Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment 2
Uploaded by
pappuyadav1996Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment 2
Uploaded by
pappuyadav1996Copyright:
Available Formats
Department of Electrical Engineering, IIT Kanpur
ESC 201A: Introduction to Electronics
11 August, 2014
Home Assignment 2
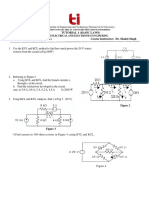
1. Use the super-mesh concept to determine the power supplied by the 2.2 V source of Fig. 1
2
4.5 A
i2
i1
5V
2.2 V
3
9
i4
2A
4
i3
3V
Fig. 1
2. (a) Find VX in the circuit of Fig. 2a if the element A is short circuited.
10
80 V
30 V
+
20
A
+
VX
30
40
-
Fig. 2a
(b) Determine the Thevenin Equivalent voltage and resistance across terminals a and b of the
network shown in Fig. 2b
Department of Electrical Engineering, IIT Kanpur
ESC 201A: Introduction to Electronics
5V
a
+
20
19
Vx
5 Vx
Fig. 2b
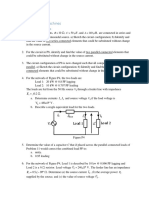
3. Using Superposition & Thevenin's theorems, determine the value of IS which would make the
output voltage V0 = 0 volts for any value of the load resistance RL in the circuit of Fig. 3
12 K
24 K
12 K
IS
24 K
6V
RL
+
V0
-
Fig. 3
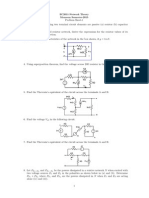
4. In Fig. 4 find the AC and DC Thevenin's equivalent circuits at AB, and thereby find the
resulting output V0(t).
Department of Electrical Engineering, IIT Kanpur
ESC 201A: Introduction to Electronics
1K
2K
I1
2mA
0.5 K
1.5 K
B
1K
V3
2cos(300t)
V2
2V
V1
5V
Fig. 4
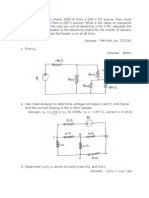
5. In the circuit of Fig. 5, determine the maximum positive current to which the source IX can be
set before any resistor exceeds its power rating and overheats.
100
W
64
6V
Ix
Fig. 5
6. Ideal current source has infinite resistance. However a practical current source can be
constructed by a voltage source in series with large resistance. Design a practical current source
using a battery of 12 V to supply a load current of 1A for any load resistance between 0 and
10K.
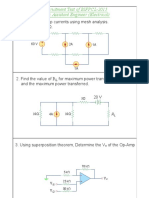
7. Find the Norton equivalent for the circuit shown in Fig. 6
Department of Electrical Engineering, IIT Kanpur
ESC 201A: Introduction to Electronics
200
a
i
Vab
2V
5i
+
-
20
Fig. 6
8. The circuit shown in Fig. 7 is equivalent circuit of an amplifier. Assume that voltage source is
a microphone and load resistance is a loudspeaker. Use Thevenin's theorem to find a suitable
value for load resistance RL such that maximum power is transferred to it.
0.5K
VS
0.5K
+
V
-
0.1V
1K
100K
RL
Fig. 7
9. If the noise in a 5 V voltage line and ground for a five volt circuit is of the order of 10 mV,
for a first order system, how many time constants will you wait to be sure you reached the
practically achievable final steady state values.
10. A capacitor is connected to a constant ideal voltage supply (VS) through a resistor of
resistance R.
(a) Show that the energy dissipated in the resistor is independent of the value of the resistor.
(b) What role does the resistor play in the charging of the capacitor.
Department of Electrical Engineering, IIT Kanpur
ESC 201A: Introduction to Electronics
(c) If the capacitor of capacitance C is charged from an initial voltage of Vi to Vf, what is the
energy drawn from the supply voltage? What is the additional energy stored in the capacitor due
to this charging?
11. In Fig. 8 the switch is closed at t=0, obtain current 'i' and capacitor voltage VC for t>0.
10
t=0
50 V
i
10
Fig. 8
2F
+
Vc
-
You might also like
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- IEE Assignment - 2Document4 pagesIEE Assignment - 2satya prakashNo ratings yet
- Circuits-2 Review B PDFDocument16 pagesCircuits-2 Review B PDFCristele Mae GarciaNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code: 22115: B.E./B.Tech - Degree Examinations, April/May 2011 Regulations 2008Document5 pagesQuestion Paper Code: 22115: B.E./B.Tech - Degree Examinations, April/May 2011 Regulations 2008Vinodh GanesanNo ratings yet
- U20EE201 - CT - Model QPDocument4 pagesU20EE201 - CT - Model QPvinothkumarNo ratings yet
- All Tutorial EEU104Document19 pagesAll Tutorial EEU104Faeez SouLzNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document4 pagesTutorial 5Dhivya NNo ratings yet
- WWW - Studyhaunters.blogspot - In: Question Paper Code: 22115Document5 pagesWWW - Studyhaunters.blogspot - In: Question Paper Code: 22115Sriram JNo ratings yet
- EEE Exclusive: Question Paper Code: 22115Document5 pagesEEE Exclusive: Question Paper Code: 22115aishuvc1822No ratings yet
- Assignment 7Document2 pagesAssignment 7Pavan KhetrapalNo ratings yet
- EEE (ELT-112 & - 110) /EEE (ECT-110) (For BE-CE, PE, CHEM, BIO-TECH, CSE, ECE)Document3 pagesEEE (ELT-112 & - 110) /EEE (ECT-110) (For BE-CE, PE, CHEM, BIO-TECH, CSE, ECE)Santosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial1 8Document9 pagesTutorial1 8Lovish BansalNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Roorkee EEN-112: Electrical Science Tutorial Sheet - 04Document2 pagesDepartment of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Roorkee EEN-112: Electrical Science Tutorial Sheet - 04Kumar ShivamNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit AnalysisDocument12 pagesElectric Circuit AnalysisMATHANKUMAR.SNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 QuestionsDocument3 pagesUnit-2 Questionsabhioptimus00No ratings yet
- Eec 249 20212022Document3 pagesEec 249 20212022Taiwo TemitayoNo ratings yet
- EC2011-Network Theory Monsoon Semester-2015Document2 pagesEC2011-Network Theory Monsoon Semester-2015AkshaySudhirNo ratings yet
- Assignemnt - No - 7a - Operational AmplifierDocument5 pagesAssignemnt - No - 7a - Operational AmplifierSudeep NayakNo ratings yet
- Krishna Institute of Engineering & Technology, GhaziabadDocument4 pagesKrishna Institute of Engineering & Technology, GhaziabadkapilkietNo ratings yet
- Electrical 02Document10 pagesElectrical 02Hary Kriz33% (3)
- Bifpcl 15Document3 pagesBifpcl 15A One ShoppersNo ratings yet
- Tutorials 1Document20 pagesTutorials 1Sahil KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 For CircuitsDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 For CircuitsAmir EyniNo ratings yet
- Electrical Question BankDocument4 pagesElectrical Question BankAmar Wali0% (1)
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document0 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.aishuvc1822No ratings yet
- Assignment IDocument1 pageAssignment ISaurabh uzumakiNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document6 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.SindhujaSindhuNo ratings yet
- Answer Key - PTEE6201 - Circuit Theory QPDocument19 pagesAnswer Key - PTEE6201 - Circuit Theory QPSiva KumarNo ratings yet
- EEE SyllabusDocument11 pagesEEE Syllabussamarpit_anandNo ratings yet
- Assignment Unit-3 AEDocument4 pagesAssignment Unit-3 AEDivyanshi UdawatNo ratings yet
- Questions Chap 7 Alternating Current - 77504 - 2023 - 01 - 14 - 22 - 53Document4 pagesQuestions Chap 7 Alternating Current - 77504 - 2023 - 01 - 14 - 22 - 53Abhay ThakurNo ratings yet
- Part B & Part C Questions - Unit Wise: Ec8251 Circuit AnalysisDocument4 pagesPart B & Part C Questions - Unit Wise: Ec8251 Circuit AnalysisAnonymous Ndsvh2soNo ratings yet
- EEE2044S 2022 Tutorial 4Document3 pagesEEE2044S 2022 Tutorial 4Junaid PietersNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document1 pageAssignment 4vikashwishNo ratings yet
- Model Questions EEE Cat-IDocument4 pagesModel Questions EEE Cat-IIKNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Alternating Current Circuits I PDFDocument20 pagesTopic 3 Alternating Current Circuits I PDFFeddy BlaizNo ratings yet
- ProblemsAC FundamentalsDocument3 pagesProblemsAC Fundamentalskrishneel100% (1)
- Lagos City Polytechnic, IkejaDocument1 pageLagos City Polytechnic, IkejaOlatidoye EzekielNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Technology AssignmentDocument3 pagesBasic Electrical Technology AssignmentSaquib FarazNo ratings yet
- Applied One Tutorial ExcerciseDocument18 pagesApplied One Tutorial ExcerciseABENEZER EPHREMNo ratings yet
- Question Bank With Answers: BE 8253 - Basic Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation EngineeringDocument93 pagesQuestion Bank With Answers: BE 8253 - Basic Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation EngineeringRajeshNo ratings yet
- Physics II ProblemsDocument1 pagePhysics II ProblemsBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- 2 Cse Ece It Ec2151Document2 pages2 Cse Ece It Ec2151BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis Assignment 1 1/5Document5 pagesPower System Analysis Assignment 1 1/5Ameer HamzaNo ratings yet
- Circuit AnalysisDocument3 pagesCircuit Analysisiamcrazy1729No ratings yet
- Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument3 pagesBasic Electrical EngineeringNikash SubediNo ratings yet
- BetDocument16 pagesBetShivendra SangwanNo ratings yet
- Mid Bee Paper Set 3Document6 pagesMid Bee Paper Set 3raghusabale1No ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering Any FiveDocument4 pagesIndian Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering Any FiveNikhil V. JoshiNo ratings yet
- Circuit SystemsDocument28 pagesCircuit SystemsRashmi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Problem 1Document2 pagesProblem 1Grace Joy RomiasNo ratings yet
- Class 12 - AC Mains QuestionsDocument6 pagesClass 12 - AC Mains QuestionsGreeshma ReddyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Ahtasham ArshadNo ratings yet
- ENGG112 Tutorial 7Document3 pagesENGG112 Tutorial 7Rojan PradhanNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 3 StudentDocument6 pagesProblem Set 3 StudentLeo Dominick MagpantayNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document4 pagesTutorial 3DavidNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current Test 1Document2 pagesAlternating Current Test 1SameerNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2Rajath Sharma100% (1)
- Updated Electronics Module 1 Question BankDocument3 pagesUpdated Electronics Module 1 Question Bankblehbo100% (1)
- 3 Spring Assignment3Document2 pages3 Spring Assignment3NeedSolutionManualsNo ratings yet
- EE 330 TUT 14 Soln-MinDocument5 pagesEE 330 TUT 14 Soln-Minpappuyadav1996No ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Familiarization With Laboratory Instruments: Oscilloscope, Function Generator, Digital Multimeter, and DC Power SupplyDocument7 pagesExperiment 1 Familiarization With Laboratory Instruments: Oscilloscope, Function Generator, Digital Multimeter, and DC Power Supplypappuyadav1996No ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document2 pagesTutorial 3pappuyadav1996No ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document5 pagesAssignment 2pappuyadav1996No ratings yet
- A 1Document1 pageA 1pappuyadav1996No ratings yet
- Department of Mathematics & StatisticsDocument1 pageDepartment of Mathematics & StatisticsHardikParwanaNo ratings yet
- IIT Kanpur Assignment MathematicsDocument2 pagesIIT Kanpur Assignment Mathematicspappuyadav1996No ratings yet
- Summer 2015Document4 pagesSummer 2015pappuyadav1996No ratings yet
- Notice For Summer RegistrationDocument1 pageNotice For Summer Registrationpappuyadav1996No ratings yet
- ProbabiltyDocument3 pagesProbabiltypappuyadav1996No ratings yet
- The Definite Article:) or Th-I On The Other Hand, If The Following Word Begins With A), or Th-UhDocument1 pageThe Definite Article:) or Th-I On The Other Hand, If The Following Word Begins With A), or Th-Uhpappuyadav1996No ratings yet
- The Definite Article:) or Th-I On The Other Hand, If The Following Word Begins With A), or Th-UhDocument1 pageThe Definite Article:) or Th-I On The Other Hand, If The Following Word Begins With A), or Th-Uhpappuyadav1996No ratings yet
- World Political MapDocument1 pageWorld Political Map0060No ratings yet
- Course Structure For Under-Graduate Programs: B.Tech. (Aerospace Engineering)Document15 pagesCourse Structure For Under-Graduate Programs: B.Tech. (Aerospace Engineering)pappuyadav1996No ratings yet
- EC PreLab4Document8 pagesEC PreLab4pappuyadav1996No ratings yet
- Ec Lab 1Document4 pagesEc Lab 1pappuyadav1996No ratings yet
- Gate 15 BrochDocument83 pagesGate 15 BrochViveen CharanNo ratings yet
- Asteroids Prospective EnergyDocument710 pagesAsteroids Prospective EnergySlavica Otovic100% (1)
- Stopping by Woods On A Snowy EveningDocument9 pagesStopping by Woods On A Snowy EveningJulia Garces100% (2)
- SR No Service CodeDocument30 pagesSR No Service CodeShiva KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Raneem AlbazazDocument33 pagesRaneem AlbazazGordana PuzovicNo ratings yet
- Keyword 4: Keyword: Strength of The Mixture of AsphaltDocument2 pagesKeyword 4: Keyword: Strength of The Mixture of AsphaltJohn Michael GeneralNo ratings yet
- Matters Signified by The Sublord of 11th Cusp in KP SystemDocument2 pagesMatters Signified by The Sublord of 11th Cusp in KP SystemHarry HartNo ratings yet
- EDS-A-0101: Automotive Restricted Hazardous Substances For PartsDocument14 pagesEDS-A-0101: Automotive Restricted Hazardous Substances For PartsMuthu GaneshNo ratings yet
- Asaali - Project Estimation - Ce155p-2 - A73Document7 pagesAsaali - Project Estimation - Ce155p-2 - A73Kandhalvi AsaaliNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Subject Complements-1 PDFDocument3 pagesKami Export - Subject Complements-1 PDFkcv kfdsaNo ratings yet
- English2 Q2 Summative Assessment 4 2Document4 pagesEnglish2 Q2 Summative Assessment 4 2ALNIE PANGANIBANNo ratings yet
- Birla MEEP Op ManualDocument43 pagesBirla MEEP Op ManualAshok ChettiyarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - 143760187HS-II, TUTORIAL ON CH-5Document14 pagesWorksheet - 143760187HS-II, TUTORIAL ON CH-5A MusaverNo ratings yet
- Hevi-Bar II and Safe-Lec 2Document68 pagesHevi-Bar II and Safe-Lec 2elkabongscribdNo ratings yet
- EXCEL For Pump DesignDocument2 pagesEXCEL For Pump Designkad-7No ratings yet
- Integration ConceptDocument34 pagesIntegration ConceptJANELLA ALVAREZNo ratings yet
- Coding DecodingDocument21 pagesCoding DecodingAditya VermaNo ratings yet
- Iec60227-3 (Ed2.1) en DDocument6 pagesIec60227-3 (Ed2.1) en Duntuk donlod aaaNo ratings yet
- List of Fatigue Standards and Fracture Standards Developed by ASTM & ISODocument3 pagesList of Fatigue Standards and Fracture Standards Developed by ASTM & ISOSatrio Aditomo100% (1)
- G-3 L-17 Internal QuestionsDocument4 pagesG-3 L-17 Internal QuestionsActivity MLZS BarhNo ratings yet
- Contoh CV / Daftar Riwayat HidupDocument2 pagesContoh CV / Daftar Riwayat HiduprusmansyahNo ratings yet
- Wang Jinhui - Competitive Physics - Thermodynamics, Electromagnetism and Relativity (2019, World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. LTD.)Document961 pagesWang Jinhui - Competitive Physics - Thermodynamics, Electromagnetism and Relativity (2019, World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. LTD.)Paritosh PandeyNo ratings yet
- 9A02502 Transmission of Electric PowerDocument6 pages9A02502 Transmission of Electric PowersivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- MC MATH 01 Syllabus SJCCDocument11 pagesMC MATH 01 Syllabus SJCCAcire NonacNo ratings yet
- WeeklyDocument8 pagesWeeklyivaldeztNo ratings yet
- Course Code:TEX3021 Course Title: Wet Processing Technology-IIDocument20 pagesCourse Code:TEX3021 Course Title: Wet Processing Technology-IINakib Ibna BasharNo ratings yet
- Designing and Building A Computer TableDocument9 pagesDesigning and Building A Computer Tablemaster_codersNo ratings yet
- Pellicon 2 Validation Guide PDFDocument45 pagesPellicon 2 Validation Guide PDFtakwahs12135No ratings yet
- DP November 2017 Examination Schedule en PDFDocument4 pagesDP November 2017 Examination Schedule en PDFSuperlucidoNo ratings yet
- Manuscript FsDocument76 pagesManuscript FsRalph HumpaNo ratings yet
- Manual of Sensorless Brushless Motor Speed Controller: Pentium SeriesDocument4 pagesManual of Sensorless Brushless Motor Speed Controller: Pentium Seriesfosavo5839No ratings yet