Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Taller Ley Ohm Resistores y Kirchoff
Uploaded by
grinllowCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Taller Ley Ohm Resistores y Kirchoff
Uploaded by
grinllowCopyright:
Available Formats
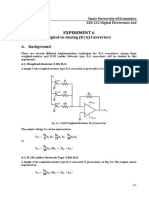
82 C H A P T E R 2 R E S I S T I V E C I R C U I T S
PROBL E MS
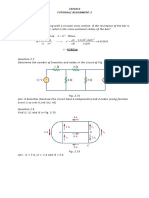
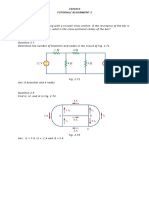
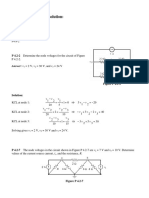
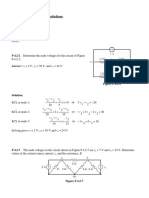
2.1 Determine the current and power dissipated in the resistor
in Fig. P2.1.
9V
12
Figure P2.1
0.5 S
2
12V
2 A 12
Figure P2.2
Figure P2.3
2.4 Given the circuit in Fig. P2.4, find the voltage across each
resistor and the power dissipated in each.
6 A
5
0.25 S
Figure P2.4
2 mA R
x
12 mA G
x
Figure P2.5
Figure P2.6
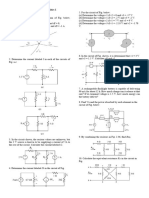
2.2 Determine the current and power dissipated in the
resistors in Fig. P2.2.
2.3 Determine the voltage across the resistor in Fig. P2.3 and
the power dissipated.
2.5 In the network in Fig. P2.5, the power absorbed by is
20 mW. Find . R
x
R
x
2.6 In the network in Fig. P2.6, the power absorbed by is
20 mW. Find . G
x
G
x
2.7 A model for a standard two D-cell flashlight is shown in
Fig. P2.7. Find the power dissipated in the lamp.
1- lamp
1.5V
1.5V
2.8 An automobile uses two halogen headlights connected as
shown in Fig. P2.8. Determine the power supplied by the
battery if each headlight draws 3 A of current.
Figure P2.8
12V
+ -
Figure P2.7
2.9 Many years ago a string of Christmas tree lights was man-
ufactured in the form shown in Fig. P2.9a. Today the
lights are manufactured as shown in Fig. P2.9b. Is there a
good reason for this change?
Figure P2.9
(a)
(b)
P R O B L E MS 83
2.10 Find in the network in Fig. P2.10.
Figure P2.10
2.11 Find in the network in Fig. P2.11.
Figure P2.11
2.12 Find and in the network in Fig. P2.12.
Figure P2.12
2.13 Find in the circuit in Fig. P2.13.
Figure P2.13
2.14 Find in the network in Fig. P2.14.
Figure P2.14
12 mA
4 mA
2I
x
3I
x
I
x
I
x
4 mA
2 mA
12 mA
I
1
I
1
2 mA
8 mA
4 mA
I
1
I
2
I
2
I
1
2 mA
6 mA
I
1
I
1
20 mA
6 mA
4 mA
I
1
I
1
2.15 Determine in the circuit in Fig. P2.15.
Figure P2.15
6 k 2 k 3 k 6 mA 3 mA
I
x
I
L
3 I
x
I
L
2.16 Find and in the circuit in Fig. P2.16.
Figure P2.16
2.17 Find in the network in Fig. P2.17.
Figure P2.17
2 mA
4 mA
2I
x
I
x
I
1
I
1
5 mA
2 mA
4 mA
3 mA I
o
I
1
I
1
I
o
84 C H A P T E R 2 R E S I S T I V E C I R C U I T S
2.18 Find , , and in the network in Fig. P2.18.
Figure P2.18
2.19 Find in the circuit in Fig. P2.19.
Figure P2.19
2.20 Find in the network in Fig. P2.20.
Figure P2.20
2.21 FindI
1
, I
2
, and I
3
in the network in Fig. P2.21.
Figure P2.21
2.22 In the network in Fig. P2.22, Find I
1
, I
2
andI
3
and show
that KCL is satisfied at the boundary.
Figure P2.22
2.23 Find in the circuit in Fig. P2.23.
Figure P2.23
2.24 Find in the network in Fig. P2.24.
Figure P2.24
2.25 Find and in the circuit in Fig. P2.25.
Figure P2.25
+ -
a b c d
e f g
2V
-
+
3V
+
-
1V
- +
1V
+ -
2V
12V 3V
- +
V
ec
V
fb
a b c
e d
4V 12V
3V 2V
+ + - -
3V
- +
V
ad
a b c
d
12V
4V
6V
2V
+
+
-
-
V
bd
I
3
I
2
I
1
4 mA
4 mA
2 mA
1 mA
2I
x
I
2
I
3
I
1
12 mA
4 mA
2I
x
I
x
2I
x
I
1
6 mA
4 mA
6 mA
I
x
I
1
4 mA
12 mA
4I
x
I
x
I
1
I
1
4 mA
3 mA
2 mA
12 mA
I
x
I
y
I
z
I
z
I
y
I
x
P R O B L E MS 85
2.26 Find and in the circuit in Fig. P2.26.
Figure P2.26
2.27 Given the circuit diagram in Fig. P2.27, find the
following voltages: , , , , , , , , ,
and .
Figure P2.27
2.28 FindV
x
andV
y
in the circuit in Fig. P2.28.
Figure P2.28
2.29 FindV
x
andV
y
in the circuit in Fig. P2.29.
Figure P2.29
2.30 FindV
1
, V
2
andV
3
in the network in Fig. P2.30.
Figure P2.30
2.31 Find in the network in Fig. P2.31.
Figure P2.31
2.32 Find in the circuit in Fig. P2.32.
Figure P2.32
+
-
+
2 I
x
V
x
+
V
x
V
o
12 4
12V
I
x
+ -
V
o
-+
+
+
4 V
x
2 V
A
V
x
V
A
+
V
o
4 2
12V
-
+
V
o
6V
4V
6V
+
V
x
2V
x
+
V
1
+
V
3
+
+
V
2
+
12V
4V
6V
+
+
V
x
+
+
V
y
+
12V
4V 6V
6V
+
+
V
x
+
V
y
+
+
-
16V
+
-
8V
+
-
14V
+
-
20V
+ + - -
8V 12V
+ + - -
12V 4V
g
h i
a b c
d e f
V
dc
V
fb
V
hf
V
ai
V
ac
V
fa
V
di
V
gc
V
bh
V
da
a b c
f
e
d
12V 6V
4V
+ -
9V
5V
-
+
6V
+
-
V
cf
V
ae
2.33 The 10-V source absorbs 2.5 mW of power. Calculate
V
ba
and the power absorbed by the dependent voltage
source in Fig. P2.33.
Figure P2.33
2.34 FindV
1
, V
2
, and V
3
in the network in Fig. P2.34.
Figure P2.34
2.35 The 10-V source in Fig. P.2.35 is supplying 50 W.
DetermineR
1
.
Figure P2.35
2.36 FindV
1
andV
2
in Fig. P2.36.
Figure P2.36
2.37 Find in the network in Fig. P2.37.
Figure P2.37
2.38 Find in the circuit in Fig. P2.38.
Figure P2.38
2.39 Find in the network in Fig. P2.39.
Figure P2.39
2.40 Find and the power supplied by the 15-V source in
the circuit in Fig. P2.40.
Figure P2.40
8 k
5 k
6 k
2 k
4 k
10V
15V
25V
V
x
V
x
6V
9V
3
2
6
4
a
b
V
ab
8V
24V
6V
4 k 6 k
+
-
V
x
V
x
a b c
d
4V 12V
3 k 1 k
V
bd
5
5
10 V
1
2 A
+
-
V
2
+
-
10V R
1
4R
1
+
6V
4V
+
12V
+
V
1
4V
x
+
V
x
+
V
3
+
-
+
+
V
2
+
V
ba
+ -
-+
2 k
a
b
3 k
10 k
2 V
x
V
x
20V
5 k
10V
-
+
86 C H A P T E R 2 R E S I S T I V E C I R C U I T S
2.41 Find in the network in Fig. P2.41.
Figure P2.41
2.42 Find the power supplied by each source, including the
dependent source, in Fig. P2.42.
Figure P2.42
2.43 Find the power absorbed by the dependent voltage
source in the circuit in Fig. P2.43.
Figure P2.43
2.44 Find the power absorbed by the dependent source in the
circuit in Fig. P2.44.
Figure P2.44
2.45 The 100-V source in the circuit in Fig. P2.45 is
supplying 200 W. Solve for V
2
.
Figure P2.45
2.46 Find the value of V
2
in Fig. P2.46 such that V
1
= 0.
Figure P2.46
2.47 Find in the network in Fig. P2.47.
Figure P2.47
2.48 Find in the network in Fig. P2.48.
Figure P2.48
2.49 Find the power supplied by each source in the circuit in
Fig. P2.49.
Figure P2.49
1 k 2 k 5 k 4 mA 2 mA
6 k 12 k 12 k 12 mA
I
o
I
o
6 k 3 k 2 k 12 mA
I
o
I
o
20V
+
V
1
+
V
2
10 20
100V
+
V
2
30
20
5
40
5
10 k
4 k
2000 I
x
10 k
6 k
20V
60V
I
x
3 k
10 k
2V
x
5 k
10 k
2 k
10V 20V
V
x
15V
+
10 k
3 k 1 k
5 k
+
3 V
x
V
x
3 mA
V
x
V
x
4
10 k 5 k
25V V
1
-
-
+
+
V
1
P R O B L E MS 87
2.50 Find the current in the circuit in Fig. P2.50.
Figure P2.50
2.51 Find in the network in Fig. P2.51.
Figure P2.51
2.52 Find in the network in Fig. P2.52.
Figure P2.52
2.53 Determine in the circuit in Fig. P2.53.
Figure P2.53
I
x
V
1
I
L
6 k 2 k 3 k
6 mA 3 mA
3 I
x
+
-
I
L
I
o
4
5 A
8
6 k
V
x
3 V
x
+
-
I
o
6 k
12 k 4 k
3 k
12 mA
I
o
I
o
1 k 2 k 5 k 4 k 7 mA 3 mA
I
A
I
A
2.54 Find the power absorbed by the dependent source in the network in Fig. P2.54.
Figure P2.54
2.55 Find in the circuit in Fig. P2.55.
Figure P2.55
2.56 Find in the network in Fig. P2.56.
Figure P2.56
6 k
2 k
3 k
4 k
1 k
A
B
R
AB
R
AB
R
AB
2 k
2 k 4 k 12 k
2 k 9 k
A
B
R
AB
1 k
2 V
A
4 k 2 k 5 k 3 mA V
A
+
-
88 C H A P T E R 2 R E S I S T I V E C I R C U I T S
2.57 Find in the circuit in Fig. P2.57.
Figure P2.57
2.58 Find in the network in Fig. P2.58.
Figure P2.58
2.59 Find in the circuit in Fig. P2.59.
Figure P2.59
2.60 Find in the network in Fig. P2.60.
Figure P2.60
2.61 Find in the circuit in Fig. P2.61.
Figure P2.61
2.62 Find in the network in Fig. P2.62.
Figure P2.62
2.63 Find the equivalent resistance in the network in
Fig. P2.63.
Figure P2.63
R
eq
12
12 12
12
12 12 12
R
eq
A
B
14
6
12 6
6
9
6
6
6
R
AB
R
AB
A
B
12
6
12 6 6
9
9 9
R
AB
R
AB
A
B
2
12
6
3
3
2
4
R
AB
R
AB
10
6
4 12
2 6
A
B
R
AB
R
AB
2
4 6
8 10
A
B
R
AB
R
AB
R
AB
1 k
1 k 2 k 2 k
2 k 2 k
1 k 2 k 2 k
A
B
R
AB
P R O B L E MS 89
2.64 Find the equivalent resistance looking in at terminals a-b in the circuit in Fig. P2.64.
Figure P2.64
4
4 6
6
8
8
10
12
20
18
8
a
8
5
4
12 10
10
8
8
9
b
90 C H A P T E R 2 R E S I S T I V E C I R C U I T S
2.65 Given the resistor configuration shown in Fig. P2.65,
find the equivalent resistance between the following sets
of terminals: (1) a and b, (2) b and c, (3) a and c, (4) d
and e, (5) a and e, (6) c and d, (7) a and d, (8) c and e,
(9) b and d, and (10) b and e.
Figure P2.65
2.66 Seventeen possible equivalent resistance values may
be obtained using three resistors. Determine the
seventeen different values if you are given resistors
with standard values: 47 , 33 , and 15 .
2.67 Find and in the circuit in Fig. P2.67.
Figure P2.67
2.68 Find and in the circuit in Fig. P2.68.
Figure P2.68
6V 12 k 4 k
2 k I
1
V
o
+
-
V
0
I
1
12V 6 k 4 k
8 k 2 k
I
1
V
o
+
-
V
0
I
1
4 4
10
12
a
5 5
b
c
d
e
2.69 Find and in the circuit in Fig. P2.69.
Figure P2.69
2.70 Find and in the network in Fig. P2.70.
Figure P2.70
2.71 Find in the network in Fig. P2.71.
Figure P2.71
2.72 Determine in the circuit in Fig. P2.72.
Figure P2.72
2.73 Determine in the network in Fig. P2.73.
Figure P2.73
2.74 Calculate in Fig. P2.74.
Figure P2.74
2.75 CalculateV
AB
in Fig. P2.75.
Figure P2.75
2.76 Calculate and V
1
in Fig. P2.76.
Figure P2.76
2.77 CalculateV
AB
in Fig. P2.77.
Figure P2.77
A B
12 k 2 k 4 k
6 k 8 k 6 k
V
AB
18V
+
6 A
V
1
a b
15 6 4
6 2 4
4
V
ab
V
ab
2 A
A
B
6 4
2
4 4 2
4 2
6
V
AB
a
b 20 12
20 18
15
30
8 75V
+
V
ab
V
ab
18 mA 3 k
5 k
1 k
30 mA
+
-
V
o
V
o
I
o
12V
2 k
6 k
4 k
4 k 16 k
12 k
-
+
I
o
12 mA 12 k 12 k 12 k
6 k
I
o
I
o
10 k 8 k
16 k
15V
I
A
V
1
+
-
I
A
V
1
4 3
1
2
2 5
20V
V
ab +
+
-
-
a b
c
d
V
dc
V
dc
V
ab
P R O B L E MS 91
92 C H A P T E R 2 R E S I S T I V E C I R C U I T S
2.78 CalculateV
AB
andI
1
in Fig. P2.78.
Figure P2.78
2.79 CalculateV
AB
andI
1
in Fig. P2.79.
Figure P2.79
2.80 Find in Fig. P2.80.
Figure P2.80
2.81 If in the network in Fig. P2.81, find
Figure P2.81
2.82 If mA in the circuit in Fig. P2.82, find
Figure P2.82
2.83 If mA in the circuit in Fig. P2.83, find
Figure P2.83
2.84 Find the value of in the network in Fig. P2.84 such
that the power supplied by the current source is 0.
Figure P2.84
2.85 In the network in Fig. P2.85, Find
.
Figure P2.85
2.86 Find the value of in the network in Fig. P2.86 such
that
Figure P2.86
+ -
8V
2
4 2 2
2
V
1
V
1
V
a
+
-
V
a
= 0.
V
1
3 k
2 k 7 k 2 k
1 k
I
S
V
o
+
-
I
S
V
o
= 6 V.
2
3
6
8
18V 3 A V
S
V
S
I
o
V
S
12 k 3 k
6 k
1 k
V
S
. I
o
= 2
I
S
4 k 2 k
I
o
= 5 mA
I
S
. I
o
= 5
V
o
= 4 V
V
S
+
-
4 k
8 k
V
S
. V
o
= 4 V
100 k
20 k
50 k
30 k
100V
+
V
ab
+
V
ab
A
B
6 k 8 k
3 k
2 k
8 k 6 k
6 k
7 k
V
AB
I
1
40V
+
A B
10 k 6 k 12 k
3 k
4 k 6 k
5 k 8 k 4 k
V
AB
40V
+
I
1
P R O B L E MS 93
2.87 If in the circuit in Fig. P2.87, find
Figure P2.87
2.88 In the network in Fig. P2.88, Find
Figure P2.88
2.89 Given that in the network in Fig. P2.89,
find
Figure P2.89
2.90 If V
R
= 15 V, find V
X
in Fig. P2.90.
Figure P2.90
2.91 If V
2
= 4 V in Fig. P2.91, calculate V
x
.
Figure P2.91
2.92 Find the value of I
A
in the network in Fig. P2.92.
Figure P2.92
2.93 Find the value of I
A
in the circuit in Fig. P2.93.
Figure P2.93
+
I
A
V
o
= 12 V
4
4
4
6
4V
-
+
+
I
A
12V
4V
+
2 2
2 2
+
5 2
2 15
3
16 2
4
24V
+
V
x
2 I
1
V
2
+
I
1
+
4
5
4 3
2 A 3 A
8V
4
V
R
V
x
+
+ -
12 k 3 k
6V
3 k
1 k
2 k
V
o
=4V
V
S
+
-
2 mA
V
S
.
V
o
= 4 V
4 k
4 k 6 k 3 k
1 k 2 k
V
S
V
1
+ -
V
S
. V
1
= 12 V.
6 k 3 k 4 k
V
1
= 5 V
+ -
I
S
I
S
. V
1
= 5 V
94 C H A P T E R 2 R E S I S T I V E C I R C U I T S
2.94 Find in value of the current source I
A
in the network in
Fig. P2.94.
Figure P2.94
2.95 Given V
o
= 12 V, find the value of I
A
in the circuit in
Fig. P2.95.
Figure P2.95
2.96 Find the value of in the network in Fig. P2.96, such
that the 5-A current source supplies 50 W.
Figure P2.96
2.97 The 5-A current source in Fig. P2.97 supplies 150 W.
CalculateV
A
.
Figure P2.97
2.98 Given mA in the circuit in Fig. P2.98, find .
Figure P2.98
2.99 Given mA in the network in Fig. P2.99,
find .
Figure P2.99
2.100 Given in the network in Fig. P2.100, find .
Figure P2.100
1 k
6V
I
A
1 k
12V
1 k
1 k
2 k V
o
=4V
+
-
I
A
V
o
+ -
V
A
1 k
I
o
6V
6 mA
1 k
1 k
2 k 2 k
V
A
I
o
= 2
6V 1 k
1 k
I
o
6V
I
A
1 k
2 k
2 k
I
A
I
o
= 2
15 5
5 4
2
2
25V
5 A
+
-
V
A
2 2
2
5V
4
4
V
x
5 A
V
x
+
2
4 4
9 4
7
2 A
I
A
+
12V
+
V
o
I
x
2 I
x
+
2
2 2
3 4
2
6V
2 A
4V
+
6V I
A
2.101 Find the value of in the circuit in Fig. P2.101 such
that the power supplied by the 5-A source is 60 W.
Figure P2.101
2.102 The 3-A current source in Fig. P2.102 is absorbing
12 W. Determine R.
Figure P2.102
2.103 If the power supplied by the 50-V source in Fig. P2.103
is 100 W, find R.
Figure P2.103
2.104 Given that , find and in the circuit in
Fig. P2.104.
Figure P2.104
2.105 Find the power absorbed by the network in Fig. P2.105.
Figure P2.105
2.106 Find the value of in the network in Fig. P2.106
such that the power supplied by the 3-A source
is 20 W.
Figure P2.106
2.107 Find the power supplied by the 24-V source in the
circuit in Fig. P2.107.
Figure P2.107
12 k
12 k
12 k
12 k
24V
12 k 12 k
gl
x
2
1
2
2
3 A
I
x
g
12 k
2 k
6 k
18 k
6 k
21V
16V
8V
V
1
1 k 2 k 2 k
6 k 4 k
4 mA
5 mA
R
B
V
A
+
+
-
-
R
B
V
A
V
1
= 4 V
2 A 50V
+
5 2
R
R
2
1
3 A 12V
+
V
x
1 1
3 A
4
2 5 A 5V 2
V
x
P R O B L E MS 95
96 C H A P T E R 2 R E S I S T I V E C I R C U I T S
2.108 Find in the circuit in Fig. P2.108.
Figure P2.108
2.109 Find in the circuit in Fig. P2.109.
Figure P2.109
2.110 Determine the value of in the network in Fig. P2.110.
Figure P2.110
2.111 Find in the circuit in Fig. P2.111.
Figure P2.111
2.112 Find in the network in Fig. P2.112.
Figure P2.112
2.113 FindI
o
in the circuit in Fig. P2.113.
Figure P2.113
2.114 FindI
o
in the circuit in Fig. P2.114.
Figure P2.114
2.115 FindV
o
in the circuit in Fig. P2.115.
Figure P2.115
2I
y
V
o
6 A
V
x
I
y
2
1
+
2
V
x
2
2 V
x
V
x
I
o
V
o
2 A
2
1
4 A
+
2I
x
I
x
I
o
6 A
V
o
2 1
+-
I
24V
2 k
4 k
2 V
o
V
o
+
-
V
o
-+
I
S
12V
3 k
5 k
2000 I
S
V
o
+
-
V
o
-
+
6 k
4 k
18 k
12 k
6 k
12V
V
o
V
o
2
12
12 4
3
5
36V
18
9
I
o
I
o
12
8
12
14
12
24V
I
o
I
o
P R O B L E MS 97
2.116 FindV
x
in the network in Fig. P2.116.
Figure P2.116
2.117 FindV
o
in the network in Fig. P2.117.
Figure P2.117
2.118 Find , , and in the circuit in Fig. P2.118.
.
Figure P2.118
2.119 Find in the network in Fig. P2.119.
Figure P2.119
I
o
8
4 V
x
6 5 A
3 V
x
+
-
I
o
8 24V 2 A 4 I
1
I
2
I
1
I
3
I
3
I
2
I
1
6 A 2V
y
V
o
V
y
4V
x
2
2
+
V
x
1
2
+
I
x
V
x
6
6
3
3
2
1
4 A
+
2I
x
V
o
2.120 A typical transistor amplifier is shown in Fig. P2.120. Find the amplifier gain G (i.e., the ratio
of the output voltage to the input voltage).
Figure P2.120
2.121 Find the value of in the network in Fig. P2.121, such that the power supplied by the 6-A source is 108 W.
Figure P2.121
6 A
6 3
6 12
4
kI
o
I
o
k
-
+
V
S
=250 mV
100
300
4 k
4*10
5
I
b
5 k 500 V
o
+
-
I
b
98 C H A P T E R 2 R E S I S T I V E C I R C U I T S
2.122 Find the power supplied by the dependent current
source in Fig. P2.122.
Figure P2.122
2.123 If the power absorbed by the 10-V source in
Fig. P2.123 is 40 W, calculate I
S
.
Figure P2.123
2.124 The power supplied by the 2-A current source in
Fig. P2.124 is 50 W, calculate k.
Figure P2.124
2.125 Given the circuit in Fig. P2.125, solve for the value
of k.
Figure P2.125
kV
2
3 mA
50V
V
2
+
+
9 k
18 k
10 k
30 k
30 k
50V 2 A
+
-
kI
1
2
5 2
4 5 I
1
0.6V
x
10V
+
+
-
V
x
I
s
6
10 15
4 5
+
-
10
10
5
0.4V
x
2 A
V
x
+
TYPI CAL PROBL E MS F OUND ON T HE F E E XAM
2FE-1 What is the power generated by the source in the
network in Fig. 2PFE-1?
a.
b.
c.
d.
Figure 2PFE-1
6 k
120V
5 k
18 k
4 k 6 k
12 k
2.4 W
3.6 W
1.2 W
2.8 W
2FE-2 Find in the circuit in Fig. 2PFE-2.
a.
b.
c.
d.
Figure 2PFE-2
5
15
10
10
a
b
4 A
V
ab
-10 V
15 V
10 V
-5 V
V
ab
T Y P I C A L P R O B L E MS F O U N D O N T H E F E E X A M 99
2FE-3 If in the circuit in Fig. 2PFE-3,
what is ?
a.
b.
c.
d.
Figure 2PFE-3
2FE-4 Find the equivalent resistance of the circuit in
Fig. 2PFE-4 at the terminals A-B.
a.
b.
c.
d.
Figure 2PFE-4
2FE-5 The 100 V source is absorbing of power in the
network in Fig. 2PFE-5. What is R?
a.
b.
c.
d.
Figure 2PFE-5
2FE-6 Find the power supplied by the source in the cir-
cuit in Fig. 2PFE-6.
a.
b.
c.
d.
Figure 2PFE-6
2FE-7 What is the current in the circuit in Fig. 2PFE-7?
a.
b.
c.
d.
Figure 2PFE-7
2FE-8 Find the voltage in the network in Fig. 2PFE-8.
a.
b.
c.
d.
Figure 2PFE-8
24 mA 3 k
1 k 2 k
6 k
6 k
12 k
V
o
+
-
12 V
36 V
10 V
24 V
V
o
12V
6 k
3 k 4 k
12 k
3 k 6 k 6 k
I
o
-
+
-0.22 mA
2.75 mA
-1.25 mA
0.84 mA
I
o
50
100 25 20 40V
100V
3 A
184 W
212 W
232 W
120 W
40 V
10 10
100V
200V
5 A
R
15.12
19.25
9.42
17.27
50 W
R
AB
12 k
6 k
6 k
4 k
12 k
12 k
12 k
A
B
20 k
8 k
12 k
4 k
2
4
8 R
2
R
eq
18
8
20
12
R
2
R
eq
= 10.8
100 C H A P T E R 2 R E S I S T I V E C I R C U I T S
2FE-9 What is the voltage in the circuit in Fig. 2PFE-9?
a.
b.
c.
d.
Figure 2PFE-9
2FE-10 Find the current in Fig. 2PFE-10.
a.
b.
c.
d.
Figure 2PFE-10
1 1
10
8 3
2
12V
I
x
83 A
32 A
53 A
12 A
I
x
2 3
1
4 A 2 A
V
o
+
-
12 V
5 V
8 V
2 V
V
o
You might also like
- Rechargeable Batteries Applications HandbookFrom EverandRechargeable Batteries Applications HandbookRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Tutorial 4Document9 pagesTutorial 4sreekantha reddyNo ratings yet
- Ternary Chalcopyrite Semiconductors: Growth, Electronic Properties, and Applications: International Series of Monographs in The Science of The Solid StateFrom EverandTernary Chalcopyrite Semiconductors: Growth, Electronic Properties, and Applications: International Series of Monographs in The Science of The Solid StateRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Análise Nodal e de MalhasDocument13 pagesAnálise Nodal e de MalhasNicoly DidonéNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Dorf Introduction - To.electric - Circuits.8eDocument11 pagesDorf Introduction - To.electric - Circuits.8eFrancisco LópezNo ratings yet
- Tut-1 Modified PDFDocument8 pagesTut-1 Modified PDFShailendra DhakadNo ratings yet
- Electric Gas Lighting How to Install Electric Gas Ignition ApparatusFrom EverandElectric Gas Lighting How to Install Electric Gas Ignition ApparatusNo ratings yet
- Answer: - 4 V: ProblemsDocument15 pagesAnswer: - 4 V: ProblemsCamilo OtaloraNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam1 F14Document11 pagesPractice Exam1 F14Islam El BakouryNo ratings yet
- 201HW2Document3 pages201HW2ojhaaaa0% (1)
- Sliptest 1Document5 pagesSliptest 1sreekantha20130% (2)
- CSET102 - Tutorial-1 - 2023-24 Sem IDocument4 pagesCSET102 - Tutorial-1 - 2023-24 Sem IShreyansh GargNo ratings yet
- tutorial 1Document3 pagestutorial 1javi.alberto.torrucoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Nodal and Mesh Equations - Circuit Theorems 3.14 ExercisesDocument45 pagesChapter 3 Nodal and Mesh Equations - Circuit Theorems 3.14 ExercisesRitchie Quinto DE TorresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Homework SolutionDocument23 pagesChapter 3 Homework SolutionsyarifahafizahNo ratings yet
- Circuit problems covering lectures 1-5Document4 pagesCircuit problems covering lectures 1-5Mohammad Al Faiyaz50% (2)
- Fundamentals of Electrical Circuits Solutions ManualDocument86 pagesFundamentals of Electrical Circuits Solutions ManualKenneth VogtNo ratings yet
- ECE SolutionsDocument14 pagesECE SolutionsLaura CarsonNo ratings yet
- ENG1030 Electrical Circuit Tutorial QuestionsDocument3 pagesENG1030 Electrical Circuit Tutorial QuestionsShaun StanleyNo ratings yet
- Ring and Radial CircuitsDocument4 pagesRing and Radial CircuitsChrisStewart0% (1)
- Activity 2-Circuit ElementsDocument2 pagesActivity 2-Circuit Elementspatrick dgNo ratings yet
- Group 5 - Laboratory Experiment No 2Document11 pagesGroup 5 - Laboratory Experiment No 2Marco YvanNo ratings yet
- Problems 5 Circuit WileyDocument28 pagesProblems 5 Circuit WileyHelloWorld25% (4)
- Problems 6 Circuit WileyDocument29 pagesProblems 6 Circuit WileyHelloWorldNo ratings yet
- Group 5 - Laboratory Experiment No 2Document11 pagesGroup 5 - Laboratory Experiment No 2Marco YvanNo ratings yet
- ECEG2121-Worksheet I IDocument4 pagesECEG2121-Worksheet I IKenenisa J7No ratings yet
- TUTO - ASG 02 - JUL2015 - Answer - Electric CircuitDocument4 pagesTUTO - ASG 02 - JUL2015 - Answer - Electric CircuitHasmizar Abd Halim (KTN)No ratings yet
- Problems Chapter 1 ContentsDocument6 pagesProblems Chapter 1 ContentsĐức ThànhNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2Document6 pagesSheet 2Toka AhmedNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 BENE1133 Ver 1.0Document2 pagesTutorial 3 BENE1133 Ver 1.0Idzuan AriffNo ratings yet
- Current Formula: R V R V V R V VDocument4 pagesCurrent Formula: R V R V V R V VMiguel VillarroelNo ratings yet
- in The Circuit in Fig. 1, Obtain,, and .: and The Power Absorbed by The 12-K ResistorDocument11 pagesin The Circuit in Fig. 1, Obtain,, and .: and The Power Absorbed by The 12-K ResistorvarshaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1IEE 19022024Document3 pagesAssignment 1IEE 19022024Maqsood Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Homework: Hint: Calculate The Power Absorbed by Each Element. Add Up All of These Powers. If TheDocument7 pagesHomework: Hint: Calculate The Power Absorbed by Each Element. Add Up All of These Powers. If TheDaniel RobertoNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document12 pagesLab 4Yap YiXienNo ratings yet
- ER CircuitosElectricosDocument2 pagesER CircuitosElectricosLito PelosNo ratings yet
- EC100 End-Sem RemoteDocument2 pagesEC100 End-Sem RemoteDhruv GandhiNo ratings yet
- DC Circuit Analysis Using Node and MeshDocument20 pagesDC Circuit Analysis Using Node and MeshRubel RiadNo ratings yet
- DRD420Document15 pagesDRD420neper14100% (2)
- CE222 Quiz 2Document1 pageCE222 Quiz 2cortez vincentNo ratings yet
- Problemas CH6 PDFDocument11 pagesProblemas CH6 PDFJuan227100% (1)
- Homework SolutionsDocument46 pagesHomework SolutionsKashif AmjadNo ratings yet
- Problems: Series Resistors 1. For Each Configuration in Fig. 5.85, Find The Individual (NotDocument12 pagesProblems: Series Resistors 1. For Each Configuration in Fig. 5.85, Find The Individual (NotYurany GracianoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 QuizDocument8 pagesModule 1 Quizconference RequirementsNo ratings yet
- TUTO - ASG 02 - JUL2015 - Electric Circuit - QuestionDocument4 pagesTUTO - ASG 02 - JUL2015 - Electric Circuit - QuestionHasmizar Abd Halim (KTN)No ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 5Document6 pagesTutorial Chapter 5SYAFIQAH ISMAILNo ratings yet
- Floyd ED9 Part1 SolutionsDocument162 pagesFloyd ED9 Part1 SolutionsEngin Yiğit75% (44)
- Bölüm Soruları - 5th-EditionDocument14 pagesBölüm Soruları - 5th-EditionBee MiteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Homework Solution:: P 4.2-2 Determine The Node Voltages For The Circuit of FigureDocument18 pagesChapter 4 Homework Solution:: P 4.2-2 Determine The Node Voltages For The Circuit of FigureManar HosnyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (1) & (2) Homework SolutionDocument18 pagesChapter 4 (1) & (2) Homework SolutionAnderson Niño Velasco0% (1)
- Tutorial 3-Semiconductor DIODEDocument6 pagesTutorial 3-Semiconductor DIODEmohammad haidzirNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1A AnsDocument4 pagesTutorial 1A AnsRISHABH JAINNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6: Digital-to-Analog (D/A) Converters A. BackgroundDocument6 pagesExperiment 6: Digital-to-Analog (D/A) Converters A. BackgroundwubbalubbadubdubNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Problems DC Equivalent Circuits, Network Theorems, and Bridge CircuitsDocument3 pagesSupplementary Problems DC Equivalent Circuits, Network Theorems, and Bridge CircuitsJomer JuanNo ratings yet
- Damian Hall Assignment7 DctheoryDocument18 pagesDamian Hall Assignment7 DctheoryDamian HallNo ratings yet
- HW2 ProblemDocument6 pagesHW2 Problem劉德信No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument5 pagesAssignmentBerentoNo ratings yet
- Ece301 HW02Document3 pagesEce301 HW02Misti TerryNo ratings yet
- AmgDocument9 pagesAmgSatishReddyNo ratings yet
- Av74 0018Document39 pagesAv74 0018Franco PugaNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document121 pagesModule 122-08420No ratings yet
- 47 LM 6200 UeDocument129 pages47 LM 6200 Ueبوند بوندNo ratings yet
- Light BulbDocument67 pagesLight BulbThierry RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Design of Ultra Low Noise AmplifiersDocument10 pagesDesign of Ultra Low Noise AmplifiersRakotomalala Mamy TianaNo ratings yet
- Apollo Series 65 Engineering GuideDocument20 pagesApollo Series 65 Engineering GuideMurtuza Zoomkhawalla50% (2)
- Guild Thunderbass 8 Tubes VersionDocument9 pagesGuild Thunderbass 8 Tubes VersiondodNo ratings yet
- Focus2 Műszercsoport TesztDocument12 pagesFocus2 Műszercsoport TesztDávid MolnárNo ratings yet
- Op Amp Selection Guide For Optimum Noise PerformanceDocument2 pagesOp Amp Selection Guide For Optimum Noise PerformancennliceNo ratings yet
- Star-Delta Motor Starter CALCULATIONDocument13 pagesStar-Delta Motor Starter CALCULATIONKamalakannan Karuppiah83% (6)
- Schematic Diagrams: DR-MH20SUC, DR-MH20SUJ, Dr-Mh30Sus, Dr-Mh30Suc Dr-Mh30Suj, Dr-Mh30StwDocument48 pagesSchematic Diagrams: DR-MH20SUC, DR-MH20SUJ, Dr-Mh30Sus, Dr-Mh30Suc Dr-Mh30Suj, Dr-Mh30StwFrancisco OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Drift Calculation for Thin Film ResistorsDocument3 pagesDrift Calculation for Thin Film ResistorsDamian Huitzil CedilloNo ratings yet
- 95-8554-13.1 (Flame X9800)Document31 pages95-8554-13.1 (Flame X9800)usamakhan205No ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument54 pagesProject ReportHarendra Kumar67% (3)
- K7QO - QRP - Laboratory PDFDocument136 pagesK7QO - QRP - Laboratory PDFdetroit_me2553100% (1)
- Nietz Electric Co.,LtdDocument164 pagesNietz Electric Co.,LtdmouradNo ratings yet
- Sharp CD Mpx850Document111 pagesSharp CD Mpx850Thomas JosephNo ratings yet
- 241 DocumentationDocument61 pages241 DocumentationPunita SinghNo ratings yet
- Arduino ProjectsDocument40 pagesArduino Projects1blahblah195% (22)
- Current Electricity AssignmentDocument8 pagesCurrent Electricity AssignmentAviram YadavNo ratings yet
- 12V Power Supply Circuit DiagramDocument20 pages12V Power Supply Circuit DiagramPrecious AdeboboyeNo ratings yet
- IEEE STD C62.92.2-1989Document25 pagesIEEE STD C62.92.2-1989abdou samiNo ratings yet
- SYLGARD™ 184 Silicone Elastomer: Features & Benefits ApplicationsDocument4 pagesSYLGARD™ 184 Silicone Elastomer: Features & Benefits ApplicationsZhan FangNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Domsttic Electtricity Textbook Suggested AnswersDocument16 pagesCH 3 Domsttic Electtricity Textbook Suggested Answers黃淑敏No ratings yet
- LED Driver IC Delivers Up to 1.5ADocument8 pagesLED Driver IC Delivers Up to 1.5AvibhanshuNo ratings yet
- Project 2Document4 pagesProject 2amolmahajanNo ratings yet
- Measuring Gigaohms With A Simple MultimeterDocument11 pagesMeasuring Gigaohms With A Simple MultimeterZIASY Shesmer100% (1)
- PRC REGISTERED MASTER ELECTRICIAN EXAMDocument6 pagesPRC REGISTERED MASTER ELECTRICIAN EXAMaeilorv infanteNo ratings yet
- IT SchematicDocument2 pagesIT SchematicsamanhgsNo ratings yet