Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Points & Straight Lines - Solutions
Uploaded by
wolfretonmathsCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Points & Straight Lines - Solutions
Uploaded by
wolfretonmathsCopyright:
Available Formats
AQA Core 1 Coordinate geometry
1 of 11 10/01/13 MEI
Section 1: Points and straight lines
Solutions to Exercise
1. (a) (i) Gradient of AB
1 2
1 2
1 4 3 3
3 7 4 4
y y
x x
= = = =
.
(ii) Gradient m of perpendicular line satisfies
3
4
1 m =
so gradient of perpendicular line
4
3
= .
(iii) Midpoint of AB ( )
+ +
| |
= =
|
\ .
3 7 1 4
, 5, 2.5
2 2
(iv) Distance AB
2 2
(3 7) (1 4)
16 9
25
5
= +
= +
=
=
(b) (i) Gradient of AB
1 2
1 2
9 ( 1) 10
2
2 3 5
y y
x x
= = = =
.
(ii) Gradient m of perpendicular line satisfies 2 1 m =
so gradient of perpendicular line
1
2
= .
(iii) Midpoint of AB ( )
+ +
| |
= =
|
\ .
9 ( 1) 2 3
, 0.5, 4
2 2
(iv) Distance AB
2 2
( 2 3) ( 9 ( 1))
25 100
125
5 5
= +
= +
=
=
2. (i) Gradient of AB
1 2
1 2
1 1
3 6 3
y y y y
x x
= = =
Gradient of AB = 2
1
2
3
1 6
7
y
y
y
=
=
(ii) Distance AB is 5
AQA C1 Coordinate geometry 1 Exercise solutions
2 of 11 10/01/13 MEI
2 2
2
2
(3 6) (1 ) 5
9 (1 ) 25
(1 ) 16
1 4
1 4 or 1 4
3 or 5
y
y
y
y
y
y
+ =
+ =
=
=
= +
=
(iii) If A, B and C are collinear, gradient of AB = gradient of AC.
Gradient of AC
1 2
1 2
1 ( 2) 3 1
3 12 9 3
y y
x x
= = = =
From (i), gradient of AB
1
3
y
=
1
1
3 3
1 1
0
y
y
y
=
=
(iv) If AB is perpendicular to BC, then grad AB grad BC = -1
From (i), gradient of AB
1
3
y
=
Gradient of BC
1 2
1 2
( 2) 2
6 12 6
y y y y
x x
+
= = =
2
2
1 2
1
3 6
(1 )( 2) 18
2 18
20 0
( 5)( 4) 0
5 or 4
y y
y y
y y
y y
y y
y y
+
=
+ =
=
+ =
+ =
= =
(v) Length AB = length BC
2 2 2 2
2 2
2 2
(3 6) (1 ) (6 12) ( ( 2))
9 (1 ) 36 ( 2)
1 2 27 4 4
0 6 30
5
y y
y y
y y y y
y
y
+ = +
+ = + +
+ = + + +
= +
=
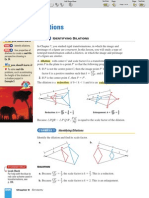
3. (i)
2 4 6 8 10 12
5
10
x
y
P (2, 1)
Q (6, 9)
R (10, 2)
AQA C1 Coordinate geometry 1 Exercise solutions
3 of 11 10/01/13 MEI
(ii) PQ = + = + =
2 2
(6 2) ( 9 1) 16 64 80
PR = + = + =
2 2
(10 2) (2 1) 64 1 65
QR = + = + =
2 2
(10 6) (2 9) 16 49 65
Since PR and QR are the same length, the triangle is isosceles.
(iii) Take the base of the triangle as PQ.
Let M be the midpoint of PQ
M ( )
+ +
| |
= =
|
\ .
1 9 2 6
, 4, 5
2 2
Height of triangle is MR = + = + =
2 2
(10 4) (2 5) 36 9 45
Area of triangle =
=
=
=
=
=
1
2
1
2
1
2
1
2
PQ MR
80 45
16 5 9 5
4 5 3 5
6 5
30
4. Gradient of EF
= = =
3 ( 1) 4
4
1 2 1
Gradient of FG
= = =
5 3 2
1
3 1 2
Gradient of GH
= = =
1 5 4
4
4 3 1
Gradient of EH
= = =
1 ( 1) 2
1
4 2 2
EF is parallel to GH and FG is parallel to EH
so EFGH is a parallelogram.
5. (i) 3 y x = +
Gradient = 1
When x = 0, y = 3
3
-3
AQA C1 Coordinate geometry 1 Exercise solutions
4 of 11 10/01/13 MEI
When y = 0, 3 0 3 x x + = =
(ii) 2 1 y x =
Gradient = 2
When x = 0, y = -1
When y = 0,
1
2
2 1 0 x x = =
(iii) 5
5
x y
y x
+ =
= +
Gradient = -1
When x = 0, y = 5
When y = 0, x = 5
(iv)
1
4
4 12
3
y x
y x
= +
= +
Gradient
1
4
=
When x = 0, y = 3
When y = 0, 12 0 12 x x + = =
(v)
1
3
3 6 0
3 6
2
y x
y x
y x
+ + =
=
=
Gradient
1
3
=
When x = 0, y = -2
When y = 0, 6 0 6 x x + = =
(vi)
2
5
5 15 2
3
y x
y x
=
=
-2
-6
AQA C1 Coordinate geometry 1 Exercise solutions
5 of 11 10/01/13 MEI
Gradient
2
5
=
When x = 0, 5 15 3 y y = =
When y = 0, 15 2 0 7.5 x x = =
6. (a) Gradient = 1, y-in tercept = 2
Equation of line is 2 y x = +
(b) Gradient =
1
2
, y-intercept = -1
Equation of line is
1
2
1 y x =
or 2 2 y x =
(c) Gradient =
1
2
, y-intercept = -2
Equation of line is
1
2
2 y x =
or 2 4 0 y x + + =
(d) Gradient =
1
4
,y- intercept = 3
Equation of line is
1
4
3 y x = +
or 4 12 y x + =
(e) Gradient =
8
3
, passes through (-1, 4)
Equation of line is
8
3
4 ( ( 1))
3( 4) 8( 1)
3 12 8 8
3 8 4
y x
y x
y x
y x
=
= +
=
+ =
7. (i) Gradient of 4 1 y x = is 4
Gradient of parallel line = 4
Equation of line is 3 4( 2)
3 4 8
4 5
y x
y x
y x
=
=
=
(ii) Gradient of 2 7 y x = + is 2
Gradient of perpendicular line is
1
2
Equation of line is
1
2
2 ( 1)
2( 2) ( 1)
2 4 1
2 5
y x
y x
y x
y x
=
=
= +
+ =
(iii)
1 10
3 3
3 10 y x y x + = = +
3
7.5
AQA C1 Coordinate geometry 1 Exercise solutions
6 of 11 10/01/13 MEI
Gradient is
1
3
Gradient of parallel line is
1
3
Equation of line is
1
3
( 1) ( 4)
3( 1) ( 4)
3 3 4
3 1
y x
y x
y x
y x
=
+ =
+ = +
+ =
(iv)
3
4
3 4 12 3 x y y x + = = +
Gradient is
3
4
Gradient of perpendicular line is
4
3
Equation of line is
4
3
0 ( ( 3))
3 4( 3)
3 4 12
y x
y x
y x
=
= +
= +
(v)
8 1
5 5
5 8 0 x y y x + + = =
Gradient is
1
5
Gradient of parallel line is
1
5
Equation of line is
1
5
( 6) ( ( 1))
5( 6) ( 1)
5 30 1
5 31 0
y x
y x
y x
y x
=
+ = +
+ =
+ + =
8. (i) Gradient of AB
1 2
1 2
6 2 4
2
1 3 2
y y
x x
= = = =
Equation of AB is 6 2( 1)
6 2 2
2 8
y x
y x
y x
=
= +
+ =
(ii) Gradient of AB
1 2
1 2
1 3 4 2
8 ( 2) 10 5
y y
x x
= = = =
Equation of AB is
2
5
( 1) ( 8)
5( 1) 2( 8)
5 5 2 16
5 2 11
y x
y x
y x
y x
=
+ =
+ = +
+ =
(iii) Gradient of AB
1 2
1 2
2 ( 4) 6 1
5 7 12 2
y y
x x
= = = =
AQA C1 Coordinate geometry 1 Exercise solutions
7 of 11 10/01/13 MEI
Equation of AB is
1
2
2 ( ( 5))
2( 2) ( 5)
2 4 5
2 1 0
y x
y x
y x
y x
=
= +
=
+ + =
(iv) Gradient of AB
1 2
1 2
5 1 6 3
3 5 8 4
y y
x x
= = = =
Equation of AB is
3
4
( 5) ( ( 3))
4( 5) 3( 3)
4 20 3 9
4 3 11
y x
y x
y x
y x
=
+ = +
+ = +
=
9. (i)
(ii) Gradient of AB
= = =
7 5 2 1
9 3 6 3
Equation of AB is =
=
=
= +
1
3
5 ( 3)
3( 5) 3
3 15 3
3 12
y x
y x
y x
y x
Gradient of BC
= = =
4 7 3
3
10 9 1
Equation of BC is =
= +
+ =
7 3( 9)
7 3 27
3 34
y x
y x
y x
Gradient of CD
= = =
2 4 2 1
4 10 6 3
Equation of CD is =
=
=
= +
1
3
4 ( 10)
3( 4) 10
3 12 10
3 2
y x
y x
y x
y x
2 4 6 8 10 12
2
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
x
y
A (3, 5)
B (9, 7)
C (10, 4)
D (4, 2)
AQA C1 Coordinate geometry 1 Exercise solutions
8 of 11 10/01/13 MEI
Gradient of AD
= = =
2 5 3
3
4 3 1
Equation of AD is =
= +
+ =
5 3( 3)
5 3 9
3 14
y x
y x
y x
AB and CD are parallel, and BC and AD are parallel.
The gradients of AB and CD are
1
3
,
and the gradients of BC and AD are -3.
Since =
1
3
3 1, AB and CD are perpendicular to BC and AD
so ABCD is a rectangle.
10. (i) Midpoint of EF
+ +
| |
= =
|
\ .
2 4 5 1
, (3, 3)
2 2
Midpoint of FG
+ +
| |
= =
|
\ .
4 ( 2) 1 ( 3)
, (1, 1)
2 2
Midpoint of EG
+ +
| |
= =
|
\ .
2 ( 2) 5 ( 3)
, (0, 1)
2 2
Median from midpoint of EF (3, 3) to G (-2, -3)
Gradient of median
= = =
3 3 6 6
2 3 5 5
Equation of median is =
=
=
=
6
5
3 ( 3)
5( 3) 6( 3)
5 15 6 18
5 6 3
y x
y x
y x
y x
Median from midpoint of FG (1, -1) to E (2, 5)
Gradient of median
= = =
5 ( 1) 6
6
2 1 1
Equation of median is =
+ =
=
( 1) 6( 1)
1 6 6
6 7
y x
y x
y x
Median from midpoint of EG (0, 1) to F (4, 1)
Gradient of median
= = =
1 1 0
0
4 0 4
Equation of median is = 1 y
(ii) Equation of first median is = 5 6 3 y x
AQA C1 Coordinate geometry 1 Exercise solutions
9 of 11 10/01/13 MEI
Substituting =
4
3
x gives = = =
=
4
3
5 6 3 8 3 5
1
y
y
so ( )
4
3
, 1 lies on the median.
Equation of second median is = 6 7 y x
Substituting =
4
3
x gives = = =
4
3
6 7 8 7 1 y
so ( )
4
3
, 1 lies on the median.
Equation of third median is = 1 y , so ( )
4
3
, 1 lies on the median.
11. (i) Let the triangle be ABC.
Let A be the intersection point of 3 11 y x + = and 3 3 y x = + .
3 11 11 3 y x y x + = =
Substituting into 3 3 y x = + gives 3(11 3 ) 3
33 9 3
30 10
3
x x
x x
x
x
= +
= +
=
=
When x = 3, 11 3 3 2 y = =
The coordinates of A are (3, 2).
Let B be the intersection point of 3 3 y x = + and 7 37 y x + =
3 3 3 3 y x x y = + =
Substituting into 7 37 y x + = gives 7 3 3 37
10 40
4
y y
y
y
+ =
=
=
When y = 4, 3 4 3 9 x = =
The coordinates of B are (9, 4).
Let C be the intersection point of 7 37 y x + = and 3 11 y x + =
3 11 11 3 y x y x + = =
Substituting into 7 37 y x + = gives 7(11 3 ) 37
77 21 37
40 20
2
x x
x x
x
x
+ =
+ =
=
=
When x = 2, 11 3 2 5 y = =
The coordinates of C are (2, 5).
The vertices of the triangle are (3, 2), (9, 4) and (2, 5).
(ii) AB is the line 3 11 11 3 y x y x + = =
so the gradient of AB is -3.
AQA C1 Coordinate geometry 1 Exercise solutions
10 of 11 10/01/13 MEI
BC is the line
1
3
3 3 1 y x y x = + = +
so the gradient of BC is
1
3
.
Gradient of AB gradient of AC
1
3
3 1 = =
so AB and AC are perpendicular, and therefore the triangle is right-
angled.
(iii)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
1
2
3
4
5
6
x
y
2 2
AB (3 9) (2 4) 36 4 40 = + = + =
2 2
AC (3 2) (2 5) 1 9 10 = + = + =
Area of triangle
1
2
1
2
1
2
1
2
AB AC
40 10
4 10 10
2 10
10
=
=
=
=
=
12. (i) B is the intersection point of 4 3 y x = and 2 1 y x = + .
4 3 2 1
2 4
2
x x
x
x
= +
=
=
When x = 2, 4 2 3 5 y = =
The coordinates of B are (2, 5).
(ii) AD is parallel to BC, so AD has gradient 2.
AD passes through the point (3, 9).
Equation of AD is 9 2( 3)
9 2 6
2 3
y x
y x
y x
=
=
= +
(iii) CD is parallel to AB, so CD has gradient 4.
CD passes through the point (7, 15).
C (2, 5)
A (3, 2)
B (9, 4)
y = 4x 3
y = 2x + 1
A
B
C
D
AQA C1 Coordinate geometry 1 Exercise solutions
11 of 11 10/01/13 MEI
Equation of CD is 15 4( 7)
15 4 28
4 13
y x
y x
y x
=
=
=
(iv) D is the intersection point of AD and CD.
2 3 4 13
16 2
8
x x
x
x
+ =
=
=
When x = 8, 2 8 3 19 y = + =
The coordinates of D are (8, 19).
You might also like
- International Comparative Studies in MathematicsDocument43 pagesInternational Comparative Studies in MathematicsAleksandra NikolicNo ratings yet
- Geometry Problems:: Circles and TrianglesDocument24 pagesGeometry Problems:: Circles and TrianglesTuong Nguyen Minh NhatNo ratings yet
- Advanced Mathematics S6 TGDocument480 pagesAdvanced Mathematics S6 TGNiyo Cavan11No ratings yet
- Difference of Two Squares r1Document23 pagesDifference of Two Squares r1Patricia RosalesNo ratings yet
- Co Ordinate GeometryDocument314 pagesCo Ordinate Geometryshubhammukri100% (1)
- Forces & Equilibrium - Solutions PDFDocument5 pagesForces & Equilibrium - Solutions PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Nelson 10 Extra Practice WorksheetsDocument137 pagesNelson 10 Extra Practice WorksheetsIqra HussainNo ratings yet
- Math 6 Sample Lesson PlansDocument31 pagesMath 6 Sample Lesson Plansapi-308562407No ratings yet
- Coordinate of Straight Lines PDFDocument24 pagesCoordinate of Straight Lines PDFCoolman PoonNo ratings yet
- Final Add Math T5 Fasa 2 DLPDocument106 pagesFinal Add Math T5 Fasa 2 DLPROSMIZAR BT AHMAD Moe100% (2)
- Sec 2 Math Admiralty Sec Sa2 2013.textmarkDocument25 pagesSec 2 Math Admiralty Sec Sa2 2013.textmarkkutaNo ratings yet
- School of Engineering Mathematics TutorialDocument30 pagesSchool of Engineering Mathematics TutorialJohn Warren100% (1)
- Unit 5Document24 pagesUnit 5christal100% (1)
- Friction Exercise PDFDocument1 pageFriction Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- On Trigonometry Class 10Document14 pagesOn Trigonometry Class 10Priyanka Garg100% (1)
- Forces & Equilibrium Exercise PDFDocument2 pagesForces & Equilibrium Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics Form 5 Module 2015Document111 pagesAdditional Mathematics Form 5 Module 2015Norah JonesNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Exercise PDFDocument2 pagesProjectile Motion Exercise PDFwolfretonmaths100% (2)
- Using Graphs Exercise PDFDocument4 pagesUsing Graphs Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Parallel and Perpendicular Equations TaskDocument14 pagesParallel and Perpendicular Equations TaskLara Hulbert100% (1)
- Using Graphs - Solutions PDFDocument5 pagesUsing Graphs - Solutions PDFwolfretonmaths100% (1)
- Page Proofs: Topic 8 AlgebraDocument47 pagesPage Proofs: Topic 8 AlgebraKalyan KumarNo ratings yet
- Using Vectors Exercise PDFDocument2 pagesUsing Vectors Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion - Solutions PDFDocument6 pagesProjectile Motion - Solutions PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCSE Math Higher Revision Guide - Page 11Document1 pageEdexcel GCSE Math Higher Revision Guide - Page 11farahgraceNo ratings yet
- ML Geometry 8-7 DilationsDocument8 pagesML Geometry 8-7 Dilationsashish663No ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion Exercise PDFDocument2 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Lines AnglesDocument31 pagesLines AnglesPriya SPNo ratings yet
- Using Vectors - Solutions PDFDocument5 pagesUsing Vectors - Solutions PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Rational Numbers DifferentiatedDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Rational Numbers Differentiatedapi-429061662No ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument177 pagesTrigonometryjohn martinNo ratings yet
- Circles - SolutionsDocument5 pagesCircles - SolutionswolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- De Moivre's Theorem1Document5 pagesDe Moivre's Theorem1kazi wahexNo ratings yet
- Applications of Analytic GeometryDocument15 pagesApplications of Analytic GeometrydaniloNo ratings yet
- Cartesian Coordinate Geometry and Straight Lines SessionDocument65 pagesCartesian Coordinate Geometry and Straight Lines SessionNishant SinhaNo ratings yet
- Maths Connect 3R Resourcebank-PackDocument176 pagesMaths Connect 3R Resourcebank-Packmusman1977No ratings yet
- Ricoh MPC 2030 3d Parts ManualDocument141 pagesRicoh MPC 2030 3d Parts Manualkostas_sanNo ratings yet
- Proofs of de Moivre's TheoremDocument4 pagesProofs of de Moivre's TheoremAfnanKhan100% (2)
- Mathematics (Syllabus D) : Paper 1Document16 pagesMathematics (Syllabus D) : Paper 1Awais MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions: Cambridge IGCSE Mathematics 0580Document37 pagesPractice Questions: Cambridge IGCSE Mathematics 0580Hayaa KhanNo ratings yet
- Answer Key p2 p1Document95 pagesAnswer Key p2 p1Nafisa AliNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Core Maths - Unit 6Document36 pagesIGCSE Core Maths - Unit 6QAmilinNo ratings yet
- Advanced Mathematics Form FiveDocument724 pagesAdvanced Mathematics Form FiveBaraka LazaroNo ratings yet
- Gce o Level 2010 Emaths 4016 Paper 1 Solutions - UnlockedDocument10 pagesGce o Level 2010 Emaths 4016 Paper 1 Solutions - UnlockedChun Khang YeeNo ratings yet
- 3D Trig PPT 1Document31 pages3D Trig PPT 1Kulsum KhanNo ratings yet
- Triangles Worksheet SolutionsDocument4 pagesTriangles Worksheet SolutionsGanesaperumalNo ratings yet
- ArithmagonDocument2 pagesArithmagonViet Hoang QuocNo ratings yet
- GCE O/L Math Revision PapersDocument206 pagesGCE O/L Math Revision PapersTharshanth Bala100% (1)
- A Level (P6) Permutations AND Combination Mark SchemeDocument22 pagesA Level (P6) Permutations AND Combination Mark SchemehhgffNo ratings yet
- Edexcel AS and A Level Modular Mathematics - Further Pure Mathematics 1 PDFDocument177 pagesEdexcel AS and A Level Modular Mathematics - Further Pure Mathematics 1 PDFStudyHub DhakaNo ratings yet
- DFMFullCoverage-PythagorasTheorem 2Document12 pagesDFMFullCoverage-PythagorasTheorem 2M MNo ratings yet
- MAT133Y: Calculus and Linear Algebra For CommerceDocument17 pagesMAT133Y: Calculus and Linear Algebra For CommerceDiverse GamingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 I Graphs of Functions II ENHANCEDocument24 pagesChapter 19 I Graphs of Functions II ENHANCEShy-Chyi LeeNo ratings yet
- CBSE Linear Equations Test Paper SolvedDocument12 pagesCBSE Linear Equations Test Paper SolvedSourabh123456789No ratings yet
- Sets, Relations and FunctionsDocument73 pagesSets, Relations and FunctionsAvnish Bhasin100% (1)
- MCAT Day 2 2016 ExamDocument12 pagesMCAT Day 2 2016 ExamNewshub100% (2)
- M.igcse .2015.002 - Sets - Exercises - 16. 09. 2013 PDFDocument6 pagesM.igcse .2015.002 - Sets - Exercises - 16. 09. 2013 PDFLatoyaWatkinsNo ratings yet
- Determining Function Machine Rule: Sub 8 Add 8 Add 6 Sub 10 Sub 11 Add 4 Add 7 Sub 14 Sub 11 Sub 15 Add 13 Add 5Document3 pagesDetermining Function Machine Rule: Sub 8 Add 8 Add 6 Sub 10 Sub 11 Add 4 Add 7 Sub 14 Sub 11 Sub 15 Add 13 Add 5api-288922072No ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry 2019 - JKCG - Lecture (Final)Document133 pagesAnalytic Geometry 2019 - JKCG - Lecture (Final)Edward RamosNo ratings yet
- CBSE Board Mock Paper 1 XII PhysicsDocument3 pagesCBSE Board Mock Paper 1 XII Physicsrohan sinhaNo ratings yet
- Patterns and Algebra AssessDocument1 pagePatterns and Algebra AssessernsteinsNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Specialist 3C3D Calc Assumed Ratified Marking Key 2015Document26 pagesMathematics Specialist 3C3D Calc Assumed Ratified Marking Key 2015Dark LordNo ratings yet
- Placing Decimals With MultiplicationDocument20 pagesPlacing Decimals With Multiplicationapi-949730870% (1)
- Interactive Math and Science Websites 1211176240676100 8Document27 pagesInteractive Math and Science Websites 1211176240676100 8Rayleight SilversNo ratings yet
- Cumulative FrequencyDocument6 pagesCumulative FrequencymelissaNo ratings yet
- Circle Theorems: Edexcel GCSEDocument8 pagesCircle Theorems: Edexcel GCSEloloperiNo ratings yet
- Pre University Maths GuideDocument30 pagesPre University Maths Guidearcanum78No ratings yet
- Y X y X: Exercise 5A (P. 5.18) Level 1 1. (A) The Equation of The Circle IsDocument9 pagesY X y X: Exercise 5A (P. 5.18) Level 1 1. (A) The Equation of The Circle IsSiu Ming LeeNo ratings yet
- Acjc h2 Math p2 SolutionsDocument8 pagesAcjc h2 Math p2 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- Three Hours and A QuarterDocument12 pagesThree Hours and A Quartersawanchhetri100% (1)
- Solutions To Home Practice Test/Mathematics: Straight Line HWT - 1Document5 pagesSolutions To Home Practice Test/Mathematics: Straight Line HWT - 1varunkohliinNo ratings yet
- Yjc h2 Math p2 SolutionsDocument8 pagesYjc h2 Math p2 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Momentum Exercise PDFDocument1 pageConservation of Momentum Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Constant Acceleration - Solutions PDFDocument6 pagesConstant Acceleration - Solutions PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Friction - Solutions PDFDocument3 pagesFriction - Solutions PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion - Solutions PDFDocument6 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion - Solutions PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Constant Acceleration Exercise PDFDocument2 pagesConstant Acceleration Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Momentum CPDocument1 pageConservation of Momentum CPwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Momentum - Solutions PDFDocument3 pagesConservation of Momentum - Solutions PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Connected Particles - Solutions PDFDocument6 pagesConnected Particles - Solutions PDFwolfretonmaths67% (3)
- Forces & Equilibrium CPDocument1 pageForces & Equilibrium CPwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Connected Particles Exercise PDFDocument2 pagesConnected Particles Exercise PDFwolfretonmaths100% (1)
- Using Vectors CPDocument1 pageUsing Vectors CPwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Connected ParticlesDocument4 pagesConnected ParticleswolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion CPDocument1 pageNewton's Laws of Motion CPwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Connected Particles CPDocument1 pageConnected Particles CPwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Using Graphs CPDocument1 pageUsing Graphs CPwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Constant Acceleration CPDocument1 pageConstant Acceleration CPwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion CPDocument1 pageProjectile Motion CPwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Constant AccelerationDocument5 pagesConstant AccelerationwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Using VectorsDocument3 pagesUsing VectorswolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Circles geometry problems and solutionsDocument7 pagesCircles geometry problems and solutionsL.ABHISHEK KUMARNo ratings yet
- Adding Mixed Numbers (Unlike Denominators) : Grade 5 Fractions WorksheetDocument6 pagesAdding Mixed Numbers (Unlike Denominators) : Grade 5 Fractions WorksheetarisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - PercentDocument6 pagesChapter 2 - PercentFahim AhmedNo ratings yet
- Math ENG Gr7 B1Document166 pagesMath ENG Gr7 B1peterNo ratings yet
- Elementary Geometry Book (561-616)Document56 pagesElementary Geometry Book (561-616)Juliana SaraivaNo ratings yet
- 11th Maths Important Questions For Quarterly Exam English Medium PDF DownloadDocument11 pages11th Maths Important Questions For Quarterly Exam English Medium PDF DownloadRaja DuraiNo ratings yet
- Class notes on parallel and skew linesDocument3 pagesClass notes on parallel and skew linesSear WitnessNo ratings yet
- Relationship of Percent, Fractions and Decimals-Math 5 Q3Document31 pagesRelationship of Percent, Fractions and Decimals-Math 5 Q3Waylon MiguelNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 - 12 - Q1 Module 2 Week 3Document4 pagesGeneral Physics 1 - 12 - Q1 Module 2 Week 3Lawrence Sean MotinNo ratings yet
- Measurement Formulas GuideDocument3 pagesMeasurement Formulas GuideHarsha RajaiNo ratings yet
- Class X Sample Test Paper 02 For Board Exam 2020 21 AnswersDocument12 pagesClass X Sample Test Paper 02 For Board Exam 2020 21 Answers11B 05 Ibrahim Mohammed IrfazNo ratings yet
- 2019 Grade 6 ATP-1Document13 pages2019 Grade 6 ATP-1Thami ZwaneNo ratings yet
- Multiplicative FunctionsDocument17 pagesMultiplicative FunctionsRose Eden AbitongNo ratings yet
- Name: - Date: - Grade & SectionDocument3 pagesName: - Date: - Grade & SectionAlyssa Jane G. AlvarezNo ratings yet
- La Consolacion College Math TestDocument4 pagesLa Consolacion College Math TestRonn De TorresNo ratings yet
- Advance Level Subjective Questions For JEE Advance: Straight Lines Circles Parabola Ellipse HyperbolaDocument22 pagesAdvance Level Subjective Questions For JEE Advance: Straight Lines Circles Parabola Ellipse HyperbolasushantNo ratings yet
- My Real WorldDocument20 pagesMy Real WorldJohn Dhell Madjad100% (4)
- Unit 1: Arithmetic 1.1 ProportionDocument10 pagesUnit 1: Arithmetic 1.1 ProportionNethra SasikumarNo ratings yet
- College Level Math TestDocument2 pagesCollege Level Math Testbill6789No ratings yet
- Identifying Types of Triangles: AI OS OI AE AS OI RI RSDocument2 pagesIdentifying Types of Triangles: AI OS OI AE AS OI RI RSDaniel BoenfieNo ratings yet
- 5 Addition and Subtraction of Rational ExpressionsDocument16 pages5 Addition and Subtraction of Rational ExpressionsKeanlyn UnwinNo ratings yet
- Quick Practice Test # 1: Date: 25-May-2020Document5 pagesQuick Practice Test # 1: Date: 25-May-2020RhombiNo ratings yet
- Calculus - Key Terms & Main Results: Chapter 1. DifferentiationDocument21 pagesCalculus - Key Terms & Main Results: Chapter 1. DifferentiationLý Kim BiênNo ratings yet
- RPT Math DLP Year 5 2022-2023 by Rozayus AcademyDocument21 pagesRPT Math DLP Year 5 2022-2023 by Rozayus AcademyrphsekolahrendahNo ratings yet
- Malaysia Final Examination: UniversitiDocument8 pagesMalaysia Final Examination: UniversitiIzzat Khair Bin MahmudNo ratings yet
- Class 6 Maths Mye 2021Document12 pagesClass 6 Maths Mye 2021abdullahNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Write Expressions CDocument2 pagesGrade 5 Write Expressions CmagmaticexodusNo ratings yet