2. No light is absorbed during total internal
reflection.
You might also like
- AF - Class-X-Icse-Light Test AnswerDocument4 pagesAF - Class-X-Icse-Light Test AnswerPrateek KhareNo ratings yet
- Refraction at Plane SurfacesDocument2 pagesRefraction at Plane SurfacesVenu GopalNo ratings yet
- Jashmeet Physics Project File PDF Made by Lallu DadaDocument12 pagesJashmeet Physics Project File PDF Made by Lallu Dadalalit palNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 12 Physics ReflectionDocument15 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 12 Physics ReflectionRaagul SaravanaKumarNo ratings yet
- Physics IP ProjectDocument17 pagesPhysics IP ProjectHimanshu yadavNo ratings yet
- Project Report on Total Internal ReflectionDocument13 pagesProject Report on Total Internal ReflectionJesmin ChakmaNo ratings yet
- CBSE TERM2 - Ray OpticsDocument132 pagesCBSE TERM2 - Ray Opticsvenom eNo ratings yet
- Refraction of Light 23-36Document50 pagesRefraction of Light 23-36chirayuaggarwal2006No ratings yet
- Refraction - Plane Surfaces - 5 PDFDocument28 pagesRefraction - Plane Surfaces - 5 PDFVasanthkumar YennamreddyNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics PDFDocument21 pagesRay Optics PDF1996vishakNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS - PROJECT - FINAL by K BharadwajDocument13 pagesPHYSICS - PROJECT - FINAL by K BharadwajKannuri BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Physics Project On Total Internal ReflectionDocument8 pagesPhysics Project On Total Internal Reflectionharnaek singhNo ratings yet
- Refraction - Plane Surfaces - 5 PDFDocument28 pagesRefraction - Plane Surfaces - 5 PDFravibabukancharlaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document58 pagesChapter 1DXN LUDHIANANo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Critical Angle and Refractive IndexDocument23 pagesRelationship Between Critical Angle and Refractive IndexNurul Syafiqah RoslanNo ratings yet
- Selina Refraction-of-Light-at-Plane-SurfacesDocument51 pagesSelina Refraction-of-Light-at-Plane-SurfacesOverRush Amaresh100% (1)
- RefractionDocument19 pagesRefractionYugandhar Veeramachaneni50% (2)
- Class 10 - Physics - Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces SolutionsDocument68 pagesClass 10 - Physics - Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces SolutionsAndrik LalNo ratings yet
- Igcse 33 LightwavesDocument36 pagesIgcse 33 LightwavesMuhammad Ahsan Ali KharalNo ratings yet
- Physics Project RealDocument18 pagesPhysics Project RealAnaconda Warriors 12 ANo ratings yet
- Refraction Through Prism ExperimentDocument16 pagesRefraction Through Prism ExperimentSahil baggaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Total Internal Reflection of LightDocument21 pagesUnderstanding Total Internal Reflection of LightSiti Arbaiyah AhmadNo ratings yet
- Total Internal Reflection - PhyDocument16 pagesTotal Internal Reflection - PhyRishabh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Refraction ExplainedDocument18 pagesRefraction ExplainedChaelaNo ratings yet
- (Chapter-9) Ray Optcis and Optical Instruments-1Document47 pages(Chapter-9) Ray Optcis and Optical Instruments-1Satyam GamingNo ratings yet
- Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces NotesDocument8 pagesRefraction of Light at Plane Surfaces NotesICSE BOARDNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes For Class 12 Chapter 9 Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument19 pagesPhysics Notes For Class 12 Chapter 9 Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsV3MON LOLNo ratings yet
- Light Waves: Edexcel Igcse / Certificate in PhysicsDocument34 pagesLight Waves: Edexcel Igcse / Certificate in PhysicsertugozNo ratings yet
- Light Compare The Rival Theories of Light Held by ScientistsDocument12 pagesLight Compare The Rival Theories of Light Held by ScientistsPhilip MooreNo ratings yet
- 03 REFRACTION OF LIGHT AT PLANE SURFACES NEWDocument14 pages03 REFRACTION OF LIGHT AT PLANE SURFACES NEWSreekar GaliNo ratings yet
- Physics Unit 7 Part 1 Notes Better 09 VersionDocument32 pagesPhysics Unit 7 Part 1 Notes Better 09 VersionTaylor Waddell-SmithNo ratings yet
- 4229 Topper 21 101 4 4 143 294 Total Internal Reflection Up201609191215 1474267517 9593Document6 pages4229 Topper 21 101 4 4 143 294 Total Internal Reflection Up201609191215 1474267517 9593Karan Singh RajawatNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes For Class 12 Chapter 9 Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument19 pagesPhysics Notes For Class 12 Chapter 9 Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsAsamNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument6 pagesOpticsAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Notes of CH - 10 Light (Refraction) Class - X-1Document12 pagesNotes of CH - 10 Light (Refraction) Class - X-1Sankalp MishraNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Light WorksheetDocument45 pagesIGCSE Light WorksheetAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- CH12 PPT 1Document49 pagesCH12 PPT 1kaungforgameNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions (In Reflection)Document13 pagesMultiple Choice Questions (In Reflection)Davinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Viva Voce Refractive IndexDocument7 pagesViva Voce Refractive Indexyourajsingh22072005No ratings yet
- Ray Optics - 2Document70 pagesRay Optics - 2Raj Kumar PerliNo ratings yet
- D.K.Pandey: Viva Voce ForDocument13 pagesD.K.Pandey: Viva Voce Forpratyush mishraNo ratings yet
- IGCSE 33 LightWavesDocument33 pagesIGCSE 33 LightWavesyatnesh.1984No ratings yet
- Ray Optics - 2Document7 pagesRay Optics - 2jiluNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument20 pagesPhysics Formula Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsJeshanth JsNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics Questions March 24Document3 pagesRay Optics Questions March 24Athish PranavNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5.3 LightDocument10 pagesLesson 5.3 LightRais RahimiNo ratings yet
- Light Physic Form 4Document15 pagesLight Physic Form 4kumuthaNo ratings yet
- Refraction of Light Plane Surfaces PDFDocument3 pagesRefraction of Light Plane Surfaces PDFPrudhvi JoshiNo ratings yet
- Refraction Notes - Speed of Light and Lens PropertiesDocument12 pagesRefraction Notes - Speed of Light and Lens PropertiesParv GuptaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Reflection and Refraction of LightDocument15 pagesUnderstanding Reflection and Refraction of Lightjesunathan44@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- G-8 Icse Physics Chapter: Light Energy Important PointsDocument29 pagesG-8 Icse Physics Chapter: Light Energy Important PointsBharath BabuNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument51 pagesOpticsUday Kiran ChNo ratings yet
- Ray OpticsDocument7 pagesRay OpticsArchana RachelNo ratings yet
- Ch9-10 CBSE 2023Document4 pagesCh9-10 CBSE 2023tebor93898No ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Light InteractionsDocument6 pagesLesson 5 - Light InteractionsKeisha Therese AllenbyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document50 pagesChapter 2raja noraisar raja rahimNo ratings yet
- A Practical Manual of the Collodion Process: Giving in Detail a Method For Producing Positive and Negative Pictures on Glass and PaperFrom EverandA Practical Manual of the Collodion Process: Giving in Detail a Method For Producing Positive and Negative Pictures on Glass and PaperNo ratings yet
- Questions SsDocument5 pagesQuestions SsAnkit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Marketing ProjectDocument26 pagesMarketing ProjectAnkit GuptaNo ratings yet
- My Project Mutual Funds - 2Document132 pagesMy Project Mutual Funds - 2Ankit GuptaNo ratings yet
- E-Bulletin MAY - JUNE 2014Document59 pagesE-Bulletin MAY - JUNE 2014Ankit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Biotech Colleges in VizagDocument5 pagesBiotech Colleges in VizagAnkit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Metals N Non Metals IcseDocument6 pagesMetals N Non Metals IcseAnkit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper - 2013 Class - IX Subject - Biology: Section ADocument3 pagesSample Paper - 2013 Class - IX Subject - Biology: Section AAnkit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Questions for Physics ExamDocument3 pagesCurrent Electricity Questions for Physics ExamAnkit GuptaNo ratings yet
- ICSE 2017 Chemistry Science Sample Paper 2 PDFDocument7 pagesICSE 2017 Chemistry Science Sample Paper 2 PDFPrabhat BhatNo ratings yet
- Project KavyaDocument98 pagesProject KavyaAnkit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Test Linear Quations in Two VariablesDocument2 pagesTest Linear Quations in Two VariablesAnkit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Hospitality Industry GuideDocument15 pagesHospitality Industry Guideamitsinghbdn67% (3)
- 14 Provisions Related To ChargeDocument7 pages14 Provisions Related To ChargeMarie AnnNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: F.M-60 Time - 1 HR 30 MinDocument2 pagesMathematics: F.M-60 Time - 1 HR 30 MinAnkit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Vikas Mahila Campus Accountancy - XIIDocument1 pageVikas Mahila Campus Accountancy - XIIAnkit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Vikas Mahila Campus Accountancy - Xi: ST STDocument1 pageVikas Mahila Campus Accountancy - Xi: ST STAnkit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument40 pagesDiabetes MellitusMansour HassanNo ratings yet
- Cultivating youth potential through self-confidenceDocument22 pagesCultivating youth potential through self-confidenceAnkit GuptaNo ratings yet
- 2Document5 pages2Ankit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Scope of Financial ManagementDocument41 pagesScope of Financial ManagementbmsoniNo ratings yet
- Aiims Housing ProjectsDocument6 pagesAiims Housing ProjectsAnkit GuptaNo ratings yet
- 05 Origin UniverseDocument59 pages05 Origin UniverseKent Francis LayaguinNo ratings yet
- A Short History of The Mahabodhi Temple in BodhgayaDocument2 pagesA Short History of The Mahabodhi Temple in BodhgayaAnkit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Photon beam characteristics & basic concepts of treatment planningDocument63 pagesPhoton beam characteristics & basic concepts of treatment planningChino PlagaNo ratings yet
- TirDocument3 pagesTircharlottechoiNo ratings yet
- High Speed Sync PresentationDocument20 pagesHigh Speed Sync Presentationcutepixel0716No ratings yet
- 6 BLP Spesifikasi Teknis 49 SMA 14920Document6 pages6 BLP Spesifikasi Teknis 49 SMA 14920Ricardo NapitupuluNo ratings yet
- To Determine The Refractive Index Using Travelling MicroscopeDocument4 pagesTo Determine The Refractive Index Using Travelling MicroscopeIrfan SergioNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual For Process Refractometer PR-01-S (-AX/FM/CS)Document107 pagesInstruction Manual For Process Refractometer PR-01-S (-AX/FM/CS)claudiotech76No ratings yet
- HSC Physics Astrophysics NotesDocument26 pagesHSC Physics Astrophysics NotesjackmaloufNo ratings yet
- Karakteristik Klinis Dan Hasil Implantasi Lensa Intra Okular Iris Claw Pada Kasus Afakia Di Rumah Sakit Mata Cicendo - Azalia LatuasanDocument10 pagesKarakteristik Klinis Dan Hasil Implantasi Lensa Intra Okular Iris Claw Pada Kasus Afakia Di Rumah Sakit Mata Cicendo - Azalia Latuasanwasobiru isbiruNo ratings yet
- The History of The Photographic FlashDocument3 pagesThe History of The Photographic FlashKatie SNo ratings yet
- Laser Tissue InteractionDocument28 pagesLaser Tissue InteractionbiomedyuvaNo ratings yet
- A Practical Approach To Clinical Photography (III)Document6 pagesA Practical Approach To Clinical Photography (III)Stefani TCNo ratings yet
- Light FittingDocument3 pagesLight FittingPrasadNo ratings yet
- PrefaceDocument75 pagesPrefacetricia ona100% (1)
- Katalog Mikroskop BiologiDocument14 pagesKatalog Mikroskop BiologiDewi Endar YatunNo ratings yet
- Advanced Optical Wireless Communication Systems PDFDocument404 pagesAdvanced Optical Wireless Communication Systems PDFPrashant KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Rugged Video Cameras DatasheetsDocument2 pagesRugged Video Cameras Datasheets99ludesterNo ratings yet
- Optical CoatingsDocument36 pagesOptical CoatingsJan NovotnyNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance & Control in RadiologyDocument6 pagesQuality Assurance & Control in RadiologyEly0% (1)
- Ijarbn Conference Proceedings Nsctls-2021Document145 pagesIjarbn Conference Proceedings Nsctls-2021ijarbn editorNo ratings yet
- Numerical Analysis of Nonlinear Pulse Propagation in Optical Fiber PDFDocument107 pagesNumerical Analysis of Nonlinear Pulse Propagation in Optical Fiber PDFhisho100% (1)
- T-REC-G.671-201202-Características de Transmisión de Los Componentes y Subsistemas ÓpticosDocument46 pagesT-REC-G.671-201202-Características de Transmisión de Los Componentes y Subsistemas ÓpticosjoaquicNo ratings yet
- David Starter Kit GBDocument25 pagesDavid Starter Kit GBcncstepNo ratings yet
- EssayDocument2 pagesEssayMiguel Torres AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Practical File 2023Document23 pagesPractical File 2023DZ GamesNo ratings yet
- Frensel Lenses - Fresnel Technologies, IncDocument12 pagesFrensel Lenses - Fresnel Technologies, IncBruce VanceNo ratings yet
- Optical CommunicationDocument25 pagesOptical CommunicationKlNo ratings yet
- Forensic Photography ModuleDocument37 pagesForensic Photography ModuleStephanie Shanne VenturaNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction of EM WavesDocument47 pagesReflection and Refraction of EM WavesFranklin GarysonNo ratings yet
- The Flying Circus of Physics, 2: Jearl WalkerDocument39 pagesThe Flying Circus of Physics, 2: Jearl WalkerPatreNo ratings yet
- An PVS-14Document2 pagesAn PVS-14ArmySGT100% (1)