Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pressure at End of Fill
Uploaded by
Daniel Müller da VeigaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pressure at End of Fill
Uploaded by
Daniel Müller da VeigaCopyright:
Available Formats
Pressure at End of Fill:
During the filling stage, the forward injection velocity of the reciprocating screw is controlled, which results in the pressure required to fill the cavity at that
velocity. The injection pressure is propagated through the molten plastic and results in a pressure drop distributed along the length of flow. The pressure at the
end of fill is a very good indication of how evenly the cavity has filled.
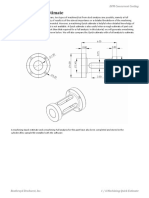
Uneven and even pressure at end of fill plots.
In the first example, an injection location was placed in the middle of an asymmetrical handle. The pressure at end of fill plot shows an uneven distribution of
pressure throughout the cavity. The second example shows that repositioning the injection location slightly to the right results in an even pressure distribution
throughout the cavity. Even pressure at all end of fill locations will improve the effects of packing pressures and cooling throughout the molded part. You should
attempt to place the injection location where the pressure at end of fill plot displays an even pressure distribution.
Note: Pressure drop is a function of flow length, part wall thickness, and melt viscosity. High pressures are required to fill thin-walled injection molded parts,
since the flow resistance through the smaller cross sectional area is greater. When SolidWorks Plastics detects a short shot, try the following:
1) Reposition the injection location: If the injection location is near the end of a part, the flow length is essentially the entire length of the part. Place the
injection location near the middle of the part to reduce the flow length to about half the length of the part. With the injection location located in the
middle, even though the plastic flow must travel in two directions, flow lengths and injection pressure requirements are reduced.
To reposition an injection location:
1) Under INPUT, Boundary Conditions, double-click Injection Location.
2) To delete the existing injection location, click either:
Delete Injection Location
Delete All Injection Locations
Note: The previous injection location turns blue, indicating that you can move it.
3) Click Yes, when prompted to delete an injection location.
4) In the Command Manager, click Mesh Model .
5) Double-click a Node located in the mesh to select the new injection location.
6) To define the new injection location, click Add Injection Location .
Note: The color of the injection location will change from blue to light purple.
7) Click OK .
8) Under RUN, double-click a fill option:
Flow
Flow + Pack (SolidWorks Plastics Premium only)
9) Click Yes, when prompted to replace the fill results.
2) Change the fill time: A shorter fill time (or injecting faster) typically lowers the viscosity of the melted plastic, allowing the material to flow further. Keep
in mind that the shorter fill time may increase the injection pressure required, shear rates and shear stress. The maximum injection pressure will be
limited by the machine, while plastic materials have maximum threshold values for shear rate and stress.
To change the fill time:
1) Under INPUT, Process Parameters, double-click Fill Settings.
2) Clear Auto.
3) For Filling Time, enter value for sec.
4) Click OK .
5) Under RUN, double-click a fill option:
Flow
Flow + Pack (SolidWorks Plastics Premium only)
6) Click Yes, when prompted to replace the fill results.
3) Increase part wall thickness: To reduce injection pressures, you can increase the wall thickness of the solid model. Then you would have to create a
new mesh and run the analysis again. Increasing the part wall thickness will increase cooling times and require more plastic material to mold the part.
To display a section view of pressure at end of fill:
1) Under RESULTS, double-click Fill Results.
2) Click Pressure at End of Fill.
3) Click Clipping Plane Mode .
The clipping plane mode of pressure at end of fill displays the internal pressure distribution throughout the cavity at end of fill (Solid Mesh only).
Pgina 1 de 1 Pressure at End of Fill:
27/10/2014 its:C:\Program Files\SolidWorks Corp\SolidWorks Plastics\Document\Xplorer_User...
You might also like
- MoldflowDocument74 pagesMoldflowRajesh PandaNo ratings yet
- BASF Snap Fit Design GuideDocument24 pagesBASF Snap Fit Design GuidewantamanualNo ratings yet
- Tm500 Lte-A 3gpp Lte TestDocument8 pagesTm500 Lte-A 3gpp Lte TestSmith KumarNo ratings yet
- AUC-Knowledge QuestionsDocument68 pagesAUC-Knowledge QuestionsFarhan SethNo ratings yet
- Molding Process PDFDocument7 pagesMolding Process PDFSreedhar PugalendhiNo ratings yet
- Nanyang Technological University School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering AY2011/2012Document13 pagesNanyang Technological University School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering AY2011/2012TibbercesNo ratings yet
- PosiTestAT-v4 0 PDFDocument45 pagesPosiTestAT-v4 0 PDFcentaury2013No ratings yet
- 3D Printer GuideDocument29 pages3D Printer GuideJay KhatalNo ratings yet
- Drawdown Analysis For Tunnel ExcavationDocument8 pagesDrawdown Analysis For Tunnel ExcavationRaghvendra ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Compression Molding and Injection MoldDocument23 pagesCompression Molding and Injection MoldKodhansNo ratings yet
- AT QuickGuide-v5.3 PDFDocument76 pagesAT QuickGuide-v5.3 PDFJesus De la RosaNo ratings yet
- Pull-Off Adhesion Tester: Quick Guide v. 5.3Document19 pagesPull-Off Adhesion Tester: Quick Guide v. 5.3PubcrawlNo ratings yet
- Tham KhaoDocument12 pagesTham KhaoTuan DoNo ratings yet
- Injection Molding Process ExplainedDocument5 pagesInjection Molding Process ExplainedRodrigo AndradeNo ratings yet
- Polymer Processing HandoutDocument68 pagesPolymer Processing HandoutibraheemNo ratings yet
- Determining The Pressure Drop Theory and PracticeDocument4 pagesDetermining The Pressure Drop Theory and PracticeAdrian Vega VelasquezNo ratings yet
- 2002 Morgan PressDocument7 pages2002 Morgan PressNaveen PadmanabhanNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Gate Location: Thick To ThinDocument3 pagesThe Importance of Gate Location: Thick To ThinVenkatesh VaraNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Molding Notes Rev 03Document43 pagesMicrosoft Word - Molding Notes Rev 03Panir Selvam Periannan100% (1)
- Gas Assisted Injection MoldingDocument13 pagesGas Assisted Injection MoldingBhupendra Singh89% (9)
- Exam Paper Format Tech.Document8 pagesExam Paper Format Tech.shashi100% (1)
- Plastic Injection Molding Write UpDocument16 pagesPlastic Injection Molding Write UpVishal MahajanNo ratings yet
- Testing & Adjusting The Patriot Metering System: Magnum Venus PlastechDocument26 pagesTesting & Adjusting The Patriot Metering System: Magnum Venus PlastechCamilo Correa100% (1)
- 3 03 Design PrinciplesDocument15 pages3 03 Design Principlesphạm minh hùngNo ratings yet
- Compressible Flow in A Nozzle: SPC 407 Supersonic & Hypersonic Fluid Dynamics Ansys Fluent Tutorial 1Document19 pagesCompressible Flow in A Nozzle: SPC 407 Supersonic & Hypersonic Fluid Dynamics Ansys Fluent Tutorial 1Jorge A. KáramNo ratings yet
- Thermoforming Design Guidelines-020810Document46 pagesThermoforming Design Guidelines-020810AmolPagdal100% (1)
- Antec Machine AuditDocument8 pagesAntec Machine AuditDivyanshu Garodia100% (1)
- Extrusion Blow MouldingDocument13 pagesExtrusion Blow Mouldingkish007rdNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Injection Molding Manufacturing For Automotive IndustryDocument5 pagesOptimization of Injection Molding Manufacturing For Automotive IndustryJessica AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 The Plasticating and Injection Unit: Key QuestionsDocument10 pagesLesson 3 The Plasticating and Injection Unit: Key QuestionsBruno RubioNo ratings yet
- Frozen Layer Fraction at End of Fill PDFDocument1 pageFrozen Layer Fraction at End of Fill PDFDaniel Müller da VeigaNo ratings yet
- Plaxis Excercise 1Document8 pagesPlaxis Excercise 1liselioNo ratings yet
- RS2 Tutorials - Tunnel Lining DesignDocument20 pagesRS2 Tutorials - Tunnel Lining Designpremnath16No ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Lab ReportDocument4 pagesMechanical Engineering Lab ReportAsif Khan NiaziNo ratings yet
- Mould Flow and Structural Analysis of inDocument5 pagesMould Flow and Structural Analysis of inHicham AhmamsiNo ratings yet
- C2C Getting StartedDocument24 pagesC2C Getting StartedKok MunNo ratings yet
- Compression MouldingDocument6 pagesCompression Mouldinglynda jerbiaNo ratings yet
- Gas Injection Technology.Document49 pagesGas Injection Technology.Irfan AliNo ratings yet
- Injection Mold Design: Dr. Naresh BhatnagarDocument65 pagesInjection Mold Design: Dr. Naresh BhatnagarAnkit Bansal88% (8)
- 15 Hold Pressure Selection PDFDocument3 pages15 Hold Pressure Selection PDFAlexNo ratings yet
- Plastic Injection Molding Process OptimizationDocument7 pagesPlastic Injection Molding Process OptimizationSachin KumarNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Bottle Wall Thickness Distribution PDFDocument6 pagesComparison of Bottle Wall Thickness Distribution PDFaleskytronNo ratings yet
- Ceramic ProcessingDocument37 pagesCeramic Processingmiroali4023No ratings yet
- Machining Quick Estimate: DFM Concurrent Costing DfmaDocument6 pagesMachining Quick Estimate: DFM Concurrent Costing Dfmaarun prakash suggulaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Setting Depth Design ProceduresDocument15 pages2 - Setting Depth Design Proceduresmahdifahem905No ratings yet
- 12 A Moulding (1)Document35 pages12 A Moulding (1)shreeghadage7No ratings yet
- Plastic Processes - FINALDocument48 pagesPlastic Processes - FINALswap dNo ratings yet
- Models - Cfd.droplet SuspensionDocument12 pagesModels - Cfd.droplet Suspensionjialuo.cmNo ratings yet
- Peng 11 2010 0580Document7 pagesPeng 11 2010 0580Arūnas PaNo ratings yet
- Injection Molding ProcessDocument12 pagesInjection Molding ProcessImane El BouchehatiNo ratings yet
- Injection Molding Process ExplainedDocument12 pagesInjection Molding Process Explainedralph2324No ratings yet
- PSG College of Technology Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument14 pagesPSG College of Technology Department of Mechanical EngineeringDeepak RajaNo ratings yet
- Plastic Injection MoldingDocument36 pagesPlastic Injection MoldingChacaquair Mutiara100% (1)
- Injection MouldinDocument32 pagesInjection MouldinKarthick KarthickNo ratings yet
- Module V - Blow and Transfer Molding ProcessesDocument17 pagesModule V - Blow and Transfer Molding ProcessesAntonius PrakosaNo ratings yet
- Setting Process Conditions - Injection MoldingDocument44 pagesSetting Process Conditions - Injection MoldingRaja PandiNo ratings yet
- Injection Molding CycleDocument3 pagesInjection Molding CyclepavankumarsrsNo ratings yet
- CFD Set Up July 10Document76 pagesCFD Set Up July 10Milos DimitrijevicNo ratings yet
- Well Control AssignmentDocument9 pagesWell Control AssignmentMathias NsimbeNo ratings yet
- Plastic Molding DefectsDocument5 pagesPlastic Molding DefectsMichaelNo ratings yet
- Hyperelastic Seal: Created in COMSOL Multiphysics 5.5Document26 pagesHyperelastic Seal: Created in COMSOL Multiphysics 5.5Lija LiaNo ratings yet
- Interacademic Collaboration Involving Higher Education Institutions in Tlaxcala and Puebla, Mexico. Presented in Collaboration with Université Clermont Auvergne (France): Case Studies of Collaborative, Multidisciplinary Applications.From EverandInteracademic Collaboration Involving Higher Education Institutions in Tlaxcala and Puebla, Mexico. Presented in Collaboration with Université Clermont Auvergne (France): Case Studies of Collaborative, Multidisciplinary Applications.No ratings yet
- Automotive Industry in GermanyDocument17 pagesAutomotive Industry in GermanyAbin KurianNo ratings yet
- Design Thinking For Educators ToolkitDocument81 pagesDesign Thinking For Educators ToolkitDaniel Müller da VeigaNo ratings yet
- Design Council - Leading Business by DesignDocument90 pagesDesign Council - Leading Business by DesignIbrahim YekinniNo ratings yet
- Samenvatting Sterkteleer BASFDocument86 pagesSamenvatting Sterkteleer BASFdroessaert_stijnNo ratings yet
- Automotive Industry in GermanyDocument17 pagesAutomotive Industry in GermanyAbin KurianNo ratings yet
- To Display A Section View of Cooling Time at End of FillDocument1 pageTo Display A Section View of Cooling Time at End of FillDaniel Müller da VeigaNo ratings yet
- Frozen Layer Fraction at End of Fill PDFDocument1 pageFrozen Layer Fraction at End of Fill PDFDaniel Müller da VeigaNo ratings yet
- Fill TimeDocument3 pagesFill TimeDaniel Müller da VeigaNo ratings yet
- 8 Tips For An Awesome Powerpoint PresentationDocument44 pages8 Tips For An Awesome Powerpoint PresentationDaniel Müller da VeigaNo ratings yet
- HM 1379581144 Rotary Brand GuidelinesDocument35 pagesHM 1379581144 Rotary Brand GuidelinesDaniel Müller da VeigaNo ratings yet
- Card Speaker PDFDocument2 pagesCard Speaker PDFDaniel Müller da VeigaNo ratings yet
- Solucionario - Termodinamica - Cengel - 7ed (1) - 519-528Document10 pagesSolucionario - Termodinamica - Cengel - 7ed (1) - 519-528Lizeth Maria lizarazoNo ratings yet
- 02 - MDS System and ControlDocument55 pages02 - MDS System and Controlchinith100% (1)
- Document 1Document14 pagesDocument 1Lê Quyên VõNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 OSDocument5 pagesAssignment 3 OSValerie ThompsonNo ratings yet
- RS124 ManualDocument13 pagesRS124 ManualSoakaosNo ratings yet
- Avista - Vegetation Management Frequently Asked QuestionsDocument5 pagesAvista - Vegetation Management Frequently Asked QuestionslgaungNo ratings yet
- Tommy Matsumoto, AT&T Jens Co. Yoshitaka Senoo, Daiichi Co.,LtdDocument7 pagesTommy Matsumoto, AT&T Jens Co. Yoshitaka Senoo, Daiichi Co.,Ltdpostscript100% (1)
- Help - Walkthrough - Creating Beam and Plate Features - AutodeskDocument5 pagesHelp - Walkthrough - Creating Beam and Plate Features - AutodeskTien HaNo ratings yet
- Bab III.2.1. Generator Sinkron (Lanjutan)Document28 pagesBab III.2.1. Generator Sinkron (Lanjutan)Hariz AudirahmawanNo ratings yet
- Advertisement No. 2/2020: Csir-Central Scientific Instruments Organisation (Council of Scientific & Industrial Research)Document3 pagesAdvertisement No. 2/2020: Csir-Central Scientific Instruments Organisation (Council of Scientific & Industrial Research)Saharsh PatelNo ratings yet
- Kotler Mktman 11ce Ch04Document34 pagesKotler Mktman 11ce Ch04Murtaza MoizNo ratings yet
- VeinFinder_VE800 Brochure V1.0Document2 pagesVeinFinder_VE800 Brochure V1.0hanrong912No ratings yet
- Medium Voltage Surge Arresters Catalog HG 31.1 2017 Low Resolution PDFDocument79 pagesMedium Voltage Surge Arresters Catalog HG 31.1 2017 Low Resolution PDFAnkur_soniNo ratings yet
- Understanding Future Tenses with "Be Going To" and "WillDocument11 pagesUnderstanding Future Tenses with "Be Going To" and "WillYasmín CastilloNo ratings yet
- 13 Standpipes Sprinklers FdnyDocument20 pages13 Standpipes Sprinklers FdnyHualy DelgadoNo ratings yet
- The Service Owner Role in ITIL v3: by Kai HolthausDocument6 pagesThe Service Owner Role in ITIL v3: by Kai HolthausSavitha MohanNo ratings yet
- Bizhub 20 Service ManualDocument508 pagesBizhub 20 Service ManualSergio Riso100% (1)
- EML3500 CH 8 SlidesDocument134 pagesEML3500 CH 8 SlidesGanesh Dongre100% (1)
- "Solid Waste Management": Visvesvaraya Technological UniversityDocument24 pages"Solid Waste Management": Visvesvaraya Technological UniversityManu MonaNo ratings yet
- Chinese Material To AstmDocument4 pagesChinese Material To Astmvalli rajuNo ratings yet
- Piston SkirtDocument2 pagesPiston SkirtAmmar OmranNo ratings yet
- TYPE 183 1.8m Extended RXTX Class I 14-11-14Document2 pagesTYPE 183 1.8m Extended RXTX Class I 14-11-14Amy KennedyNo ratings yet
- Steam Condensate Pot SizingDocument1 pageSteam Condensate Pot SizingSaeid Rahimi MofradNo ratings yet
- Elizabeth Hokanson - Resume - DB EditDocument2 pagesElizabeth Hokanson - Resume - DB EditDouglNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument329 pagesReportHovik ManvelyanNo ratings yet
- Radio Amateur's Software GuideDocument251 pagesRadio Amateur's Software GuideZdenko NagyNo ratings yet
- Covey Stephen RDocument90 pagesCovey Stephen RcemgallNo ratings yet
- Process Control Valves TrainingDocument12 pagesProcess Control Valves TrainingpptmnltNo ratings yet