Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Headwork
Uploaded by
Israel Smith Matías CabreraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Headwork
Uploaded by
Israel Smith Matías CabreraCopyright:
Available Formats
UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL PEDRO RUIZ GALLO
ESCUELA PROFESIONAL DE INGENIERIA CIVIL
that make up the dam, is going to be used the
intake works as a work of diversion, we will
have to project a kind of socket with its
ducts or tunnels to a level, as low as
possible, to easily achieve the diversion of
the river.
HEADWORKS:
It is called work of taking the set of
structures that are built with the purpose of
removing the water in a controlled manner
and be able to use it with the purpose for
JACK WORKS IN DOWNLOAD: In the
which it was projected its use.
case of, that the work of jack you intend to
use as drainage for the rapid draining of the
glass, it will be necessary to place its ducts
or tunnels to a level as low as possible and
with sections designed to drain at a time that
s convenient the beaker
INTAKE
DAMS:
There are works of Socket for power
generation, construction of irrigation intake ,
intake works for provision of drinking
water , the work of Jack For Current
diversion
IN
STORAGE
The dams have with various works that
ensure its efficient operation under various
circumstances: curtain, intake works and
work of leave. The water that flows through
the channel of a river is caught and stored by
means of the curtain, and its utilization is
carried out through a work of takes.Among
the elements that can be presented are:
CLASSES OF HEADWORKS:
FUNCTIONS OF A INTAKE WORKS
WORKS
The works of jack for water supplies are
used in dams to control, regulate and derive
the spending toward driving.
The works of jack can also operate as
regulators, to provide an outlet for waters
temporarily stored in the space for flood
control, or to dislodge with anticipation to
the arrival of avenues.
OBJECTIVES OF A WORK OF TAKES
INTAKE
WORKS
FOR
POWER
GENERATION: The discharge is to the
river, and the entry of the water should be as
high as possible to take advantage of the
height of the drop.
INTAKE FOR FORWARDING: If during
the construction of the different structures
Input Structure ,ducts,
Mechanisms
of
regulation
and
emergencies with its operation Team ,
Devices for energy dissipation.
DESCRIPTION
OF
CAPABILITIES OF USE
THE
N. A. M. E: relates to the maximum level
that reach the waters of a stream under
conditions of maximum flow occurred in
rainy season high-return period in which
houses the collection
N. A. M. OR:Known as N. A. N. (Normal
water level) and is defined by the level of the
high ridge.
UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL PEDRO RUIZ GALLO
ESCUELA PROFESIONAL DE INGENIERIA CIVIL
N. A. min: minimum water level of
operation in the body of water and place the 2. CUT AND COVER THE LINES:
catchment, corresponds to the volume
If a closed passage that must be provided
destined to the blockages.
and the foundation conditions are not
suitable for a tunnel, or if the size required
Cr: Capacity for flood control, this is
for the navigation is too small to justify the
understood as the volume stored between the
NAME and the NAMO
minimum size tunnel, a cut-and-duct cover
must be used. Due to this kind of conduit or
C. U: directly exploitable volume of the dam
passes through the dam, conservative and
SELECTION
OF ELEMENTS
safe the designs must be used.
OF WORK OF OUTPUT:
The design of a work output is influenced by 3.
many conditions relating to the hydraulic
requirements, adaptability to the site, to the
interrelationship of the output and the
procedure of construction, and to other units
within the development. Topography geology.
Depending on the position of the control
device, the duct or tunnel can be free
flowing, flowing under the pressure of a part
of its length, or flowing under pressure in its
entire length. Incorporation can be organized
to draw water from the bottom of the tank, or
the entry of the side rails can be placed at
any level within the tank top, Dispelling
devices can be used in the rear end of the
passage.
OUTPUT ELEMENTS IN WORKS OF
TAKES
1. Tunnels:
Due to its inherent advantages, an exit
tunnel is preferable in works of abutment
and the conditions that will allow its
foundation and is cheaper than other types
of output. A tunnel is not in direct contact 4.
with the dam embankment and, therefore,
provides a much safer and more durable
available that can be achieved with a cover
of ducts.
CONTROL DEVICES:
The use of special devices that involve
expensive design and manufacturing costs
should be avoided. Cast Iron sliding doors,
which can be used for the control and
protection doors, are available for both the
rectangular and circular openings. However,
installations
require greater
disenosde special doors. The control gate of
a output operates can be placed at the
upper end of the passage, at an
intermediate point in its entire length, or at
the bottom end of the structure. Where the
flow of a control gate is released directly
into the open free download, only the part
of the duct before the door is under
pressure. In the event of a control or needle
valve is placed at the bottom end of the
structure, the full internal pressure should
be considered in the design of the tunnel or
tube. If the controls are located at some
intermediate point in the high pressure line,
doors, sliding doors, doors and radial can be
used.
4. INTAKE STRUCTURES: a structure of
admission can accommodate control
devices. Intake structures may appear in
many forms. The type of structure of
admission should be based on several
UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL PEDRO RUIZ GALLO
ESCUELA PROFESIONAL DE INGENIERIA CIVIL
factors: the functions that should serve, the
range of tank that should work, the
performance should handle, the frequency
of use of the tank, depending on the need
for the frequency of cleaning of the
protective grilles, the tank action of the
waves that could affect the stability, and
other similar considerations. The need for
a protective grilles in output works depends
on the size of the sluice or conduit, the type
of control device used, the use of water, the
need to trash except for the small of the
output, and other factors. These factors
determine the type of protective grille,
and the size of the openings.
5. 5. ELEMENTS OF DISSIPATION OF ENERGY:
6. The discharge of an electrical outlet, either
a gate valve, conduit or free flow, will be
released at high speed, usually in a nearly
horizontal direction. If the erosion resistant
rock exists at a shallow depth, the flow can
be discharged directly into the river.
Otherwise, should be directed to the tip of
the dam of a deflector. Where erosion is
reduced to the minimum necessary , the fall
can be excavated basin and lined with riprap
or concrete is when you need it
most energy sinks. The hydraulic jump
basin is most often used for power
dissipation of the discharges from the works
of output. However, the flow can be seen
from the output in the form of a free jet, as
is the case of the pressure control valve of
ducts, should be oriented to the transition
to the basin floor so are distributed evenly
before entering the basin. Otherwise, the
power dissipation will not get.
7. INPUT AND OUTPUT OF THE CHANNEL: a
channel input and an output channel are
often needed for a tunnel or cut lines and
cover design. An input channel may be
needed to express deviation flows to a
conduit or in a recess for the water supply
to the output of admission deposited works
under. And an output channel may be
required to transmit the discharges from
the end of the exit to the downstream or to
a channel.
INTAKE FOR IRRIGATION
OF THE TYPE OF RIO additions:
They are the ones that extract water from
the river entries continues without any
appreciable storage before the diversion . A
typical diagram of admission to comply with
special characteristics, such as steep slopes,
high peaks and short duration flood flows
and high sediment loads, shown in Figure
THE TYPE OF TANK INLET: Where the
outflows is provided for the irrigation of
storage built for this purpose. Depending on
the head, this is a category of low: Low Level
(up to 15 m), Medium Level (15 to 30 m),
yNivel high (above 30 m).
Admission to concrete or masonry dams:
In the case of concrete dams, intake
structure may be located at the tip when
operating head is low or in the body of the
dam.
Intake of earth dams:
When the reservoir is formed by an
embankment dam, irrigation is tunnel
beneath it or in the foundation. The intake
structure for this type of situations will be a
leaning tower of admission or type of
consumption.. measures as the provision of
steel coatings and adequate drainage after
the core, the provisions of the joints for
differential settlements when not founded
UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL PEDRO RUIZ GALLO
ESCUELA PROFESIONAL DE INGENIERIA CIVIL
on the rock should be considered in the case
of conduits are always under the earth
dams.
Tickets directly from the tank by
buttresses:
In this case, the prey is separated from the
structure of admission. The dam can be of
any material (concrete, dirt, etc. ), but the
consumption is built by the classification the
left or the right buttresses and outlet tubes
through the surrounding hills.
MAKING STRUCTURES WATER
WATER SURFACE AND SUB SURFACE
Content:
1. Introduction
2. Types
3. Control of Water Quality
1. Introduction
A reservoir is constructed to store water
as required. The stored water is removed
from the tank in order to use the power
of water or water itself. In this chapter,
the withdrawal of water from a reservoir
is described and the relationship
between removal, reservoir
environment, and the role of the intake
structure is described.
To improve the efficiency of annual use,
even in reservoirs of hydropower
generation. The water can be supplied to
the river downstream, using the stored
water in the tank, in order to provide
ecological benefits during dry periods.
There is a difference between the
deposit and withdrawal of a direct
removal of a river or ground water. The
water stream storage affects the quality
of water reservoir and the flow rate and
the quality of the river water channel
below.
2. Types
In temperate and subtropical
regions, river water low temperature
flowing in autumn and winter is stored in
the lower layer of the shell. The solar
radiation at the surface of the deposit
intensified in early spring, and the water
surface heated. The temperature of the
water stored in the upper layer of the
tank is further increased by the inflow,
because its temperature also rises at this
time. The thermal stratification,
stabilization of the upper and lower
layers, therefore, occurs in summer. The
quality of water, dissolved oxygen and
nutrients, and distribution of suspended
matter, depends on this stratification.
1) The intake surface
An intake surface is used to take water
from the surface of the tank when it is
comparatively light. Obviously, the
withdrawal must follow fluctuations in
the tank level. It is necessary to prevent
contamination of the lower layers to
make efficiently the water surface.
hydraulic test is performed to determine
the distribution of the approach speed
and depth of the water removed.
2) subsurface Consumption (Intak
e submerged)
Whatever the level of water in the tank,
an intake subsoil takes water from a low
level in the tank. The intake will have a
simple, because this system can set the
level of intake. The water temperature of
UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL PEDRO RUIZ GALLO
ESCUELA PROFESIONAL DE INGENIERIA CIVIL
the water is usually low, and contains
little phytoplankton.
3) The intake of multiple levels
(Selective Removal)
Selective removal is carried out in an
optional position to take the desired
water quality. The shape of the density
stratification is positively controlled by
this system in order to effectively use the
stratification in the tank. The shape of
the installation is similar to the intake
surface, but there is some difference in
the top of the installation. Sometimes,
the intake is in the middle layer, when
the upper and lower layers are prone to
contamination
3. Control Water
Quality
Water quality problems in relation to
water
temperature,
muddy water,
eutrophication, etc. are particularly likely
to occur in reservoirs including natural
lakes. Control of water quality is an
important
consideration
in
the
withdrawal of deposits and the various
facilities described in this section are
used
to
provide
this
control.
Problems of water quality include those
caused by the quality of water discharged
into the river downstream. This effect
can be mitigated by choosing the most
appropriate level of consumption.
Changes in water quality attributable to
storage tap water can impair or limit the
use of water. This can be reduced by
controlling the change in the quality of
water in the tank.
Such water quality problems are the
result of processes operating in the
environment of container, such as water
stratification. Efforts are therefore, made
to keep the water quality by reducing
stratification. The methods available to
control stratification include reducing
thermocline selective uptake, and
destruction of the thermocline by
circulating water.
1) The work Outlet
2) Installation selective Retirement
3) Water Curtain Quality Control
4) Circulation
The technique circulation all
layers destroys the thermocline, and the
whole mixture reservoir. When this
happens, the lower layer is supplied with
oxygen, and the bottom layer of cold
water with surface water is mixed. This
avoids the problem of cold water, and
also disperses phytoplankton. Control
flow phenomena using current density is
also an effective way to solve various
problems of water quality in reservoirs.
In this case, the thermocline is
maintained, and the method movement
of the entire layer and not suitable.
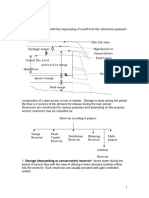
DESIGN OF HYDRAULIC STRUCTURES
INTRODUCTION
Any hydraulic structure that supplies
water to the intake channel is called a
main word.
Frame can be:
1. Headwork storage.
2. Headwork Diversion.
A headwork storage involves building a
dam on the river. It stores water during
the period of oversupply and released
when the demand exceeds the available
supply.
UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL PEDRO RUIZ GALLO
ESCUELA PROFESIONAL DE INGENIERIA CIVIL
A headwork deviation serves to deflect
the supply necessary for the river
channel.
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
A diversion works head is a built
across a river in order to raise the
water level in the river so it can
be diverted to the channel
structure.
diversion headworks are generally
constructed in perennial rivers
that have adequate flow
throughout the year
and, therefore, no need for a
storage tank.
A head diversion works differs
from a work storage or dam. A
dam built on the river to create a
storage tank. The works of
storage for storing water in a nonperennial river or is require river
with inadequate flow throughout
the year.
On the other hand, in the works
of a head of diversion, there is
very little storage, if any.
If storage in the upstream of a
diversion
works
head
is
significant, it is called a storage
dam.
A diversion headworks builds on
the downstream of a dam to
divert water released from the u /
s dam channels is called a garbage
collection.
g.
In general, the dam is built
on the rock or mountain range of
the river, where the conditions
are right for a dam and a
catchment dam is built near the
commanded in the stretch of river
alluvial area.
Features a fun Headworks
The water level rises in the
upstream side.
Water supply is regulated
channels.
Sediment inputs is controlled
channels
A small pond (no reservoir) in
its upward and provides some is
created.
Helps control the vagaries of the
river.
List of components
Alluvium
Undersluicespared
Divide ladder
Regulator head
Channel
Excluder
Work training (marginal
and guide banks dikes)
UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL PEDRO RUIZ GALLO
ESCUELA PROFESIONAL DE INGENIERIA CIVIL
GATES
Friction Head Loss (h f)
The friction losses are due to fluid friction
with the walls of the duct.
A gate is a mechanism of control and
emergency, which are designed for
maximum load; consists of a movable,
flat or curved plate, which permits
adjusting the height up hole is discovered
that, while controlling the discharge
produced.
The gates are used to control spending,
with peculiarities in its operation and
parts thereof; by design are classified
into different types, following are some
of them:
Sliding gates
Rolling Gates
Radial Gates
DROPS
Loss in the changes of direction (h b)
Occur when there is a change in the
circulation flow between the inlet and
the outlet section and control
mechanisms due to changing flow
speeds, producing separation zones on
the inner side of the curve and increases
pressure on the outside, with spiral
movement extending over distances up
to 50 times the diameter or height of the
duct.
Pressure Drop for Enlargement (h ex)
In calculating losses expansion equation
(8.5), where the coefficient Ka depends
on the abruptness of enlargement and to
obtain its value equation (8.6) and the
values of Table 8.1 is used is used. The
minimum load loss has to spread angle
= 8; for = 50 the abrupt enlargement is
as reliable as gradual.
(
UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL PEDRO RUIZ GALLO
ESCUELA PROFESIONAL DE INGENIERIA CIVIL
( )
Pressure Drop by Reduction (h c)
In reducing load losses reduction of such
a phenomenon occurs when the
expansion
and
seeks
also
be
gradual; losses are smaller than the
expansion coefficient Kr and the angle
depends on the contraction.
Type Reja
Rectangular section
With rounded edges
With the extreme end
thinned
Circular cross-section
2.42
1.83
1.63
1.79
Loss of load per entry (h e)
Pressure Drop in Output (h v2)
The losses in the output is a function of
the
velocity
and
shape
of
departure; losses are calculated using
equation (8.8). When the output is open,
the output coefficient Ks is equal to one
and if you want to recover part of the
velocity divergent forms should be
used. If the output is drowned, take into
account equation (8.9)
( )
(
Pressure Drop for Grids (h t)
Is important to consider, in the case of
the grids comprised of slabs, in which the
separation between these is small, this
structure losses generated.
LOCATION OF DECISION REGARDING
THE LEVELS OF RESERVOIR
1) They must be sufficiently below the
minimum operating level that is
sufficient burden for the minimum flow
operation, either may or may not
coincide with the corresponding capacity
dead volume level.
2) Given that it is common to reserve a
dead storage, decision should be above
this level enough to ensure a certain
quality of water is removed.
They should note that tickets should be
placed at points in the vessel where algae
can accumulate or where prevailing
winds trash and floating objects in
general
UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL PEDRO RUIZ GALLO
ESCUELA PROFESIONAL DE INGENIERIA CIVIL
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- RTT Mass, EnergyDocument5 pagesRTT Mass, EnergyPatrick Joseph RoblesNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Building and Flood Mitigation Structure DesignDocument73 pagesAgricultural Building and Flood Mitigation Structure DesignPrescila QuietaNo ratings yet
- Energy Work I - The Key - Peter DexheimerDocument78 pagesEnergy Work I - The Key - Peter DexheimerEvans67% (3)
- Runoff Calculation ManuallyDocument64 pagesRunoff Calculation Manuallyepidamus1980No ratings yet
- Tarea 2-Problemas de Los Temas 1 y 2 v2Document2 pagesTarea 2-Problemas de Los Temas 1 y 2 v2Andy PastranaNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering: Fluid Machinery Lab (MEPC 319)Document5 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering: Fluid Machinery Lab (MEPC 319)Brijesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Tamakoshi-9 DSR - 29 May 2018Document22 pagesTamakoshi-9 DSR - 29 May 2018Manoj BaralNo ratings yet
- Watershed ReportDocument11 pagesWatershed Reportapi-489811187No ratings yet
- Dambrk Modeling MethodologyDocument38 pagesDambrk Modeling MethodologyDevi DephieNo ratings yet
- C5304 - Hydrology (Kertas Soalan Politeknik-Politeknik Malaysia Kejuruteraan Awam)Document7 pagesC5304 - Hydrology (Kertas Soalan Politeknik-Politeknik Malaysia Kejuruteraan Awam)Azil14No ratings yet
- RESERVOIRSDocument26 pagesRESERVOIRSFelix HabarugiraNo ratings yet
- Camarines Norte State College: College of Engineering SummDocument4 pagesCamarines Norte State College: College of Engineering Summshuckss taloNo ratings yet
- LiDAR Surveys and Flood Mapping of Cabadbaran RiverDocument169 pagesLiDAR Surveys and Flood Mapping of Cabadbaran RiverHakeem DarpsNo ratings yet
- Assignment IIDocument3 pagesAssignment IItedy yidegNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 22-Surface RunoffDocument15 pagesLecture - 22-Surface RunoffDanny ChengNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Fluid MechanicsDocument31 pagesLecture 9 Fluid MechanicsAbdullah IrshadNo ratings yet
- Chap 3Document12 pagesChap 3Kevin John VelascoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Hydrology Solutions Report Part 1Document4 pagesEngineering Hydrology Solutions Report Part 1Gogireddy Srinivasareddy1346No ratings yet
- Calculation For Detention-Tank ProvisionDocument2 pagesCalculation For Detention-Tank ProvisionluishorquiaNo ratings yet
- Lecture (6) Classification of Channel Bed SlopesDocument14 pagesLecture (6) Classification of Channel Bed Slopesjonk smithNo ratings yet
- Hidrologi Teknik Chapter 8 Storage OutflowDocument24 pagesHidrologi Teknik Chapter 8 Storage Outflowkpop is moodNo ratings yet
- Hydrological Model VidraDocument14 pagesHydrological Model VidrarobinvarzaruNo ratings yet
- Coupled TanksDocument32 pagesCoupled TanksAnkur MondalNo ratings yet
- Overland Flow Time of Concentration On Flat TerrainsDocument134 pagesOverland Flow Time of Concentration On Flat Terrainssatria11No ratings yet
- Barry Et Al., 2004Document22 pagesBarry Et Al., 2004Anonymous jA6yJ8VnxNo ratings yet
- Flow Rate & Size Selection - Litres/Minute: 14.5038 Conversion Factor For Bar To PSIDocument3 pagesFlow Rate & Size Selection - Litres/Minute: 14.5038 Conversion Factor For Bar To PSIMohd AzharNo ratings yet
- CEE3430 Engineering Hydrology practice exam questionsDocument9 pagesCEE3430 Engineering Hydrology practice exam questionsMohmmed HusseinNo ratings yet
- Modelling Catchment CharacteristicsDocument48 pagesModelling Catchment Characteristicsintern kncesbNo ratings yet
- Module6 Fluid MechanicsDocument23 pagesModule6 Fluid MechanicsPaolo Martinez PHNo ratings yet
- Is 6966 1 1989 PDFDocument19 pagesIs 6966 1 1989 PDFPrachita RautNo ratings yet